Peer review process
Not revised: This Reviewed Preprint includes the authors’ original preprint (without revision), an eLife assessment, public reviews, and a provisional response from the authors.
Read more about eLife’s peer review process.Editors
- Reviewing EditorMichael PotenteMax Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research, Bad Nauheim, Germany
- Senior EditorDidier StainierMax Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research, Bad Nauheim, Germany
Reviewer #1 (Public Review):
Summary:
Shi and colleagues report the use of modified Cre lines in which the coding region of Cre is disrupted by rox-STOP-rox or lox-STOP-lox sequences to prevent the expression of functional protein in the absence of Dre or Cre activity, respectively. The main purpose of these tools is to enable intersectional or tamoxifen-induced Cre activity with minimal or no leaky activity from the second, Cre-expressing allele. It is a nice study but lacks some functional data required to determine how useful these alleles will be in practice, especially in comparison with the figure line that stimulated their creation.
Strengths:
The new tools can reduce Cre leak in vivo.
Weaknesses:
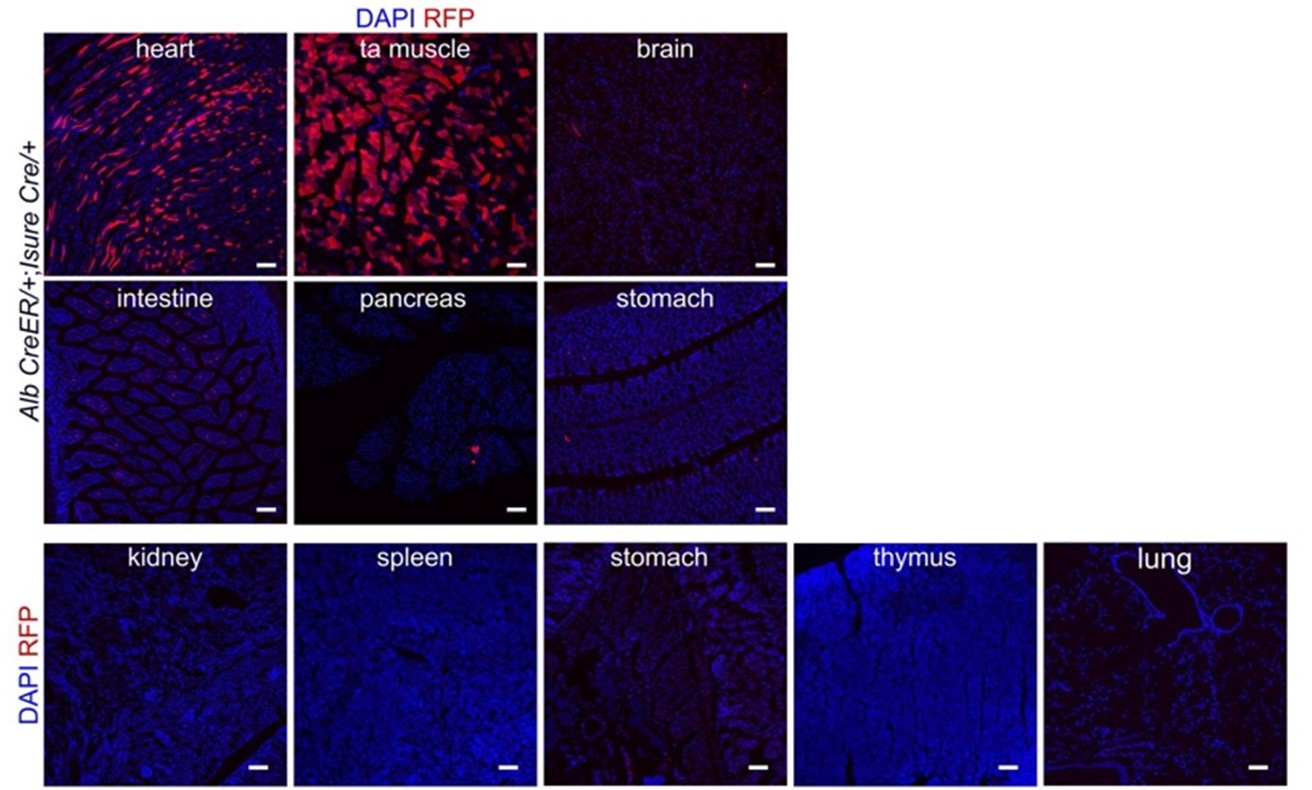
(1) Activity of R26-loxCre line. As the authors point out, the greatest value of this approach is to accomplish a more complete Cre-mediated gene deletion using CreER transgenes that are combined with low-efficiency floxed alleles using their R26-loxCre line that is similar to the iSure Cre reported by Benedito and colleagues. The data in Figure 5 show strong activity at the Confetti locus, but the design of the newly reported R26-loxCre line lacks a WPRE sequence that was included in the iSure-Cre line to drive very robust protein expression. Thus while the line appears to have minimal leak, as the design would predict, the question of how much of a deletion increase is obtained over simple use of the CreER transgene alone is a key question for use by investigators. This is further addressed in Figure 6 where it is compared with Alb-CreER alone to recombine the Ctnnb1 floxed allele. They demonstrate that recombination frequency is clearly improved, but the western blot in Figure 6E does not look like there was a large amount of remaining b-catenin to remove. These data are certainly promising, but the most valuable experiment for such a new tool would be a head-to-head comparison with iSure (or the latest iSure version from the Benedito lab) using the same CreER and target floxed allele. At the very least a comparision of Cre protein expression between the two lines using identical CreER activators is needed.
(2) In vivo analysis of mCre activities. Why did the authors not use the same driver to compare mCre 1, 4, 7, and 10? The study in Figure 2 uses Alb-roxCre for 1 and 7 and Cdh5-roxCre for 4 and 10, with clearly different levels of activity driven by the two alleles in vivo. Thus whether mCre1 is really better than mCre4 or 10 is not clear.
(3) Technical details are lacking. The authors provide little specific information regarding the precise way that the new alleles were generated, i.e. exactly what nucleotide sites were used and what the sequence of the introduced transgenes is. Such valuable information must be gleaned from schematic diagrams that are insufficient to fully explain the approach.
Reviewer #2 (Public Review):
Summary:
This work presents new genetic tools for enhanced Cre-mediated gene deletion and genetic lineage tracing. The authors optimise and generate mouse models that convert temporally controlled CreER or DreER activity to constitutive Cre expression, coupled with the expression of tdT reporter for the visualizing and tracing of gene-deleted cells. This was achieved by inserting a stop cassette into the coding region of Cre, splitting it into N- and C-terminal segments. Removal of the stop cassette by Cre-lox or Dre-rox recombination results in the generation of modified Cre that is shown to exhibit similar activity to native Cre. The authors further demonstrate efficient gene knockout in cells marked by the reporter using these tools, including intersectional genetic targeting of pericentral hepatocytes.
Strengths:
The new models offer several important advantages. They enable tightly controlled and highly effective genetic deletion of even alleles that are difficult to recombine. By coupling Cre expression to reporter expression, these models reliably report Cre-expressing i.e. gene-targeted cells, and circumvent false positives that can complicate analyses in genetic mutants relying on separate reporter alleles. Moreover, the combinatorial use of Dre/Cre permits intersectional genetic targeting, allowing for more precise fate mapping.
Weaknesses:
The scenario where the lines would demonstrate their full potential compared to existing models has not been tested. Mosaic genetics is increasingly recognized as a key methodology for assessing cell-autonomous gene functions. The challenge lies in performing such experiments, as low doses of tamoxifen needed for inducing mosaic gene deletion may not be sufficient to efficiently recombine multiple alleles in individual cells while at the same time accurately reporting gene deletion. Therefore, a demonstration of the efficient deletion of multiple floxed alleles in a mosaic fashion would be a valuable addition.
In addition, a drawback of this line is the constitutive expression of Cre. When combined with the confetti line, the reporter cassette will continue flipping, potentially leading to misleading lineage tracing results. Constitutive expression of Cre is also associated with toxicity, as discussed by the authors in the introduction. These drawbacks should be acknowledged.
Reviewer #3 (Public Review):
Summary:
The authors report a new version of the iSuRe-Cre approach, which was originally developed by Rui Benedito's group in Spain (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10239-4). Shi et al claim that their approach shows reduced leakiness compared to the iSuRe-Cre line. Shi et al elaborate strongly about the leakiness of iSuRe-Cre mice, although leakiness is rather minor according to the original publication and the senior author of the study wrote in a review a few years ago that there is no leakiness (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100509). Furthermore, a new R26-roxCre-tdT mouse line was established after extensive testing, which enables efficient expression of the Cre recombinase after activation of the Dre recombinase.
Strengths:
The authors carefully evaluated the efficiency and leakiness of the new strains and demonstrated the applicability by marking peri-central hepatocytes in an intersectional genetics approach, amongst others. I can only find very few weaknesses in the paper, which represents the result of an enormous effort. Carefully conducted technical studies have considerable value. However, I would have preferred to see a study, which uses the wonderful new tools to address a major biological question, rather than a primarily technical report, which describes the ongoing efforts to further improve Cre and Dre recombinase-mediated recombination.
Weaknesses:
Very high levels of Cre expression may cause toxic effects as previously reported for the hearts of Myh6-Cre mice. Thus, it seems sensible to test for unspecific toxic effects, which may be done by bulk RNA-seq analysis, cell viability, and cell proliferation assays. It should also be analyzed whether the combination of R26-roxCre-tdT with the Tnni3-Dre allele causes cardiac dysfunction, although such dysfunctions should be apparent from potential changes in gene expression.
The R26-GFP or R26-tdT reporters, Alb-roxCre1-tdT, Cdh5-roxCre4-tdT, Alb-roxCre7-GFP, and Cdh5-roxCre10-GFP demonstrate no leakiness without Dre-rox recombination (Figure S1-S2). Is there any leakiness when the inducible DreER allele is introduced but no tamoxifen treatment is applied? This should be documented. The same also applies to loxCre mice.
The enhanced efficiency of loxCre and roxCre systems holds promise for reducing the necessary tamoxifen dosage, potentially reducing toxicity and side effects. In Figure 6, the author demonstrates an enhanced recombination efficiency of loxCre mice, which makes it possible to achieve efficient deletion of Ctnnb1 with a single dose of tamoxifen, whereas a conventional driver (Alb-CreER) requires five dosages. It would be very helpful to include a dose-response curve for determining the minimum dosage required in Alb-CreER; R26-loxCre-tdT; Ctnnb1flox/flox mice for efficient recombination.
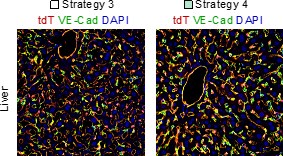
In the liver panel of Figure 4F, tdT signals do not seem to colocalize with the VE-cad signals, which is odd. Is there any compelling explanation?
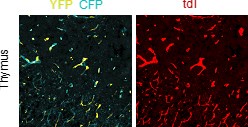
The authors claim that "virtually all tdT+ endothelial cells simultaneously expressed YFP/mCFP" (right panel of Figure 5D). Well, it seems that the abundance of tdT is much lower compared to YFP/mCFP. If the recombination of R26-Confetti was mainly triggered by R26-loxCre-tdT, the expression of tdT and YFP/mCFP should be comparable. This should be clarified.
In several cases, the authors seem to have mixed up "R26-roxCre-tdT" with "R26-loxCre-tdT". There are errors in #251 and #256. Furthermore, in the passage from line #278 to #301. In the lines #297 and #300 it should probably read "Alb-CreER; R26-loxCre-tdT;Ctnnb1flox/flox"" rather than "Alb-CreER;R26-tdT2;Ctnnb1flox/flox".