A transfer-learning approach to predict antigen immunogenicity and T-cell receptor specificity
Figures
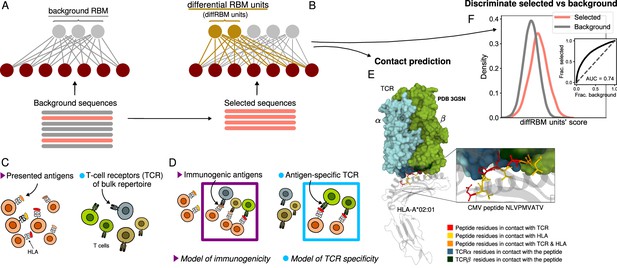
Cartoon of the differential RBM (diffRBM) learning approach.
(A) The parameters of background RBM (gray) are learnt from the ‘background’ sequence dataset. (B) The diffRBM units (gold) are learnt from a small subset of ‘selected’ sequences. (C) We consider the application of diffRBM to modeling peptide immunogenicity or T-cell receptor (TCR) antigen specificity, whereby the background dataset consists, respectively, of all antigens presented by a given Human Leukocyte Antigen class I complex (HLA) or of generic TCRs from the bulk repertoire. (D) The selected sequences correspond to HLA-specific antigens validated to be immunogenic or to TCRs that are antigen-specific responders. The inferred parameters associated to the diffRBM units allow one to identify putative contact positions in the peptide-HLA-TCR structure (E) and more generally to assign scores that distinguish the selected from the background sequences (F). E is an example of a peptide-HLA-TCR structure for the CMV peptide NLVPMVATV (PDB-ID:3GSN), where the contact points along the peptide and the TCR are highlighted in different colors (image obtained with Mol* Sehnal et al., 2018).
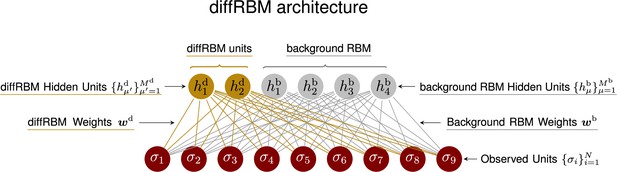
DiffRBM architecture recapitulating the mathematical notation used in Materials and methods.
In this cartoon example, we have assumed , and (corresponding to the length of the actual sequence input in the case of peptides, see Figure 2A and Figure 2—figure supplement 1).
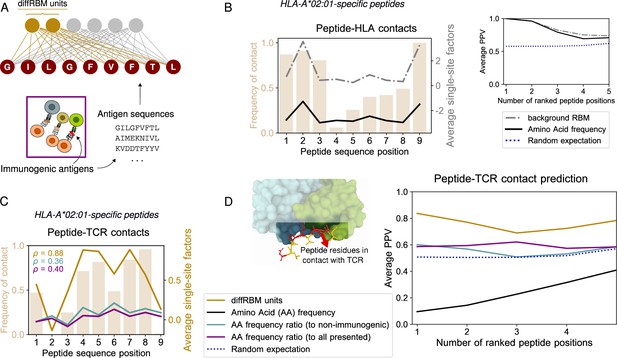
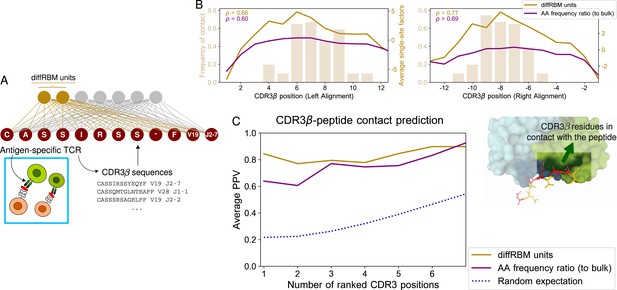
DiffRBM model of immunogenicity and structural interpretation of its parameters.
(A) DiffRBM units are learnt from HLA-specific peptides annotated as immunogenic. (B) HLA contact frequency for each peptide position across 41 structures (bars, left-axis). On the right-axis, log-frequency of amino-acids in the background dataset of HLA-A*02:01-presented antigens (black line), and single-site factor magnitude predicted by the background RBM (HLA-A*02:01-specific presentation model, gray line), both averaged over the 41 structures. Right inset: Average Positive Predictive Value (PPV) for the prediction of peptide positions in contact with the HLA as a function of the number of ranked positions, averaged over the 41 structures. The average PPV over a uniformly random prediction is shown in blue (dotted line, see Materials and methods). (C) Same as B, but for peptide-TCR contacts. Single-site factors as calculated from the diffRBM units of the immunogenicity model. Immunogenic to either non-immunogenic or all presented peptides’ amino acid frequency ratios are also shown (legend in D). denotes the correlation coefficient between the contact frequency distribution and single-site factor magnitudes. Peptide contact positions are those within 3.5 Å (4 Å) to the HLA (TCR) in the crystal structure. (D) Peptide-TCR contact prediction PPV for each peptide position, sorted by single-site factor magnitude, and averaged over 46 structures (4 for HLA-B*35:01, 41 for HLA-A*02:01, 1 for HLA-B*07:02). Predictions are made using the HLA-specific immunogenicity model for each peptide. Average PPVs are reweighed by a sequence similarity between peptide entries, see Materials and methods (Figure 2—figure supplement 3A–B, Figure 2—figure supplement 4A–B).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
List of TCR-pMHC structures from PDB and estimated contact positions at 4Å.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85126/elife-85126-fig2-data1-v2.xls
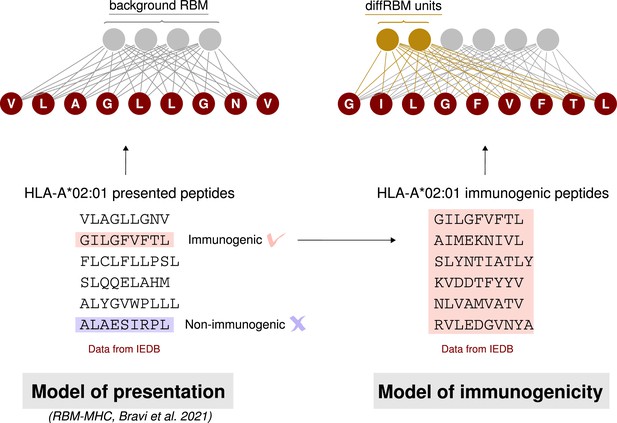
Schematic summary of the construction of a diffRBM model of immunogenicity.
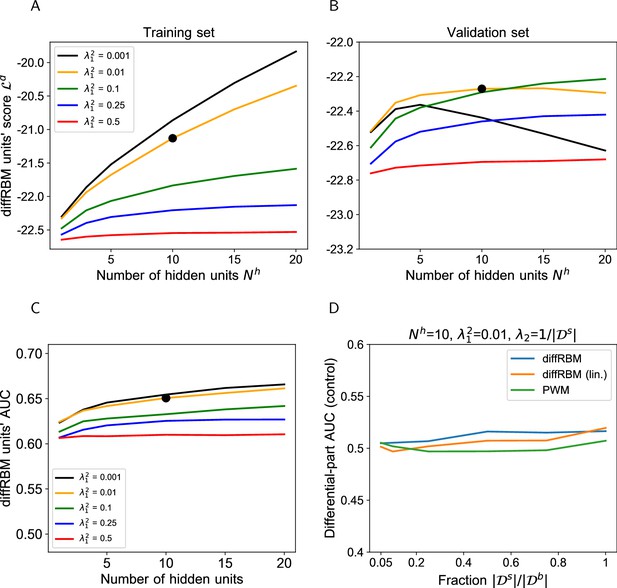
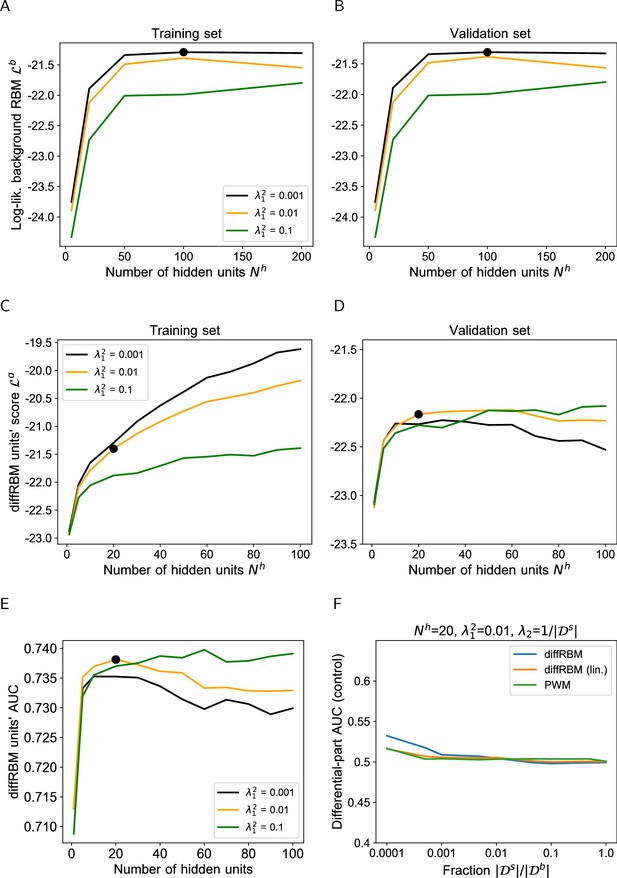
Hyperparametric search for the diffRBM model of immunogenicity.
(A-B) The hyperparametric search for the diffRBM model of immunogenicity is performed by monitoring the value of the diffRBM units’ score (Equation 10) as a function of the number of differential hidden units () and the regularization (). The score values plotted are averages over 50 randomly selected partitions into a training (A) and validation set (B), see Materials and methods. Dataset used: immunogenic peptides presented on HLA-A*02:01 ( = 1682). The optimal combination of and is marked by the black bold dot. (C) AUC of discrimination between immunogenic and non-immunogenic in the test set (averaged over 50 random training-test set partitions) given by diffRBMs with different and parameters. (D) Control of sampling effects on the predictive power of diffRBM with the optimal parameters (, ), its version where the differential part is linear (diffRBM lin.) and a PWM approach. Here PWM refers to the approaches described in Supporting Methods (section ‘PWM-based approach’), whereby the equivalent of the differential model part is given by the ratio of the PWM learnt on selected data and the PWM learnt on the background data. Differential models are trained on a randomly drawn portion of the background dataset of size , for varying , instead of a training set of immunogenic-only sequences, and then the differential part is used to estimate the AUC of discrimination between immunogenic and non-immunogenic sequences in the test set. Differential models, as expected in this control dataset, have no power at discriminating immunogenic from non-immunogenic peptides (AUC ∼0.5) for all values of the ratio .
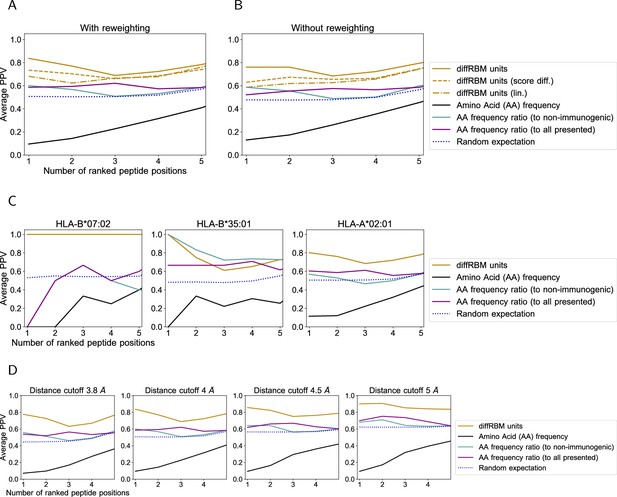
Prediction of peptide contact positions with the TCR.
(A) The average PPV shown in Figure 2D is compared to the PPV obtained from: the single-site factors from diffRBM units with fields only (‘diffRBM units (lin.)’, dashed-dotted line); a prediction based on a difference of diffRBM units’ scores (Equation 25). The later is marked as ‘diffRBM units (score diff.)’ (dashed line) to distinguish it from the prediction by diffRBM single-site factors (Equation 11, simply denoted as ‘diffRBM units’). (B) is the same plot as A but obtained without applying the reweighting to account for peptide sequence similarity (Materials and methods). (C) Same plot as Figure 2D, where predictions are divided by HLA allele. The number of structures considered is as follows: 4 structures for HLA-B*35:01, 41 for HLA-A*02:01, and 1 for HLA-B*07:02. (D) Same plot as Figure 2D varying the threshold in Å to define a contact. In all plots, the blue dotted line marks the result of predicting at random the contact positions (Materials and methods).

Prediction of peptide contact positions with the HLA.
(A) The average PPV of contact prediction shown in Figure 2B (inset) is compared to the PPV obtained from: the single-site factors from a background RBM with all parameters (bold gray line); a prediction based on a difference of background RBM log-likelihoods (‘background RBM (score diff.)’, dashed line). (B) is the same plot as A but obtained without applying the reweighting to account for peptide sequence similarity (Materials and methods). (C) Same plot as Figure 2B (inset) where the prediction is shown separately for each HLA (4 structures for HLA-B*35:01, 41 for HLA-A*02:01, and 1 for HLA-B*07:02). (D) Same plot as Figure 2B (inset) varying the threshold in Å to define a contact. In all plots, the blue dotted line marks the result of predicting at random the contact positions (Materials and methods).
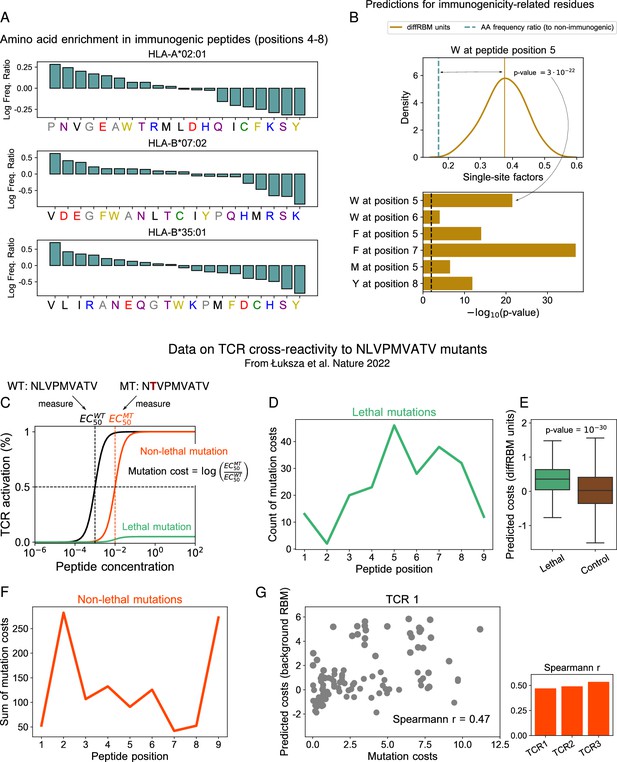
DiffRBM units encode molecular features of immunogenicity.
(A) Amino-acid usage log-enrichment of immunogenic to non-immunogenic peptides, across central positions (4-8) for each HLA type. The color code indicates amino acid properties: negatively charged (red), positively charged (blue), polar (purple), aromatic (yellow), aliphatic hydrophobic (black), cysteine (green), tiny (grey). (B) DiffRBM predicts a positive contribution to immunogenicity of key residues, in agreement with observations. (Top) DiffRBM single-site factors distribution evaluated across HLA-A*02:01-specific immunogenic sequences with W at position 5. (Bottom) The single-site factors given by the immunogenic vs non-immunogenic amino acid frequency ratio, which do not include the sequence context (Materials and methods), predict a much lower contribution to immunogenicity, as indicated by the p-values of their difference with respect to the average of the diffRBM single-site factors distribution. (C) Illustration of TCR activation curves from Łuksza et al., 2022 for wild-type () peptide NLVPMVATV and its point-mutants (). (D) Total count of lethal mutation costs (214 of 513 TCR-mutant combinations), plotted per mutated peptide position. (E) DiffRBM units predicted costs of lethal mutations are mostly positive (Materials and methods). (F) Non-lethal mutation costs sum (299 of 514 TCR-mutant combinations) per mutated peptide position. (G) Experimental vs background RBM predicted costs for non-lethal mutations, for one TCR (TCR1). Spearmann correlation coefficients are comparable across all 3 TCRs, with p-values ≤10-6 (Figure 3—figure supplement 1B).
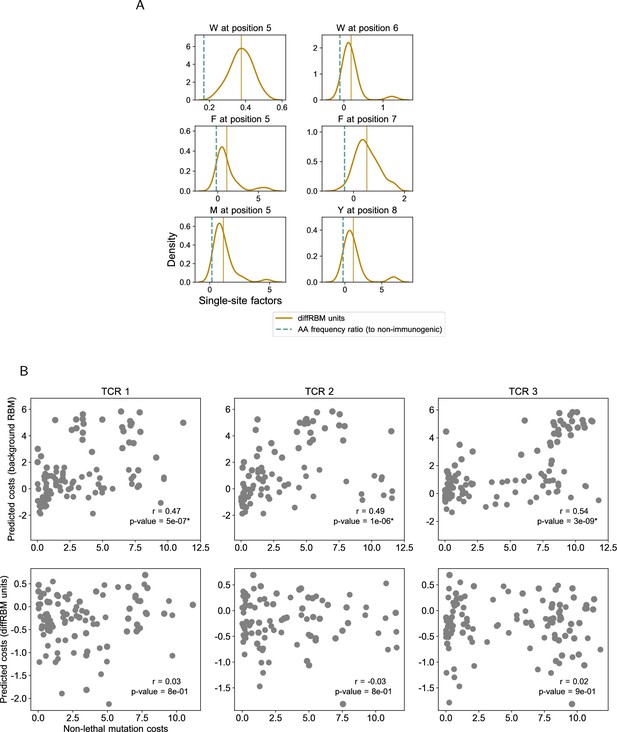
Prediction of immunogenicity-related residues and mutation costs.
(A) Same as Figure 3B for all the key residues: W at position 5 (39 sequences) and position 6 (20 sequences), F at position 5 (104 sequences) and position 7 (107 sequences); M at position 5 (33 sequences); Y at position 8 (90 sequences). (B) Experimental vs predicted mutation costs of non-lethal mutations (like in Figure 3G) for all 3 TCRs analyzed in Łuksza et al., 2022, showing the predictions both by background RBM and the diffRBM units. The Spearmann correlation coefficient for the predictions by background RBM is significant across the 3 TCRs (p-value ≤10-6).
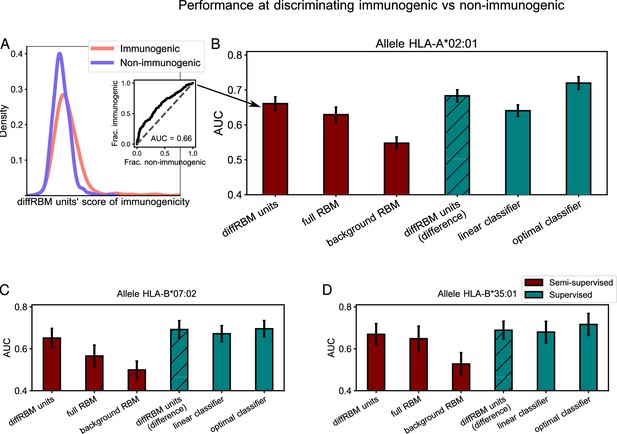
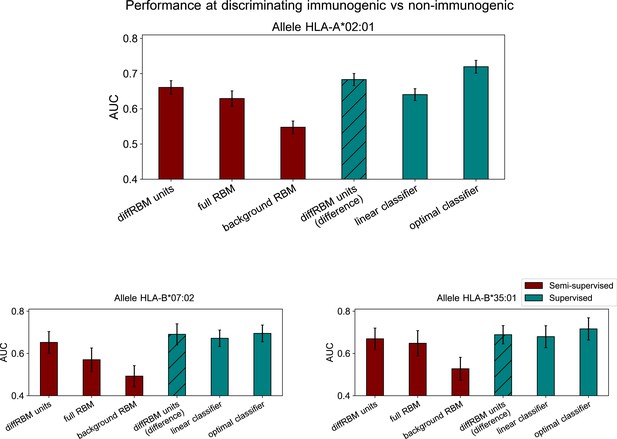
Immunogenic vs non-immunogenic peptide discrimination performance.
(A) The Area Under the Curve (AUC, see Materials and methods) is computed for HLA-specific diffRBM units’ scores of immunogenic and non-immunogenic held-out peptides. (B) Performance of diffRBM units, full RBM, background RBM, and other methods, for the HLA-A*02:01 dataset. Semi-supervised methods (red) are trained only on immunogenic (or presented) peptides. Supervised methods (green) are trained with immunogenic and non-immunogenic peptides. ‘DiffRBM units (difference)’ is intermediate, exploiting the annotation of peptides as immunogenic and non-immunogenic a-posteriori (but it is not trained for the discrimination task). (C–D) Same as B, for HLA-B*07:02 (C) and HLA-B*35:01 (D). All AUC values are the averaged over 50 train/test set partitions, and error bars give the corresponding standard deviation (Materials and methods).

Comparison of performance of differential models of immunogenicity.
Comparison of performance, in terms of the AUC of immunogenic vs non-immunogenic discrimination, between diffRBM, its version where the differential part is linear (diffRBM lin.) and a PWM approach. Here PWM refers to the approaches described in Supporting Methods (section ‘PWM-based approach’), where the ‘Full model’ is given by the PWM learnt on the selected data (immunogenic peptides) while the ‘Differential part’ corresponds to the ratio of the PWM learnt on selected data and the PWM learnt on the background data. AUCs are averages over 50 training-test partitions and error bars give the corresponding standard deviation (Materials and methods).
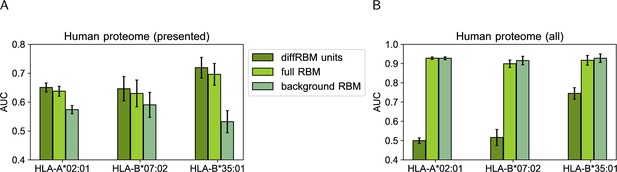
Score comparison between immunogenic peptides and peptides from the human proteome.
We have drawn at random 105 peptides from all the possible 9-mers in the human proteome and we have assigned to them scores under the HLA-specific models listed in the legend. We have measured via the AUC the extent to which scores assigned by these models to HLA-specific immunogenic peptides are higher than the ones assigned either to only the peptides predicted to be presented on the corresponding HLA by NetMHCpan4.1 (A) or to all the 105 human proteome peptides (B). AUCs are averages over 50 training-test partitions and error bars give the corresponding standard deviation (Materials and methods).
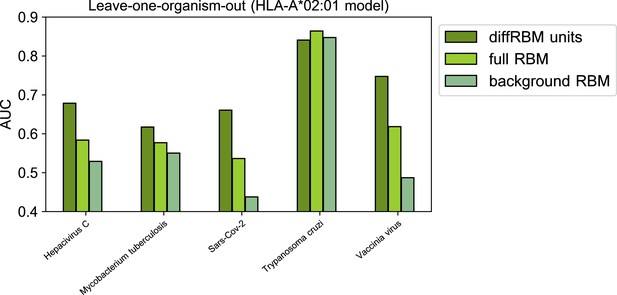
Leave-one-organism-out cross-validation for HLA-A*02:01-specific model (Materials and methods).
The case of Trypanosoma cruzi visibly constitutes an outlier, whereby the binding affinity to the HLA alone discriminates accurately immunogenic and non immunogenic antigens (AUC = 0.85). This result is confirmed by scoring the peptides via NetMHCpan4.1 (AUC=0.85). Excluding this case, the average diffRBM units AUC = 0.68, which is comparable to the AUC obtained via standard validation (average AUC = 0.66, Figure 4B).
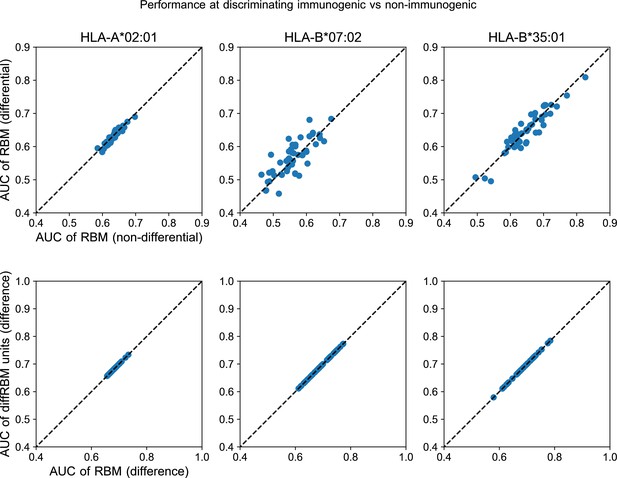
Further comparison of diffRBM and RBM scores.
Upper row: the AUC of classification of immunogenic vs non-immunogenic peptides given by the full RBM (trained in part on the background dataset and in part on the selected data and indicated as ‘RBM (differential)’) is essentially the same as the one of an RBM with the same hyperparameters trained only on selected data (denoted as ‘RBM (non-differential)’). The comparison is made separately for each HLA. In these scatter plots every point gives the AUC of discrimination of the two models compared for one of the 50 random partitions into training and test sets of the corresponding HLA-specific dataset (Materials and methods). Bottom row: we consider the AUC of immunogenic vs non-immunogenic classification obtained through the difference of scores between the diffRBM units trained on immunogenic peptides and the ones trained on non-immunogenic peptides. The scatter plots show that such performance (on the y-axis), as it should, is equivalent to the one attained by the difference of the full RBM log-likelihoods (x-axis).

Hyperparametric search for the classifier of immunogenicity.
The hyperparametric search for the classifier is based on the optimal performance on the validation dataset at discriminating immunogenic vs non-immunogenic peptides as measured by the AUC. We show the mean AUC over 50 random partitions into training set (A) and validation set (B). The labels on the x-axis denote different classifier architectures, which are described in C, while the label ‘WD’ stands for the coefficient of weight decay used. (C) Tested architectures for the classifier of immunogenicity. All classifiers alternate dense linear layers with LeakyReLU (Maas et al., 2013) activation functions. The models differ in the number of layers (column Depth) and the width of intermediate layers (column Intermediate widths). The first layer is always of input size 180 = 21×9, and corresponds to one-hot encoded sequences of length 9 with 20 amino-acid + 1 gap letters. The last layer always has an output of size 1 giving the predicted log-odds that the input sequence is immunogenic. Model C1 has no intermediate layers and corresponds to the linear classifier whose results are shown in Figure 4.
Performance of differential models of immunogenicity with sample reweighting.
Performance at discriminating immunogenic vs non-immunogenic peptides (like in Figure 4) where a reweighting scheme based on sequence similarity is applied during training (Materials and methods).
DiffRBM model of TCR epitope specificity and structural interpretation.
(A) DiffRBM units are learnt from CDR3β sequences of antigen-specific TCRs. (B) Contact frequency distribution (bars) with peptide at each CDR3β position, across 12 structures (2 for YLQPRTFLL, 3 for NLVPMVATV, 1 for GLCTLVAML, 6 for GILGFVFTL). CDR3β positions are given as distances to either the left or right anchor sites. Contacts are sites with distance ≤4 Å between CDR3β and peptide. Magnitude of single-site factors based on the diffRBM units or the amino acid frequency ratio (of peptide-specific sequences relative to bulk-repertoire sequences) averaged over the 12 CDR3β are shown as lines. (C) PPV of CDR3β-peptide contact positions, averaged over the 12 structures, using single-site factors from the peptide-specific models (diffRBM or amino-acid frequency ratios). PPVs are reweighed by CDR3β sequence similarity (Materials and methods, Figure 5—figure supplement 3A–B).

Schematic summary of the construction of a diffRBM model of TCR epitope-specificity.
Hyperparametric search for the diffRBM model of TCR specificity.
(A-B) Hyperparametric search for the background RBM model using the dataset from Emerson et al., 2017 (Materials and methods). Due to the large sample size, the differences between training and validation sets arising from sampling are minimal and as a result the model’s performance is largely equivalent. (C-D) Hyperparametric search for the diffRBM units, performed in the same way as for the immunogenicity model (Figure 2—figure supplement 2A–B). The diffRBM units’ scores plotted are averages over 50 random partitions into a training (C) and validation set (D), see Materials and methods. Dataset used: set of sequences specific to the CMV peptide NLVPMVATV ( = 4548). (E) AUC of discrimination between epitope-specific and generic sequences in the test set (averaged over 50 random training-test set partitions) varying and . The black bold dot in A–B and C–E marks the combination of and chosen, respectively, for background RBM (, ) and diffRBM units (, ). (F) As a control, differential models are trained on a randomly drawn portion of the background dataset of size , for varying , instead of a training set of epitope-specific sequences, and then their differential part is used to estimate the AUC of discrimination between epitope-specific and generic sequences in the test set, see the caption of Figure 2—figure supplement 2D.

Prediction of CDR3β contact positions with the peptide.
(A) Similarly to Figure 2—figure supplement 3A, the average PPV of contact prediction shown in Figure 5C is compared to the PPV by two alternative predictors, the expression (Equation 25) (‘diffRBM units (score diff.)’, dashed line) and the single-site factors from diffRBM units with fields only (‘diffRBM units (lin.)’, dashed-dotted line). (B) is the same plot as A but obtained without applying the reweighting to account for peptide sequence similarity (Materials and methods). (C) Same plot as Figure 5C, where predictions are divided by epitope specificity. The number of structures considered is as follows: 2 structures for YLQPRTFLL, 3 for NLVPMVATV, 1 for GLCTLVAML, and 6 for GILGFVFTL. (D) Same plot as Figure 5C varying the threshold in Å to define a contact. The cutoff 5 Å is the one used in Calis et al., 2012; Glanville et al., 2017; Ostmeyer et al., 2019; Milighetti et al., 2021. In all plots, the blue dotted line marks the result of predicting at random the contact positions (Materials and methods).
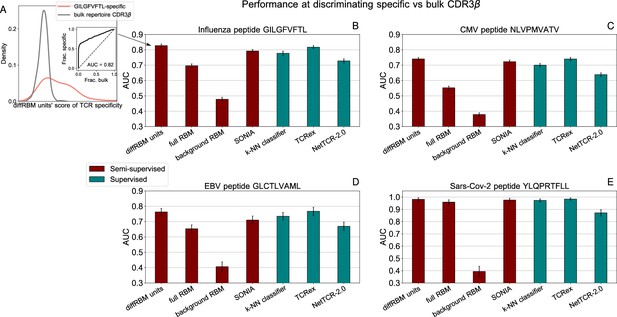
Performance at discriminating antigen-specific from generic T-cell receptors.
(A) For a given epitope model (e.g. the Influenza epitope GILGFVFTL), we assign diffRBM units’ scores to held-out sets of antigen-specific CDR3β and generic CDR3β from the bulk repertoire, and we measure the discrimination performance via the Area Under the Curve (AUC), see Materials and methods. (B) AUC of the diffRBM units, full RBM, background RBM and other methods trained and tested on CDR3β sequences specific to the Influenza epitope GILGFVFTL. (C–E) The performance assessment illustrated in A–B is repeated for the models of specific response to the CMV epitope NLVPMVATV (C) EBV epitope GLCTLVAML (D), and the Sars-Cov-2 epitope YLQPRTFLL (E). AUC values shown are the average over 50 partitions into training and test sets and error bars give the corresponding standard deviation (Materials and methods).
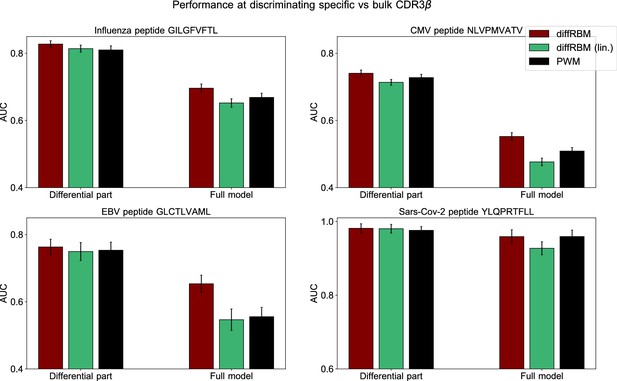
Comparison of performance of differential models of TCR specificity.
Comparison of performance, in terms of the AUC of epitope-specific vs bulk sequences discrimination, between diffRBM, its version where the differential part is linear (diffRBM lin.) and a PWM approach, see caption of Figure 4—figure supplement 1.

Comparison of performance of differential models of TCR specificity with different background datasets.
The plots show, for each epitope, the AUC of discrimination between the epitope-specific and naive sequences for the diffRBM units, full RBM and background RBM in the case where the background dataset is drawn from the Britanova et al., 2016 dataset, compared to the values obtained for a background dataset from Emerson et al., 2017 (the one used in Figure 6). AUCs are averages over 50 training-test partitions and error bars give the corresponding standard deviation (Materials and methods).
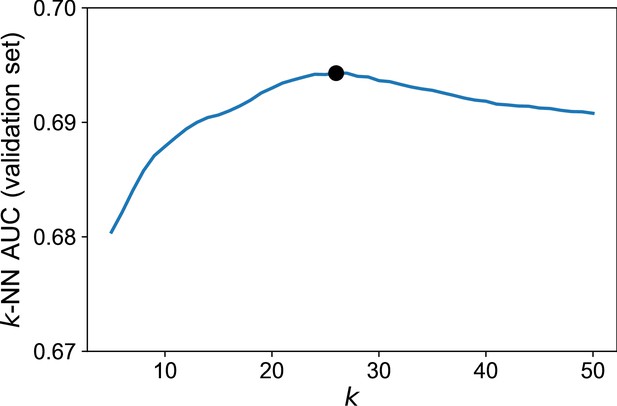
Hyperparametric search of the optimal for the -NN algorithm.
The optimal (=26, indicated by the black bold dot) is chosen by looking at the maximal AUC of discrimination between epitope-specific and background sequences in the validation set. For each , the plot shows the average AUC over 50 independent partitions into training and validation sets (Materials and methods). Dataset used: set of sequences specific to the CMV peptide NLVPMVATV (=4548).

Comparison of performance of models of TCR specificity without V and J type.
Given that NetTCR2.0 (Montemurro et al., 2021) does not account for V and J type in its input, we report the performance of the diffRBM units, full RBM and background RBM for the 4 epitope-specific models under consideration when only the CDR3β amino acid sequence has been used to train and test the models. AUCs are averages over 50 training-test partitions and error bars give the corresponding standard deviation (Materials and methods).
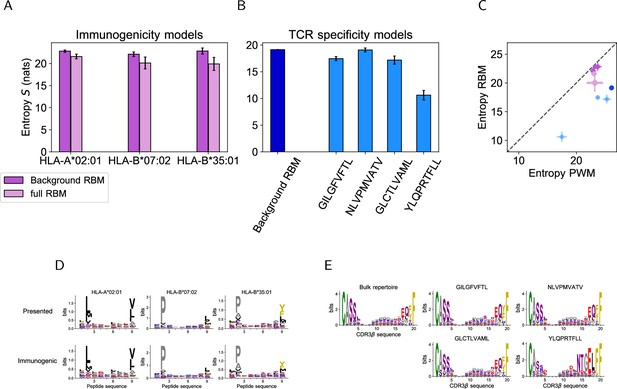
Model-based entropy estimation.
(A) Entropy (expressed in nats) of the space of HLA-specific presented antigens (evaluated by background RBM) and of HLA-specific immunogenic antigens (evaluated by the full RBM) for the 3 HLAs. Error bars represent the sampling-related uncertainty on the estimated entropy and was calculated as in Marchi et al., 2019. (B) The entropy of the background dataset (CDR3 bulk repertoire) obtained from background RBM is compared to the entropy of epitope-specific CDR3 obtained from the full RBM models of TCR specificity to GILGFVFTL, NLVPMVATV, GLCTLVAML and YLQPRTFLL. (C) The entropies calculated from background RBM and the full RBM plotted in A and B is lower than the one estimated from independent-site models of the same data (Entropy PWM), because RBM models can account for correlations between sequence sites, hence for additional constraints on sequence diversity. (Colors are the same as in A, B). The entropy values from RBM and PWM models show a highly correlated trend across datasets, reflecting their different degree of heterogeneity in amino acid composition, as shown by the sequence logos of peptide (D) and CDR3 (E) data we considered.





