A conserved cell-pole determinant organizes proper polar flagellum formation
Figures
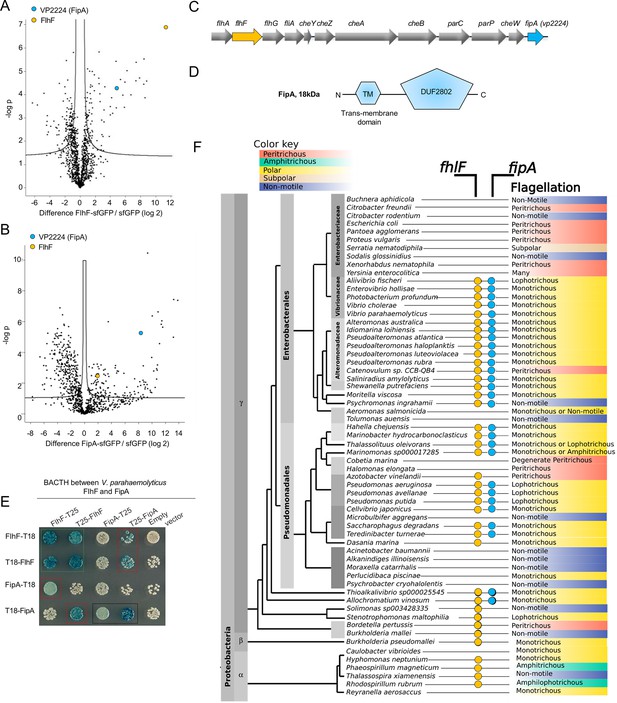
FipA constitutes a new family of FlhF interaction partners.
Volcanoplots representing Log-ratios versus significance values of proteins enriched in (A) FlhF-sfGFP or (B) FipA-sfGFP purifications using shotgun proteomics and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; sfGFP was used as control. The full list of pulled-down proteins can be found in the Supplementary file 1a. (C) Organization of the flagellar/chemotaxis gene region encoding FlhF and FipA in V. parahaemolyticus. (D) Domain organization of FipA (TM, transmembrane region; DUF, domain of unknown function). (E) Bacterial two-hybrid confirming the interaction between FipA and FlhF from V. parahaemolyticus. The indicated proteins (FipA, FlhF) were fused N- or C-terminally to the T18- or T25-fragment of the Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase. In vivo interaction of the fusion proteins in Escherichia coli is indicated by blue color. The corresponding assay in P. putida and S. putrefaciens is displayed in Figure 1—figure supplement 2. (F) Dendrogram of γ-proteobacteria, indicating the presence of FlhF or FipA homologues and the corresponding flagellation pattern. An extended version and sources are available in Supplementary file 1b.
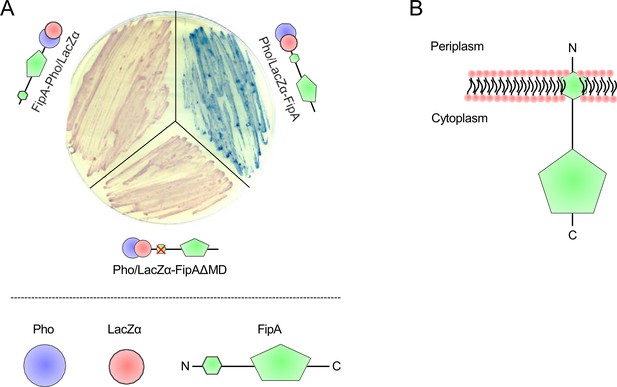
Membrane topology of FipA.
(A) Topology analysis and (B) the corresponding model. A Pho/LacZα cassette was translationally fused to the N- or the C-terminus of FipA and the fusion is expressed in a suitable E. coli strain. Pho is only active in the periplasm, while LacZα can functionally complement β-galactosidase activity within the cytoplasm. The enzyme activities can then be tested using suitable color reactions. Expression of Pho-Lac-FipA resulted in blue colonies whereas expression of FipA-Pho-Lac resulted in red colonies, hence suggesting that the FipA N-terminus is positioned in the periplasm and the C-terminus in the cytoplasm (B). Deletion of the predicted membrane spanning domain in Pho-Lac-FipA (aa 6–28, Pho-Lac-FipAΔMD) resulted in red E. coli colonies (A). This suggests that in the absence of the membrane spanning domain the N-terminus of FipA resides in the cytoplasm, and thus further supports that FipA is a transmembrane protein anchored in the inner membrane via the 6–28 aa N-terminal membrane spanning domain and is oriented with the 1–5 aa N-terminal in the periplasm and the 29–163 aa C-terminal in the cytoplasm (B).
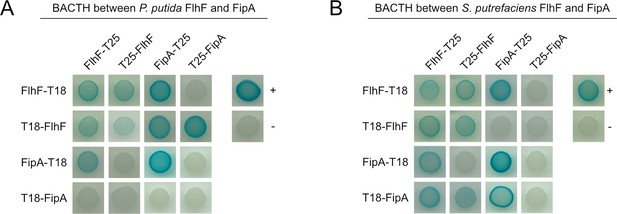
FlhF interacts with FipA in a bacterial two-hybrid analysis (BACTH) in P. putida and S. putrefaciens.
FlhF and FipA were produced as N-terminal or as C-terminal fusions to the T18 and T25 fragments of the B. pertussis adenylate cyclase in the given combinations within a single strain. In vivo protein-protein interactions result in active adenylate cyclase activity and high cAMP levels, indicated by blue coloring of the colonies on X-Gal-containing agar.
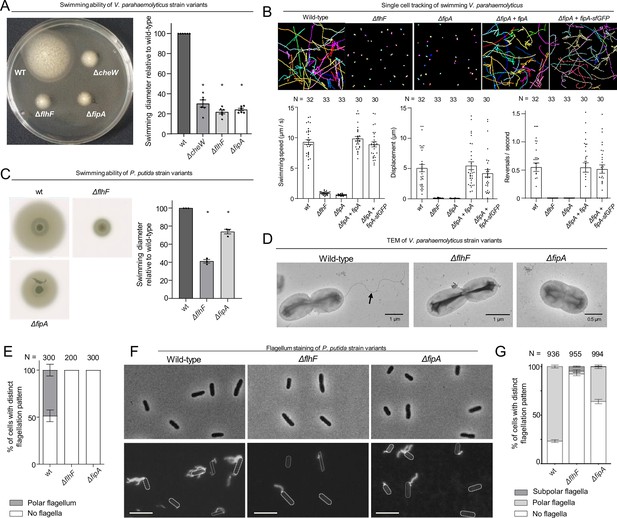
FipA is required for correct flagellum formation.
(A, C) Representative soft-agar swimming assay of V. parahaemolyticus (A) or P. putida (C) strains (left panels) and the corresponding quantification (right panels). For the latter, the halo diameter measurements were normalized to the halo of the wild type on each plate. Data presented are from six (A) or three (C) independent replicates, asterisks represent a p-value < 0.05 (according to ANOVA + Tukey tests). (B) Single-cell tracking of V. parahaemolyticus. Shown are representative swimming trajectories and quantification of swimming speed, total displacement and reversal rate. N indicates number of cells tracked among three biological replicates (ANOVA + Tukey test). (D) Representative electron micrographs of the indicated V. parahaemolyticus strains stained with uranyl acetate. (E) Quantification of flagellation pattern in the populations of the indicated V. parahaemolyticus strains. (F) Flagellum stain of indicated P. putida strains with Alexa Fluor 488-C5-maleimide and (G) quantification of the corresponding flagellation in the population. N indicates the number of cells counted among three biological replicates. For S. putrefaciens, see Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
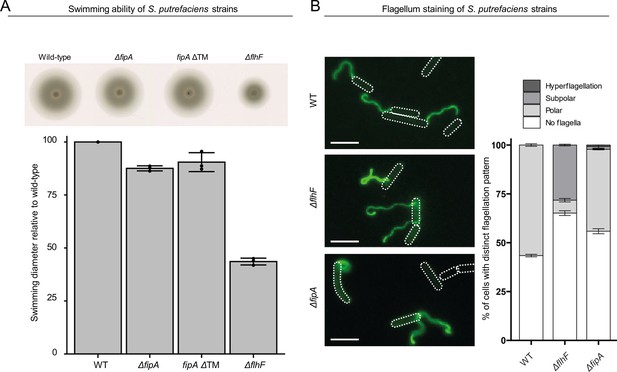
Deletions of or in FipA and FlhF affect S. putrefaciens flagellation.
(A) Upper panel: Spreading of the indicated strains in soft agar. fipA ΔTM indicates that the transmembrane region of FipA was deleted. The images shown were compiled from a single plate. Lower panel: the corresponding quantification given as diameter; three independent experiments were conducted. The error bar marks the standard deviation. (B) Left: Shown are fluorescent micrographs where the flagellar filament(s) of the indicated strains were fluorescently labeled by maleimide dye. The position of the cell bodies was outlined in the figure. The scale bare equals 5 µm. Right: The corresponding quantification of flagellation. The number of cells (n) for each experiment was >300 from three indepenedent experiments. The error bar between the different populations shows the standard deviation.
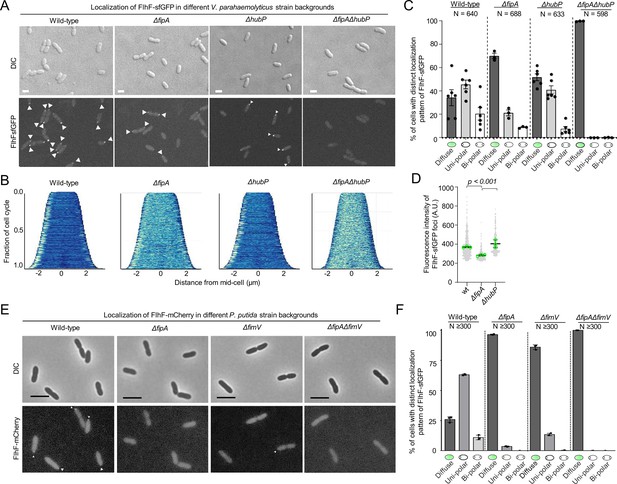
Localization of FlhF depends on FipA and HubP.
(A) Representative micrographs of the indicated strains of V. parahaemoloyticus expressing FlhF-sfGFP from its native promoter. Upper panel shows the DIC image, the lower panel the corresponding fluorescence image. Fluorescent foci are highlighted by white arrows. Scale bar = 2 μm. For an enlargment see Figure 3—figure supplement 3. (B) Demographs displaying FlhF-sfGFP fluorescence intensity along the cell length within the experiments shown in (A). (C) Quantification of localization patterns and (D) foci fluorescence intensity of the fluorescence microscopy experiment presented in (A). The data was combined from the given number (N) of cells combined from three biological replicates. (E) Representative micrographs of the indicated P. putida strains expressing FlhF-sfGFP from its native promoter. The upper panels show the DIC and the lower panels the corresponding fluorescence images. Fluorescent foci are marked by small white arrows. The scale bar equals 5 µm. The low intensity of the foci did not allow a quantitative analysis of foci intensities or the generation of demographs. For an enlargement of the micrographs see Figure 3—figure supplement 4. (F) Quantification of FlhF-sfGFP localization patterns in the corresponding strains of P. putida from the experiments shown in (E). Corresponding data on the localization of FlhF in S. putrefaciens is displayed in Figure 3—figure supplement 5.
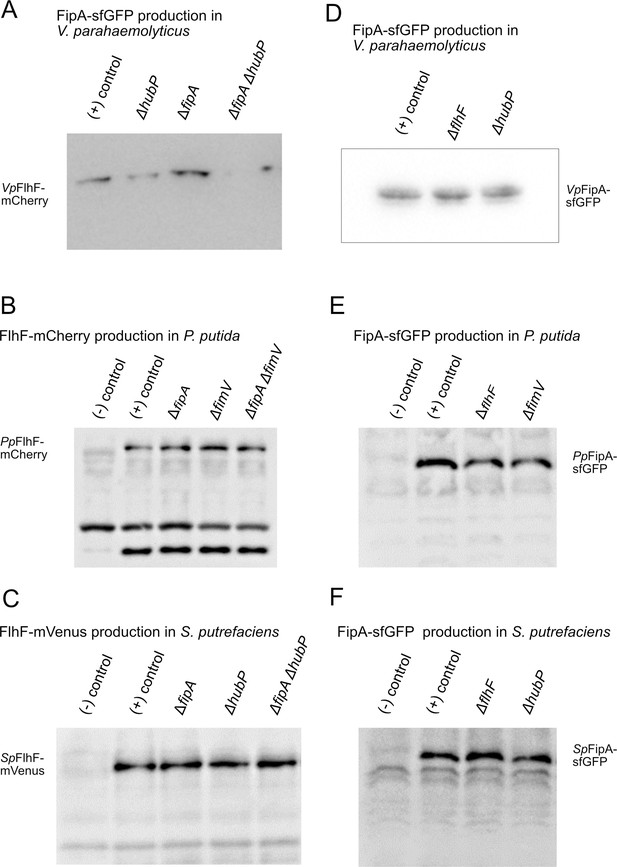
Western analysis on the protein levels of FlhF and FipA fusions to fluorescent proteins.
Crude protein extracts from the corresponding (mutant) strains of V. parahaemolyticus (A, D), P. putida (B, E) and S. putrefaciens (C, F) were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to membranes and visualized by western blotting using antibodies against GFP (A, C–F) and mCherry (B). The same OD units from the culture were loaded for each sample. The corresponding strain background is indicated above the lanes.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Scans of the original western blots for Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93004/elife-93004-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Scans of the original western blots for Figure 3—figure supplement 1 with labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93004/elife-93004-fig3-figsupp1-data2-v1.zip
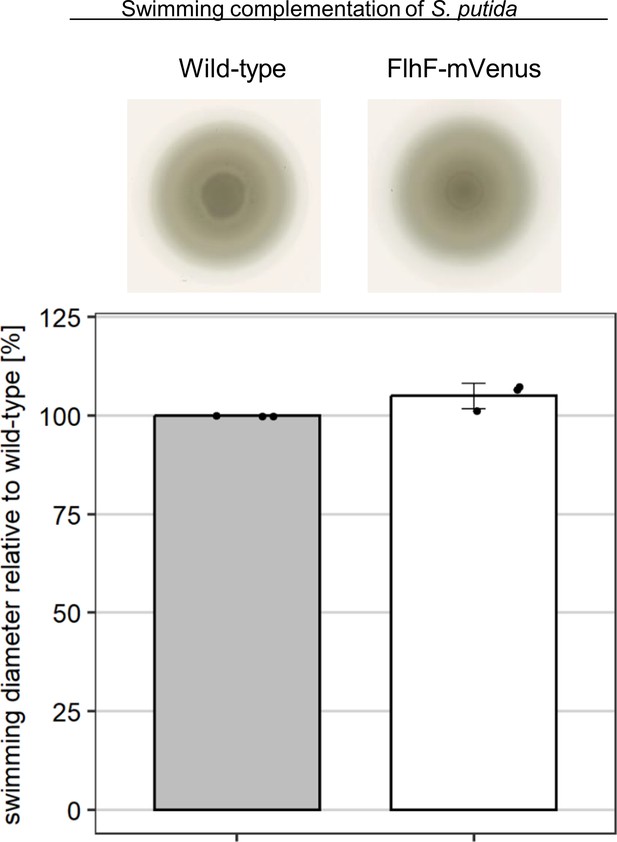
N-terminal tagging of PpFlhF with mCherry does not negatively affect spreading motility in soft agar.
The upper panel shows the spreading in soft agar, the lower panel shows the corresponding quantification. The images shown are from the same plate, three independent experiments were conducted. The corresponding standard error bar is shown.
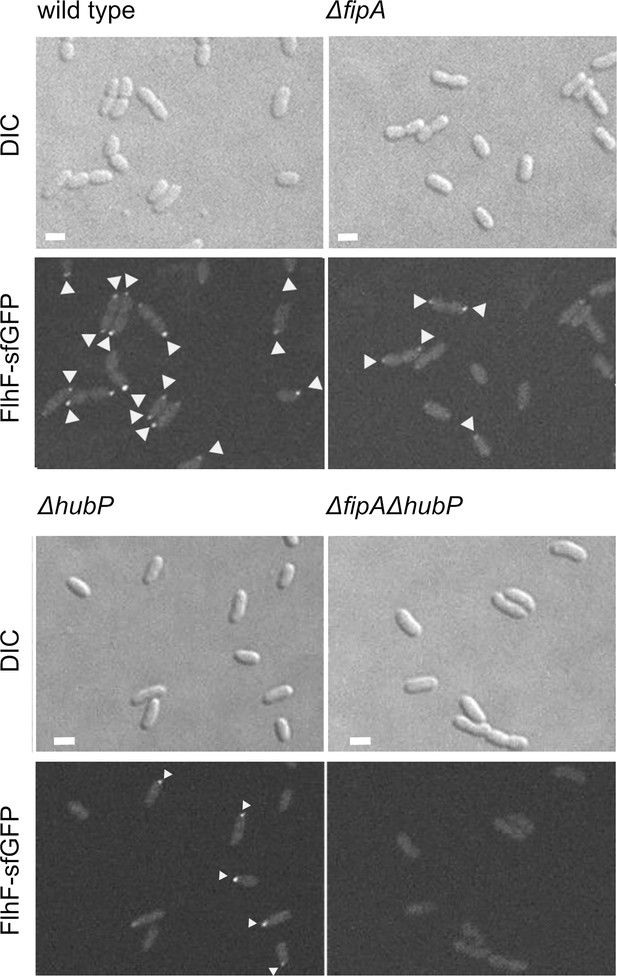
Localization of FlhF depends on FipA and HubP.
Shown are enlargments of Figure 3A, representative micrographs of the indicated strains of V. parahaemoloyticus expressing FlhF-sfGFP from its native promoter. The upper panel shows the DIC image, the lower panel the corresponding fluorescence image. Fluorescent foci are highlighted by white arrows. Scale bar = 2 μm.
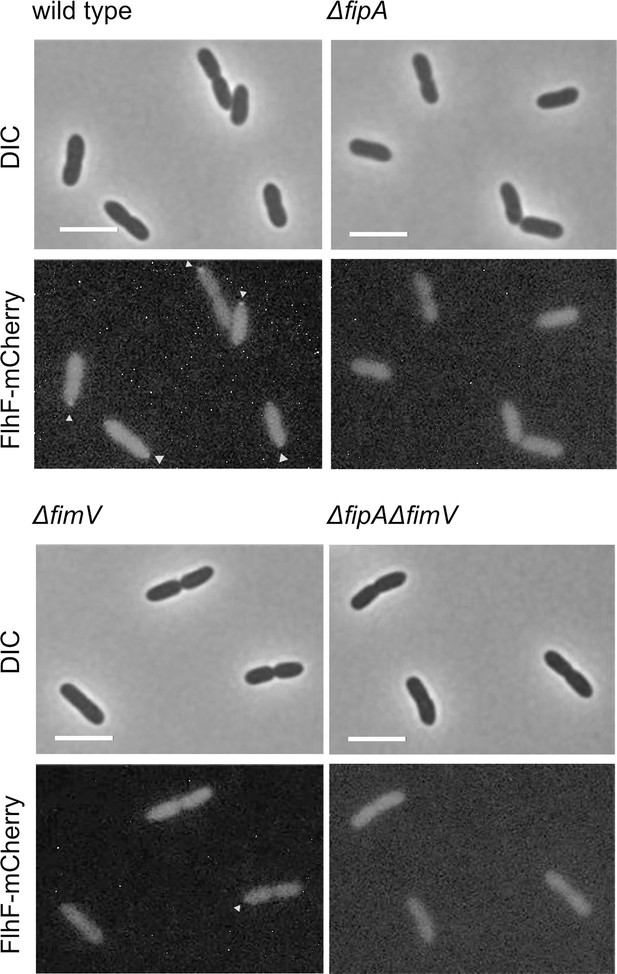
Localization of FlhF depends on FipA and HubP.
Shown are enlargments of Figure 3E, representative micrographs of the indicated strains of P. putida expressing FlhF-sfGFP from its native promoter. The upper panel shows the DIC image, the lower panel the corresponding fluorescence image. Fluorescent foci are highlighted by white arrows. Scale bar = 5 μm.
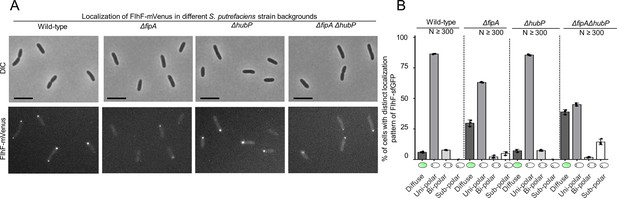
SpFipA and SpHubP concertedly affect polar SpFlhF localization.
A) Fluorescence microscopy on the indicated (mutant) strains each bearing an flhF-mvenus hybrid gene replacing native flhF on the chromosome. The upper panel shows DIC micrographs, the lower panel the corresponding fluorescent images. The scale bar equals 5 µm. (B) Quantification of the FlhF-mVenus localization patterns, using the data from >300 cells (n) from three independent experiments, the corresponding standard error is shown as error bar.
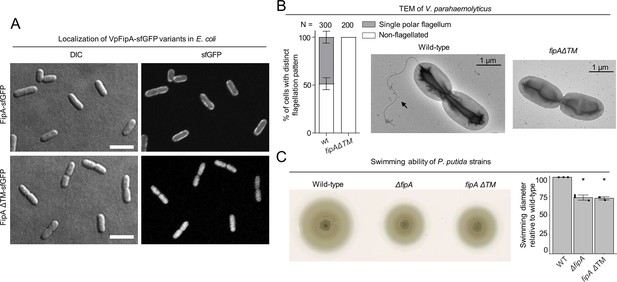
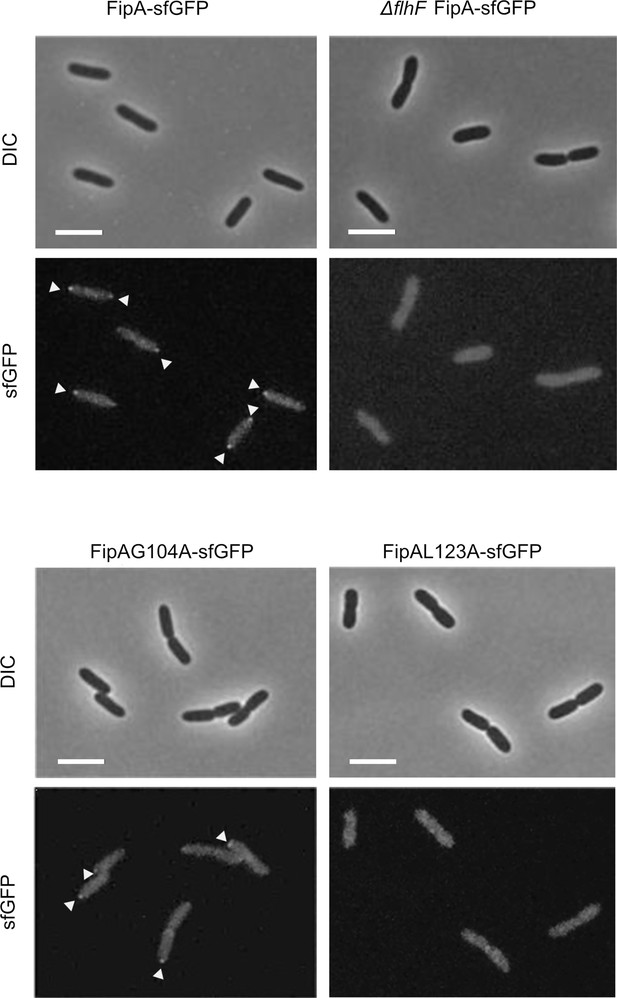
Activity of FipA depends on FlhF and on its transmembrane domain.
(A) Micrographs of E. coli cells expressing FipA-sfGFP from V. parahaemolyticus, and a truncated version lacking the transmembrane domain (ΔTM). The left panels display the DIC and the right panels the corresponding fluorescence images. The scale bar equals 5 μm. (B) Electron micrographs of V. parahaemolyticus wild-type and mutant cells lacking the transmembrane domain of fipA, respectively. The corresponding quantification of the flagellation pattern is shown to the left of the micrographs. Note that the data for the wild-type cells is the same as in Figure 2D and E. (C) Spreading behavior of the indicated P. putida strains (left) with the corresponding quantification (right). Loss of the FipA TM region phenocopies a complete fipA deletion.
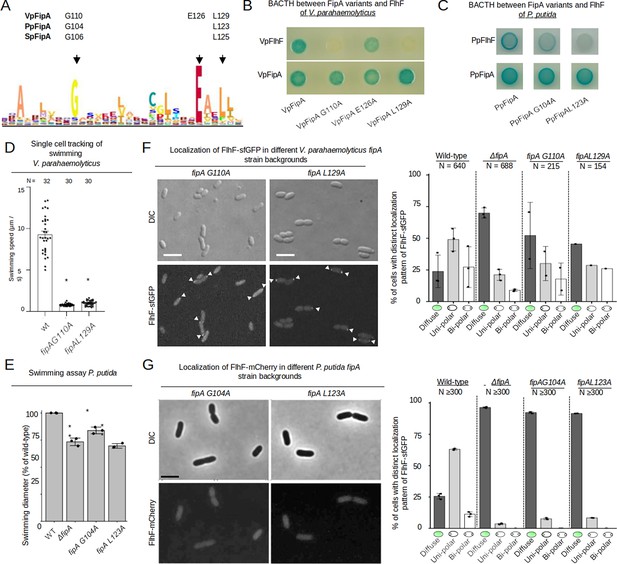
Conserved residues in the domain of unknown function of FipA are essential for interaction with FlhF.
(A) Weight-based consensus sequence of the conserved region of DUF2802 as obtained from 481 species. The residues targeted in the FipA orthologs of V. parahaemolyticus, P. putida and S. putrefaciens are indicated along with their appropriate residue position. (B, C) Bacterial two-hybrid assay of FipA variants of V. parahaemolyticus (B) or P. putida (C) with an alanine substitution in the conserved residues indicated in (A). The constructs were tested for self-interaction and interaction with FlhF. In vivo interaction of the fusions in E. coli is indicated by blue coloration of the colonies. (D) Quantification from single-cell tracking of swimming V. parahaemolyticus cells expressing FipA bearing the indicated substitution in the DUF2802 domain (see Figure 2B for wild-type behavior). Asterisks indicate a p-value <0.05 (ANOVA + Tukey test) (F) Localization of VpFlhF in the absence of FipA or in cells with substitutions in the DUF2802 domain. Left: Micrographs showing the localization of FipA-sfGFP in the indicated strains; the upper panels display the DIC and the lower panels the corresponding fluorescence images (for an enlargement see Figure 5—figure supplement 1). The scale bar equals 5 µm. Right: the corresponding quantification of the FlhF-sfGFP patterns in the indicated strains. (E) Soft-agar spreading assays of P. putida wild-type and indicated mutant strains, asterisks display a p-value of 0.05 (*) or 0.01 (**) (ANOVA). (G) Localization of P. putida FlhF in strains bearing substitutions in the DUF2802 interaction site. Left: micrographs displaying the localization of FlhF-mCherry in the indicated strains. Upper panels show the DIC and lower panels the corresponding fluorescence images. The scale bar equals 5 µm (for an enlargement see Figure 5—figure supplement 1). Right: Corresponding quantification of the FlhF localization pattern in the indicated strains. Data for S. putrefaciens is displayed in Figure 5—figure supplement 2.
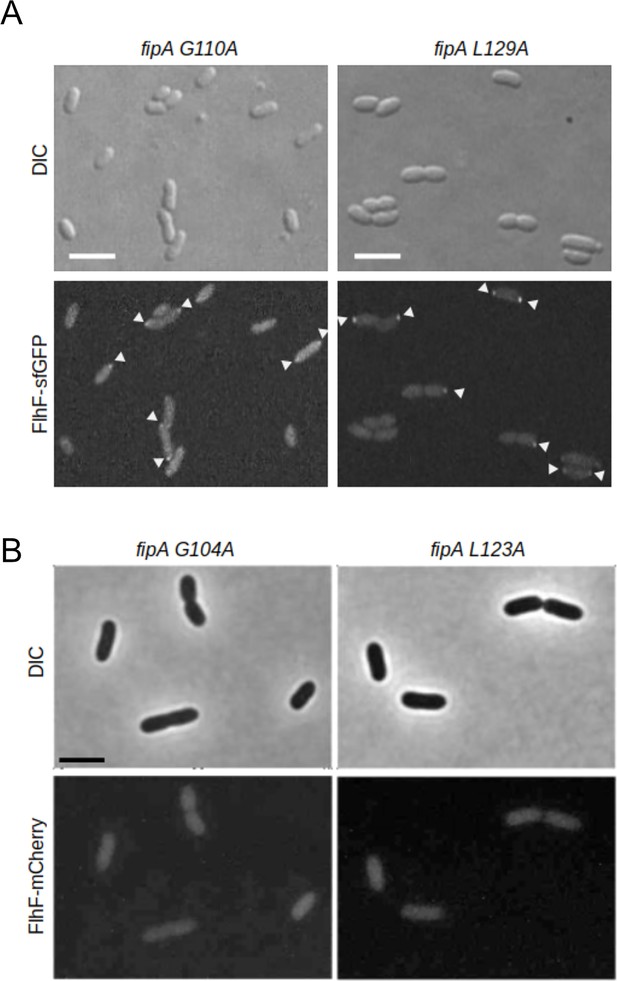
Conserved residues in the domain of unknown function of FipA are essential for interaction with FlhF in P. putida.
(A) Localization of VpFlhF in cells with substitutions in the DUF2802 domain. Micrographs are showing the localization of FipA-sfGFP in the indicated strains; the upper panels display the DIC and the lower panels the corresponding fluorescence images. The scale bar equals 5 µm. (B) The same analysis for P. putida FlhF-mCherry. The images are enlargements of Figure 5F (A) and Figure 5G (B).
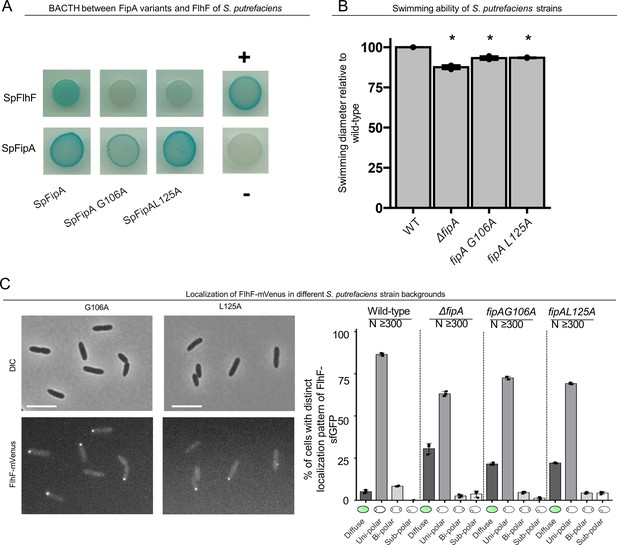
Targeted residue substitution in FipA affects FlhF positioning and function in S. putrefaciens.
(A) BACTH analysis (see, e.g. Figure 2) suggests that G106A and L125A in SpFipA does not disrupt but maybe weakens (G106A) the interaction between SpFipA and SpFlhF. (B) Spreading of the indicated S. putrefaciens strains in soft agar reveals a small but sigifnificant (asterisk = p < 0.05) and based on three independent experiments. (C) Left: micrographs showing DIC (upper panels) and fluorescent imaging on mVenus-tagged FlhF cells in mutant backgrounds bearing the given substutions in SpFipA with the corresponding quantification (n>300 cells, right). The in vivo analysis suggests that the residue substitutions in SpFipA give rise to phenotypes that are similar to that of a fipA deletion.
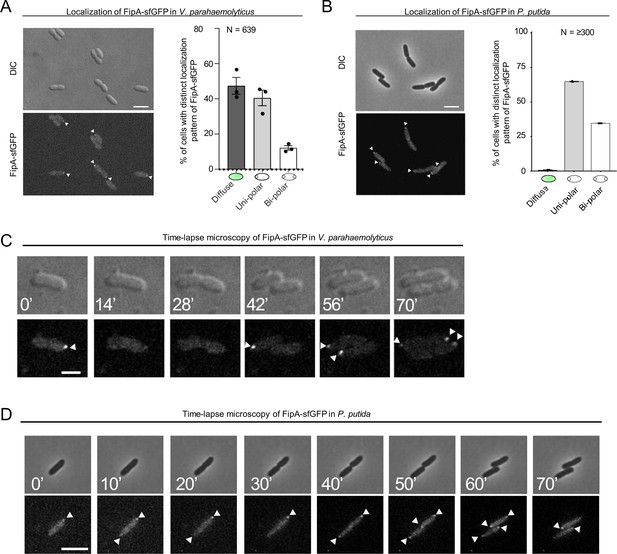
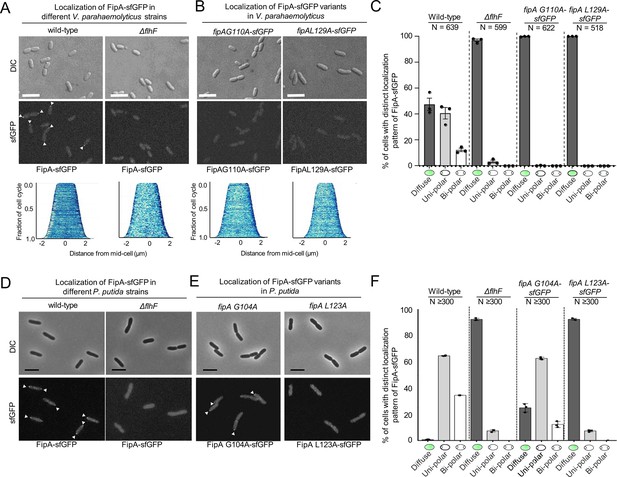
The localization pattern of FipA.
(A, B) Localization pattern of fluorescently labeled FipA in V. parahaemolyticus and P. putida. (A) Representative micrographs of V. parahaemolyticus expressing FipA-sfGFP from its native promoter. Scale bar = 2 μm. The upper panel shows the DIC and the lower panel the corresponding fluorescence channel. To the right the localization was quantified accordingly. (B) The same analysis for P. putida. (C, D) Time lapse analysis of FipA-sfGFP localization over a cell cycle in V. parahaemolyticus (C) and P. putida (D). The numbers in the upper DIC micrographs show the minutes after start of the experiment. The scale bars equal 1 µm (C) and 5 µm (D).
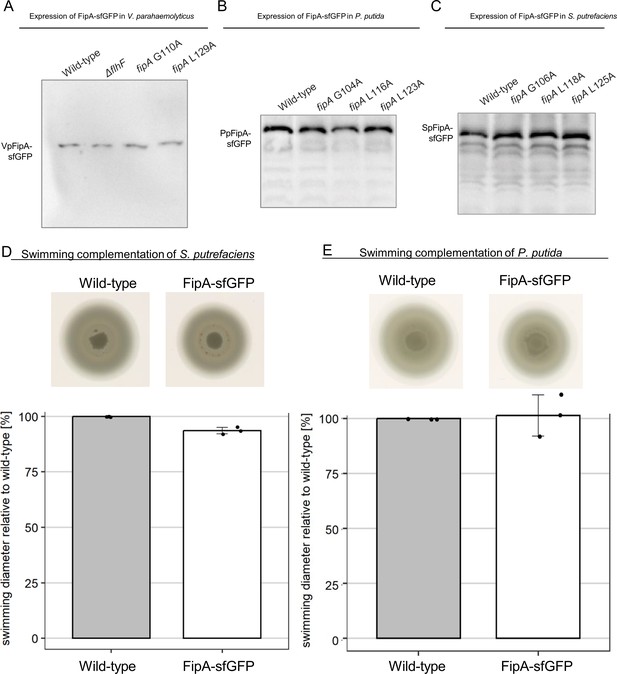
Production and function of FipA derivatives.
The three panels show western blotting analysis of PAGE protein separations from V. parahaemolyticus (A), P. putida (B) and S. putrefaciens (C) bearing FipA-sfGFP with substitutions in conserved residues as indicated, using antibodies raised against sfGFP. V. parahaemolyticus also includes a mutant deleted in flhF. The loaded samples are normalized by OD units. (D) The C-terminal fusion of sfGFP has only minor effects on FipA function in S. putrefaciens and P. putida. The upper panels show the spreading in soft agar (taken from the same soft agar plate), the lower the corresponding quantification. The error bars are the standard deviation from three independent experiments.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Scans of the original western blots for Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93004/elife-93004-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Scans of the original western blots for Figure 6—figure supplement 1 with labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93004/elife-93004-fig6-figsupp1-data2-v1.zip
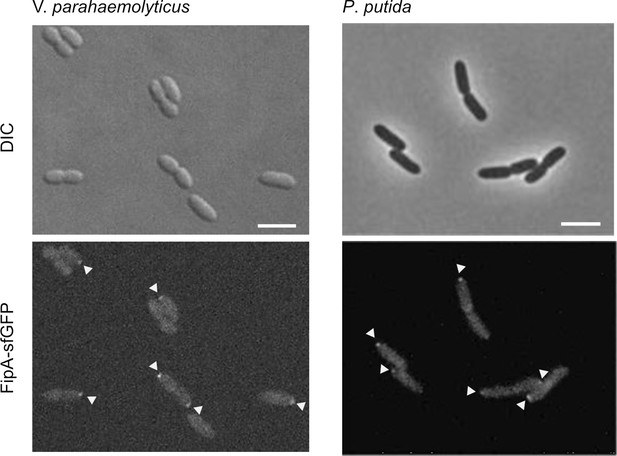
The localization pattern of FipA.
Localization pattern of fluorescently labeled FipA in V. parahaemolyticus and P. putida. Left: Representative micrographs of V. parahaemolyticus expressing FipA-sfGFP from its native promoter. Scale bar = 2 μm. The upper panel shows the DIC and the lower panel the corresponding fluorescence channel. Right: The same analysis for P. putida. The images are enlargements of the micrographs in Figure 6A and B.
Normal localization of FipA depends on interaction with FlhF.
(A, B) Localization pattern of V. parahaemolyticus FipA-sfGFP in the indicated wild-type and mutant strains. The upper panels display the DIC micrographs, the middle panel the corresponding fluorescence imaging (scale bar equals 5 µm), and the lower panel the corresponding demograph showing the fluorescence of FipA-sfGFP along the cell length. (C) Quantification of the cell localization pattern from the experiment shown in (A, B) as combined from three biological replicates. (D, E, F) The same analysis for the corresponding P. putida strains as indicated. The scale bar equals 5 µm. The data for S. putrefaciens is displayed in Figure 7—figure supplement 3.
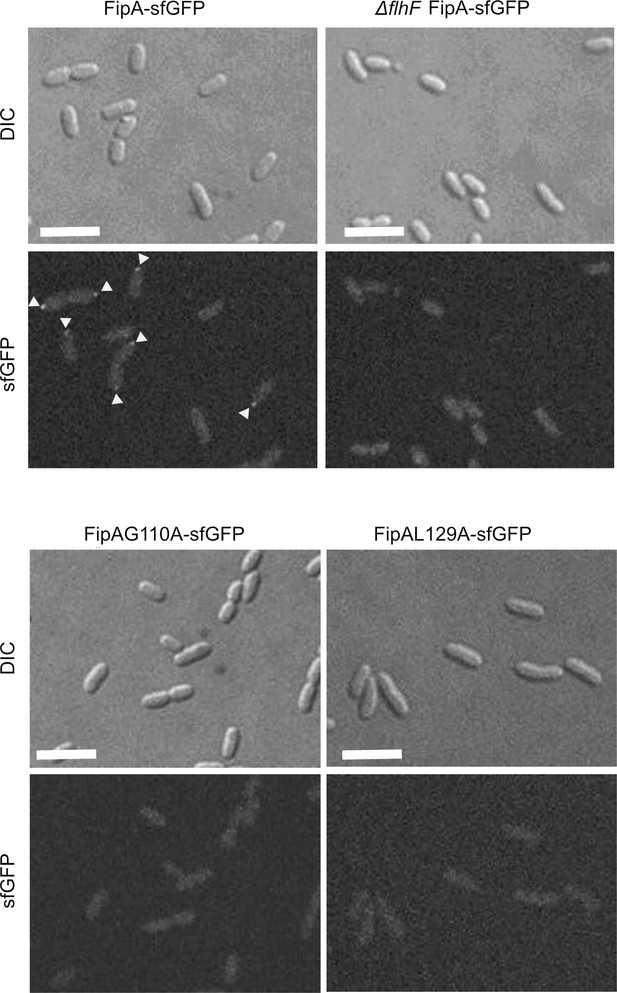
Normal localization of FipA depends on interaction with FlhF.
Localization pattern of V. parahaemolitycus FipA-sfGFP in the indicated wild-type and mutant strains. The upper panels display the DIC micrographs, the lower panel the corresponding fluorescence imaging (scale bar equals 5 µm). The images are enlargements of the micrographs in Figure 7A (upper) and 7B (lower).
Normal localization of FipA depends on interaction with FlhF.
Localization pattern of P. putida FipA-sfGFP in the indicated wild-type and mutant strains. The upper panels display the DIC micrographs, the lower panel the corresponding fluorescence imaging (scale bar equals 5 µm). The images are enlargements of the micrographs in Figure 7D (upper) and 7E (lower).
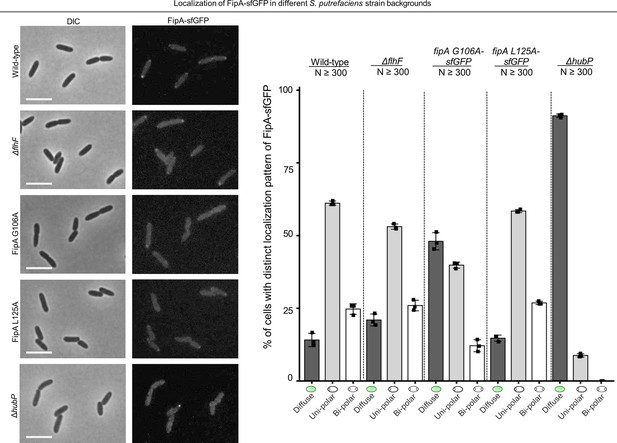
Localization of SpFipA in different strain backgrounds.
Left: Micrographs showing DIC (left) and fluorescence (right) microscopy on cells with FipA-sfGFP in different background strains as indicated. The scale bar equals 5 µm. The corresponding quantification (N>300, three independent experiments) is shown to the right. FipA loses its polar localization in a mutant lacking HubP and in a mutant with the L125A substitution in FipA.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | fipA | KEGG | VP2224 | |
| Gene (Pseudomonas putida) | fipA | KEGG | PP_4331 | |
| Gene (Shewanella putrefaciens) | fipA | KEGG | Sputcn32_2550 | |
| Gene (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | flhF | KEGG | VP2234 | |
| Gene (Pseudomonas putida) | flhF | KEGG | PP_4343 | |
| Gene (Shewanella putrefaciens) | flhF | KEGG | Sputcn32_2561 | |
| Strain (Escherichia coli) | SM10λpir | Simon et al., 1983 | ||
| Strain (Escherichia coli) | DH5pir | Miller and Mekalanos, 1988 | ||
| Strain (Escherichia coli) | BTH101 | Euromedex | ||
| Strain (Escherichia coli) | WM3064 | Metcalf, University of Illinois, Urbana‐Champaign | ||
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | RIMD 2210633 | Makino et al., 2003 | Wild type | |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2234 (ΔflhF), Δvpa1548 (ΔlafA) | Arroyo-Pérez and Ringgaard, 2021 | EP12 | |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2225 (ΔcheW) | Ringgaard et al., 2014 | SR58 | |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvpa1548 (ΔlafA) | Arroyo-Pérez and Ringgaard, 2021 | JH2 | |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2224 (ΔfipA), Δvpa1548 (ΔlafA) | this study | EP15 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2234 (ΔflhF) | Arroyo-Pérez and Ringgaard, 2021 | PM60 | |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2224 (ΔfipA) | this study | SW01 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2191 (ΔhubP) | Arroyo-Pérez and Ringgaard, 2021 | JH4 | |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2234::vp2234-sfgfp (ΔflhF::flhF-sfgfp) | Arroyo-Pérez and Ringgaard, 2021 | PM69 | |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2234::vp2234-sfgfp (ΔflhF::flhF-sfgfp), Δvp2224 (fipA) | this study | PM77 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2234::vp2234-sfgfp (ΔflhF::flhF-sfgfp), Δvp2191 (hubP) | Arroyo-Pérez and Ringgaard, 2021 | EP11 | |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2234::vp2234-sfgfp (ΔflhF::flhF-sfgfp), Δvp2224 (fipA), Δvp2191 (hubP) | this study | EP09 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | vp2224 (fipA) L129A | this study | PM65 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | vp2224 (fipA) G110A | this study | PM66 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2234::vp2234-sfgfp (ΔflhF::flhF-sfgfp), vp2224 (fipA) L129A | this study | EP16 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2234::vp2234-sfgfp (ΔflhF::flhF-sfgfp), vp2224 (fipA) G110A | this study | EP17 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | vp2224 L129A, Δvpa1548(lafA) | this study | EP13 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | vp2224 G110A, Δvpa1548(lafA) | this study | EP14 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2224::vp2224-sfgfp (ΔfipA::fipA-sfgfp) | this study | PM64 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2224::vp2224-sfgfp (ΔfipA::fipA-sfgfp), Δvp2234 (flhF) | this study | PM68 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2224::vp2224 L129A-sfgfp (ΔfipA L129A::fipA-sfgfp) | this study | PM71 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Vibrio parahaemolyticus) | Δvp2224::vp2224 G110A-sfgfp (ΔfipA G110A::fipA-sfgfp) | this study | PM72 | Materials and Methods |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | KT2440 | Nelson et al., 2002 | Wild type | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C | Hintsche et al., 2017 | ||
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C ΔflhF | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | ΔfipA | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C ΔfipA | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FipA -DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C ΔflhF FipA-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FlhF-GS-mCherry | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C ΔfimV FipA -DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | ΔfipA FlhF-GS-mCherry | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FipA G104A | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FipA L123A | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FipA L123A | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FipA-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FipA L116A | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FipA G104A-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FipA L123A-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FipA L116A-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FlhF-GS-mCherry ΔfimV | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C ΔfipA FipA KI | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FlhF-GS-mCherry ΔfimV ΔfipA | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FlhF-GS-mCherry FipA L123A | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FlhF-GS-mCherry FipA L116A | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FlhF-GS-mCherry FipA G104A | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FlhF D362A-GS-mCherry | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FlhF-GS-mCherry FipA ΔTMD | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FlhF-GS-mCherry FipA ΔTMD | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Pseudomonas putida) | FliC S267C FipA ΔTMD-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | CN-32 | Fredrickson et al., 1998 | Wild type | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | ΔflhF | Rossmann et al., 2015 | ||
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | CheA-mCherry | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | flgE1 T183C | Rossmann et al., 2019 | ||
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | flaB1 T166C flaA1 T174C ΔflagL | Kühn et al., 2017 | ||
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | ΔfipA | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | CheA-mCherry ΔfipA | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | flaB1 T166C flaA1 T174C ΔflagL ΔfipA | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FlhF-GS-mVenus | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FlhF-GS-mVenus ΔfipA | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FlhF-GS-mVenus ΔflhG | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA-DILEL-sfGFP ΔflhF | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FlhF-GS-mVenus ΔhubP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FlhF-GS-mVenus ΔfipA ΔhubP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | flgE1 T183C ΔflagL | Hook et al., 2020 | ||
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA-DILEL-sfGFP ΔhubP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | HubP-mCherry FlhF-GS-Venus | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FlhF-GS-mVenus ΔhubP ΔSputcn32_3157 | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | flaB1 T166C flaA1 T174C ΔflagL FipA-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | flaB1 T166C flaA1 T174C ΔflagL ΔflhF | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | ΔfipA fipA (Sputcn32_2550) KI | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA L118A | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA G106A | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA L118-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA G106A-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | flgE1 T183C ΔflagL FliM1-GS-sfGFP | Hook et al., 2020 | ||
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA L125A | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | flaB1 T166C flaA1 T174C ΔflagL ΔfipA ΔhubP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA L125A-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FlhF-mCherry FipA-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA L118A FlhF-GS-mVenus | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA G106A FlhF-GS-mVenus | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA L125A FlhF-GS-mVenus | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA ΔTMD | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FlhF-GS-mVenus FipA ΔTMD | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Strain (Shewanella putrefaciens) | FipA ΔTMD-DILEL-sfGFP | this study | Materials and Methods | |
| Antibody | JL-8 anti-GFP (mouse monoclonal) | Takarabio | 632380 | WB (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | Amersham ECL mouse IgG (sheep, polyclonal) | General Electric | NA931 | WB (1:5,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (mouse) | Roche | 11814460001 | WB (1:5,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-mCherry (rabbit) | Biovision | 5993–100 | WB (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse | Sigma | A3562 | WB (1:5,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit | Sigma | A8025 | WB (1:20,000) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pDM4 | Milton et al., 1996 | Suicide vector for gene deletions in Vibrio sp. | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pJH036 | Iyer et al., 2020 | pBAD33 derivative for sfGFP C-terminal fusion | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT | Lassak et al., 2010 | Suicide vector for gene deletions in P. putida and S. Putrefaciens | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 | Karimova et al., 1998 | For bacterial two hybrid assay | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 | Karimova et al., 1998 | For bacterial two hybrid assay | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 | Karimova et al., 1998 | For bacterial two hybrid assay | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C | Karimova et al., 1998 | For bacterial two hybrid assay | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pJH003 | Heering and Ringgaard, 2016 | For deletion of vpa1548(lafA) | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pSW022 | This work | For deletion of vp2224(fipA) | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM188fip | Arroyo-Pérez and Ringgaard, 2021 | For insertion of vp2234- sfgfp (flhF-sfgfp), replacing native flhF | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM178 | this work | For insertion of vp2224- sfgfp (fipA-sfgfp), replacing native fipA | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM179 | this work | For insertion of vp2224 (fipA) G110A point mutation in the chromosome in the native locus | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM180 | this work | For insertion of vp2224 (fipA) L129A point mutation in the chromosome in the native locus | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM191 | this work | For insertion of vp2224 (fipA) G110A fused to sfGFP in the chromosome in the native locus | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM187 | this work | For insertion of vp2224 (fipA) L129A fused to sfGFP in the chromosome in the native locus | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM039 | Arroyo-Pérez and Ringgaard, 2021 | For deletion of vp2191 (hubP) | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM194 | this work | For overexpression of VP2224(FipA) Δ7–27 -sfGFP | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM146 | this work | For overexpression of VP2224(FipA) | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM159 | this work | For overexpression of VP2224(FipA)-sfGFP | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT flhF KO (PP_4343) | this study | For deletion of the flhF gene (PP_4343) in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FlhF K235A (PP_4343) | this study | For in frame complementation of flhF (PP_4343) with FlhF K235A mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FlhF-GS-mCherry (PP_4343) | this study | For in frame complementation of flhF (PP_4343) with FlhF-GS-mCherry in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FlhF K235A-GS-mCherry (PP_4343) | this study | For in frame complementation of flhF (PP_4343) with FlhF K235A-GS-mCherry mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FlhF D301A-GS-mCherry (PP_4343) | this study | For in frame complementation of flhF (PP_4343) with FlhF D301A-GS-mCherry mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FlhF D362A-GS-mCherry (PP_4343) | this study | For in frame complementation of flhF (PP_4343) with FlhF D362A-GS-mCherry mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT fipA KO (PP_4331) | this study | For deletion of the fipA gene (PP_4331) in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT fipA KI (PP_4331) | this study | For in frame complementation of fipA (PP_4331) with wild type fipA in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA ΔTMD (AS5-22) (PP_4331) | this study | For in frame complementation of fipA (PP_4331) with FipA ΔTMD mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA G104A (PP_4331) | this study | For in frame complementation of fipA (PP_4331) with FipA G104A mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA L116A (PP_4331) | this study | For in frame complementation of fipA (PP_4331) with FipA L116A mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA L123A (PP_4331) | this study | For in frame complementation of fipA (PP_4331) with FipA L123A mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA-DILEL-sfGFP (PP_4331) | this study | For in frame complementation of fipA (PP_4331) with FipA-DILEL-sfGFP in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA ΔTMD-DILEL-sfGFP (AS5-22) (PP_4331) | this study | For in frame complementation of fipA (PP_4331) with FipA ΔTMD-DILEL-sfGFP mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA G104A-DILEL-sfGFP (PP_4331) | this study | For in frame complementation of fipA (PP_4331) with FipA G104A-DILEL-sfGFP mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA L116A-DILEL-sfGFP (PP_4331) | this study | For in frame complementation of fipA (PP_4331) with FipA L116A-DILEL-sfGFP mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA L123A-DILEL-sfGFP (PP_4331) | this study | For in frame complementation of fipA (PP_4331) with FipA L123A-DILEL-sfGFP mutant in P. putida KT2440; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT polar flagellar cluster KO (Sputcn32_2548–2608) | this study | plasmid for deletion of the polar flagellar gene cluster (Sputcn32_2548–2608) in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT lateral flagellar cluster KO (Sputcn32_3444–3485) | Lassak et al., 2010 | plasmid for deletion of the lateral flagellar gene cluster (Sputcn32_3444–3485) in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT flagL KO (Sputcn32_3455, Sputcn32_3456) | Rossmann et al., 2015 | plasmid for deletion of the lateral flagellin genes (Sputcn32_3455, Sputcn32_3456) in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT hubP KO (Sputcn32_2442) | Rossmann et al., 2015 | plasmid for deletion of the hubP gene (Sputcn32_2442) in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT flhF KO (Sputcn32_2561) | Rossmann et al., 2015 | plasmid for deletion of the flhF gene (Sputcn32_2561) in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT flhG KO (Sputcn32_2560) | Schuhmacher et al., 2015a | plasmid for deletion of the flhG gene (Sputcn32_2560) in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FlhF-GS-Venus (Sputcn32_2561) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of flhF (Sputcn32_2561) with FlhF-GS-mVenus in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT fipA KO (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for deletion of the fipA gene (Sputcn32_2550) in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT fipA KI (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of fipA (Sputcn32_2550) with wild type fipA in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA ΔTMD (AS5-23) (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of fipA (Sputcn32_2550) with FipA ΔTMD mutant in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA G106A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of fipA (Sputcn32_2550) with FipA G106A mutant in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA L118A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of fipA (Sputcn32_2550) with FipA L118A mutant in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA L125A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of fipA (Sputcn32_2550) with FipA L125 mutant in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA-DILEL-sfGFP (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of fipA (Sputcn32_2550) with FipA-DILEL-sfGFP in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA ΔTMD-DILEL-sfGFP (AS5-23) (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of fipA (Sputcn32_2550) with FipA ΔTMD-DILEL-sfGFP mutant in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA G106A-DILEL-sfGFP (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of fipA (Sputcn32_2550) with FipA G106A-DILEL-sfGFP mutant in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA L116A-DILEL-sfGFP (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of fipA (Sputcn32_2550) with FipA L116A-DILEL-sfGFP mutant in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FipA L125A-DILEL-sfGFP (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for in frame complementation of fipA (Sputcn32_2550) with FipA L125A mutant in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pNPTS138-R6KT FliM1-GS-sfGFP (Sputcn32_2569) | Hook et al., 2020 | plasmid for in frame complementation of fliM1 (Sputcn32_2569) with FliM1-GS-sfGFP in S. putrefaciens CN-32; Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pSW74 | this study | T25-vp2224(fipA)Δ1–27 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pSW119 | this study | T18-vp2224(fipA)Δ1–27 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM118 | this study | vp2224(fipA)Δ1–27 T18 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM119 | this study | vp2224(fipA)Δ1–27 T25 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM124 | this study | vp2234(flhF)-T18 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM128 | this study | vp2234(flhF)-T25 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM132 | this study | T18-vp2234(flhF) | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM136 | this study | T25-vp2234(flhF) | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM160 | this study | T18-vp2224(fipA) Δ1–27 G110A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM161 | this study | T18-vp2224(fipA) Δ1–27 E126A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPM162 | this study | T18-vp2224(fipA) Δ1–27 L129A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FlhF (PP_4343) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FlhF (PP_4343); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FlhF (PP_4343) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FlhF-T25 (PP_4343); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FlhF (PP_4343) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FlhF-T18 (PP_4343); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FlhF (PP_4343) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FlhF (PP_4343); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FlhF K235A (PP_4343) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FlhF K235A (PP_4343); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FlhF K235A (PP_4343) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FlhF K235A -T25 (PP_4343); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FlhF K235A (PP_4343) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FlhF K235A -T18 (PP_4343); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FlhF K235A (PP_4343) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FlhF K235A (PP_4343); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FipA (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FipA (PP_4331); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FipA (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA-T25 (PP_4331); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FipA (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA-T18 (PP_4331); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FipA (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FipA (PP_4331); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FipA G104A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FipA G104A (PP_4331); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FipA G104A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA G104A -T25 (PP_4331); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FipA G104A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA G104A -T18 (PP_4331); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FipA G104A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FipA G104A (PP_4331); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FipA L116A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FipA L116A (PP_4331); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FipA L116A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA L116A -T25 (PP_4331); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FipA L116A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA L116A -T18 (PP_4331); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FipA L116A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FipA L116A (PP_4331); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FipA L125A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FipA L123A (PP_4331); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FipA L125A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA L123A -T25 (PP_4331); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FipA L125A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA L123A -T18 (PP_4331); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FipA L125A (PP_4331) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FipA L123A (PP_4331); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FlhF (Sputcn32_2561) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FlhF (Sputcn32_2561); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FlhF (Sputcn32_2561) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FlhF-T25 (Sputcn32_2561); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FlhF (Sputcn32_2561) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FlhF-T18 (Sputcn32_2561); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FlhF (Sputcn32_2561) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FlhF (Sputcn32_2561); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FipA (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FipA (Sputcn32_2550); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FipA (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA-T25 (Sputcn32_2550); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FipA (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA-T18 (Sputcn32_2550); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FipA (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FipA (Sputcn32_2550); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FipA G106A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FipA G106A (Sputcn32_2550); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FipA G106A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA G106A -T25 (Sputcn32_2550); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FipA G106A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA G106A -T18 (Sputcn32_2550); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FipA G106A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FipA G106A (Sputcn32_2550); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FipA L116A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FipA L116A (Sputcn32_2550); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FipA L116A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA L116A -T25 (Sputcn32_2550); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FipA L116A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA L116A -T18 (Sputcn32_2550); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FipA L116A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FipA L116A (Sputcn32_2550); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKT25 FipA L125A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T25-FipA L125A (Sputcn32_2550); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKNT25 FipA L125A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA L125A -T25 (Sputcn32_2550); Kanr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18 FipA L125A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying FipA L125A -T18 (Sputcn32_2550); Ampr | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUT18C FipA L125A (Sputcn32_2550) | this study | plasmid for BACTH assay carrying T18-FipA L125A (Sputcn32_2550); Ampr | |
| Sequence-based reagent | VP2224-del-a | this study | PCR primers | CCCCC tctaga ACGTTGTCATGCTTGGTGAAAGCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | VP2224-del-b | this study | PCR primers | AGTCTCTTCAGCCATCGTCATTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | VP2224-del-c | this study | PCR primers | gaatgacgatggctgaagagact cgacgataaagagaataaaaagaagc |
| Sequence-based reagent | VP2224-del-d | this study | PCR primers | CCCCC tctaga ACGCGACGCTGCTGACCCGCAGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | VP2224-check | this study | PCR primers | acaaactccgtggggatgaatac |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224 AA1-6/28-end w/o Stop | this study | PCR primers | ccccc ctcaga atg gctgaagagacttttctgcgc |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18C/pKT25-vp2234-cw | this study | PCR primers | ccccc tctaga G aaaataaagcgattttttgccaaagac |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18C/pKT25-vp2234-ccw | this study | PCR primers | ccccc ggtacc ctagagtccttcgttgtcactg |
| Sequence-based reagent | vpa1548-del-d | this study | PCR primers | Ccccc ctcgag TTATGTGTTCCGCCTTCCTCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | vpa1548-del-chk | this study | PCR primers | aagtagccacatcccaaacgc |
| Sequence-based reagent | VP2191-del-d | this study | PCR primers | ccccc tctaga GACAATGCGCTGCACGGAAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | VP2191-del-chk | this study | PCR primers | gatggaaaacggctacacca |
| Sequence-based reagent | del vp2234(FlhF)-d | this study | PCR primers | CCCCC tctaga GAATACATGCTACGAGCTCAAGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | del vp2234(FlhF)-chk | this study | PCR primers | GTTTACGGCATGATTGATGGCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224-Gly110Ala-cw | this study | PCR primers | gagcaaccaaaatggtgcagttaGCGgctgatatcaacgagctaatcg |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224-Gly110Ala-ccw | this study | PCR primers | CGATTAGCTCGTTGATATCAGCcgcTAACTGCACCATTTTGGTTGCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224-Glu126Ala-cw | this study | PCR primers | agagtgtgaactgccaaaagcaGCAgcagagttgatgctctctttgc |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224-Glu126Ala-ccw | this study | PCR primers | GCAAAGAGAGCATCAACTCTGctgCTGCTTTTGGCAGTTCACACTCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224-Leu129Ala-cw | this study | PCR primers | tgaactgccaaaagcagaagcagag GC gatgctctctttgcagaaaaaactg |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224-Leu129Ala-ccw | this study | PCR primers | CAG TTT TTT CTG CAA AGA GAG CAT CGC CTC TGC TTC TGC TTT TGG CAG TTC A |
| Sequence-based reagent | C-term sfGFP-vp2224-a | this study | PCR primers | CCCCC actagt ATGGCTGAAGAGACTTTTTTATCTGTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | C-term sfGFP-vp2224-b | this study | PCR primers | gagctcgaggatgtc TCGTCGACGCCCACGTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | C-term sfGFP-vp2224-c | this study | PCR primers | gacatcctcgagctc atgagcaaaggagaagaacttttcac |
| Sequence-based reagent | C-term sfGFP-vp2224-d | this study | PCR primers | tta tttgtagagctcatccatgcc |
| Sequence-based reagent | C-term sfGFP-vp2224-e | this study | PCR primers | ggcatggatgagctctacaaa taa AGAGAATAAAAAGAAGCTTCGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | C-term sfGFP-vp2224-f | this study | PCR primers | ccccc gcatgc TTTGTTTGTCGATTGCTGTTAGTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | del AA7-27 vp2224-b | this study | PCR primers | AAAAGTCTCTTCAGCCATCGTCATTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | del AA7-27 vp2224-c | this study | PCR primers | GAATGACGATGGCTGAAGAGACTTTT CTGCGCATTCGTGCTAGTTTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224-cw-pBAD | this study | PCR primers | CCCCC tctaga atggctgaagagacttttttatctg |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224-ccw-pBAD | this study | PCR primers | CCCCC gcatgc ttatcgtcgacgcccacg |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224 cw restore deletion | this study | PCR primers | ACCTATAATTGGCTGAATGACG ATGGCTGAAGAGACTTTTTTATCTGTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | downstream vp2224 cw | this study | PCR primers | AGAGAATAAAAAGAAGCTTCGGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18/pKNT25- vp2224-cw | this study | PCR primers | ccccc TCTAGA atggctgaagagacttttttatctgtac |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18/pKNT25- tr-vp2224-cw | this study | PCR primers | ccccc TCTAGA ATG cgcattcgtgctagtttgc |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18/pKNT25-vp2222 -ccw | this study | PCR primers | ccccc GGTACC CG tcgtcgacgcccacgtg |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18C/pKT25-vp2224-cw | this study | PCR primers | ccccc tctaga G gctgaagagacttttttatctgtac |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18C/pKT25-vp2224-ccw | this study | PCR primers | ccccc ggtacc ttatcgtcgacgcccacgtg |
| Sequence-based reagent | tr2224 put18C cw | this study | PCR primers | ccccc tctaga G ATG cgcattcgtgctagtttgcaaaa |
| Sequence-based reagent | sfGFP-1-ccw | this study | PCR primers | ccccc tctaga tttgtagagctcatccatgccatg |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224 C-term PhoA-LacZ cw | this study | PCR primers | CCCCC tctaga g atggcccggacaccagaaatg |
| Sequence-based reagent | end -LacZ w/o STOP ccw | this study | PCR primers | gcgccattcgccattcaggctgc |
| Sequence-based reagent | LacZ to vp2224 w/o ATG | this study | PCR primers | CCT GAA TGG CGA ATG GCG C GCT GAA GAG ACT TTT TTA TCT GTA CC |
| Sequence-based reagent | end vp2224 ccw | this study | PCR primers | CCCCC aagctt ttatcgtcgacgcccacgtgg |
| Sequence-based reagent | vp2224 ccw restore deletion | this study | PCR primers | GCCGAAGCTTCTTTTTATTCTCT TTATCGTCGACGCCCACGTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | M13 | this study | PCR primers | TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | M13r | this study | PCR primers | CACACAGGAAACAGCTATGACC |
| Sequence-based reagent | flhF1-flhG1 fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGCTGAGTGTGTTGATCCAAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV FliM1 N-term fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCTCATTGAAGATGCTCTCCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV FliM1 N-term rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATAATAAAACTGCGGCCCACTTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-GFP FliM1-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCAGTTCAGATGAGTCATCCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-GFP FliM1 KO-rev | this study | PCR primers | GACATTTTGGCAGTTGATGCGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL FliM1 GFP rev | this study | PCR primers | GAAAAGTTCTTCTCCTTTGCTGCTGCCTAATTCAGATATATCTCTAGCTTTGCCTTTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL FliM1 GFP fwd | this study | PCR primers | GGATGAGCTCTACAAAGGATCCTAAGGTGAAGCAAGATGAGCACAGAAGATA |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV FlhF C-term fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCAAGAAATGGTTGGACAGCCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV FlhF C-term rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCCACATCTAAAAATCGGTCGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-FlhF-FLAG-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCATCAGTCAATGCAAGCAACC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FlhF-Venus rev | this study | PCR primers | CACGCTGCCCTCAAATGCACAGGCCATATTATCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL_Venus fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCATTTGAGGGCAGCGTGAGCAAGGGCGAGGAGCTGTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL_Venus rev | this study | PCR primers | GTCATAACTTTACTTGTACAGCTCGTCCATGCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FlhF-Venus fwd | this study | PCR primers | TACAAGTAAAGTTATGACCCTGGATCAAGCAAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | FlhF-Ven Seq_Primer | this study | PCR primers | GCTGAGTTAGTACGAGCACTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | FlhG-Ven Seq_Primer | this study | PCR primers | CGATATTATTGTCCGTGGGCCT |
| sequence-based reagent | FlhF-Ven Seq_Primer fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCTGTTGTAGTTGTACTCCAGC |
| sequence-based reagent | EcoRV FlhF C-term rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCCACATCTAAAAATCGGTCGG |
| sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-2550-GFP-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCCATCAATAACGGAAAAGGGG |
| sequence-based reagent | OL-2550-GFP-rev | this study | PCR primers | GAAAAGTTCTTCTCCTTTGCTCAGTTCCAGAATATCTTTACGATGTAACCGGATCAATAATTCAGC |
| sequence-based reagent | OL-2550-GFP-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GGATGAGCTCTACAAAGGATCCTAACGAAGTGTAGGGGCTAAGACG |
| sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-2550-GFP-rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCCTTTGTTTATATGCTCGACGG |
| sequence-based reagent | Check-2550-GFP-fwd | this study | PCR primers | CGATGAAGAATGGGCTGAACTC |
| sequence-based reagent | Check-2550-GFP-rev | this study | PCR primers | CGAAGGATGCGAGAATGACGAA |
| sequence-based reagent | OL-2069_FlhF-rev | this study | PCR primers | AATCTTCACTAGCATCCCCGTACATTGAACTC |
| sequence-based reagent | OL-FlhF-Ven-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GGGATGCTAGTGAAGATTAAACGATTTTTTGCCAAAGAC |
| sequence-based reagent | OL-FlhF-Ven-rev | this study | PCR primers | AACATTAGCTTACTTGTACAGCTCGTCCATGC |
| sequence-based reagent | OL-2068-fwd | this study | PCR primers | TACAAGTAAGCTAATGTTTTAGGGTCTTACGCG |
| sequence-based reagent | BACTH 2550 pkT25 fwd | this study | PCR primers | CAGGGTCGACTCTAGAGGGCGATGAATTTTTGATCGCGG |
| sequence-based reagent | BACTH 2550 pkT25 rev | this study | PCR primers | TTAGTTACTTAGGTACCCGGGGTTTACGATGTAACCGGATCAATAATTCAGC |
| sequence-based reagent | BACTH 2550 fwd | this study | PCR primers | CTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGGGCGATGAATTTTTGATCGCGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH 2550 rev | this study | PCR primers | GAGCTCGGTACCCGGGGTTTACGATGTAACCGGATCAATAATTCAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL_FliM1 mCh rev | this study | PCR primers | TTTGTATAACTCATCCATACCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | FlhF-Ven Seq_Primer rev | this study | PCR primers | GCTGGAGTACAACTACAACAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-GFP-fwd | this study | PCR primers | AGCAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-GFP-rev | this study | PCR primers | GGATCCTTTGTAGAGCTCATCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL -mCherry fwd | this study | PCR primers | GTTTCCAAAGGGGAAGAGGACA |
| Sequence-based reagent | pKT25-for | this study | PCR primers | CACTGACGGCGGATATCGACATGTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | pKT25-rev | this study | PCR primers | CCGCCGGACATCAGCGCCATTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18-for | this study | PCR primers | CCAGGCTTTACACTTTATGCTTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18-rev | this study | PCR primers | GACGCGCCTCGGTGCCCACTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | pKNT25-for | this study | PCR primers | CCCAGGCTTTACACTTTATGCTTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | pKNT25-rev | this study | PCR primers | GTTTTTTTCCTTCGCCACGGCCTTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18C-for | this study | PCR primers | CGGCGTGCCGAGCGGACGTTCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | pUT18C-rev | this study | PCR primers | TCAGCGGGTGTTGGCGGGTGTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | FlhF Seq_Primer fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCCCACTTTGGATCAACACACT |
| Sequence-based reagent | FlhF Seq_Primer rev | this study | PCR primers | CGTGCTCACAAAACTCGATGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV FliFG1 KO fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCCGAAAACTTGTGGCTGAAAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL- FliFG1 KO rev | this study | PCR primers | ATCGCCACCCCCGACAATCATTTCTGTGCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL- FliFG1 KO fwd | this study | PCR primers | ATTGTCGGGGGTGGCGATGAGTTCCTCTAAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV FliFG1 KO rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCAACCTAATAGTCACTGCTTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-fipA L118A rev | this study | PCR primers | AGCTTCAGCTTTGGGCGCTTCACA |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-fipA L118A fwd | this study | PCR primers | ATAAAAGAGTGTGAAGCGCCCAAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-fipA G106A rev | this study | PCR primers | TTCATCGACTCCCGCGGCAAGTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-fipA G106A fwd | this study | PCR primers | AAAATGGTCGGACTTGCCGCGGGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-PPfipA G104A rev | this study | PCR primers | CATCGATACTCGCAGCCATCCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-PPfipA G104A fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCTGGTGGGGATGGCTGCGAGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-PPfipA L123A rev | this study | PCR primers | ACACCTTGCTCATCGCCTCCGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-PPfipA L123A fwd | this study | PCR primers | GGCCGAGGCGGAGGCGATGAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-flhF KO-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCATAGGCGTCGGTGATTGAGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-flhF KO-rev | this study | PCR primers | TAAGTGAAGGCATTTGAGTAGAGTTATGACCCTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-flhF KO-fwd | this study | PCR primers | CTCAAATGCCTTCACTATGCGTCCTCTACTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-flhF KO-rev | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCTAAGCATTCTCCTAAGCTTGTTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-fipA L125A rev | this study | PCR primers | TAACCGGATCAAGGCTTCAGCTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-fipA L125A fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCTGAAGCTGAAGCCTTGATCCGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV FlhF sub rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCTCGTCACATACAACGACTAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH 2550 L125A pkT25 rev | this study | PCR primers | TTAGTTACTTAGGTACCCGGGGTTTACGATGTAACCGGATCAAGGCTTCAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH 2550 L125A rev | this study | PCR primers | GAGCTCGGTACCCGGGGTTTACGATGTAACCGGATCAAGGCTTCAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FipA L125A-GFP-rev | this study | PCR primers | GAAAAGTTCTTCTCCTTTGCTCAGTTCCAGAATATCTTTACGATGTAACCGGATCAAGGCTTCAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH FlhF pkT25 fwd | this study | PCR primers | CAGGGTCGACTCTAGAGAAGATTAAACGATTTTTTGCCAAAGACA |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH FlhF pkT25 rev | this study | PCR primers | TTAGTTACTTAGGTACCCGGGGCTCAAATGCACAGGCCATATTATCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH FlhF fwd | this study | PCR primers | CTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGAAGATTAAACGATTTTTTGCCAAAGACA |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH FlhF rev | this study | PCR primers | GAGCTCGGTACCCGGGGCTCAAATGCACAGGCCATATTATCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH FlhF GTG fwd | this study | PCR primers | CTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGGTGAAGATTAAACGATTTTTTGCCAAAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV_FipA KO fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATTTTTAGGTATCATTAACTTACGTGGTAATGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FipA KO rev | this study | PCR primers | ACACTTCGCTATTTACGATGATCGCCCATTAAAAATCCTTATGCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FipA KO fwd | this study | PCR primers | AAGGATTTTTAATGGGCGATCATCGTAAATAGCGAAGTGTAGGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-FipA KO rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGAACTGATCGCCTTTGTTTATATGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-FipA KO fwd | this study | PCR primers | AAGAAATGTCGCAGCCGTAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-FipA KO rev | this study | PCR primers | CCAGTTGCGACAATCTTCGGAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-PPfipA L116A rev | this study | PCR primers | CATCAACTCCGCCTCGGCCTGGGTCGCGCCGCAGCTCTGGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-PPfipA L1164A fwd | this study | PCR primers | GAGTTGACCCAGAGCTGCGGCGCGACCCAGGCCGAGGCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-PP_4331 (FipA) fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCTTACGAACAGAACGCAAGGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-PP_4331 (FipA) rev | this study | PCR primers | GCAATACGTGATTTCGGTGCAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-PP_4331 KO-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCAGATGCACGCCAAACAGAAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | PP_4331 KO-OL-rev | this study | PCR primers | TCAAGGAGCTAGGATCAACTCAGATGTTCTCCAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | PP_4331KO-OL-fwd | this study | PCR primers | TTGATCCTAGCTCCTTGACGGGGTACCCTCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-PP_4331 KO-rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCATGAATTGCCTGTACAACACCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-PP_4331KO-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAAACGATCGATCAGGTCGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-PP_4331KO-rev | this study | PCR primers | GCACCGTAATCGAACACATGTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-PP_4331-GFP-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCAGATGCACGCCAAACAGAAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | PP_4331-GFP-OL-rev | this study | PCR primers | GAAAAGTTCTTCTCCTTTGCTCAGTTCCAGAATATCAGGAGCCCGGTACACCTTGCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | PP_43310-GFP-OL-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GGATGAGCTCTACAAAGGATCCTGACGGGGTACCCTCGGCAGCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-PP_4331-GFP-rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCATGAATTGCCTGTACAACACCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-FlhF-mCh-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCATGGACAGCTTCCGTATCGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | FlhF-mCh-OL-rev | this study | PCR primers | CTCTTCCCCTTTGGAAACGCTGCCACCCGCTCGCCGTGGGTTGTGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | FlhF-mCh-OL-fwd | this study | PCR primers | ATGGATGAGTTATACAAATGACCATGAAGCGTGTGCAAAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-FlhF-mCh-rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCCAACACACGGAAACGGTTCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-PP_4343 KO-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCCTGAAATCGAGCCGATCGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-PP_4343 KO-rev | this study | PCR primers | GCGTCGGTAATCGAGGTAGGTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH PP FipA pkT25 fwd | this study | PCR primers | CAGGGTCGACTCTAGAGATCCTAGAGGTTGCTGTCATCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH PP FipA pkT25 rev | this study | PCR primers | TTAGTTACTTAGGTACCCGGGGAGGAGCCCGGTACACCTTGCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH PP FipA fwd | this study | PCR primers | CTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGATCCTAGAGGTTGCTGTCATCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH PP FipA rev | this study | PCR primers | GAGCTCGGTACCCGGGGAGGAGCCCGGTACACCTTGCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH PP FlhF pkT25 fwd | this study | PCR primers | CAGGGTCGACTCTAGAGCAAGTTAAGCGATTTTTCGCCGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH PP FlhF pkT25 rev | this study | PCR primers | TTAGTTACTTAGGTACCCGGGGACCCGCTCGCCGTGGGTTGTGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH PP FlhF fwd | this study | PCR primers | CTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGCAAGTTAAGCGATTTTTCGCCGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | BACTH PP FlhF rev | this study | PCR primers | GAGCTCGGTACCCGGGGACCCGCTCGCCGTGGGTTGTGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV FlhF sub fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCATCAGTCAATGCAAGCAACC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-FlhF KI/O-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCCACTGGGTAGTGTCGTAAAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FlhF D328A rev | this study | PCR primers | CCCCATACCAGCGGTGGCTATCAATAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FlhF D328A fwd | this study | PCR primers | AAGCTAGTATTGATAGCCACCGCTGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV PPFlhF sub fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCATGTTCTGGCGTATCAGGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FlhF K235A rev | this study | PCR primers | GCGCGCGGCCAGCGCGGCCAGGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FlhF K235A fwd | this study | PCR primers | GGCAAGACCACCACCCTGGCCGCGCTGGCCGCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV PPFlhF sub rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCATGCTACCCATGTCTGTTCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Check-PP_4343 KI-fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCTACCAGTGATTACCCTGGAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV PPFlhF sub 1 rev | this study | PCR primers | GCCAAGCTTCTCTGCAGGATGCGTCGGTAATCGAGGTAGGTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | KT2440 FlhF Seq primer rev | this study | PCR primers | GCTGGTGAGCATGGACAGCTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | EcoRV-FipA dTM fwd | this study | PCR primers | GCGAATTCGTGGATCCAGATGCCGTAGCTGCAAGTAAAGATG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FipA dTM rev | this study | PCR primers | CTGCTTTTGTTCATCGCCCATTAAAAATCCTTATGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-FipA dTM fwd | this study | PCR primers | GGCGATGAACAAAAGCAGTTGAGTAAATTACGTAATAAAGTTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-PP_FipA dTM rev | this study | PCR primers | GCTGTAGTTCTCTAGGAT CAACTCAGATGTTCTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OL-PP_FipA dTM fwd | this study | PCR primers | ATCCTAGAGAACTACAGCAAGCGCCAGCGCG |
| Software, algorithm | cellProfiles (R package) | Cameron et al., 2014; Cameron, 2018 | https://github.com/ta-cameron/Cell-Profiles | |
| Software, algorithm | MicrobeJ | Ducret et al., 2016 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Supplementary tables.
(a) Enriched proteins in Co-IP FlhF-sfGFP vs. sfGFP. The genes with the largest enrichment in FlhF-sfGFP vs. sfGFP are shown. The corresponding protein designation is indicated if available. (b) Flagellation pattern and presence of FipA and FlhF in bacteria. (c) Bacterial strains used in this study. (d) Plasmids used in this study. (e) Oligonucleotides used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93004/elife-93004-supp1-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93004/elife-93004-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx
-
Source data 1
Contains the data used for generation of the indicated figure panels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93004/elife-93004-data1-v1.xlsx





