Peer review process
Revised: This Reviewed Preprint has been revised by the authors in response to the previous round of peer review; the eLife assessment and the public reviews have been updated where necessary by the editors and peer reviewers.
Read more about eLife’s peer review process.Editors
- Reviewing EditorSamuel PleasureUniversity of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, United States of America
- Senior EditorKathryn CheahUniversity of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Reviewer #1 (Public Review):
Summary:
In this manuscript the authors re-examine the developmental origin of cortical oligodendrocyte (OL) lineage cells using a combination of strategies, focussing on the question of whether the LGE generates cortical OL cells. The paper is interesting to myelin biologists, the methods used are appropriate and, in general, the study is well-executed, thorough, and persuasive, but not 100% convincing.
Strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations:
The first evidence presented that the LGE does not generate OLs for the cortex is that there are no OL precursors 'streaming' from the LGE during embryogenesis, unlike the MGE (Figure 1A). This in itself is not strong evidence, as they might be more dispersed. In fact, in the images shown, there is no obvious 'streaming' from the MGE either. Note that in Figure 1 there is no reference to the star that is shown in the figure.
The authors then electroporate a reporter into the LGE at E13.5 and examine the fate of the electroporated cells (Figures 1C-E). They find that electroporated cells became neurons in the striatum and in the cortex but no OLs for the cortex. There are two issues with this: first, there is no quantification, which means there might indeed be a small contribution from the LGE that is not immediately obvious from snapshot images. Second, it is unexpected to find labelled neurons in the cortex at all since the LGE does not normally generate neurons for the cortex! Electroporations are quite crude experiments as targeting is imprecise and variable and not always discernible at later stages. For example, in Figure 1D, one can see tdTOM+ cells near the AEP, as well as the striatum. Hence, IUE cannot on its own be taken as proof that there is no contribution of the LGE to the cortical OL population.
The authors then use an alternative fate-mapping approach, again with E13.5 electroporations (Figure 2). They find only a few GFP+ cells in the cortex at E18 (Figures 2C-D) and P10 (Figure 2E) and these are mainly neurons, not OL lineage cells. Again, there is no quantification.
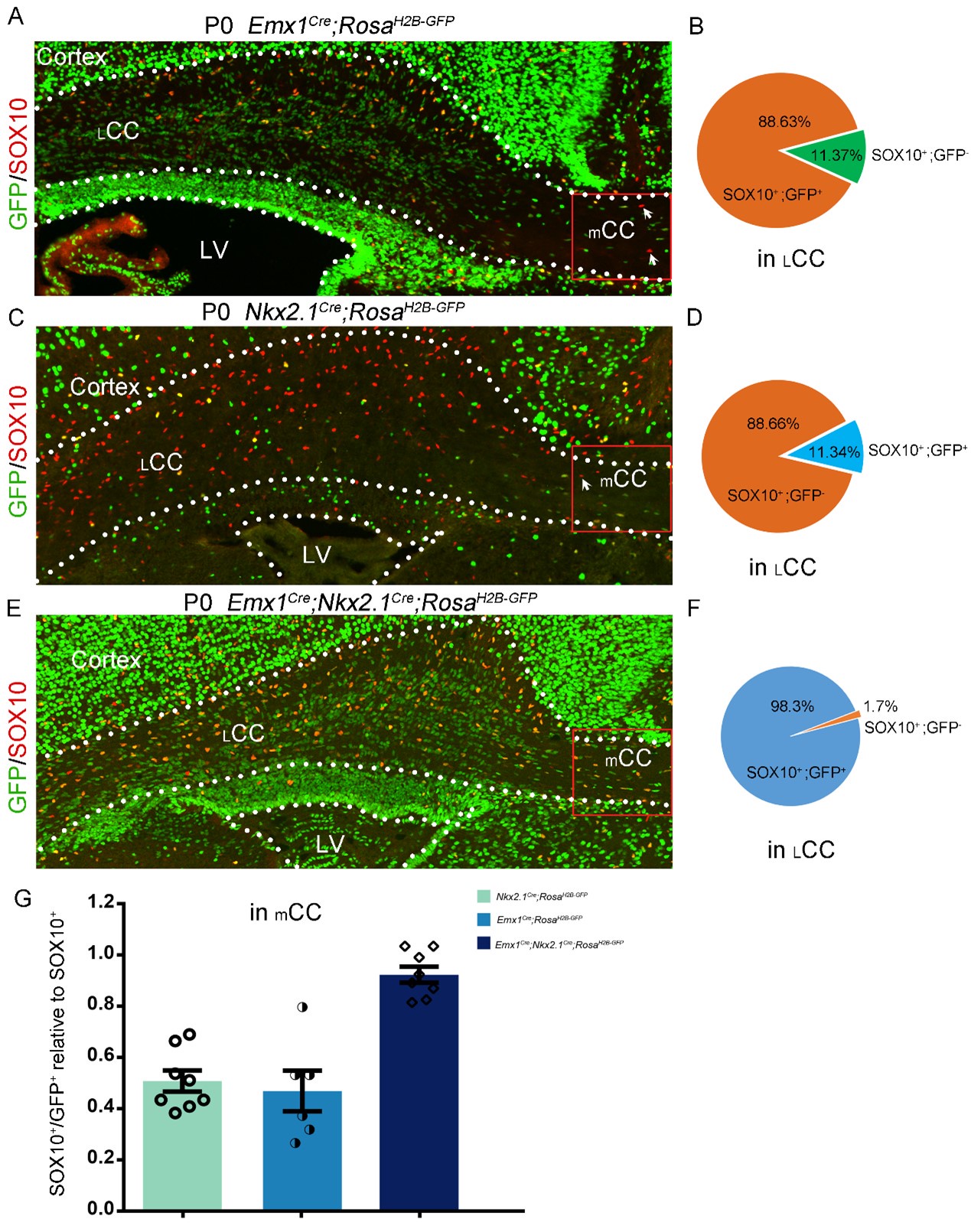
Figure 3 is more convincing, but the experiments are incomplete. Here the authors generate triple-transgenic mice expressing Cre in the cortex (Emx1-Cre) and the MGE (Nkx2.1-Cre) as well as a strong nuclear reporter (H2B-GFP). They find that at P0 and P10, 97-98% of OL-lineage cells (SOX10+ or PDGFRA+) in the cortex are labelled with GFP (Figure 3). This is a more convincing argument that the LGE/CGE might not contribute significant numbers of OL lineage cells to the cortex, in contrast to the Kessaris et at. (2006) paper, which showed that Gsh2-Cre mice label ~50% of SOX10+ve cells in the motor cortex at P10. The authors of the present paper suggest that the discrepancy between their study and that of Kessaris et al. (2006) is based on the authors' previous observation (Zhang et al 2020) (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.03.027) that GSH2 is expressed in intermediate precursors of the cortex from E18 onwards. If correct, then Kessaris et al. might have mistakenly attributed Gsh2-Cre+ lineages to the LGE/CGE when they were in fact intrinsic to the cortex. However, the evidence from Zhang et al 2020 that GSH2 is expressed by cortical intermediate precursors seems to rest solely on their location within the developing cortex; a more convincing demonstration would be to show that the GSH2+ putative cortical precursors co-label for EMX1 (by immunohistochemistry or in situ hybridization), or that they co-label with a reporter in Emx1-driven reporter mice. This demonstration should be simple for the authors as they have all the necessary reagents to hand. Without these additional data, the assertion that GSX2+ve cells in the cortex are derived from the cortical VZ relies partly on an act of faith on the part of the reader.
Note that Tripathi et al. (2011, "Dorsally- and ventrally-derived oligodendrocytes have similar electrical properties but myelinate preferred tracts." J. Neurosci. 31, 6809-6819) found that the Gsh-Cre+ OL lineage contributed only ~20% of OLs to the mature cortex, not ~50% as reported by Kessaris et al. (2006). If it is correct that these Gsh2-derived OLs are from the cortical anlagen as the current paper claims, then it would raise the possibility that the ventricular precursors of GSH2+ intermediate progenitors are not uniformly distributed through the cortical VZ but are perhaps localized to some part of it. Then the contribution of Gsh2-derived OLs to the cortical population could depend on precisely where one looks relative to that localized source. It would be a nice addition to the current manuscript if the authors could explore the distribution of their GSH2+ intermediate precursors throughout the developing cortex. In any case, Tripathi et al. (2011) should be cited.
Finally, the authors deleted Olig2 in the MGE and found a dramatic reduction of PDGFRA+ and SOX10+ cells in the cortex at E14 and E16 (Figure 4A-F). This further supports their conclusion that, at least at E16, there is no significant contribution of OLs from ventral sources other than the MGE/AEP. This does not exclude the possibility that the LGE/CGE generates OLs for the cortex at later stages. Hence, on its own, this is not completely convincing evidence that the LGE generates no OL lineage cells for the cortex.
Comments on the latest version:
The revised manuscript has addressed the issues we raised previously. The addition of the new Figure 3 supplement 1A-C demonstrating that Gsx2+ve cells in the cortex are generated from Emx1-Cre precursors is convincing, although there is nothing to prove that the GFP+, Gsh2+ double-labelled nuclei are oligodendrocyte lineage and not, for example, astrocytes. It would be helpful to include a Gsh2, Olig2 (or Gsh2, Sox10) double-label image to prove this point. Also, to make the figure more clear, the authors should also show a small area at high magnification, splitting the green and red channels so that the reader can see more clearly that all the red cells are also green.
Reviewer #2 (Public Review):
Traditional thinking has been that cortical oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) arise in the development of the brain from the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE), lateral/caudal ganglionic eminence (LGE/CGE), and cortical radial glial cells (RGCs). Indeed a landmark study demonstrated some time ago that cortical OPCs are generated in three waves, starting with a ventral wave derived from the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE) or the anterior entopeduncular area (AEP) at embryonic day E12.5 (Nkx2.1+ lineage), followed by a second wave of cortical OLs derived from the lateral/caudal ganglionic eminences (LGE/CGE) at E15.5 (Gsx2+/Nkx2.1- lineage), and then a final wave occurring at P0, when OPCs originate from cortical glial progenitor cells (Emx1+ lineage). However, the authors challenge the idea in this paper that cortical progenitors are produced from the LGE. They have found previously that cortical glial progenitor cells were also found to express Gsx2, suggesting this may not have been the best marker for LGE-derived OPCs. They have used fate mapping experiments and lineage analyses to suggest that cortical OPCs do not derive from the LGE.
Strengths:
(1) The data is high quality and very well presented, and experiments are thoughtful and elegant to address the questions being raised.
(2) The authors use two elegant approaches to lineage trace LGE derived cells, namely fate mapping of LGE-derived OPCs by combining IUE (intrauterine electroporation) with a Cre recombinase-dependent IS reporter, and Lineage tracing of LGE-derived OPCs by combining IUE with the PiggyBac transposon system. Both approaches show convincingly that labelled LGE-derived cells that enter the cortex do not express OPC markers, but that those co-labelling with oligodendrocyte markers remain in the striatum.
(3) The authors then use further approaches to confirm their findings. Firstly they lineage trace Emx1-Cre; Nkx2.1-Cre; H2B-GFP mice. Emx1-Cre is expressed in cortical RGCs and Nkx2.1-Cre is specifically expressed in MGE/AEP RGCs. They find that close to 98% of OPCs in the cortex co-label with GFP at later times, suggesting the contribution of OPCs from LGE is minimal.
(4) They use one further approach to strengthen the findings yet further. They cross Nkx2.1-Cre mice with Olig2 F/+ mice to eliminate Olig2 expression in the SVZ/VZ of the MGE/AEP (Figures 4A-B). The generation of MGE/AEP-derived OPCs is inhibited in these Olig2-NCKO conditional mice. They find that the number of cortical progenitors at E16.5 is reduced 10-fold in these mice, suggesting that LGE contribution to cortical OPCs is minimal.
Impact of Study:
The authors show elegantly and convincingly that the contribution of the LGE to the pool of cortical OPCs is minimal. The title should perhaps be that the LGE contribution is minimal rather than no contribution at all, as they are not able to rule out some small contribution from the LGE. These findings challenge the traditional belief that the LGE contributes to the pool of cortical OPCs. The authors do show that the LGE does produce OPCs, but that they tend to remain in the striatum rather than migrate into the cortex. It is interesting to wonder why their migration patterns may be different from the MGE-derived OPCs which migrate to the cortex. The functional significance of these different sources of OPCs for adult cortex in homeostatic or disease states remains unclear though.