Biobank-wide association scan identifies risk factors for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease and endophenotypes
Figures
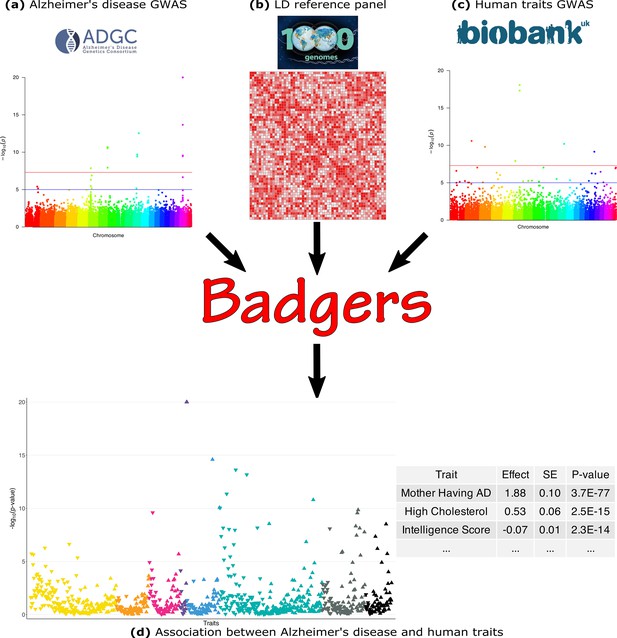
Biobank-wide Association Discovery using GEnetic Risk Scores (BADGERS) Workflow.
BADGERS takes (a) Alzheimer’s disease genome-wide association studies (GWAS), (b) linkage disequilibrium (LD) reference panel, and (c) Human traits GWAS from the UK biobank as input. The generated result will be the (d) Association between Alzheimer’s disease and human traits. In graph (d), each triangle represents one human trait, and different colors represent different trait categories.
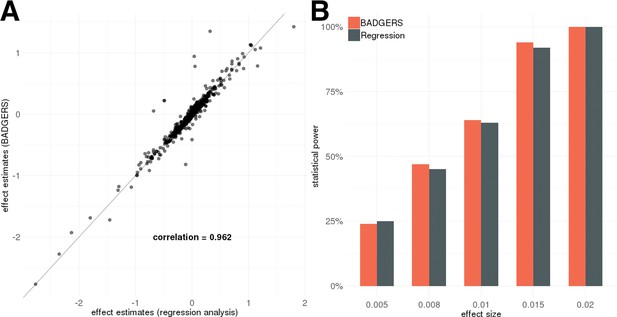
Simulation results.
Biobank-wide Association Discovery using GEnetic Risk Scores (BADGERS) and regression analysis based on individual-level data showed (A) highly consistent effect size estimates for 1738 polygenic risk scores (PRS) in simulation and (B) comparable statistical power (setting 3).
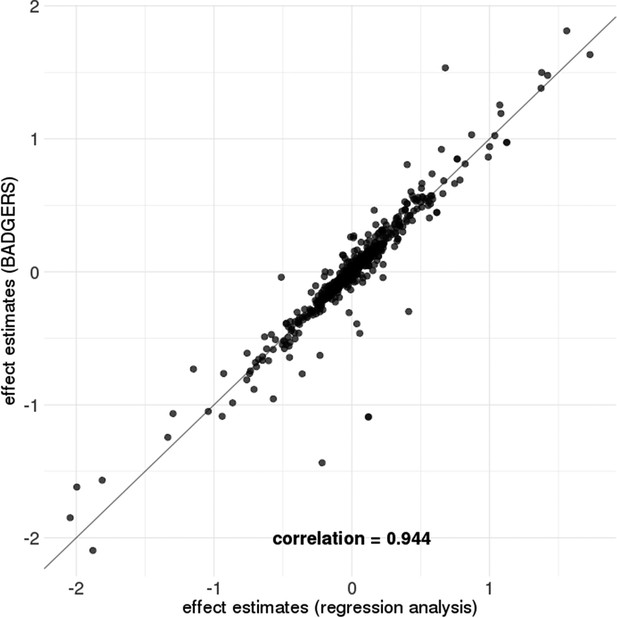
Comparison of effect size estimates from Biobank-wide Association Discovery using GEnetic Risk Scores (BADGERS) and regression analysis based on individual-level data.
BADGERS and regression analysis showed highly consistent effect size estimates for 1738 polygenic risk scores (PRS) in simulation setting 2.

Comparison of p-values from Biobank-wide Association Discovery using GEnetic Risk Scores (BADGERS) and regression analysis based on individual-level data.
BADGERS and regression analysis provided highly consistent p-value results for 1738 polygenic risk scores (PRS) in simulation (A) setting 1 and (B) setting 2.

Comparison of effect size estimates from Biobank-wide Association Discovery using GEnetic Risk Scores (BADGERS) and regression analysis based on individual-level data when p-values are smaller than 0.05.
The effect size between two algorithms is highly consistent.
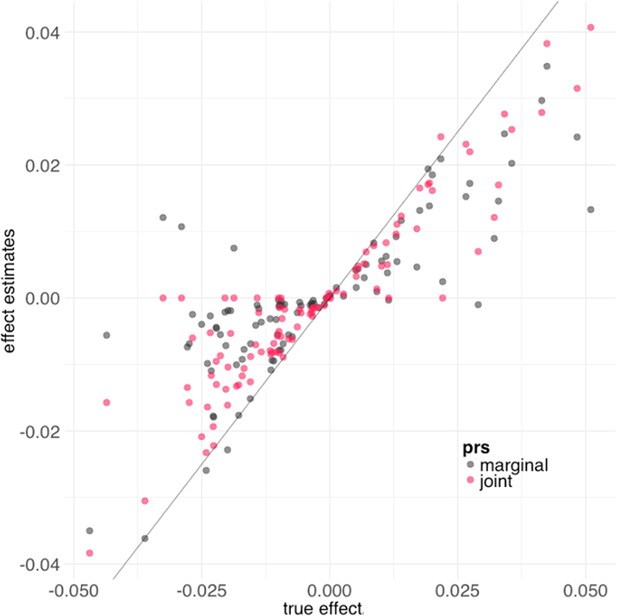
Biobank-wide Association Discovery using GEnetic Risk Scores (BADGERS) estimates using marginal polygenic risk scores (PRS) and joint PRS.
Both methods showed consistent effect size estimates with true effect size in simulation.
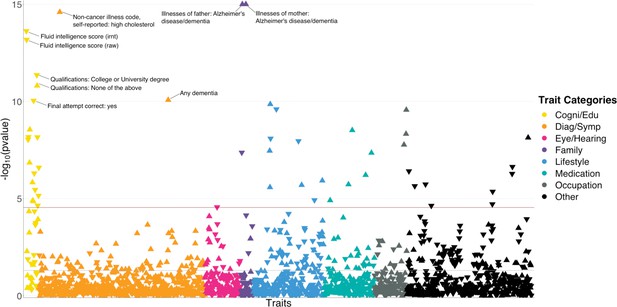
polygenic risk score (PR)S-based biobank-wide association scan (BWAS) identifies risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Meta-analysis p-values for 1738 heritable traits in the UK biobank are shown in the figure. p-values are truncated at 1e-15 for visualization purposes. The horizontal line marks the Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold (i.e. p=0.05/1738). Positive associations point upward, and negative associations point downward.
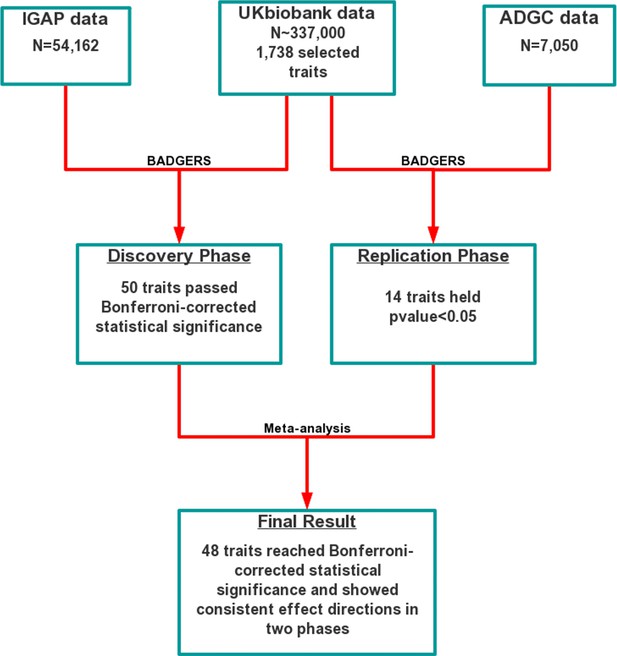
Workflow of the two-stage biobank-wide association scan (BWAS) for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
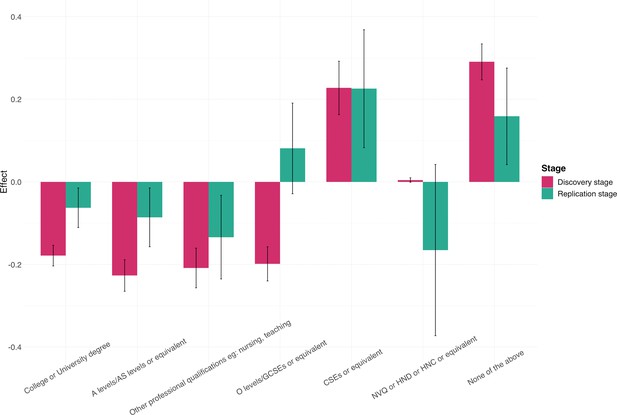
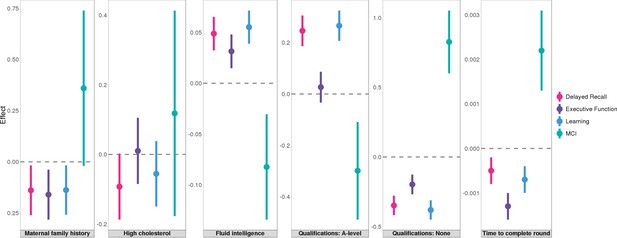
Associations between Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and education attainment in two independent analyses.
Error bars denote the standard error of effect estimates.
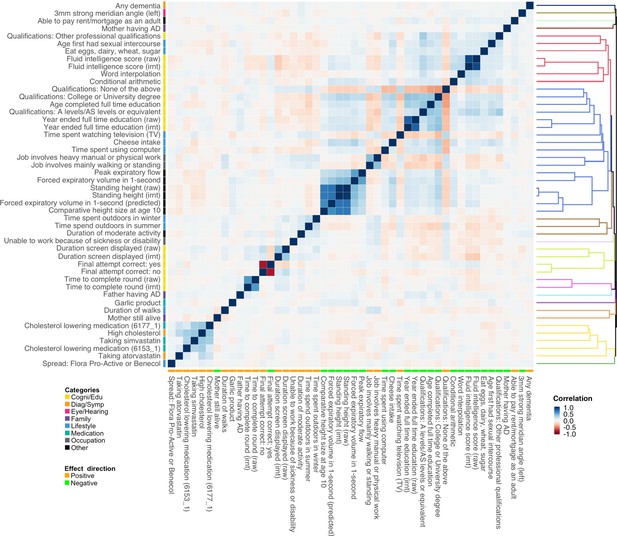
Polygenic risk score (PRS) correlation matrix for the 48 traits identified in marginal association analysis.
Trait categories and association directions with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are annotated. The dendrogram indicates the results of hierarchical clustering. We used 1000 genome samples with European ancestry to calculate PRS and evaluate their correlations. Label ‘irnt’ means that trait values were standardized using rank-based inverse normal transformation in the genome-wide association study (GWAS) analysis.
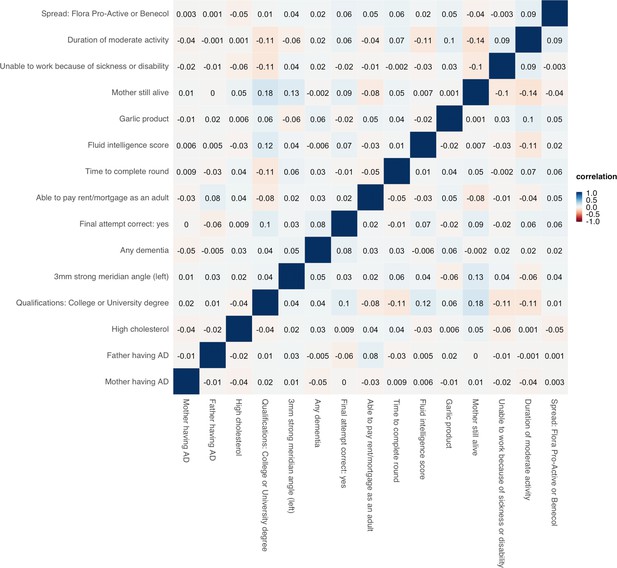
Correlation heatmap for the 15 representative traits selected based on hierarchical clustering.
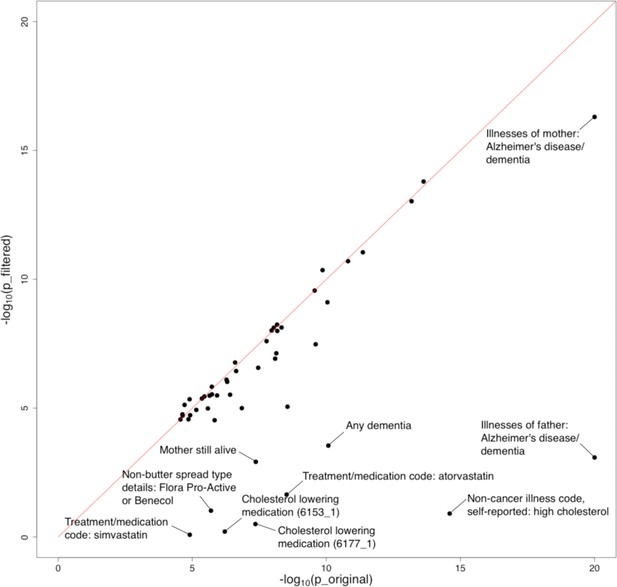
Influence of the APOE region on trait-Alzheimer’s disease (AD) associations.
The horizontal and vertical axes denote association p-values before and after removal of the APOE region, respectively. Original p-values (i.e. the x-axis) were truncated at 1e-20 for visualization purposes.
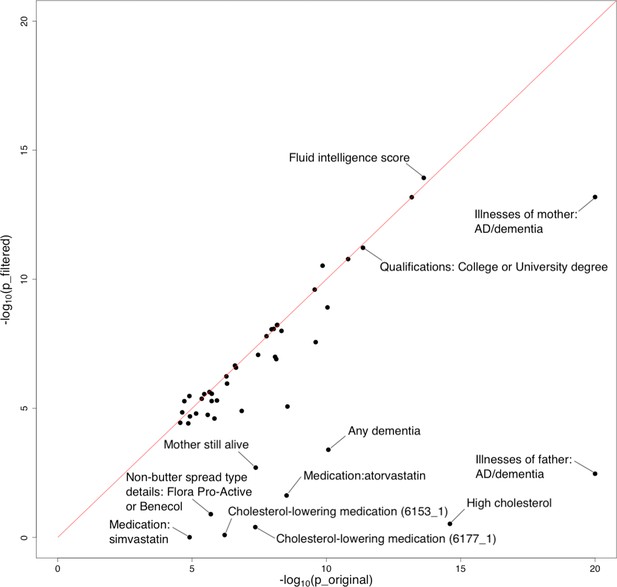
Influence of a wider APOE region on polygenic risk score (PRS)-Alzheimer’s disease (AD) associations.
A region of more than 2 Mb was removed from genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics for this analysis (chr19: 44,409,039–46,412,650). The horizontal and vertical axes denote association p-values before and after removal of the extended APOE region, respectively. Original p-values (i.e. the x-axis) were truncated at 1e-20 for visualization purposes.
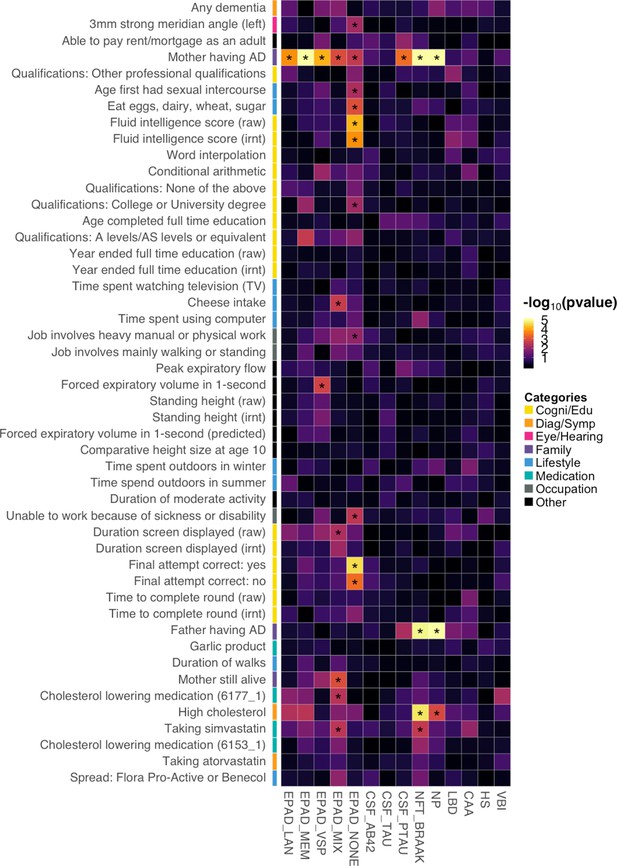
Associations between identified Alzheimer’s disease (AD) risk factors and various AD subgroups, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers, and neuropathologic features.
Asterisks denote significant associations based on an false discovery rate (FDR) cutoff of 0.05. p-values are truncated at 1e-5 for visualization purposes.
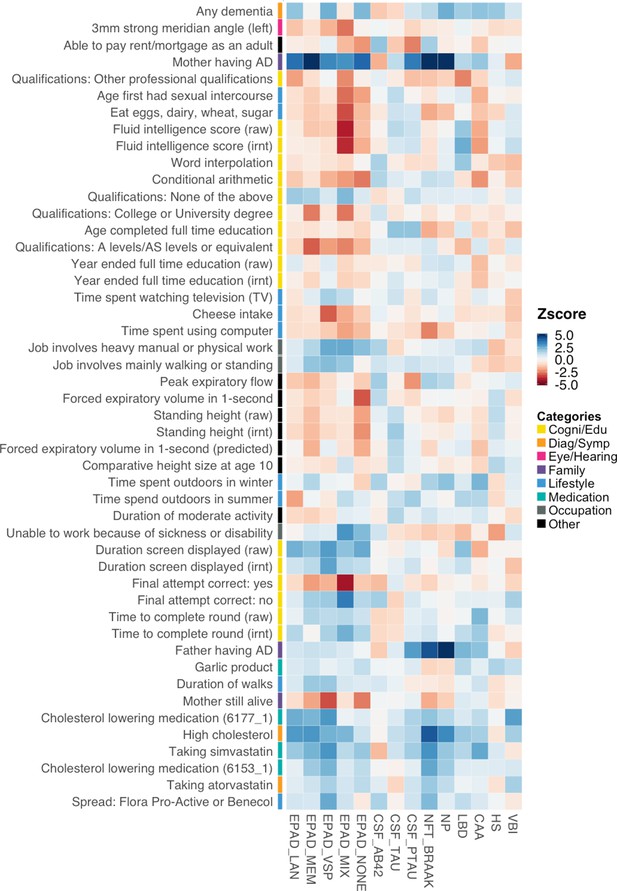
Association directions between identified Alzheimer’s disease (AD) risk factors and AD endophenotypes.
Z-scores are truncated at 5 and –5 for visualization purposes.
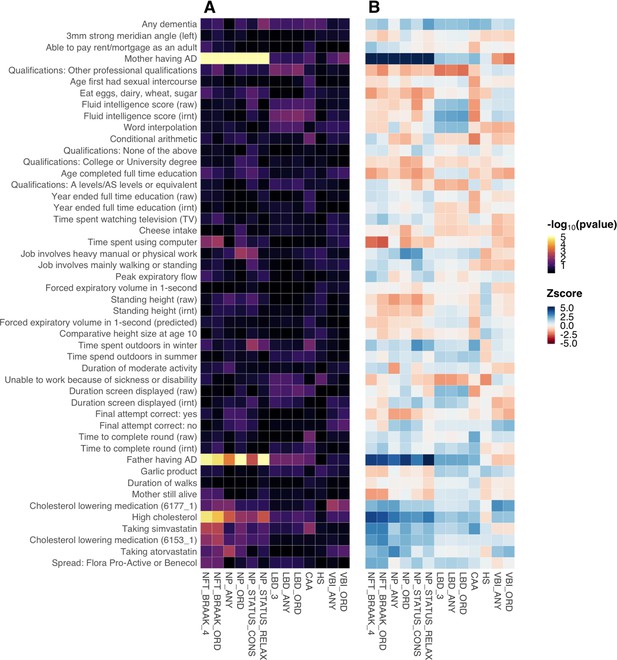
Association results for the complete set of 13 neuropathologic features for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other dementias.
(A) Association p-values; (B) Association z-scores. p-values are truncated at 1e-5 and z-scores are truncated at 5 and –5 for visualization purposes.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Simulation result; Result from Mendelian randomization and GSMR; Acknowledgements to Alzheimer’s Disease Genetics Consortium (ADGC).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91360/elife-91360-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Full association result between UK-biobank traits and Alzheimer’s disease/endophenotypes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91360/elife-91360-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91360/elife-91360-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx