Evolution of haploid and diploid populations reveals common, strong, and variable pleiotropic effects in non-home environments
Figures
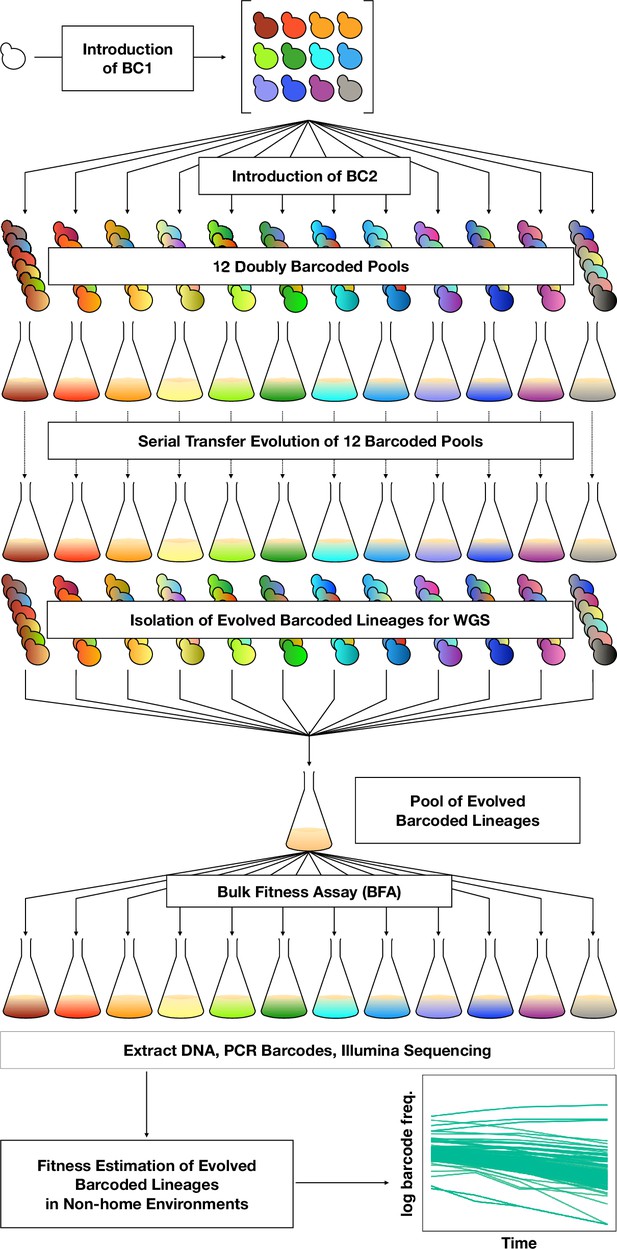
DNA double-barcoding strategy enables massively parallel bulk ‘common garden’ fitness remeasurements across many environments.
For both ploidies (1N and 2N) 12 pools of singly barcoded yeast were generated. A second, high complexity barcode was then introduced into each pool, creating 24 (12 haploid and 12 diploid) pools of uniquely double barcoded yeast. Each pool was evolved in a specific environment (Table 1) for up to 440 generations (55 transfers). Evolved strains were isolated from each pool and whole-genome sequenced to identify any mutations that arose. Strains were pooled for bulk fitness assays in the same environments used for the evolutions, in duplicate or triplicate. The barcodes were then sequenced and the barcode frequencies were used to estimate fitness.
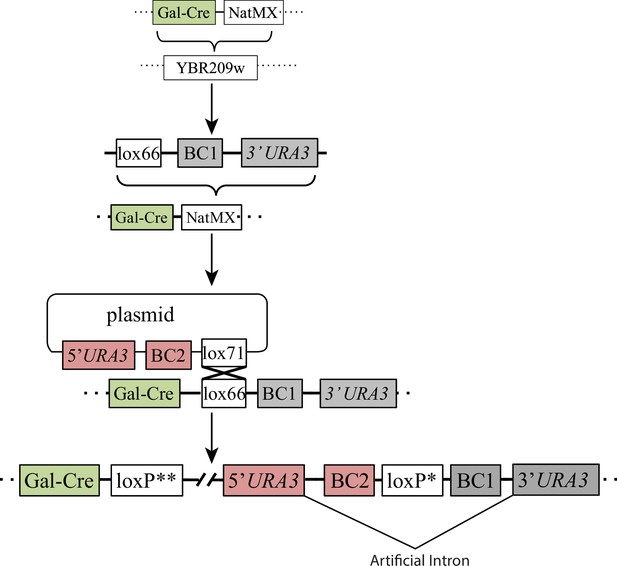
Double barcoding system.
A Gal-Cre-NatMX cassette was homologously recombined into the YBF209W dubious open reading frame region in an S288C derivative, BY4709. The NatMX marker was replaced with a DNA fragment containing a lox66 site, a random sequence of 20 nucleotides (BC1), half of an artificial intron (AI) and the 3’ half of the URA3 selectable marker. This strain was then transformed with a plasmid library containing the 5’ half of the URA3 selectable marker, another random sequence of 20 nucleotides (BC2), the other half of an artificial intron, and a lox71 site. Gal-Cre-induced recombination between the lox66 and plasmid lox71 sites was used to insert the plasmid region containing BC2, AI, and the 5’ half of the URA3 marker. This insertion creates a genomic locus that contains a complete URA3 artificial intron, BC2, a crippled loxP site, BC1, and a complete URA3 gene. The barcodes residing in between the artificial intron regions are maintained due to selection for URA3.
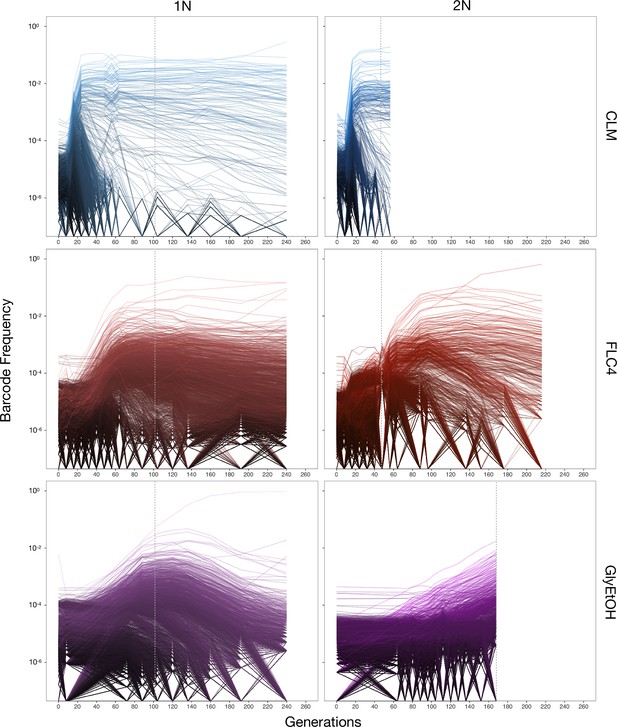
Lineage tracking data for evolutions in clotrimazole, fluconazole, and glycerol/ethanol.
The lines correspond to 10,000 barcoded lineages (the 5000 lineages with highest abundance, and 5000 additional randomly chosen lineages). The intensity of the color of the line indicates the highest barcode frequency reached by that lineage. The y axis represents the barcode frequency in log scale. The dashed vertical lines indicate from which timepoint clones were isolated.
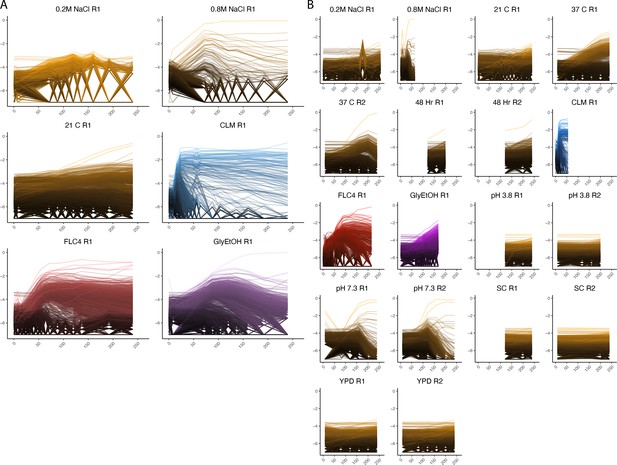
Lineage tracking for all evolutions.
(A) Lineage tracking data for each haploid experimental evolution. The lines correspond to barcoded lineages. Each row represents the home environment in which the evolution was conducted. Each column represents the ploidy. (B) Lineage tracking data for each diploid experimental evolution.
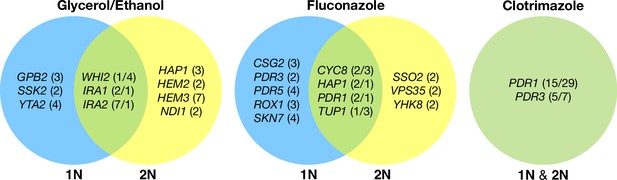
Haploid and diploid mutational spectra.
For each focal condition, the mutations are grouped by the ploidy they were identified in: blue (haploids), yellow (diploids). The genes listed in the overlap region are genes that had acquired mutations in evolutions of both ploidies. The number listed in parentheses is the number of unique mutations observed in that gene for that ploidy. Genes listed in the green overlap region are observed to have mutations in both ploidies. In the parentheses, the left number is the number of mutations observed in haploid evolutions and the number on the right is the number of mutations observed in that gene in the diploid evolutions. See Methods for selection criteria of mutations.
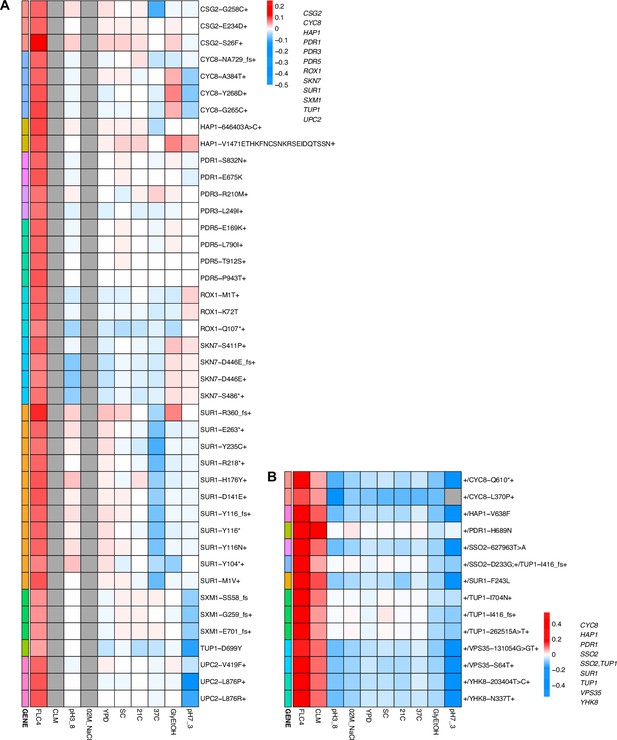
Heatmaps representing pleiotropic profiles of adaptive mutant lineages from populations evolved in fluconazole.
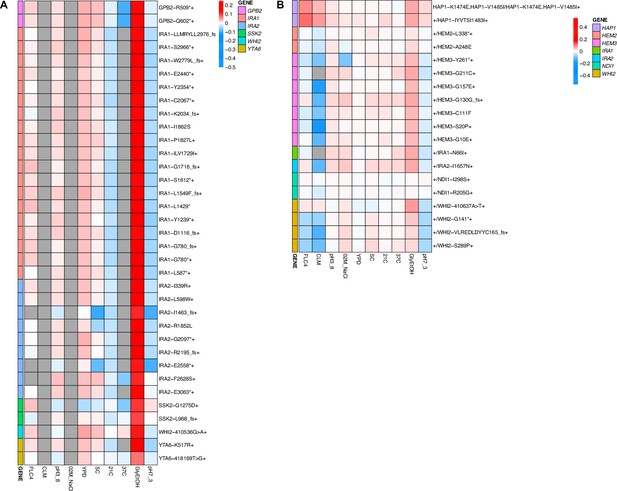
Each heatmap shows the lineages evolved in a particular condition and their fitness remeasurements in a specific bulk fitness assay. Each square on the heatmap shows the average fitness of the lineage measured in each environment (columns) for approximately 40 generations, specifically for mutant lineages we identified in Table 1 (rows). The ‘+’ indicates that in that lineage there are other background mutations, the ‘++’ indicates that this specific mutation was observed in multiple lineages and what is shown in the row is the median fitness of all the lineages that have that mutation. (A) shows the haploids and (B) shows the diploids from the fluconazole evolution.
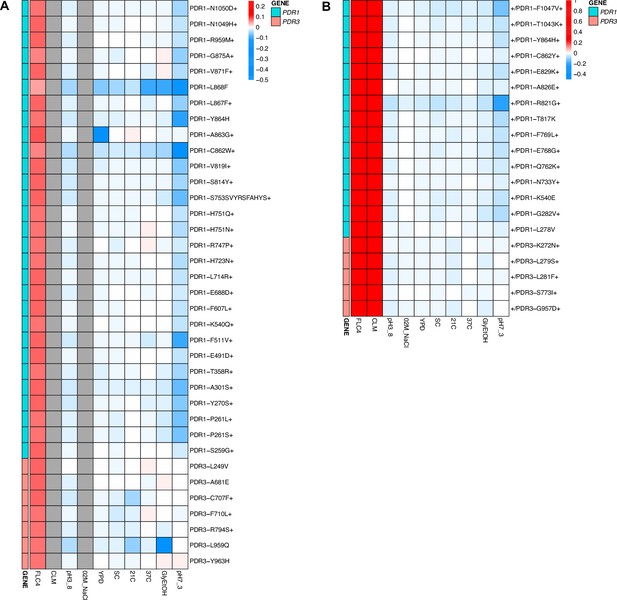
Heatmaps representing pleiotropic profiles of adaptive mutant lineages from populations evolved in clotrimazole.
Each heatmap shows the lineages evolved in a particular condition and their fitness remeasurements in a specific bulk fitness assay. Each square on the heatmap shows the average fitness of the lineage measured in each environment (columns) for approximately 40 generations, specifically for mutant lineages we identified in Table 1 (rows). The ‘+’ indicates that in that lineage there are other background mutations, the ‘++’ indicates that this specific mutation was observed in multiple lineages and what is shown in the row is the median fitness of all the lineages that have that mutation. (A) shows the haploids and (B) shows the diploids from the fluconazole evolutions.
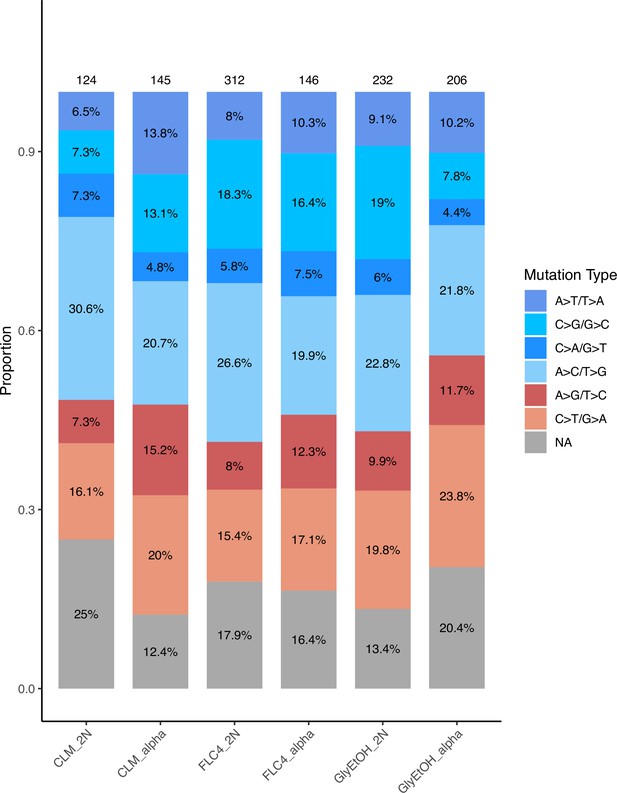
Relative mutation rates of each of the six possible nucleotide changes for each condition and ploidy tested.

Lineage Tracking Data for Fitness Remeasurement Assays.
(A) Lineage tracking data of haploid bulk fitness assay (hBFA) for lineages evolved in fluconazole, clotrimazole, and glycerol/ethanol. Each column represents a replicate. The columns are grouped together by the evolution environment: fluconazole, clotrimazole, glycerol/ethanol. Each row represents the ‘test environment’. Each line represents one lineage evolved in the home environments that corresponds with its column group. The color of the line indicates the test environment in which that lineage was remeasured. (B) Lineage tracking data of diploid bulk fitness assay (dBFA) for lineages evolved in fluconazole, clotrimazole, and glycerol/ethanol. (C) Lineage tracking data of combined bulk fitness assay (cBFA) for lineages evolved in fluconazole, clotrimazole, and glycerol/ethanol.

Comparison of replicates for each bulk fitness assay (BFA).
Each panel corresponds to a BFA and two replicates within that assay. Each row corresponds to a test environment. We plot the fitness of a lineage in one replicate against its fitness in another replicate. Haploid BFA (hBFA) only had two replicates.
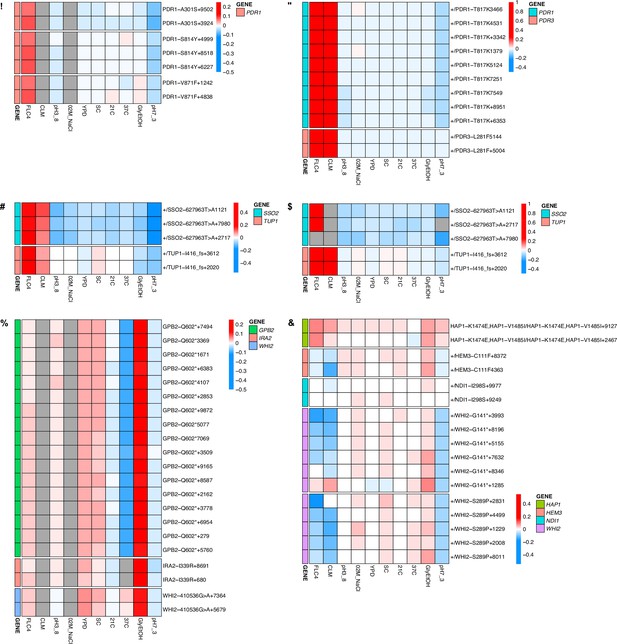
Heatmaps for all adaptive lineages with shared mutations.
These heatmaps show the fitnesses of all lineages including lineages that had the same mutation and were collapsed into a single row using the median fitnesses in Figure 4. The number at the end of the name represents numerical barcode identification number. (A) Mutations identified in clotrimazole 1N measured in haploid bulk fitness assay (hBFA). (B) Mutations identified in clotrimazole 2N measured in diploid bulk fitness assay (dBFA). (C) Mutations identified in fluconazole 2N measured in combined bulk fitness assay (cBFA). (D) Mutations identified in fluconazole 2N measured in dBFA. (E) Mutations identified in glycerol/ethanol 1N measured in hBFA. (F) Mutations identified in glycerol/ethanol 2N measured in cBFA.
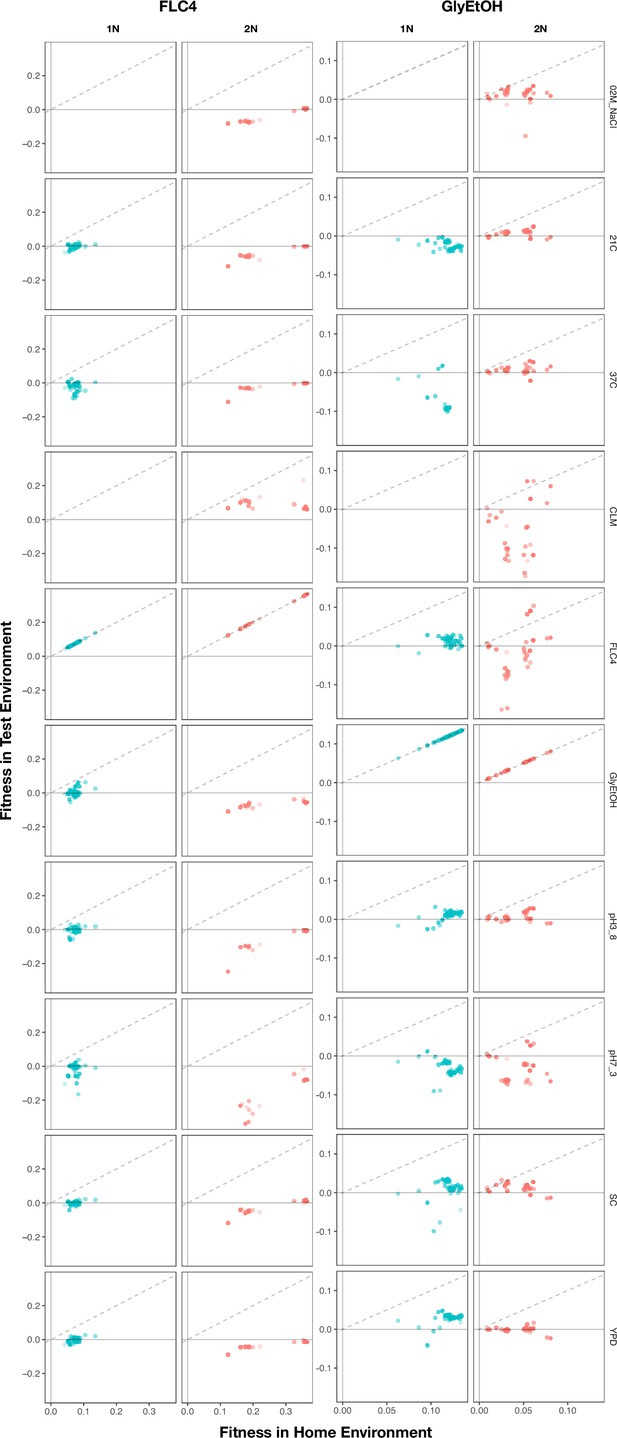
Home environment compared to test environments for all adaptive lineages.
The columns are the home environments that lineages evolved in and the rows are the test environments in which their fitnesses were remeasured. X axis is the fitness of the lineages remeasured in the bulk fitness assay (BFA) in their home environment. Y axis is the fitness of the lineages in a non-home environment. No fitness remeasurements are available from BFAs grown in clotrimazole.
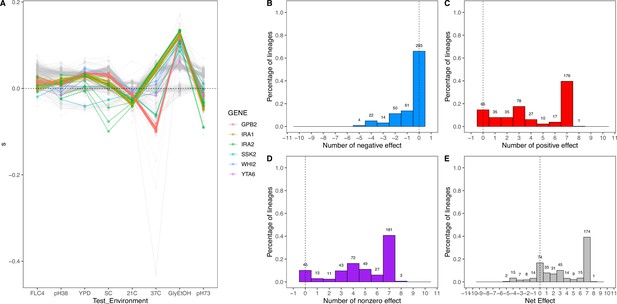
Net effect of mutant haploid lineages evolved in glycerol/ethanol.
(A) Fitness measurements, s, of haploid lineages adapted to glycerol/ethanol. The colored lines represent lineages that have a mutation identified to be adaptive. The colors represent which gene the mutation is in. (B) Negative effect of lineages adapted to glycerol/ethanol. This describes the number of lineages that had a negative effect (fitness <–0.018) in a specific number of non-home environments. (C) Positive effect of lineages adapted to glycerol/ethanol. This describes the number of lineages that had a positive effect (fitness >0.018) in a specific number of non-home environments. (D) Nonzero effect of lineages adapted to glycerol/ethanol. This describes the number of lineages that had a nonzero effect (fitness >0.018 or fitness <–0.018) in a specific number of non-home environments. (E) Net effect of lineages adapted to glycerol/ethanol. The sum of each lineage’s effect across all non-home environment.
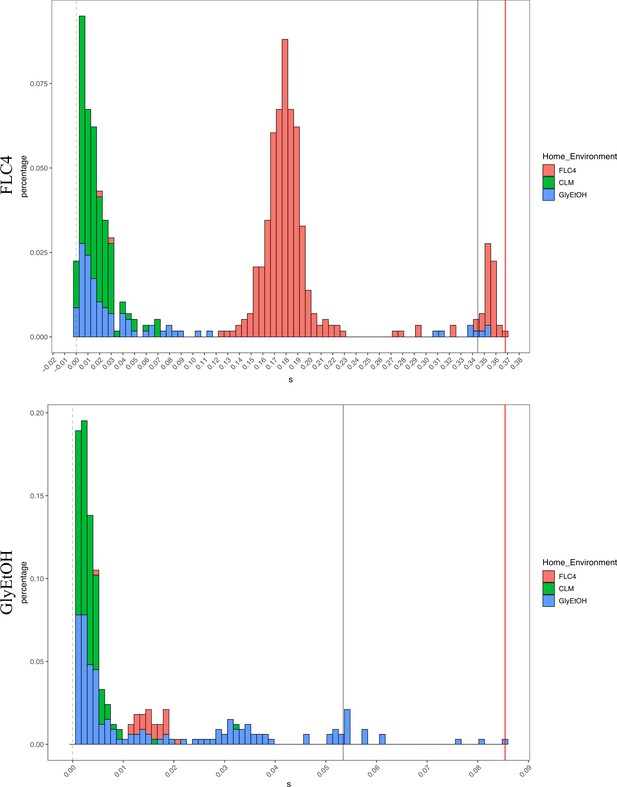
Distribution of fitness effects for fitness estimates of all adaptive diploid lineages remeasured in clotrimazole, fluconazole, and glycerol/ethanol.
The distribution of fitness effects for all adaptive diploid lineages remeasured in clotrimazole, fluconazole, and glycerol/ethanol. The gray vertical line delineates the fitness threshold of the top 10% of mutants that were evolved in the labeled environment. The red line delineated the top fitness of all mutants that were evolved in the labeled environment. The y axis delineates the percentage of mutants that have a specific fitness (x axis).
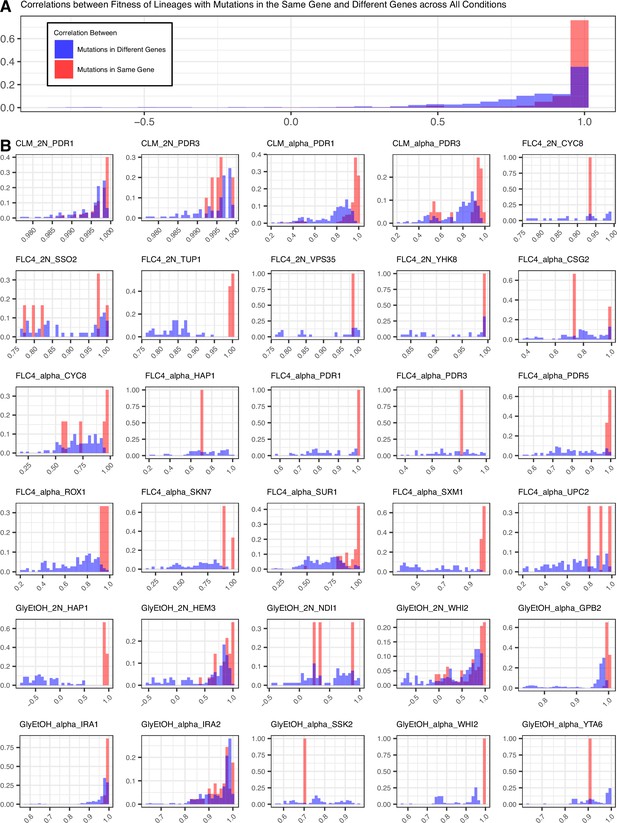
Mutations in the same gene tend to lead to more similar pleiotropic profiles than in different genes for the same evolution condition.
(A) Correletions aggregated across all conditions. (B) Correlations by condition and ploidy. The fitnesses of lineages with candidate adaptive mutations in the same gene that arose in the same condition were compared to each other and a Pearson correlation was calculated for each comparison. Then the fitnesses of lineages with candidate adaptive mutations in the same gene were compared to the fitnesses of all the other lineages evolved in that condition that have adaptive mutations in a different gene and a Pearson correlation was calculated for each comparison.
Heatmaps representing pleiotropic profiles of adaptive mutant lineages from populations evolved in glycerol/ethanol.
Each heatmap shows the lineages evolved in a particular condition and their fitness remeasurements in a specific bulk fitness assay. Each square on the heatmap shows the average fitness of the lineage measured in each environment (columns) for approximately 40 generations, specifically for mutant lineages we identified in Table 1 (rows). The ‘+’ indicates that in that lineage there are other background mutations, the ‘++’ indicates that this specific mutation was observed in multiple lineages and what is shown in the row is the median fitness of all the lineages that have that mutation. (A) shows the haploids and (B) shows the diploids from the fluconazole evolutions.
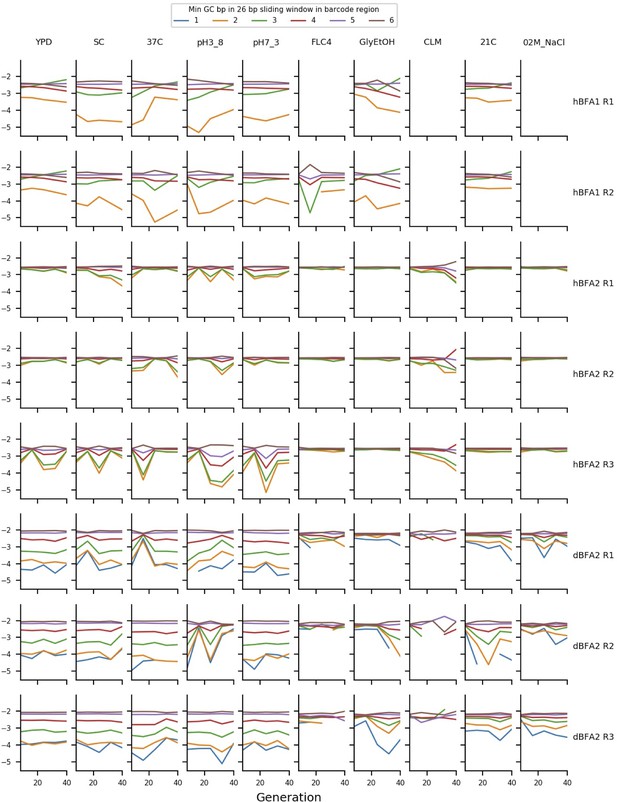
The mean frequency of putatively neutral barcodes with different minimum GC-contents.
The y axis represents the log10 of the mean frequency of the putatively neutral barcodes with different minimum GC-contents of a 26 bp sliding window measured across the barcode region. The ordering of the deviations here demonstrates that GC-content bias is affecting measured frequency.
Tables
Environmental conditions used in this study.
Evolution conditions used in this study, after how many generations clones were isolated, whether adaptive mutations were identified, and abbreviations used.
| Environment | Description | Evolution condition | Putative adaptation observed | Lineage tracking data available for evolution conditions | Fitness measurements available for bulk fitness assay pools | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haploids | Diploids | Haploids | Diploids | Haploids | Diploids | hBFA | dBFA | cBFA | ||
| SC | Defined rich medium | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | X | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| CLM | Antifungal drug, 2 mg/L clotrimazole | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | ✓ |
| FLC4 | Antifungal drug, 4 mg/L fluconazole | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| GlyEtOH | Nonfermentable carbon source and diluted every 48 hr, 2% glycerol + 2% ethanol | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 0.2 M NaCl | Low salt concentration | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | ✓ |
| 0.8 M NaCl | High salt concentration | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | X |
| 21°C | Low temperature | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 37°C | High temperature | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | X | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| pH 3.8 | Defined rich media buffered to pH 3.8 | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | X | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| pH 7.3 | Defined rich media buffered to pH 7.3 | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | X | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 48 hr | Defined rich media, diluted every 48 hr | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | X | ✓ | X | X | X |
| YPD | Undefined rich medium, YP + 2% glucose | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | X | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Summary of adaptive mutations.
Mutations are grouped by the home environment and the ploidy of the population in which they arose. The mutations are tabulated by gene. Genes are listed multiple times because mutations arose in those genes in different home environments. ‘In/Del’ stands for short ‘insertion/deletion’ mutations, ‘fs’ designates frameshift mutations, ‘*’ designating a stop codon, and if the mutation was in a non-coding region the mutation is displayed as the chromosome position, reference allele, a right pointing chevron, and mutant allele (i.e. 646403A>C). This table only shows unique mutations within that home environment, but mutations could have arisen in multiple lineages in the same condition or in different conditions. For diploids ‘+/’ indicates a heterozygous mutation.
| Home environment | Ploidy | Gene | Total mutations | Missense | Nonsense | Coding In/Del | Non-coding | List of unique mutations/amino acid change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLM | 2N | PDR1 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +/E768G; F1047V; +/C862Y; +/T817K; +/K540E; +/G282V; +/E829K; +/N733Y; +/T1043K; +/F769L; +/Y864H; +/Q762K; +/L278V; +/A826E; +/R821G |
| PDR3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +/S773I; +/L281F; +/G957D; +/L279S; +/K272N | ||
| CLM | 1N | PDR1 | 29 | 28 | 0 | 1 | 0 | N1050D; P261L; P261S; L868F; V871F; H751N; H751Q; S753SVYRSFAHYS; C862W; H723N; Y270S; K540Q; R959M; E688D; N1049H; A301S; Y864H; T358R; S814Y; F607L; R747P; L867F; L714R; G875A; E491D; F511V; A863G; S259G; V819I |
| PDR3 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | R794S; C707F; F710L; L249V; L959Q; Y963H; A681E | ||
| FLC4 | 2N | CYC8 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | +/Q610*; +/L370P |
| HAP1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +/V638F | ||
| PDR1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +/H689N | ||
| SSO2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | +/627963T>A; +/D233G | ||
| TUP1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | +/I416_fs; +/I704N; +/262515A>T | ||
| VPS35 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | +/131054G>GT; +/S64T | ||
| YHK8 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | +/N337T; +/203404T>C | ||
| FLC4 | 1N | CSG2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | S26F; E234D; G258C |
| CYC8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | G265C; NA729_fs; A384T; Y268D | ||
| HAP1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 646403A>C; V1471ETHKFNCSNKRSEIDQTSSN | ||
| PDR1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | S832N; E675K | ||
| PDR3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | L249I; R210M | ||
| PDR5 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | P943T; E169K; L790I; T912S | ||
| ROX1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Q107*; K72T; M1T | ||
| SKN7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | D446E_fs; D446E; S486*; S411P | ||
| SUR1 | 11 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 0 | Y116_fs; Y116N; Y235C; E263*; Y104*; D141E; M1V; R218*; Y116*; H176Y; R360_fs | ||
| SXM1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | SS58_fs; E701*_fs; G259_fs | ||
| TUP1 | 1 | 1 | D699Y | |||||
| UPC2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | V419F; L876R; L876P | ||
| GlyEtOH | 2N | HAP1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | K1474E, V1485I/K1474E,V1485I; +/IYVTSI1483I |
| HEM2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | +/L338*; +/A248E | ||
| HEM3 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | +/S20P; +/G10E; +/G130G_fs; +/C111F; +/Y261*; +/G157E; +/G211C | ||
| IRA1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +/N66I | ||
| IRA2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +/I1657N | ||
| NDI1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +/I298S; +/R205G | ||
| WHI2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | +/S289P; +/G141*; +/410637A>T; +/VLREDLDYYC165_fs | ||
| GlyEtOH | 1N | GPB2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Q602*; R509* |
| IRA1 | 19 | 3 | 9 | 7 | 0 | D1116_fs; L1429*; ILV1729I; P1827L; K2034_fs; Y2354*; L1549F_fs; E2440*; S1612*; G780_fs; G780*; S2966*; W2779L_fs; C2067*; I1862S; LLMRYLL2976_fs; Y1239*; L587*; G1716_fs | ||
| IRA2 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0 | G2097*; I339R; E3063*; L598W; F2628S; R1852L; I1463_fs; E2558*; R2195_fs | ||
| SSK2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | G1275D; L968_fs | ||
| WHI2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 410536G>A | ||
| YTA6 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | K517R; 418169T>G |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Table of isolation timepoints and bulk fitness assay (BFA) composition: The information regarding the BFA pools such as the number of isolated lineages and the evolutions and the timepoints from which they were isolated.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92899/elife-92899-supp1-v3.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Table of conditions and number of unique lineages sequenced: For each environment, the number of lineages with unique barcodes isolated is listed along with the number of lineages sequenced that had identifiable mutations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92899/elife-92899-supp2-v3.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Table of mutations identified in each sequenced clone.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92899/elife-92899-supp3-v3.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Summary of clone fitnesses from each evolved population across test environments.
Lineages from each evolution are categorized according to whether their fitness is positive or negative or neutral in each test environment.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92899/elife-92899-supp4-v3.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Landing pad diploid strains – the sequences of each BC1 landing pad barcode, and the environment in which that barcoded population was evolved.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92899/elife-92899-supp5-v3.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 6
Table of timepoints excluded from fitness estimation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92899/elife-92899-supp6-v3.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92899/elife-92899-mdarchecklist1-v3.docx





