Recruitment of Polo-like kinase couples synapsis to meiotic progression via inactivation of CHK-2
Figures
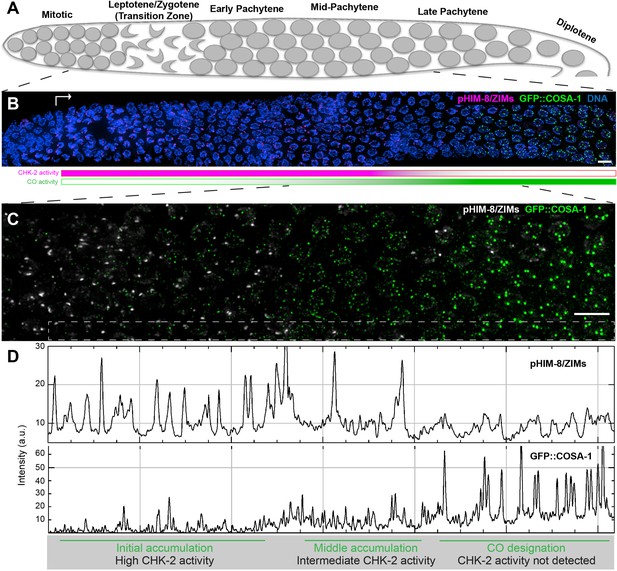
Temporal profile of CHK-2 activity and crossover designation during meiotic prophase in C. elegans.
(A) Schematic of meiotic prophase in the C. elegans hermaphrodite germline. The distal tip of the gonad is oriented on the left side in this schematic and in all other figures. Meiotic progression is readily visualized due to the simple organization of the germline. Cells exit proliferation and enter meiosis in the distal ‘arms’ of the gonad and move proximally toward the spermatheca and uterus at a velocity of about one cell row per hour (Deshong et al., 2014). Homolog pairing and synapsis and double-strand break (DSB) induction normally occur during the first few hours following meiotic entry, in the ‘transition zone’ region corresponding to leptotene and zygotene. DSBs are then processed to form recombination intermediates, which increase in abundance during early pachytene. At mid-pachytene, a transition occurs that leads to disappearance of most intermediates. One recombination intermediate on each pair of chromosomes becomes ‘designated’ as an eventual crossover site. (B) Images of representative prophase nuclei from meiotic onset, labeled with markers for crossover intermediates (GFP::COSA-1, green) and CHK-2 activity (phospho-HIM-8 and ZIM-1/-2/-3, magenta). Bright GFP::COSA-1 foci are detected following inactivation of CHK-2. White arrow indicates meiotic onset. Scale bars, 5 µm. (C) Enlargement of the mid-pachytene nuclei shown in (B). phospho-HIM/ZIMs was pseudo colored to white for easy observation. Scale bars, 5 µm. (D) Line profiles indicating the relative fluorescence intensity of staining for phospho-HIM-8/ZIMs immunofluorescence (upper) and GFP::COSA-1 (lower) in the boxed region indicated in (C). Accumulation of pro-CO proteins can be stratified into three stages: an early stage with high CHK-2 activity and variable numbers of dim GFP::COSA-1; an intermediate stage with brighter and more abundant GFP::COSA-1 foci, and a post-designation stage, with a single CO-designated site per chromosome pair marked by bright GFP::COSA-1 fluorescence. The intensity of GFP::COSA-1 foci remains fairly constant throughout this last stage. In this work, we use the appearance of bright COSA-1 foci as a proxy for crossover designation and the mid-pachytene cell cycle transition.
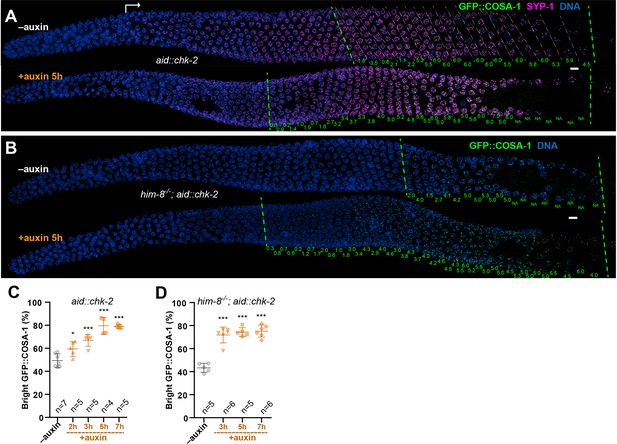
CHK-2 inhibits crossover (CO) designation.
(A) Representative hermaphrodite gonads stained for GFP::COSA-1 (green), SYP-1 (magenta), and DNA (blue). Nuclei with bright COSA-1 foci are observed at a more distal position following CHK-2 depletion. Worms were exposed to 1 mM auxin (or 0.25% ethanol lacking auxin) for 5 hr before fixation. Dashed green lines on the left and right indicate the earliest nuclei with bright COSA-1 foci and the end of pachytene, respectively. White arrow indicates meiotic onset. The average number of bright COSA-1 foci per nucleus in each row is indicated below each image in green. Scale bars, 5 µm. (B) Germline from a him-8 mutant hermaphrodite stained for GFP::COSA-1 (green), and DNA (blue), showing early appearance of bright COSA-1 foci upon CHK-2 depletion. Worms were treated with 1 mM auxin or solvent (0.25% ethanol) control for 5 hr before analysis. Scale bars, 5 µm. Note: the same image with RAD-51 is shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1C. (C) CO designation occurs earlier upon CHK-2 depletion, as described in (A). Worms were exposed to auxin (or solvent control) for 2, 3, 5, or 7 hr before analysis. We define the ‘Bright GFP::COSA-1 zone’ as the length of the region from where bright GFP::COSA-1 foci appear to the end of pachytene, before oocytes form a single row of cells. Since the length of each meiotic stage region varies among individual animals, while the ratio between stages is relatively constant. We used the ratio of the length of ‘Bright GFP::COSA-1 zone’ to the length of the region from meiotic onset to the end of pachytene to reflect the timing of bright GFP::COSA-1 foci appearance and crossover designation. To simplify, we hereafter use ‘bright GFP::COSA-1 (%)’ in graphs to indicate this ratio. Meiotic onset was determined by the staining of meiosis-specific proteins SYP-1 and/or HTP-3. n = number of gonads scored for each condition. *p = 0.0161 and ***p = 0.0003, or <0.0001, respectively, two-sided Student’s t-test. (D) Quantitative comparison of the timing of CO designation in worms as described in (B). Worms were treated with or without 1 mM auxin for 3, 5, or 7 hr before analysis. Quantification was performed as described in (C). ***p < 0.0001, two-sided Student’s t-test.
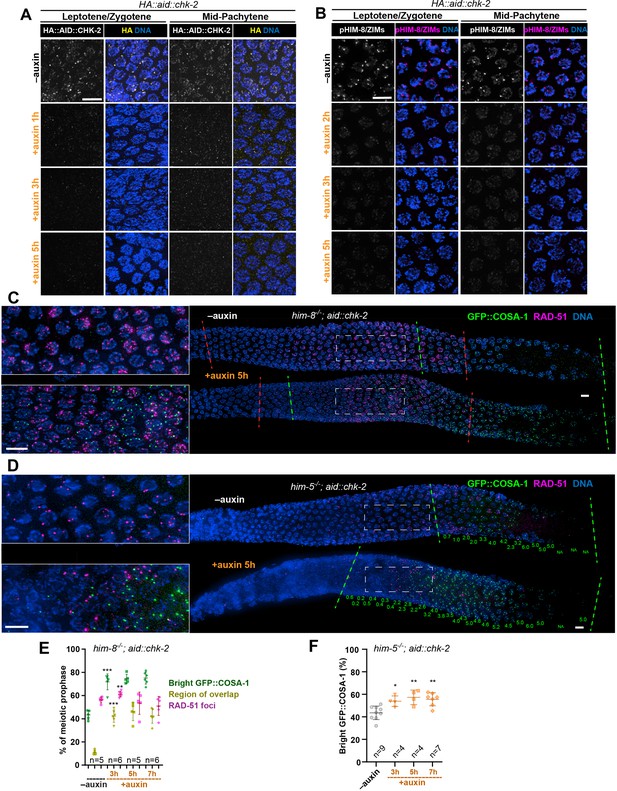
Depletion of CHK-2 activity results in earlier crossover designation.
(A) Representative leptotene/zygotene and mid-pachytene nuclei stained for HA::AID::CHK-2 (anti-HA) and DNA, showing efficient depletion of CHK-2 following auxin treatment. Worms were incubated with 1 mM auxin (or 0.25% ethanol lacking auxin) for 1, 3, or 5 hr before analysis. CHK-2 was undetectable within 3 hr of auxin exposure. Scale bars, 5 µm. (B) Representative leptotene/zygotene and mid-pachytene nuclei stained for phosphorylated HIM-8/ZIMs and DNA, showing efficient depletion of CHK-2 activity within 3 hr of auxin treatment. Scale bars, 5 µm. Representative germlines from him-8 (C) and him-5 (D) mutant hermaphrodites stained for GFP::COSA-1 (green), RAD-51 (magenta), and DNA (blue), revealing earlier appearance of bright COSA-1 foci upon CHK-2 depletion. Worms were transferred to plates prepared with 1 mM auxin (or 0.25% ethanol as a control) for 5 hr before fixation. Dashed green lines indicate where bright COSA-1 foci start to appear and where pachytene ends. Dashed red lines in (C) indicate RAD-51-positive zone. Note: the same image in (C) without RAD-51 is shown in Figure 2B. The average number of bright COSA-1 foci per nucleus in each row is indicated below each image in green in (D). Scale bars, 5 µm. (E, F) Quantitative comparison of the RAD-51-positive zone upon CHK-2 depletion in him-8 mutants and the timing of appearance of bright COSA-1 foci upon CHK-2 depletion in him-5 mutants. Worms were exposed to auxin for 3, 5, or 7 hr before fixation and analysis. The bright GFP::COSA-1 zone was defined as a region from where bright COSA-1 foci start to appear to the end of pachytene, before oocytes form a single row. The ‘bright GFP::COSA-1 (%)’ in the graph was defined as the ratio of the length of bright GFP::COSA-1 zone to the length of the region from meiotic onset to the end of pachytene. Meiotic onset was determined by the localization of meiosis-specific proteins SYP-1 and/or HTP-3. The RAD-51 zone and the region of overlap between the RAD-51 and bright COSA-1 zones were measured and expressed in the same way. See ‘Materials and methods’ for details. **p = 0.001 and ***p < 0.0001 in (E), *p = 0.0114, **p = 0.0032 and 0.0012 in (F), respectively, two-sided Student’s t-test.
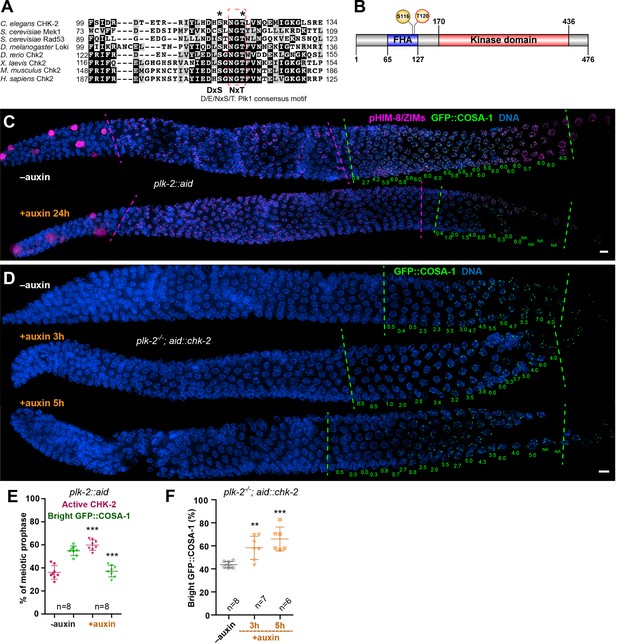
Inactivation of CHK-2 by Polo-like kinase promotes timely crossover (CO) designation.
(A) Sequence alignment of CHK-2 orthologs from various eukaryotes generated with T-Coffee (Notredame et al., 2000), showing the conservation of Ser116 and Thr120 (asterisks). Thr120 is a direct target of PLK-2; Ser116 corresponds to a Plk1 site identified in mammlian cells (van Vugt et al., 2010). Black and gray shading indicate identical and similar residues, respectively. Both Ser116 and Thr120 match the Plk1 consensus motif [D/E/N]-X-[S/T] (Santamaria et al., 2011). (B) Schematic showing the domain organization of CHK-2 protein and the positions of two phosphorylation sites, Ser116 and Thr120. FHA: forkhead-associated domain. Numbers indicate amino acid positions. C. elegans CHK-2 and budding yeast Mek1 are meiosis-specific kinases that share the FHA and serine/threonine kinase domains of mammalian Chk2 and yeast Rad53, but lack the N-terminal SQ/TQ cluster that regulates activation of Chk2 by ATM. (C) Depletion of PLK-2 delays both CHK-2 inactivation and the appearance of bright COSA-1 foci. Worms were treated with 1 mM auxin for 24 hr and stained for pHIM-8/ZIMs (magenta), GFP::COSA-1 (green), and DNA (blue). Dashed magenta lines indicate the CHK-2-active zone. Green lines indicate the bright COSA-1 zone. The average number of bright COSA-1 foci per nuclei in each row is indicated in green below each image. Scale bars, 5 µm. (D) Depletion of CHK-2 restores early appearance of bright COSA-1 foci in plk-2 mutants. Worms were treated with or without 1 mM auxin for 3 or 5 hr. Scale bars, 5 µm. (E, F) Quantification of the extension of the CHK-2-active zone and delay in appearance of bright COSA-1 foci in worms depleted for PLK-2, as described in (C) and of bright COSA-1 foci appearance in plk-2 mutants upon depletion of CHK-2 as described in (D), respectively. n = number of gonads scored for each condition. **p = 0.0018 and ***p < 0.0001, two-sided Student’s t-test.
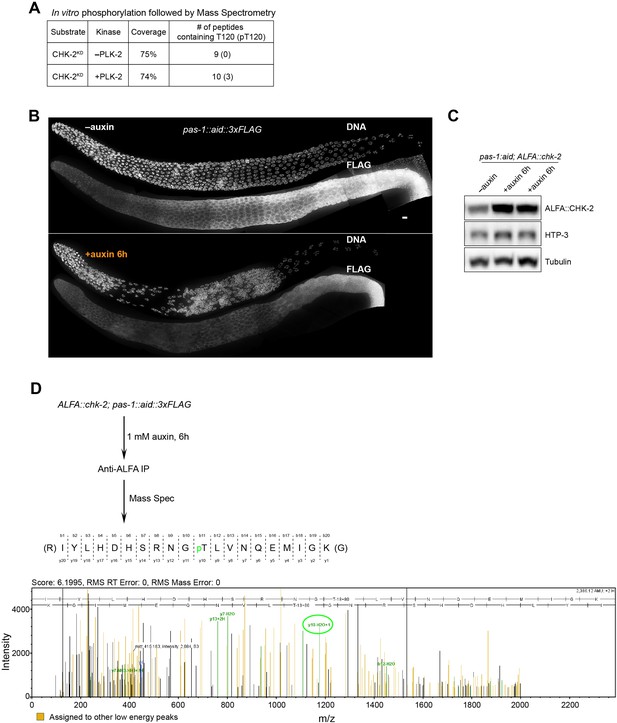
Phosphorylation of CHK-2 by PLK-2.
(A) Recombinant kinase-dead CHK-2 protein (CHK-2KD) was phosphorylated in vitro by PLK-2 kinase and then subjected to mass spectrometry analysis for phosphorylation site identification. CHK-2 Thr120 was identified as a target of PLK-2. (B) Representative hermaphrodite gonads stained for PAS-1::AID::3xFLAG (anti-3xFLAG) and DNA, showing efficient depletion of PAS-1 in the germline upon 1 mM auxin treatment for 6 hr. PAS-1 is a subunit of the 20S proteasome and is essential for the proteasome activity. Scale bars, 5 µm. (C) A western blot shows increased abundance of ALFA::CHK-2 following depletion of proteasome subunit PAS-1. Worms were transferred to media containing 1 mM auxin for 6 hr before analysis. ALFA::CHK-2 was blotted using anti-ALFA nanobody. HTP-3 and tubulin were blotted as loading controls. The two right lanes are biological replicates. (D) ALFA::CHK-2 was immunoprecipitated from adult hermaphrodites following depletion of PAS-1 for 6 hr. Mass spectrometry identified CHK-2 Thr120 as a phosphorylated site in vivo.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Western blotting raw images in Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84492/elife-84492-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
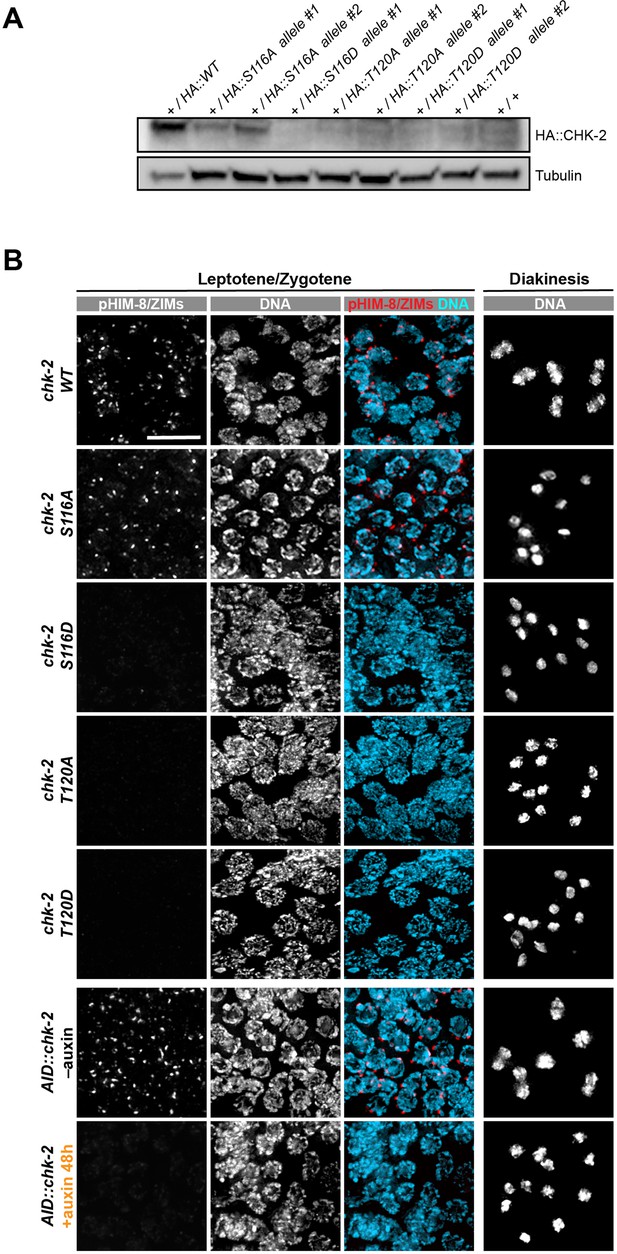
Characterization of CHK-2 phospho-mutants.
(A) Worm strains expressing the indicated HA-tagged wild-type and mutant CHK-2 proteins were compared by western blot: HA::CHK-2 WT, S116A, S116D, T120A, and T120D were all measured in heterozygotes as these point mutations result in very few viable progeny and cannot be readily balanced. HA::CHK-2 WT and S116A were readily detected, while other mutant proteins were near or below the limit of detection. HA::CHK-2 was blotted using anti-HA antibody. Tubulin was probed as a loading control. (B) Representative leptotene/zygotene and diakinesis nuclei stained for phosphorylated HIM-8/ZIMs and DNA, showing CHK-2 activity and chiasma formation in CHK-2 WT, S116A, S116D, T120A, T120D, and CHK-2 depleted homozygotes. For auxin treatment, worms were incubated with 1 mM auxin (or 0.25% ethanol lacking auxin) for 48 hr before analysis. Like CHK-2 depleted worms, CHK-2 activity and bivalents were not detected in CHK-2 S116D, T120A, and T120D mutants. Scale bars, 5 µm.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Western blotting raw images in Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84492/elife-84492-fig3-figsupp2-data1-v2.zip
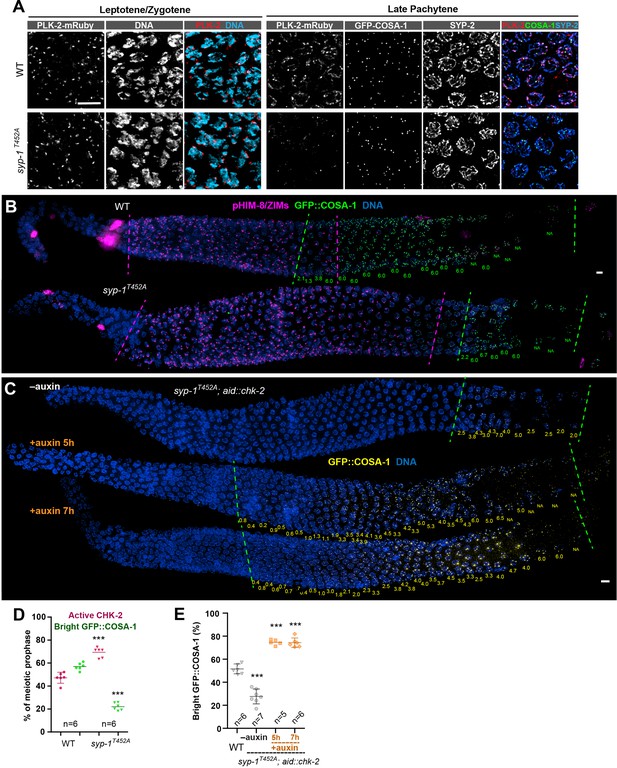
CHK-2 inactivation requires recruitment of Polo-like kinases to the synaptonemal complex (SC).
(A) Representative leptotene/zygotene or late pachytene nuclei in wild-type or syp-1T452A hermaphrodite gonads stained for PLK-2::mRuby (red), DNA (cyan), GFP::COSA-1 (green), and SYP-2 (blue). A conserved Polo box recruitment motif on the SC is absent in syp-1T452A mutants. PLK-2 localized to pairing centers in leptotene/zygotene nuclei but failed to localize to SC in pachytene nuclei in syp-1T452A mutants. (B) Representative hermaphrodite gonads stained for pHIM-8/ZIMs (magenta), GFP::COSA-1 (green), and DNA (blue), showing extension of CHK-2-active zone and delayed appearance of bright COSA-1 foci in syp-1T452A mutants. Dashed magenta lines indicate the CHK-2-active zone, while green lines indicate the bright COSA-1 zone. The average number of bright COSA-1 foci per nuclei in each row is indicated in green below each image. Scale bars, 5 µm. (C) Representative hermaphrodite gonads stained for GFP::COSA-1 (yellow) and DNA (blue), showing that depletion of CHK-2 in syp-1T452A mutants leads to early appearance of bright COSA-1 foci. Worms were treated with or without 1 mM auxin for 5 or 7 hr. Dash lines indicate the zone with bright COSA-1 foci. Scale bars, 5 µm. (D) Quantification of the extension of CHK-2-active zone and the delay in appearance of bright COSA-1 foci in worms as described in (B). n = number of gonads scored for each condition. ***p < 0.0001, two-sided Student’s t-test. (E) Quantification of bright COSA-1 zone in worms maintained and treated as in (C). Wild-type worms were used as control. n = number of gonads scored for each condition. ***p < 0.0001, two-sided Student’s t-test.
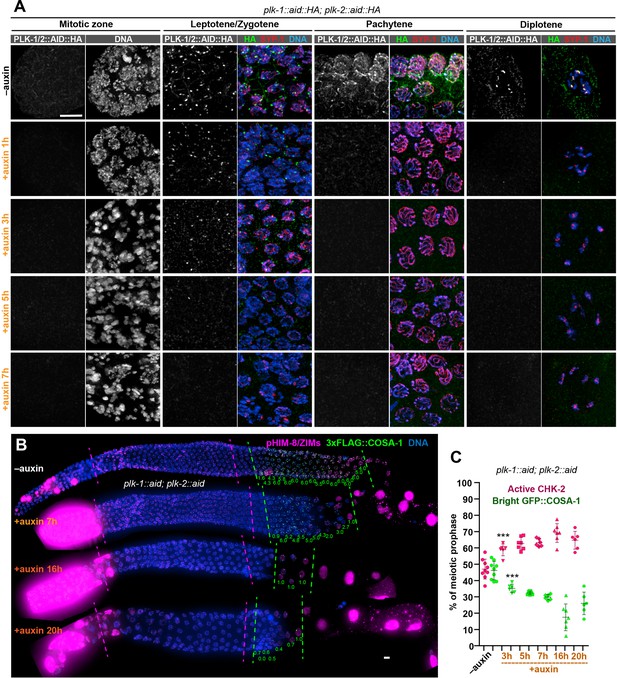
PLK-1 is not required to override the crossover assurance checkpoint in the absence of PLK-2.
(A) Representative nuclei at different stages showing efficient co-depletion of PLK-1 and PLK-2 in the germline. One hour of auxin treatment was sufficient to eliminate detectable PLK-1/PLK-2 in the germline except at Pairing Centers in early meiotic nuclei, where full depletion required 5 hr. Scale bars, 5 µm. (B) Images of representative hermaphrodite gonads stained for pHIM-8/ZIMs (magenta), 3xFLAG-COSA-1 (green), and DNA (blue), showing inactivation of CHK-2 and appearance of bright COSA-1 foci in the absence of PLK-1 and PLK-2. Dashed magenta lines indicate CHK-2-active zone, while green lines indicate the region of nuclei with bright COSA-1 foci. When PLK-1 and PLK-2 were co-depleted for longer than 16 hr, COSA-1 foci were greatly diminished (in most nuclei, only one bright 3xFLAG::COSA-1 focus can be detected). This likely reflects defects in pairing and synapsis, which prevent the formation of crossover precursors. However, bright COSA-1 foci were still observed when both PLK-1 and PLK-2 were depleted. Since COSA-1 appears only after inactivation of crossover assurance checkpoint, this suggested that crossover assurance checkpoint can still be overridden in the absence of PLK-1 and PLK-2. The average number of bright COSA-1 foci per nucleus in each row was indicated below each image in green. Since the signal in pre-meiotic nuclei depleted of PLK-1/2 was extremely high due to mitotic arrest, the brightness of pHIM-8/ZIMs was adjusted in order to see the signal in meiotic nuclei, but the background intensity outside of meiotic nuclei was kept the same among different conditions. Scale bars, 5 µm. (C) Graphs showing extension of CHK-2-active zone and delay in appearance of bright COSA-1 foci in worms co-depleted for PLK-1 and PLK-2. The bright COSA-1 zones and CHK-2-active zones were measured and presented as described in Figure 2—figure supplement 1E. n = 9, 6, 7, 6, 7, and 6 gonads, respectively. ***p = 0.0007 and 0.0009, respectively, two-sided Student’s t-test.
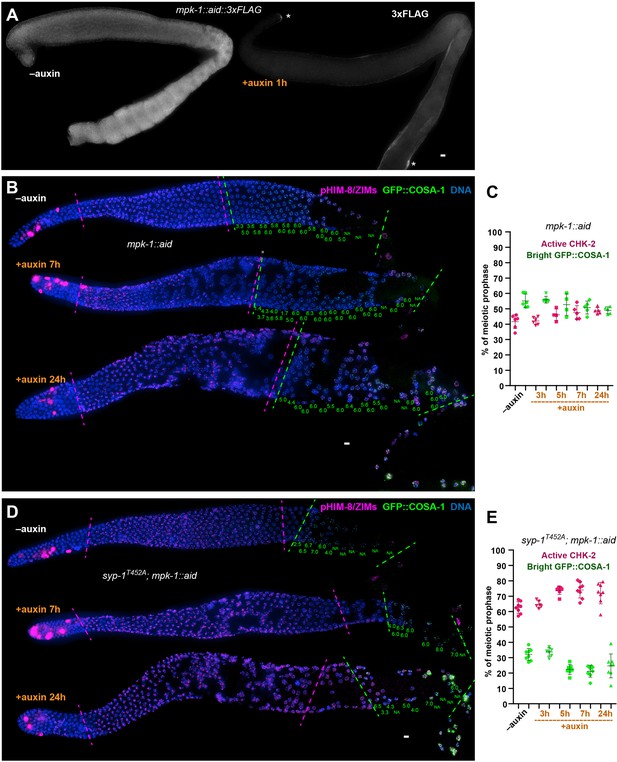
MPK-1 does not silence the crossover assurance checkpoint.
(A) Representative hermaphrodite gonads showing efficient, germline-specific depletion of MPK-1. Asterisks indicate the somatic distal tip and seam cells, where MPK-1 persists following degradation since TIR1 is expressed only in germ cells. Scale bars, 5 µm. (B) Representative hermaphrodite gonads stained for pHIM-8/ZIMs (magenta), GFP::COSA-1 (green), and DNA (blue), showing inactivation of CHK-2 and appearance of bright COSA-1 foci in the absence of MPK-1. Magenta dashed lines indicate CHK-2-active zone, while green lines indicate bight COSA-1 zone. The number of bright COSA-1 foci per nucleus in each row was indicated at the bottom of each image in green. Scale bars, 5 µm. (C) Graphs showing CHK-2-active zone and bright COSA-1 zone in worms depleted for MPK-1 for various length of time. In this case, the bright GFP::COSA-1 zones and CHK-2-active zones were measured and presented as a fraction of the region from meiotic onset to the turn of the gonad instead of the end of pachytene, because MPK-1 depletion perturbs pachytene exit and formation of a single line of oocytes. n = 6, 6, 4, 5, and 5 gonads, respectively. (D) Images of representative hermaphrodite gonads stained for pHIM-8/ZIMs (magenta), GFP::COSA-1 (green), and DNA (blue), showing inactivation of CHK-2 and bright COSA-1 foci formation in the syp-1T452A worms depleted for MPK-1. Scale bars, 5 µm. (E) Quantification of the CHK-2-active zone and bright COSA-1 zone in syp-1T452A hermaphrodites depleted for MPK-1 for various lengths of time. ‘bright GFP::COSA-1 zone’ and ‘CHK-2-active zone’ were measured and presented as described in (C). n = 8, 6, 7, 8, and 8 gonads, respectively.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | chk-2 | WormBase | Wormbase ID: WBGene00000499 | |
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | plk-2 | WormBase | Wormbase ID: WBGene00004043 | |
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | plk-1 | WormBase | WormBase ID: WBGene00004042 | |
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | mpk-1 | WormBase | WormBase ID: WBGene00003401 | |
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | cosa-1 | WormBase | WormBase ID: WBGene00022172 | |
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | syp-1 | WormBase | WormBase ID: WBGene00006375 | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | OP50 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) | N/A | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | DH10Bac | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. #10361012 | Competent E. coli |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans) | For C. elegans allele and strain information, see Supplementary file 1b, d | This paper | N/A | Strains are available in Abby Dernburg’s lab |
| Genetic reagent (Caenorhabditis elegans) | For C. elegans mutations, see Supplementary file 1b, d | This paper | N/A | Mutations are available in Abby Dernburg’s lab |
| Cell line (Spodoptera frugiperda) | Sf9 insect cells | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. #11496015 | |
| Antibody | anti-SYP-1 (Goat polyclonal) | (Harper et al., 2011) PMID: 22018922 | N/A | IF (1:300) |
| Antibody | anti-RAD-51 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Novus Biologicals | Cat. #29480002; RRID:AB_2284913 | IF (1:5000) |
| Antibody | anti-pHIM-8/ZIMs (Rabbit polyclonal) | (Kim et al., 2015) PMID: 26506311 | N/A | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-SYP-2 (Rabbit polyclonal) | (Colaiácovo et al., 2003) PMID: 12967565 | N/A | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-β-tubulin (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat. #ab6046; RRID:AB_2210370 | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | anti-HTP-3 (Chicken polyclonal) | (MacQueen et al., 2005) PMID: 16360034 | N/A | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-HTP-3 (Guinea pig polyclonal) | (MacQueen et al., 2005) PMID: 16360034 | N/A | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-α-tubulin (Mouse monoclonal) | Millipore Sigma | Cat. #05-829; RRID:AB_310035 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | anti-HA (Mouse monoclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. #26183; RRID:AB_10978021 | IF (1:400), WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-GFP (Mouse monoclonal) | Millipore Sigma | Cat. #11814460001; RRID:AB_390913 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-FLAG (Mouse monoclonal) | Millipore Sigma | Cat. #F1804; RRID:AB_262044 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-ALFA-At647N (Alpaca monoclonal, Nanobody clone 1G5 produced in E. coli) | Nanotag Biotechnologies | Cat. #N1502-At647N | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | HRP-conjugated anti-ALFA sdAb (Alpaca monoclonal, Nanobody clone 1G5 produced in E. coli) | Nanotag Biotechnologies | Cat. #N1505-HRP | WB (1:1000) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pFastBac1 GST-CHK-2KD (plasmid) | (Kim et al., 2015) PMID: 26506311; This paper | N/A | Generously provided by Yumi Kim |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pFastBac1 GST-PLK-2 (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | Generously provided by Yumi Kim |
| Sequence-based reagent | CRISPR tracrRNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Cat. #1072534 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | dpy-10 crRNA | (Arribere et al., 2014) PMID: 25161212; Integrated DNA Technologies | N/A | 5′-GCUACCAUAGGCACCACGAG-3′ |
| Sequence-based reagent | dpy-10 (cn64) repair template | (Arribere et al., 2014) PMID: 25161212; Integrated DNA Technologies | N/A | Oligo: 5′-CACTTGAACTTCAATACGGCAAGATGAGAATGACTGGAAACCGTACCGCATGCGGTGCCTATGGTAGCGGAGCTTCACATGGCTTCAGACCAACAGCCTAT-3′ |
| Sequence-based reagent | crRNAs, repair templates and genotyping primers | This paper | N/A | Supplementary file 1c |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | S. pyogenes Cas9-NLS purified protein | QB3 MacroLab at UC Berkeley | N/A | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | ALFA selector | Nanotag Biotechnologies | Cat. #N1511 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Glutathione Sepharose | GE Life Sciences | Cat. #17-5132-01 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SuperSignal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. #34095 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Auxin, indole-3-acetic acid | Acros Organics | Cat. #122160250 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DAPI (4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. #62247 | |
| Software, algorithm | SoftWorx package | Applied Precision; GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences | http://www.sussex.ac.uk/gdsc/intranet/pdfs/softWoRx%20user%20manual | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | NIH | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij | |
| Software, algorithm | Adobe Photoshop 2021 | Adobe Systems | https://www.adobe.com | |
| Software, algorithm | Adobe Illustrator 2021 | Adobe Systems | https://www.adobe.com | |
| Software, algorithm | T-COFFEE | Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (Notredame et al., 2000) PMID:10964570 | http://tcoffee.vital-it.ch/apps/tcoffee | |
| Software, algorithm | IBS_1.0.1 | (Liu et al., 2015) PMID: 26069263 | http://ibs.biocuckoo.org/download.php | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Software, Inc | http://www.graphpad.com | |
| Software, algorithm | Protein Lynx Global Server (PLGS) version 3.0.3 | Waters | https://www.waters.com/waters/en_US/ProteinLynx-Global-SERVER-(PLGS)/nav.htm?cid = 513,821 | |
| Other | Polyacrylamide gels (10 wells) | Genscript | Cat. #M00652 | Protein electrophoresis, see ‘Materials and methods’ section in the paper for details |
| Other | Polyacrylamide gels (15 wells) | Genscript | Cat. #M00654 | Protein electrophoresis, see ‘Materials and methods’ section in the paper for details |
| Other | SlowFade Glass Antifade Mountant | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. #S36917 | See ‘Materials and methods’ section in the paper for details |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
This file includes four tables (Supplementary file 1a-d).
Supplementary file 1a reports the viability and fertility of representative transgenic worm strains used in this study, which indicates that all epitope- and degron-tagged alleles support normal meiosis and development. Supplementary file 1b lists the worm alleles generated in this study. Supplementary file 1c lists the crRNA, repair templates, and genotyping primers generated in this study. Supplementary file 1d lists the worm strains used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84492/elife-84492-supp1-v2.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84492/elife-84492-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx





