A novel sphingolipid-TORC1 pathway critically promotes postembryonic development in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
Regulation of animal development in response to nutritional cues is an intensely studied problem related to disease and aging. While extensive studies indicated roles of the Target of Rapamycin (TOR) in sensing certain nutrients for controlling growth and metabolism, the roles of fatty acids and lipids in TOR-involved nutrient/food responses are obscure. Caenorhabditis elegans halts postembryonic growth and development shortly after hatching in response to monomethyl branched-chain fatty acid (mmBCFA) deficiency. Here, we report that an mmBCFA-derived sphingolipid, d17iso-glucosylceramide, is a critical metabolite in regulating growth and development. Further analysis indicated that this lipid function is mediated by TORC1 and antagonized by the NPRL-2/3 complex in the intestine. Strikingly, the essential lipid function is bypassed by activating TORC1 or inhibiting NPRL-2/3. Our findings uncover a novel lipid-TORC1 signaling pathway that coordinates nutrient and metabolic status with growth and development, advancing our understanding of the physiological roles of mmBCFAs, ceramides, and TOR.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00429.001eLife digest
Animals require nutrients, including carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids, for development and growth, and to maintain the normal functioning of cells. However, in most natural environments, the availability of food tends to fluctuate. Some animals have therefore acquired the ability to dramatically reduce their metabolic activity, and thus their energy and nutrient needs to survive fasting conditions.
Caenorhabditis elegans is a transparent nematode worm that is used extensively as a model organism. When C. elegans larvae hatch in a food-free environment, they enter a quiescent state in which they suspend growth and cell division to conserve energy. However, the mechanisms that underlie this ability are not fully understood.
Here, Zhu et al. reveal that a type of lipid called a sphingolipid is required for C. elegans larvae to begin postembryonic development. When this lipid is absent in the environment and not synthesized internally, the larvae remain in a state of arrested development, which can be overcome by resupplying the lipid. Zhu et al. show that the lipid acts through a signaling pathway involving an enzyme complex called TORC1 and that the effect of the lipid can be blocked by another protein complex called NPRL-2/3. TORC1 is well known for its role in sensing amino acids and growth factors, but this is the first time that it has been shown to be involved in detecting lipids. Strikingly, Zhu et al. also show that, in the absence of the lipid, postembryonic growth and development can be initiated by activating TORC1 or inhibiting NPRL-2/3.
The work of Zhu et al. thus reveals a novel regulatory function of a specific fatty acid and sphingolipid variant that is used by C. elegans to coordinate its growth and development with its metabolic status or the availability of nutrients. Since all components of the pathway are conserved in mammals, the results could help to improve our understanding of how caloric restriction influences human health and aging.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00429.002Introduction
Regulation of animal growth and development in response to nutritional cues is an intensely studied problem (Hietakangas and Cohen, 2009; Zoncu et al., 2011). In animals, nutrient signals are perceived in specialized tissues and are then communicated to all other tissues to coordinate growth and development. The target of rapamycin (TOR) complexes (TORC1 and TORC2) are known to function in sensing various nutrient signals (Ma and Blenis, 2009; Laplante and Sabatini, 2012; Zoncu et al., 2012), and their roles are connected to growth, metabolism, stress responses, and cancers (Hansen et al., 2008; He and Klionsky, 2009; Howell and Manning, 2011). While amino acids, energy, and growth factors have been described as nutrient inputs to TOR complexes, roles of lipid molecules as signals to these systems in controlling postembryonic growth and development were not known. Clearly, it is also essential to use whole-animal models to investigate how different signaling systems in different tissues interact to specify decisions regarding postembryonic development and behaviors.
In Caenorhabditis elegans, the first larval stage has been established as a model system for the study of animal growth and development in response to food availability. When hatched in food-free surroundings, this nematode enters a quiescent state, termed L1 diapause (Johnson et al., 1984; Munoz and Riddle, 2003; Baugh and Sternberg, 2006). An insulin/IGF-1 receptor signaling (IIS) pathway plays a critical role in the induction of L1 diapause and survival of the developmentally arrested animals (Gems et al., 1998; Baugh and Sternberg, 2006; Kniazeva et al., 2008; Lee and Ashrafi, 2008; Jones et al., 2009; Soukas et al., 2009). Moreover, TOR complexes have also been indicated to play prominent roles in regulating postembryonic growth and lifespan in C. elegans (Vellai et al., 2003; Syntichaki et al., 2007; Hansen et al., 2008; Honjoh et al., 2009; Lucanic et al., 2011).
Monomethyl branched-chain fatty acids (mmBCFAs) are widely present in bacteria, plants, and animals, including humans (Nicolaides and Ray, 1965; Ran-Ressler et al., 2008). In mammals, mmBCFAs are derived from branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) (Morii and Kaneda, 1982; Oku et al., 1994), although the remainder of the de novo pathway has not been delineated. The physiological roles of these FA variants are essentially unknown, even though they were found to be present at very high levels in certain tissues (Nicolaides and Ray, 1965; Ran-Ressler et al., 2008). In C. elegans, readily detectable mmBCFAs C15ISO and C17ISO are synthesized from the BCAA leucine (Kniazeva et al., 2004). The key enzymes in this de novo synthesis pathway, including the branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC), an FA elongase (ELO-5), and an acyl CoA synthetase (ACS-1), are evolutionarily conserved (Kniazeva et al., 2004, 2008).
We have previously shown that newly hatched C. elegans that are deficient for mmBCFAs cannot initiate postembryonic growth and development, and instead enter L1 diapause. Further genetic analysis suggested that this developmental arrest is independent of the IIS pathway (Kniazeva et al., 2004, 2008). It was not clear whether the essential roles of mmBCFAs and their derived lipids were due to structural requirements for animal development, as was suggested by other studies, or due to regulatory functions specific to cellular signaling processes. Testing these hypotheses using model organisms is highly significant because roles of fatty acids and lipids function as nutrient signals for postembryonic development are in general poorly understood.
In this study, we discovered that (1) an mmBCFA-derived glucosylceramide (d17iso-GlcCer) mediates the function of mmBCFAs in promoting postembryonic growth and development and (2) d17iso-GlcCer acts through a signaling system that includes the NPRL-2/NPRL-3 protein complex (negative factor) and TORC1 (positive factor) to promote postembryonic development.
Results
A sphingolipid composed of a mmBCFA-derived long chain base mediates the essential role of mmBCFAs in the initiation of postembryonic growth and development
elo-5 loss-of-function mutants (termed elo-5(−) hereafter) are deficient for mmBCFAs and are developmentally arrested at the early L1 stage. This phenotype is completely rescued by dietary supplementation of mmBCFAs (Kniazeva et al., 2004, 2008). We found that in mmBCFA-deficient elo-5(−) larvae, the amount of mmBCFA-containing sphingolipids were dramatically reduced and thus asked if this mmBCFA function is mediated by a sphingolipid.
Sphingolipids are a class of well-known bioactive lipids (Hannun and Obeid, 2008) that are composed of an aliphatic amino alcohol backbone called the sphingoid base or long chain base (LCB), and usually an N-acylated fatty acid (FA) side chain (Figure 1A). In C. elegans, both the LCB and the FA side chain may derive from mmBCFAs, such as C15ISO and C17ISO (Chitwood et al., 1995; Gerdt et al., 1997; Figure 1A). In this study, a sphingolipid with a mmBCFA-derived LCB is termed d17iso-sphingolipid, whereas a sphingolipid with a C17ISO-derived FA side chain and a straight LCB is termed c17iso-sphingolipid. The ‘d’ and ‘c’ refer to carbon atoms on the LCB and FA chain, respectively.
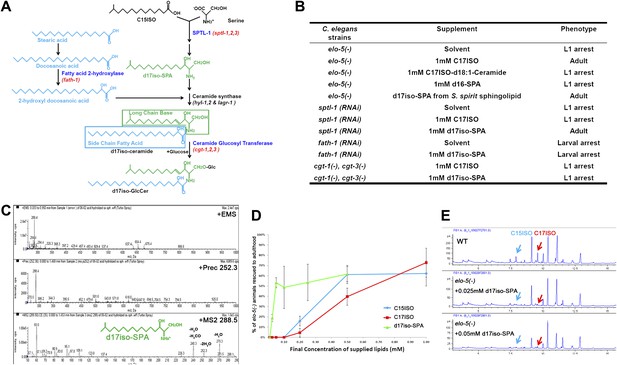
Iso-branched d17iso-sphinganine rescues elo-5(-) L1 arrest.
(A) Sphingolipid biogenesis pathway in C. elegans, including the catalytic enzymes (blue) and corresponding genes (red) used in this study. Molecular structures in green and in light blue indicate the long chain base and side chain fatty acid, respectively. (B) Summary of growth phenotype of various mutants with indicated lipid supplementations. elo-5(gk208), cgt-1(tm1027), and cgt-3(tm504) were the alleles of the (−) mutants. LCB: long chain base; SPA: sphinganine. See Supplementary file 1 for numerical data or more detailed description of the phenotypes. (C) Mass spectrometry of iso-branched d17iso-sphinganine (d17iso-SPA) isolated from the bacteria S. spiritivorum. The major peak (m/z = 288.4) corresponds to d17iso-SPA in each panel. The lower panel shows fragmentation of d17iso-SPA by MS-MS scan. The fragment peaks are labeled with the name of lost residues. (D) d17iso-SPA rescues elo-5(−) animals more efficiently than C15ISO and C17ISO. Error bar, SD. (E) Gas chromatography of methyl-esterified fatty acid extracts from rescued elo-5(−) animals fed with d17iso-SPA. Low concentration of d17iso-SPA (second and third panels) supplement did not restore C15iso or C17iso fatty acid levels.
We then examined if dietary supplementation with either of these two types of sphingolipids could substitute for mmBCFAs to rescue elo-5(−) animals from L1 arrest. Because the d17iso-LCB was not commercially available, we purified d17iso-sphinganine (d17iso-SPA; Figure 1A) from a d17iso-sphingolipid producing bacteria S. spiritivorum (Yabuuchi et al., 1983) using mass spectrometry analysis. This purified d17iso-SPA fraction, but not a chemically synthesized c17iso-sphingolipid with a straight-chain d18:1-LCB or a straight-chain LCB d16-SPA, was found to be sufficient to overcome elo-5(−) L1 arrest (Figure 1B,C; Supplementary file 1). Additionally, efficient rescue was also achieved with a custom synthesized d17iso-SPA (Figure 1D). Therefore, d17iso-sphingolipid is sufficient to promote the postembryonic growth and development of mmBCFA-deficient animals.
We then carried out further tests to confirm that this rescue effect of d17iso-SPA supplementation resulted from the function of this metabolite itself, but not from its catabolic conversion back to C15ISO or C17ISO. First, we fed elo-5(−) larvae with various quantities of C15ISO, C17ISO, or d17iso-SPA. We observed that d17iso-SPA suppressed the L1 arrest at a much lower concentration than C15ISO or C17ISO (Figure 1D). Second, we observed that the low concentrations of d17iso-SPA suppressed the L1 arrest without restoring mmBCFA levels (Figure 1E). Finally, we found that supplementation with d17iso-SPA, but not mmBCFAs, also suppressed the L1 arrest phenotype caused by feeding RNAi of sptl-1, a gene encoding a serine palmitoyltransferase homolog in C. elegans required for d17iso-SPA biosynthesis (Figure 1A,B; Seamen et al., 2009). We thus conclude that mmBCFAs promote postembryonic development through d17iso-SPA.
This growth-promoting function of d17iso-SPA may be mediated by a more complex sphingolipid derived from it. Because it is technically difficult to purify or synthesize sphingolipids of more complex structure (e.g., glucosylceramide [GlcCer]) and directly test their effect by dietary supplementation, we examined additional enzymes involved in sphingolipid synthesis. Specifically, fath-1(C25A1.5) encodes a homolog of mammalian fatty acid 2-hydrolase (FA2H) responsible for the synthesis of the FA side chain of ceramides, whereas cgt-1 and cgt-3 encode two ceramide glucosyltransferases that glucosylate ceramides to GlcCer (Figure 1A). Both fath-1(RNAi)-treated animals (Figure 1B; Supplementary file 1) and the cgt-1(−);cgt-3(−) double mutant (Marza et al., 2009) cause larval arrest. We found the arrest under either condition could not be overcome by feeding d17iso-SPA (Figure 1B; Supplementary file 1). Disrupting the function of glycosyltransferases that further modify GlcCer does not cause larval arrest (Griffitts et al., 2003). These results suggest that d17iso-glucosylceramide (d17iso-GlcCer) (Figure 1A) may be the lipid molecule that mediates the role of mmBCFAs and d17iso-SPA in promoting postembryonic growth and development in C. elegans.
Mutation ku540 permits mmBCFA-depleted C. elegans to bypass L1 arrest and propagate continuously
d17iso-sphingolipid may play either a structural or regulatory role for the initiation of postembryonic development. If it is the latter, the requirement of d17iso-sphingolipid for postembryonic development might be bypassed by genetically activating the downstream regulatory pathway. To test this possibility and identify the mechanism, we performed a genetic screen, modified from a previous screen (Seamen et al., 2009), for mutations that could suppress the L1 arrest of elo-5(−) mutants (Figure 2A). Among four suppressors identified in this screen, and the tat-2 mutations from a previous elo-5(−) suppressor screen (Seamen et al., 2009), ku540 was the only mutation that rescued elo-5(−) larvae to adults and permitted growth for more than one generation without mmBCFA supplementation or restoration of mmBCFA synthesis (Figure 2B–E; see ‘Materials and methods’). In fact, elo-5(−);ku540 homozygous animals could propagate continuously, even though they displayed slow growth, smaller body size, and smaller brood size (Figure 2C).
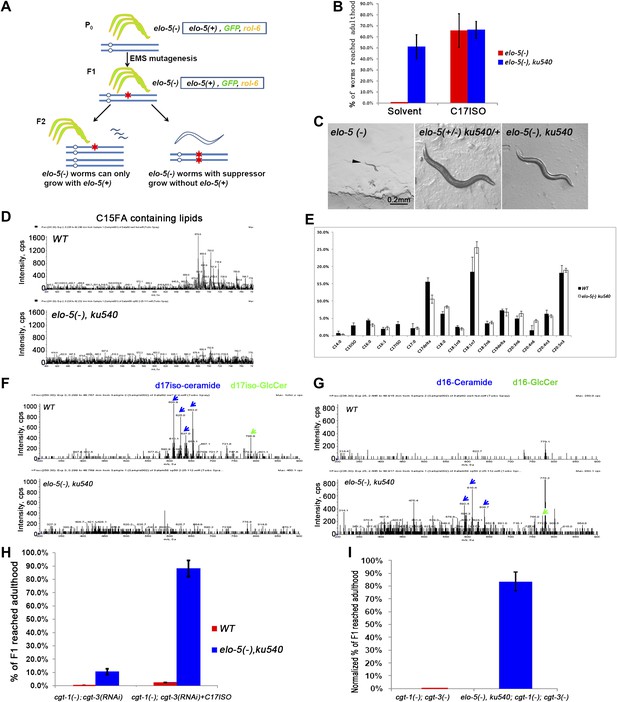
ku540 mutant suppresses L1 arrest of mmBCFA and sphingolipid biosynthetic mutants without restoring the levels of mmBCFAs.
(A) Screening strategy to isolate elo-5(−) suppressors. Green-colored C. elegans carry the extrachromosomal array containing copies of the elo-5(+), sur-5-gfp, and rol-6(dn) genes. (B) Percentages of animals reaching adulthood (bypass L1 arrest) when fed with/without C17ISO supplement. elo-5(−);ku540 mutant animals reach adulthood without C17ISO supplement. Error bar, SD. (C) Images showing that elo-5(−) animals arrested at L1 and elo-5(−);ku540 animals reached adulthood. (D) Mass spectrometry by precursor scan m/z = −241.2 showing no detectable C15FA-containing lipids in elo-5(−);ku540 animals. Numeric data for the levels of PA and PE are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1A. (E) Bar graph of relative FA composition by gas chromatography (GC) of methyl-esterified fatty acid extracts. These data indicate no detectable C15ISO or C17ISO was restored in elo-5(−) ku540 animals. GC graph is shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1B. (F) and (G) Mass spectrometry of d17iso-ceramide–containing lipids by precursor scan m/z = +250.3, and d16-ceramide–containing lipids by precursor scan m/z = +236.3 (F). d17iso-ceramides and d17iso-glucosylceramides are detectable in wild-type but not elo-5(−);ku540 animals (G). In contrast, d16-ceramides and d16-glucosylceramides are present in elo-5(−);ku540, but not wild-type, animals. Numeric data for relevant peaks are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1C,D. (H) and (I) Percentages of animals of the indicated genotypes and treatment that reached adulthood. Error bar, SD. (H) The addition of ku540 dramatically suppressed the L1 arrest phenotype of cgt-1(−);cgt-3(RNAi) with and without the C17ISO supplement. The inclusion of elo-5(−) was due to its close linkage with ku540. When C17ISO was added to remove the negative effect of elo-5(−), about 90% of elo-5(−);ku540; cgt-1(−);cgt-3(RNAi) animals reached adulthood. C17ISO itself does not rescue the phenotype. (I). ku540 suppressed the L1 arrest phenotype the cgt-1(−);cgt-3 (−) double mutants (83.4%, n = 126). In this particular test, elo-5(−) ku540;cgt-1(−);cgt-3(−) homozygous animals were the progeny of elo-5(−/+) ku540(−/+);cgt-1(−/+);cgt-3(−) heterozygous mothers, and the presented data were obtained after normalizing against heterozygous populations (see ‘Materials and methods’). In all the other tests shown in Figure 2, elo-5(−) ku540 homozygous animals were the progeny of homozygous mothers.
Mass spectrometry (MS) and gas chromatography (GC) analyses indicated that elo-5(−);ku540 did not restore mmBCFA levels, and consequently the levels of d17iso-sphingolipids (Figure 2D–G). elo-5(−);ku540 animals had no detectable C15ISO-containing or C17ISO-containing lipids (Figure 2D,E, Figure 2—figure supplement 1A,B). In contrast to wild type animals, elo-5(-);ku540 animals had ceramides and glucosylceramides containing straight chain d16LCB rather than d17isoLCB (Figure 2F,G, Figure 2—figure supplement 1C,D), which is similar to the elo-5(−) single mutant (Entchev et al., 2008). These data indicated that the suppression of L1 arrest by the ku540 mutation is neither due to a change in mmBCFA nor the metabolism of the derived sphingolipids. Therefore, our data suggest that ku540 renders mmBCFAs nonessential for C. elegans development.
Mutation ku540 also permits animals to bypass the requirement for d17iso-GlcCer in postembryonic development
The above results suggested that ku540 might modify a signaling pathway downstream of d17iso-sphingolipids. If so, ku540 should also suppress mutations disrupting the biosynthesis of this sphingolipid. This question was addressed by the following tests. As shown above, RNAi of fath-1, or mutating both cgt-1 and cgt-3, caused larval arrest that could not be rescued by feeding with either mmBCFAs or d17iso-SPA (Figure 1A,B). We found that the L1 arrest under both conditions, just like the arrest caused by elo-5(−), was effectively suppressed by ku540 (Figure 2H,I and Figure 2—figure supplement 2). These results provided strong evidence that d17iso-GlcCer mediated the roles of mmBCFAs and d17iso-SPA in postembryonic development. Taken together, our biochemical and genetic data indicate that ku540 bypasses the requirement of mmBCFAs and d17iso-GlcCer in development and does so by modifying a regulatory function downstream of d17iso-GlcCer.
ku540 is a loss-of-function mutation of nprl-3 that may function with nprl-2
We cloned the gene containing the ku540 mutation by genetic mapping and whole-genome sequencing (Figure 3—figure supplement 1A). The gene was annotated as F35H10.7 (wormbase.org) that encodes a protein structurally conserved from budding yeast (NPR3, Nitrogen Permease Regulator 3) to humans (NPRL-3, Nitrogen Permease Regulator Like 3; Figure 3B). We named the gene nprl-3 (NPRL-3 for protein). nprl-3(ku540) is a C-T substitution that changes a conserved proline to serine (Figure 3A). RNAi of nprl-3 by dsRNA injection also rescued the L1 arrest of elo-5(−) and cgt-1(−);cgt-3(−) animals (Figure 3C), indicating that ku540 is likely a partial loss-of-function or reduction-of-function mutation. A transcriptional GFP fusion transgene (nprl-3::GFP) was observed to express ubiquitously throughout development and adulthood (Figure 3—figure supplement 1B).
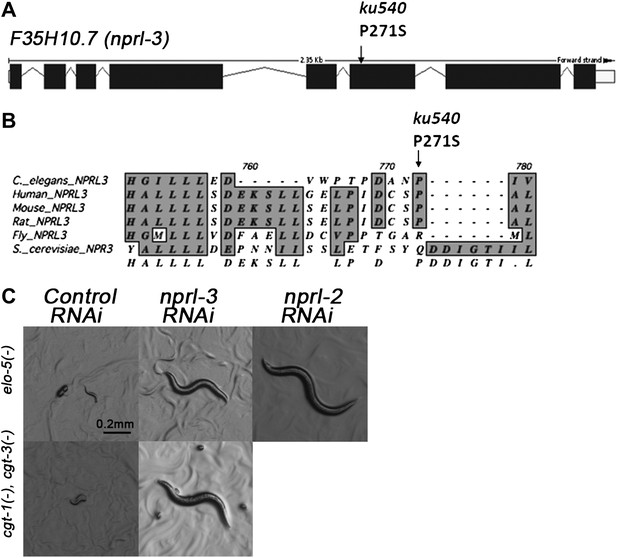
ku540 is a loss-of-function missense mutation of nprl-3.
(A) Predicted structure and position of the ku540 mutation in the nprl-3 gene (F35H10.7). (B) Abbreviated alignment of C. elegans NPRL-3 with its orthologs in other organisms. (C) C. elegans images showing nprl-3(RNAi) mimics the effect of the ku540 mutation in rescuing the L1 arrest phenotype caused by blocking mmBCFA or glucosyl-ceramide biosynthesis. nprl-3 dsRNA injection rescued 61.0% of elo-5(−) (n = 123) and 6.8% of cgt-1(−) cgt-3(−) (n = 71) animals to or beyond L3 stage. nprl-2 dsRNA injection also rescued 42.4% of elo-5(−) animals to or beyond L3 stage (n = 128). All data have been normalized to heterozygous populations (see ‘Materials and methods’).
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, NPR3 was shown to form a heterodimer with NPR2. Mutations in both proteins cause multiple growth defects when cells were cultured in low-quality amino acid conditions (Neklesa and Davis, 2009). We found that RNAi by dsRNA injection of the C. elegans NPR2 homolog nprl-2 (F49E8.1) also suppressed the developmental arrest of elo-5(−) larvae (Figure 3C). This suggested that NPRL-2 and NPRL-3 in C. elegans may also function in a complex to negatively impact mmBCFA/d17iso-GlcCer-mediated L1 growth.
NPRL-3 regulates d17iso-GlcCer function in L1 growth by repressing TORC1 activity
The NPR2/3 complex was proposed to be a negative regulator of the TOR pathway in S. cerevisiae, based on the observations that mutations in these two genes caused growth defects in an amino acid scarce environment and that the defects could be effectively suppressed by blocking the TOR pathway (Neklesa and Davis, 2009). We thus explored the possibility that TOR Complex 1 (TORC1) is also the downstream target of NPRL2/3 in growth regulation in C. elegans and that nprl-3(ku540) alleviates d17iso-GlcCer deficiency-induced growth arrest by activating the TORC1 pathway.
We reasoned that if reducing nprl-2/3 activity rescued elo-5(−) L1 growth by up-regulating the TORC1 pathway in C. elegans, then reducing, but not eliminating, TORC1 activity may reverse the rescue effects of nprl-3(ku540) on elo-5(−) mutant background. Caenorhabditis elegans has orthologs of key components of mammalian TORC1, including regulatory elements raga-1 (RagA) and rheb-1 (Rheb) (Long et al., 2002; Schreiber et al., 2010). Feeding RNAi of raga-1 and rheb-1 have been shown to be specific and effective to reduce, but not eliminate, TORC1 function (Hansen et al., 2007; Syntichaki et al., 2007; Lemire et al., 2009; Figure 4—figure supplement 1; see ‘Materials and methods’). We thus tested the effect of raga-1(RNAi) and rheb-1(RNAi) on elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540) mutants.
While nprl-3(ku540) effectively suppressed the L1 arrest phenotype of elo-5(−), the suppression dramatically decreased when raga-1(RNAi) or rheb-1(RNAi) were applied to the elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540) double mutant (Table 1). This indicates that the rescue effect of nprl-3(ku540) on elo-5(−) depends on intact TORC1 activity.
Intact TORC1 function is necessary for mmBCFA-mediated growth regulation
| Genotype | RNAi | Dietary C17ISO | Normalized % of F1 reached adulthood | N | p |
| elo-5(−) | Vector | − | 0 | 208 | |
| elo-5(−) | Vector | + | 86.9 | 205 | 0 |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | Vector | − | 71.5 | 69 | |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | Vector | + | 111.5 | 103 | 0.24 |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | raga-1 (a) | − | 35.5 | 56 | |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | raga-1 (a) | + | 102.5 | 83 | 0.031 |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | raga-1 (b) | − | 25.5 | 214 | |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | raga-1 (b) | + | 88.0 | 279 | 0.00001 |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | rheb-1 (a) | − | 14.2 | 351 | |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | rheb-1 (a) | + | 64.6 | 526 | 0.0000001 |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | rheb-1 (b) | − | 32.5 | 201 | |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | rheb-1 (b) | + | 86.0 | 116 | 0.0037 |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | rsks-1 (a) | − | 15.0 | 68 | |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | rsks-1 (a) | + | 72.5 | 83 | 0.022 |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | rsks-1 (b) | − | 19.0 | 183 | |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | rsks-1 (b) | + | 61.0 | 180 | 0.0034 |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | ife-2 (a) | − | 10.5 | 144 | |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | ife-2 (a) | + | 71.5 | 49 | 0.003 |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | ife-2 (b) | − | 0 | 103 | |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | ife-2 (b) | + | 103.5 | 150 | 0 |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | let-363 | − | 0 | >100 | |
| elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) | let-363 | + | 0 | >100 | NA |
-
Percentages of elo-5(−);nprl-3(ku540) homozygotes with the indicated RNAi treatments that reached adulthood, where (a) and (b) indicate two different RNAi constructs targeting different parts of the same gene. The presented percentage of elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540) animals that reached adulthood was calculated by normalizing against the percentage of elo-5(−/+) nprl-3(ku540)/+ heterozygotes (see ‘Materials and methods’ for detail). Without C17ISO supplementation, RNAi knockdown of multiple TORC1 components reverted elo-5(−);nprl-3(ku540) animals to larval arrest.
We carried out further analyses by repeating the above tests in the presence of dietary C17ISO that rescues the defects of elo-5(−). We found that the effects of raga-1(RNAi) and rheb-1(RNAi) in the above tests were essentially eliminated by C17ISO supplementation (Table 1). This result further indicates that the reversal of the nprl-3(ku540) suppression by raga-1(RNAi) or rheb-1(RNAi) depends on mmBCFA deficiency. In other words, reducing, but not eliminating, TORC1 activity neutralized the effect of nprl-3(ku540) and restored the L1 arrest phenotype of elo-5(−).
To further examine whether the rescuing effect of nprl-3(ku540) on elo-5(−) L1 arrest required the canonical activity of TORC1, we used RNAi to knock down C. elegans orthologs of elf4E (ife-2) and p70S6K(rsks-1), two well-known downstream targets of TORC1 (Long et al., 2002; Syntichaki et al., 2007; Anjum and Blenis, 2008; Sheaffer et al., 2008). We found that elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540) animals treated with ife-2(RNAi) or rsks-1(RNAi), with or without C17ISO supplement, yielded results similar to those obtained with raga-1(RNAi) and rheb-1(RNAi) (Table 1). Taken together, these results indicate that TORC1 acts downstream of d17iso-GlcCer and is negatively regulated by NPRL-3.
The let-363/TOR(−) mutations cause late larval arrest and other severe defects (Long et al., 2002), but injection RNAi causes an early embryonic lethal phenotype (Sonnichsen et al., 2005), indicating that LET-363/TOR, a key component of both TORC1 and TORC2, plays critical regulatory roles in a broad range of developmental stages and a maternal effect largely masks its roles in earlier stages, including its likely functions during L1 growth. The defects caused by feeding RNAi of let-363/TOR (Long et al., 2002) are more severe than that by feeding RNAi of other TORC1 components, described above. elo-5(−) nprl-3(−);let-363(RNAi) animals displayed pleiotropic phenotypes that could not be rescued by C17ISO supplement (Table 1), which is consistent with TORC1 acting downstream of ELO-5.
Hyperactivation of TORC1 bypasses mmBCFA deficiency–induced L1 arrest
If d17iso-GlcCer mainly acts through TORC1 for the growth regulation function, constitutive activation of TORC1 should be sufficient to overcome the L1 arrest of elo-5(−) animals, mimicking the effect of nprl-3(ku540). We used three different established methods to test this possibility. We first followed the scheme by Sancak et al. (2010), in which fusion of one of the TOR binding partners, Raptor, with a C-terminal lysosome localization signal from Rap-1 can localize mTOR to the lysosome and thus constitutively activate the TOR pathway. Both Rap-1 and Raptor proteins are highly conserved in C. elegans (encoded by rap-1 and daf-15; Long et al., 2002; Pellis-van Berkel et al., 2005). We fused a 22-amino acid fragment of the C-terminal end of rap-1 to the C-terminal end of daf-15 and named it daf-15::rap-1(22). We found that 56.0% of elo-5(−) mutants carrying daf-15::rap-1(22) bypassed L1 arrest and reached L3 to adult stage (n = 161; normalized against elo-5(−/+) heterozygotes containing the transgene; Figure 4A,B). This indicates that hyperactivation of TORC1 was sufficient to support L1 growth in mmBCFA-depleted animals.
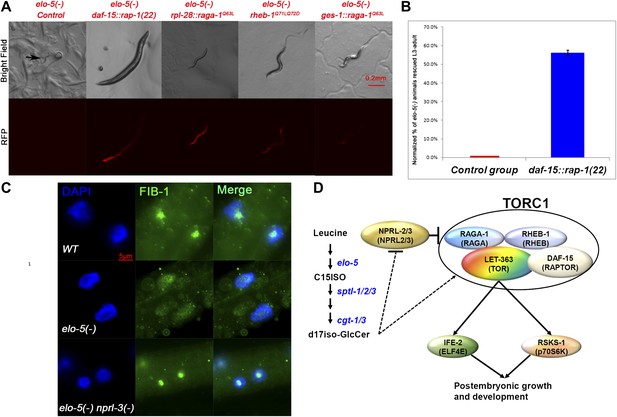
TORC1 activation is sufficient for mmBCFAs-mediated growth regulation.
(A) Representative florescent images showing that elo-5(−) animals with each of four RFP-marked transgenes, which constitutively activated TORC1, bypass L1 arrest to reach beyond L3 stage (statistical data are described in the text and Figure 4B). The rpl-28 promoter drives ubiquitous expression, whereas the ges-1 promoter drives the expression specifically in the intestine (Edgar and McGhee, 1986). Arrow in the upper left panel marks an arrested L1. (B) Percentage of homozygous elo-5(−) animals carrying the daf-15::rap-1(22) transgene reached L3-adult stages (n = 161). The data were normalized against that of elo-5(−/+) heterozygous animals. Error bar, SD. (C). Immunofluorescence images showing FIB-1 expression and localization in intestinal cells of L3 larvae. DAPI-stained nuclei are blue. Green fluorescence indicates the staining of antibody against FIB-1. FIB-1 localization in the nucleoli is largely abolished in elo-5(−) animals and restored by the nprl-3(−) mutation (the percentages of condensed nucleoli localization for the three genotypes from top to bottom are 95% [n=42], 24% [n=112] and 93% [n=68]). (D) A model for the regulation of postembryonic growth and development by mmBCFAs and GlcCer.
The second TORC1-activating transgene used was raga-1Q63L that has been proven to constitutively activate TORC1 both in mammals and C. elegans (Kim et al., 2008; Schreiber et al., 2010). We found that 50.4% of elo-5(−) mutants containing the raga-1Q63L transgene bypassed L1 arrest and reached L3–L4 stage (n = 248, p=1.0 × 10−6; normalized against elo-5(−/+) heterozygotes containing the transgene; Figure 4A) while none of elo-5(−) mutants without this transgene did (n = 136). Finally, we also tested a third TORC1-activating transgene, rheb-1Q71LQ72D, and found that it also permitted 41.4% of elo-5(−) animals to grow beyond the L1 stage (n = 169; normalized against elo-5(−/+) heterozygotes containing the transgene; Figure 4A). These results led to the conclusion that TORC1 acts downstream of d17iso-GlcCer to promote L1 growth and development and that this activity is negatively regulated by NPRL-2/3.
The mmBCFA/d17iso-GlcCer/TORC1 pathway acts in the intestine to promote postembryonic development
Previous studies on elo-5, acs-1, tat-2, and cgt-1/cgt-3 mutants suggested that biosynthesis and localization of mmBCFAs and their derived sphingolipids in the intestine are essential and sufficient for postembryonic development (Marza et al., 2009; Seamen et al., 2009; Kniazeva et al., 2012). The fact that elo-5(−);nprl-3(ku540) animals treated with ife-2 RNAi, that targets intestinal but not neuronal expression of the gene (Syntichaki et al., 2007), are L1 arrested (Table 1) also points to the requirement of TORC1 activity in the intestine. To directly evaluate a role of intestinal TORC1 in mmBCFA/d17iso-GlcCer regulated growth, we made a raga-1Q63L TORC1 hyperactivating transgene driven by the intestinal-specific promoter ges-1 (Edgar and McGhee, 1986). We found that elo-5(−) animals containing this transgene bypassed the L1 arrest (37.9%, n = 132, normalized against elo-5(−/+) heterozygotes containing the transgene; Figure 4A). The rescue with the intestinal expression was similar to that by a ubiquitously expressed raga-1Q63L transgene (above). A neuronal-specific rgef-1 promoter–driven (Brignull et al., 2006) raga-1Q63L, however, could not suppress the L1 arrest of elo-5(−) animals (0%, n > 100). These results suggest that the intestinal d17iso-GlcCer/TORC1 pathway regulates postembryonic growth.
Although the genetic data described above sufficiently indicate that TORC1 acts downstream of d17iso-GlcCer and NPRL-2/3 for L1 growth, we carried out further tests to observe downstream activity of TORC1 in the intestine. Because the biochemical assay for p70S6K phosphorylation has not been established in C. elegans’ TOR-related studies, we adopted the strategy by Sheaffer et al. (2008), where localization of FIB-1, a Box C/D small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein (snoRNP) was used as a marker of TORC1 activation in C. elegans. In wild-type animals, FIB-1 is highly expressed and localized in the nucleolus, where it methylates pre-rRNAs during ribosome maturation, but the expression is decreased and no longer localized to the nucleolus in let-363/TOR(−) animals (Sheaffer et al., 2008). We found that the nucleolar localized FIB-1 was dramatically reduced in intestinal cells of mmBCFA-deficient [elo-5(RNAi)] animals (Figure 4C). Furthermore, nprl-3(−) rescued the FIB-1 expression and nucleolar localization in elo-5(−) back to that of wild type (Figure 4C). Combining the results from the functional and biochemical assays described above, we conclude that TORC1 is the key downstream factor mediating mmBCFA and d17iso-GlcCer functions in the intestine to promote postembryonic growth and development (Figure 4D).
Discussion
Roles of the mmBCFA/GlcCer/TORC1 pathway in promoting postembryonic development
In this study, we uncovered and characterized a novel GlcCer-stimulated TORC1 pathway that promotes postembryonic development (Figure 4D). This discovery reveals a specific link between lipids and the TORC1 signaling pathway. Both ceramide and TORC1 have been individually implicated for roles in stress response, apoptosis, cancers, and other cellular processes by studies in C. elegans and mammals (Hannun and Obeid, 2008; Hansen et al., 2008; He and Klionsky, 2009; Howell and Manning, 2011; Laplante and Sabatini, 2012; Menuz et al., 2009; Zoncu et al., 2011). It is conceivable that some of these functions are mediated by this GlcCer/TORC1 signaling pathway. Moreover, our data suggest that this GlcCer/TORC1 pathway may serve as a ‘check point’ to coordinate metabolic status in the intestine with postembryonic growth and development. d17iso-GlcCer is a sphingolipid metabolite rather than a nutrient directly absorbed from food (Merrill et al., 1997); it is the product of a long biosynthetic pathway involving many enzymatic steps and thus may reflect the availability of many metabolites and enzymes.
Although leucine is a precursor molecule of mmBCFA biosynthesis, this long lipid synthesis pathway is unlikely part of a mechanism to specifically sense the level of essential amino acids. Furthermore, mmBCFA levels are stable in starved L1 larvae (Kniazeva et al., 2008; Figure 4—figure supplement 4C), suggesting that mmBCFA levels do not directly reflect the feeding status through a direct substrate–product relationship. There are several reported leucine-sensing mechanisms, based on studies using tissue culture cells (Bonfils et al., 2012; Duran et al., 2012; Han et al., 2012; Zoncu et al., 2012). To test if such a pathway acts in parallel to the mmBCFA/d17iso-GlcCer pathway to promote TORC1 in the C. elegans intestine, we supplemented elo-5(−) animals with a high level of dietary leucine (10 mM) and failed to observe any suppression of the L1 arrest phenotype (Figure 4—figure supplement 2), consistent with the idea that TORC1 activation by mmBCFA/d17iso-GlcCer is essential in the intestine of L1 larvae and cannot be effectively compensated by another leucine/TORC1 mechanism in C. elegans.
In C. elegans, both the IIS and DAF-7/TGF-β pathways have been shown to play critical roles in the regulation of postembryonic growth and development in response to nutrient/food availability (Baugh and Sternberg, 2006; Mukhopadhyay and Tissenbaum, 2007; Fielenbach and Antebi, 2008; Lee and Ashrafi, 2008; Jones et al., 2009; Soukas et al., 2009). Our previous data and this study indicated that the GlcCer/TORC1 pathway is initiated in the intestine (Figure 4) and is independent of the IIS pathway (Kniazeva et al., 2008). Our additional analysis also suggests that the GlcCer/TORC1 pathway is DAF-7/TGF-β pathway independent (Figure 4—figure supplement 3). This independence may facilitate the role of such a pathway to promote specific developmental events under specific physiological conditions.
The GlcCer/TORC1 signaling pathway is likely conserved in mammals
There are several reasons for us to believe that such a GlcCer/TORC1 pathway is likely conserved in mammals. First, the components of TORC1 are conserved between C. elegans and mammals. The NPRL-3 protein we identified in this pathway is conserved in all eukaryotes, and its negative regulatory role on TOR has been characterized in budding yeast (Neklesa and Davis, 2009). Several proteins (such as NPR2 and IML1) that are reported to form a complex with NPR3 in budding yeast have orthologs in C. elegans as well as mammals (Neklesa and Davis, 2009; Wu and Tu, 2011). NPRL2 (human ortholog of NPR2) and DEPDC5 (human ortholog of IML1) have been reported to function as tumor suppressors (Merrill et al., 1997; Li et al., 2004; Neklesa and Davis, 2009). This property is consistent with the role of this complex in repressing TOR-mediated growth regulation that was identified in budding yeast and this study. Second, a role for GlcCer in nutrient sensing is consistent with studies showing that ceramide and sphingolipids play roles in cell signaling and growth control in both invertebrates and mammals (Deng et al., 2008; Hannun and Obeid, 2008; Menuz et al., 2009). The finding that mouse mutants with blocked GlcCer biosynthesis die as early embryos suggests the essential role of these lipids in growth and development (Yamashita et al., 1999). Third, the TOR pathway is down-regulated by inhibiting the abnormally high GlcCer biosynthesis in polycystic kidney disease in mouse models (Natoli et al., 2010), suggesting a possible conserved link between GlcCer and TOR activities.
It is currently unknown whether an iso-branched LCB is also required for the potential role of GlcCer in mammals, given that most LCBs in mammals are straight-chain LCBs. However, it is important to note that mmBCFAs (derived from branched-chain amino acids) are also present in mammals. For example, they are constituents of sphingolipids in skin cells and the intestinal tract of human newborns. They are also found to be incorporated into LCBs (to form an iso- or an anteiso-LCB similar to that in C. elegans) in multiple mammalian tissues (Aungst, 1989; Karlsson, 1997; Oku et al., 2000; Ran-Ressler et al., 2008). Therefore, their important physiological functions, including possible roles in ceramide-involved growth regulation, may be assumed, albeit not yet uncovered experimentally.
Activation of TORC1 by d17iso-GlcCer
How does d17iso-GlcCer regulate the activity of TORC1? Recent work in mammalian cells has indicated that TORC1, for its role in sensing amino acids, localizes at the surface of the lysosome, likely in lipid rafts (Nada et al., 2009). If such a mechanism is conserved in all animals, conceptually, d17iso-GlcCer could act as a ligand that binds to a ‘receptor’ to either repress the NPRL-2/3 complex or activate the TOR complex at the surface of the lysosome. Alternatively, this lipid could be required for lysosome biogenesis or could be an essential constituent of the membrane microdomain that permits the proper localization or activity of TORC1 on the lysosome. By examining lysosomal markers LMP-1::GFP (Artal-Sanz et al., 2006; O’Rourke et al., 2009; Rabbitts et al., 2008), GLO-1::GFP (Schroeder et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2010), and Neutral red (Long et al., 2002), we did not observe obvious defects in lysosome formation in elo-5(−) mutants (Figure 4—figure supplements 4 and 5). Major defects in lysosome formation would also be inconsistent with our genetic suppression data and previous studies on GlcCer by others (Entchev et al., 2008; van der Poel et al., 2011). One possible mechanism is that d17iso-GlcCer acts through the V-ATPase pathway, since the lysosomal V-ATPase has been shown to be stimulated by GlcCer and to play an essential role in TORC1 activation in studies using tissue culture cells (van der Poel et al., 2011; Zoncu et al., 2011; Bar-Peled et al., 2012). Further biochemical and genetic analyses are needed to test this hypothesis in C. elegans.
It may be important to point out again that activation of TORC1 bypasses the robust L1 arrest phenotype caused by either mmBCFA or d17iso-GlcCer deficiency. Remarkably, the elo-5(−); nprl-3(ku540) double mutants, still deficient for these lipids, propagate continuously. Therefore, the only essential biochemical role of d17iso-GlcCer might be to activate TORC1 or repress NPRL-3. In other words, the biochemical mechanism underlying this role of d17iso-GlcCer appears to be very specifically connected to TORC1 activation.
Materials and methods
Caenorhabditis elegans strains and maintenance
Request a detailed protocolThe following strains were obtained from the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center Database (CGC) or as indicated; wild-type N2 Bristol, elo-5(gk208), rrf-3(pk1426), daf-3(mgDf90), bra-1(nk1), daf-5(e1386), asna-1(ok938)/hT2[bli-4(e937)let?(q782)qIs48], let-363 (ok3018), pwIs50[lmp-1::GFP + Cbr-unc-119(+)], hjIs9 [ges-1p::glo-1::GFP + unc-119(+)]. The cgt-1(tm1027) and cgt-3(tm504) mutants were provided by the Mitani Lab (National BioResource Project, Tokyo, Japan). Caenorhabditis elegans were maintained at 20°C on NGM plates (referred to as standard plates) with Escherichia coli OP50 bacterial food (OP50/NGM). Washes and bleaching were done according to standard protocols (Stiernagle, 2006).
Dietary supplements
Request a detailed protocolFatty acids C13ISO, C17ISO (Larodan), C16:1 n7, C18:1 n7, and C20:4 n6 (Sigma), as well as C17iso-d18:1-Ceramide and d17iso-SPA (custom synthesis; Larodan) were prepared as 10 mM stocks in DMSO. Leucine (Sigma) was prepared as a 100 mM stock in water. A stock solution was mixed with 500 µl of OP50 overnight bacterial suspension in a 1:10 ratio.
Preparation of the C17ISO-deficient eggs and larvae
Request a detailed protocolUsing elo-5(gk208) mutants. elo-5(gk208) adults maintained on the plates with S. maltophlia (Kniazeva et al., 2008) were washed off in M9 buffer, bleached, and eggs were plated on NGM plates spotted with 300 µl of OP50 overnight liquid culture supplemented with 1 mM C13ISO, which is a less efficient mmBCFA supplement than C17ISO and allows apparent normal growth only in the first generation followed by uniformly arrested C17ISO-deficient L1s in the second generation. Control animals were prepared in the same way, except C17ISO was used as a supplement for the N2 strain instead of elo-5(gk208).
Using RNAi. Adult animals of the corresponding strains were washed off OP50/NGM plates, bleached, and eggs plated on elo-5(RNAi) plates prepared according to the standard protocol. Adults of the next generation were bleached for eggs, producing C17ISO-deficient larvae.
Preparation of C17ISO-deficient late larvae and adults
Request a detailed protocolA mixed population of elo-5(gk208) mutants maintained on plates with C17ISO supplement, which promoted wild-type growth and proliferation, were collected, washed, and incubated for 1 hr in M9 before replating on OP50/NGM plates without supplement. The next day, animals were washed off and used in the corresponding experiments. Depletion of C17ISO was confirmed by GC analysis of the FA composition in total lipid extracts from a representative group of animals.
Lipid analysis by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry
Request a detailed protocolGas chromatography method was described in a previous report (Kniazeva et al., 2008). Mass spectrometry sample preparation was described in our previous report (Kniazeva et al., 2012). Briefly, lipid extracts were dissolved in 1 ml of methanol with 1 mM formic acid and subjected to quantitative lipid analysis using a 4000 Q-Trap mass spectrometer (AB Sciex). Samples were infused at a flow rate of 8 μl/min using a Harvard Apparatus syringe pump (Harvard Apparatus). The detailed scan modes are described in the figure legends.
Purification of d17iso-LCB from Sphingobacterium spiritivorum
Request a detailed protocolThe S. spiritivorum strain was obtained from ATCC (#33861) and cultured under the conditions suggested by www.atcc.org. The total lipids were extracted by the method of Bligh and Dyer (1959). The alkaline stable lipid fraction was purified as described previously (Naka et al., 2003). The hydrolysis of sphingolipids to generate side chain fatty acid and LCB fractions was done as described previously (Naka et al., 2003), with an additional last step using 100% methanol to extract the dry LCB fraction after evaporation of the chloroform solvent. The final fraction of LCB was verified by mass spectrum.
Isolation of nprl-3(ku540) through a genetic screen
Request a detailed protocolWe performed a screen that was significantly different from our previously published screen that resulted in isolation of three tat-2(−) alleles that suppress elo-5(gk208) (Seamen et al., 2009). The original strain used in this genetic screen was elo-5(gk208) injected with elo-5(genomic rescuing), elo-5Promoter::GFP (Kniazeva et al., 2004), and rol-6(dn) constructs. L4-staged P0 animals were mutagenized with standard EMS treatment and then single cloned to 10-cm plates containing 1 mM C13ISO. Suppressor candidates were determined in the F2 generation by the ability to reach gravid adulthood without carrying the GFP or rol-6 marker and the ability to grow to gravid adulthood without any supplement. From ∼2000 haploid genomes, 4 suppressor candidates were isolated. Among these four, and several suppressor mutations isolated in a previous screen (Seamen et al., 2009), only ku540 permits elo-5(−) animals to grow indefinitely without any mmBCFA supplementation and without recovering the production of mmBCFAs.
In our previously published screen (Seamen et al., 2009), we isolated three mutations in tat-2 that can suppress elo-5(−)–induced L1 arrest in the presence of C13ISO, or temporarily suppress the L1 arrest for one generation without C13ISO supplement. The hypothesis was that tat-2(−) alters the subcellular localization of certain mmBCFA-containing lipids so that their levels (from a slow C13ISO to C17ISO conversion or from maternal sources) are sufficiently maintained for one more generation. Therefore, tat-2(−) does not bypass the requirement of mmBCFAs for growth. The tat-2(−) mutations were also found to partially and temporarily suppress the lethality associated with disrupting the function of the enzyme (SPTL-1) in the first step of sphingolipid biosynthesis, suggesting a potential link between sphingolipids and mmBCFAs. However, this observation may not be interpreted as the proof that mmBCFAs function through sphingolipids for the following reasons. (1) Unlike feeding d17iso-SPA or the downstream suppressor nprl-3(ku540) that fully suppresses mmBCFA deficiency [elo-5(−)]–induced L1 arrest (this study), tat-2(−)does not bypass the requirement of mmBCFAs for growth for more than one generation. (2) sptl-1(−) disrupts all sphingolipid biosynthesis and its phenotype is, in contrast to elo-5(−), highly pleiotropic, as animals showed various morphological and growth defects and die at various larval stages. (3) tat-2 does not exclusively function with mmBCFA-containing lipids; it is also a critical player in steroid metabolism as exemplified by a recent article (Liu et al., 2012). Therefore, the link between mmBCFA and sphingolipids through their interactions with tat-2 could be indirect and the partial suppression of sptl-1(−) by tat-2(−) could be due to suppression of mmBCFA-unrelated functions of sphingolipids.
SNP mapping of ku540 and cloning of the nprl-3 gene
Request a detailed protocolFor SNP mapping of ku540, we used a Hawaii strain based elo-5(gk208) mutant (Seamen et al., 2009) to cross with elo-5(gk208) ku540 animals and determined the locus of ku540 by linkage analysis (Davis et al., 2005). The three-point-mapping strain dpy-13(e184)elo-5(gk208)unc-24(e138) was also used in this study. The elo-5(−)ku540 genomic DNA was prepared using the Genomic DNA Sample Preparation Kit (Illumina) and sent for Illumina deep sequencing (High Throughput Next-Generation Sequencing Core, University of Colorado). The raw data was analyzed using Maqgene (Bigelow et al., 2009), and candidate mutations were confirmed by PCR and sequencing. Homologs of NPRL-2 and NPRL-3 were identified at ensembl.org. The alignment among NPRL3 homologs was done using MacVector software.
Analysis of elo-5(gk208) nprl-3(ku540) double mutants
Request a detailed protocolExcept for Figure 2I, all elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540) animals being tested for Figure 2 were from homozygous mothers. For Figure 2I, because the control cgt-3(−);cgt-1(−) animals were fully arrested at L1 and were derived from cgt-3(−);cgt-1(−)/nT1[qIs51] heterozygotes, we had to use heterozygous cgt-3(−);elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540)/nT1[qIs51];cgt-1(−)/nT1[qIs51] P0 animals to generate cgt-1(−);cgt-3(−);elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540) homozygous animals to generate comparable data. Because it is difficult to determine the genotype of arrested L1 animals, the ratios of homozygous cgt-1(−);cgt-3(−);elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540) animals that reached adulthood were calculated by the ratio of the homozygous animals in the total adult population, with a normalization by dividing by the expected ratio of 20%, from the Mendelian distribution of strains containing a recessive lethal translocation balancer (Edgley et al., 2006).
Generation of elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540) homozygous animals for the tests shown in Table 1 and Figure 4B is described below.
RNAi analysis by feeding and injection
Request a detailed protocolAll RNAi by feeding, except cgt-3(RNAi) and let-363(RNAi), used bacterial clones from the MRC RNAi library (Kamath et al., 2003) or the ORF-RNAi Library (Open Biosystems) (Figures 1–3). cgt-3(RNAi) and let-363(RNAi) constructs were made as described (Marza et al., 2009; Honjoh et al., 2009). Feeding RNAi experiments were done as previously described (Kniazeva et al., 2008). The DNA templates for nprl-3 and nprl-2 dsRNA synthesis were amplified from the RNAi-containing bacterial strain (MRC RNAi library) by PCR using T7 primers. dsRNA was synthesized using a MEGAscript RNAi Kit (Life Technologies) and then injected into adults of elo-5(−)/nT1[qIs51], elo-5(-)nprl-3(ku540)/nT1[qIs51], or cgt-3(-);cgt-1(-)/nT1[qIs51]. The eggs were collected from the 8th to 24th hr after injection. Nongreen F1 adult animals were verified by PCR to confirm the homozygosity of elo-5(−) or cgt-1(−);cgt-3(−) animals.
Feeding RNAi analysis of TORC1 components and downstream targets
Request a detailed protocolAll RNAi (raga-1, rheb-1, rsks-1, ife-2) by feeding used sequence confirmed bacterial clones from both the MRC RNAi library (Kamath et al., 2003) or the ORF-RNAi Library (Open Biosystems) (Table 1). These RNAi clones have been extensively used for TORC1-related studies in many publications/meeting abstracts, and their efficiency and specificity have been well established. Furthermore, results from those references and our experiments have shown RNAi feeding of these genes did not reproduce the strong larval lethal phenotype (Hansen et al., 2007; Syntichaki et al., 2007; Lemire et al., 2009; Ching et al., 2010; Polley and Fay, 2012). This difference indicates that TORC1 function is not completely eliminated by RNAi feeding of these genes (raga-1, rheb-1, rsks-1, ife-2).
The elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540) animals were balanced by a GFP-labeled nT1[qIs51] balancer and treated with feeding RNAi. In the next generation, similar to the method described above, the ratios of homozygous elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) animals that reached adulthood were calculated by the ratio of homozygous elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) animals in the total adult population, with a normalization by dividing by the expected ratio 20%. As reported, RNAi knockdown of TORC1 components and the downstream target genes would affect the normal development of C. elegans (Long et al., 2002; Syntichaki et al., 2007; Zoncu et al., 2011). In our experiments, the usage of the heterozygous elo-5(−) nprl-3(ku540)/nT1[qIs51] animals for the RNAi knockdown experiment allowed us to exclude the potential negative effect from RNAi treatment of TORC1 components and TORC1 target genes themselves. Any of those elo-5(−) nprl-3(−)–independent negative effects from those RNAi treatments would affect the heterozygous as well as the homozygous elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) animals, and therefore not be included in the ratio in the data presented in Table 1.
Generation of transgenes
Request a detailed protocolFor the pPD95.77-nprl-3::GFP plasmid, we cloned the potential 1 kbps promoter region upstream of the operon containing nrpl-3 and inserted it into the pPD95.77 vector (Figure 4A,B). For raga-1Q63L, the genomic DNA including the full coding region was cloned into pPD95.77, driven by a ubiquitous RPL28 promoter. For ges-1::raga-1Q63L, the genomic DNA including the full coding region was cloned into pPD95.77, driven by an intestinal-specific ges-1 promoter. For rheb-1Q71LQ72D, the genomic DNA including the full coding region and about 1 kbps of upstream sequence was cloned into pPD95.77. Amino acid mutations in both mutants were introduced by replacement with PCR-generated DNA fragments containing the designed mutations. For daf-15::rap-1(22), the genomic DNA of daf-15, including the full coding region and the 1 kbps potential promoter region upstream of daf-15, was cloned from the fosmid WRM061cH04. After the stop codon of daf-15 was removed, it was fused with the genomic DNA encoding the last 22 amino acids and the 3′ UTR of rap-1. For pPD95.77-nprl-3::GFP, 25 ng/μl of plasmid was injected in wild-type animals. For the daf-15::rap-1(22) rescue experiment, elo-5(−)/nT1[qIs51] animals were injected with 10 ng/µl daf-15::rap-1(22) and 25 ng/µl psur-5::RFP plasmid. In the next generation, the ratios of homozygous elo-5(−) animals that reached L3-young adulthood were calculated by the ratio of homozygous elo-5(−) nprl-3(−) animals in RFP-positive L3-young adult population, with a normalization by dividing by the expected ratio 20%, as described above. The reason for using heterozygous elo-5(−)/nT1[qIs51] animals for this experiment is similar to that for the RNAi knockdown experiment we described above. By this method, we exclude the negative effect we observed from constitutively active TORC1 transgenes (daf-15::rap-1(22), raga-1Q63L, ges-1::raga-1Q63L or rheb-1Q71LQ72D) for their rescue effects.
Neutral red staining
Request a detailed protocolThe Neutral red staining was performed following Long et al. (2002). Animals were fed with Neutral red containing bacteria food for <10 min before evaluation by microscopy.
Microscopy
Request a detailed protocolAnalysis of GFP expression and phenotypic abnormalities were performed with Nomarski optics using a Zeiss Axioplan2 microscope and a Zeiss AxioCam MRm CCD camera. Plate phenotypes were observed using a Leica MZ16F dissecting microscope, and pictures were taken with a Hamamatsu C4742-95 CCD camera.
Statistical analysis
Request a detailed protocolAll statistical analyses, except the dsRNA feeding for TOR-related genes, were performed using Student’s t-test, and p<0.05 was considered a significant difference. The Fisher’s exact test was used for analysis of the TOR-related dsRNA feeding experiments and raga-1Q63L rescue experiment, and p<0.05 was considered a significant difference.
References
-
The RSK family of kinases: emerging roles in cellular signallingNat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:747–758.https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2509
-
A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purificationCan J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917.https://doi.org/10.1139/o59-099
-
WormBookWormBook, The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, 10.1895/wormbook.1.89.1.
-
Two pleiotropic classes of daf-2 mutation affect larval arrest, adult behavior, reproduction and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegansGenetics 150:129–155.
-
Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipidsNat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:139–150.https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2329
-
mTOR couples cellular nutrient sensing to organismal metabolic homeostasisTrends Endocrinol Metab 22:94–102.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2010.12.003
-
BookAnalysis of intact polar lipids by high-pressure liquid chromatography mass spectrometry/tandem mass spectrometry with use of thermospray or atmospheric pressure ionizationIn: Hamilton RJ, editors. In Lipid analysis in oils and fats. London: Blackie Academics and Professional. pp. 290–316.
-
Regulation of TORC1 by Rag GTPases in nutrient responseNat Cell Biol 10:935–945.https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1753
-
Molecular mechanisms of mTOR-mediated translational controlNat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:307–318.https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2672
-
Sphingolipids–the enigmatic lipid class: biochemistry, physiology, and pathophysiologyToxicol Appl Pharmacol 142:208–225.https://doi.org/10.1006/taap.1996.8029
-
Reproduction and longevity: secrets revealed by C. elegansTrends Cell Biol 17:65–71.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2006.12.004
-
Positive selection of Caenorhabditis elegans mutants with increased stress resistance and longevityGenetics 163:171–180.
-
WormBookWormBook, The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, 10.1895/wormbook.1.101.1.
-
Sphingobacterium gen. nov., Sphingobacterium spiritivorum comb. nov., Sphingobacterium multivorum comb. nov., Sphingobacterium mizutae sp. nov., and Flavobacterium indologenes sp. nov.: Glucose-Nonfermenting Gram-Negative Rods in CDC Groups IIK-2 and IIbInt J Syst Bacteriol 33:580–598.https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-33-3-580
-
A vital role for glycosphingolipid synthesis during development and differentiationProc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:9142–9147.https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.16.9142
-
Genetic and dietary regulation of lipid droplet expansion in Caenorhabditis elegansProc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:4640–4645.https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912308107
-
mTOR: from growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageingNat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:21–35.https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3025
Article and author information
Author details
Funding
Howard Hughes Medical Institute
- Huanhu Zhu
The funder had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Acknowledgements
We thank S Mitani, V Göbel, O Hobert, K. Sheaffer, S Mango, S Takagi, A Fire, W Wood, E Seamen, and the C. elegans Knockout Consortium and CGC (funded by NIH [P40OD010440]) for strains and advice. We thank H Tang, T Euler, C Teng, J Cavaleri, M Hynes-Grace, R Wang, for assistance; M Tucker for editing the manuscript; and W Wood, M Cui, and our laboratory members for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Copyright
© 2013, Zhu et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 3,502
- views
-
- 571
- downloads
-
- 91
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Citations by DOI
-
- 91
- citations for umbrella DOI https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00429





