HSF-1 activates the ubiquitin proteasome system to promote non-apoptotic developmental cell death in C. elegans
Figures
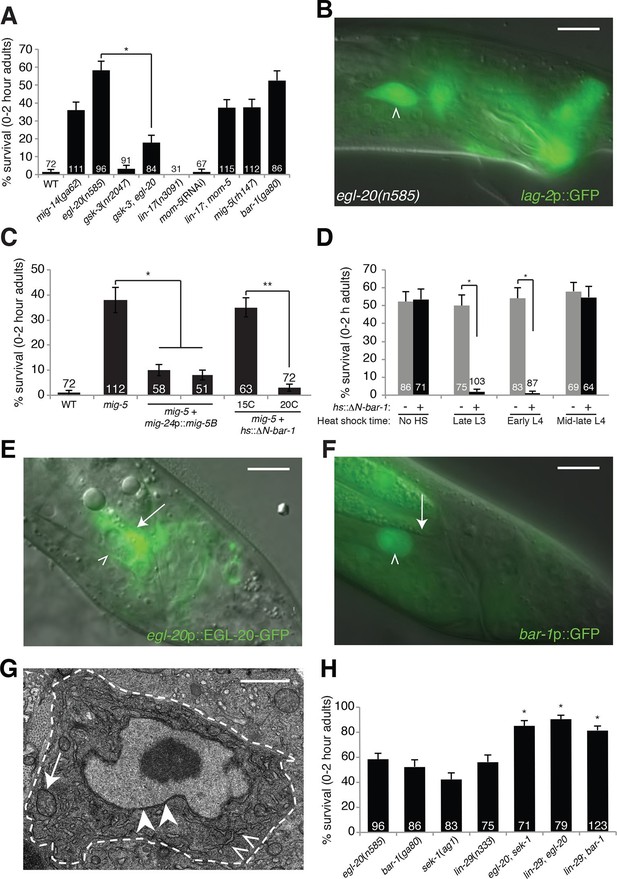
An egl-20/Wnt pathway promotes Llnker cell death.
(A) Linker cell survival in indicated genotypes. Strains contain qIs56[lag-2p::GFP] linker cell reporter transgene and him-5(e1490) for males. gsk-3(nr2047) is linked to unc-101(sy216). *p<10–4, no. animals scored is inside bars. (B) Adult egl-20(n585) male expressing lag-2p::GFP. (C) Linker cell survival in mig-5(rh147) animals with indicated transgenes. *p<10–4, **p<.002. (D) bar-1(ga80) rescue with hsp-16.2p::ΔN-BAR-1. *p<10–4. (E) egl-20p::EGL-20::GFP expression in L4 male. (F) bar-1p::GFP expression in L4 male. In (B), (E), (F), white caret, linker cell; arrow, Ul/r.p cells; scale bar, 10 μm. (G) EM of surviving linker cell in bar-1(ga80) adult. Arrow, mitochondria. Arrowheads, nuclear envelope. Carets, healthy ER. Scale bar, 1 μm. (H) Linker cell survival in indicated genotypes. *p<10–4 from the single mutant.

Surviving linker cells in egl-20 mutants are not engulfed, but dying ones are.
(A,B) 2h-old egl-20(n585) adult male with a surviving linker cell. lag-2p::GFP marks the linker cell (white carets). lin-48::mCherry marks the U.l/rp cells (arrowheads). Note that in (A), the U.l/rp cells abut the surviving linker cell without surrounding it completely, whereas in (B), the U.l/rp cells have entirely engulfed the linker cell. Scale bars, 10 μm.

Expression of receptive Wnt components in the linker cell.
(A,B) Shown are typical L4 males harboring reporters for (A) mig-5; (B) lin-17. White carets and dashed circles, linker cell. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Expression of lin-44p::GFP reporter in an L4 male. Intestinal expression is an artifact of the vector. Dashed circle, linker cell. Scale bars, 10 μm. (D) Expression of wrm-1p::GFP in an L4 male. Dashed circle, linker cell. Scale bars, 10 μm.
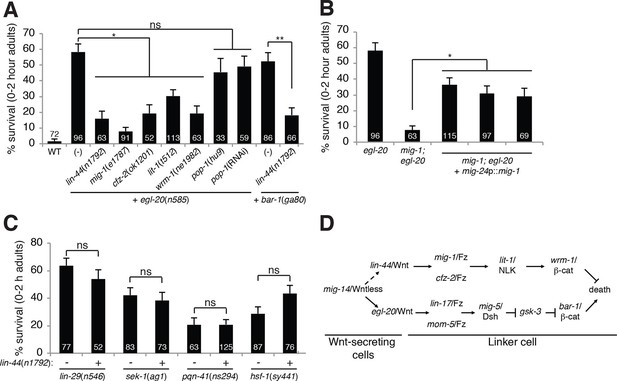
A lin-44/Wnt pathway promotes linker cell survival.
(A) Linker cell survival in indicated genotypes. In (A-C) strains also contain qIs56 and him-5(e1490). *p<10–3; **p <10–4; ns, not significant; Fisher’s exact test. lit-1(t512) is linked to unc-32(e189). (B) Linker cell survival in egl-20(n585) and mig-1(e1787); egl-20(n585) animals harboring a mig-24p::mig-1 transgene. *p<0.001. (C) Linker cell survival in indicated genotypes. ns, not significant; Fisher’s exact test. (D) Model for Wnt pathway interactions in LCD.
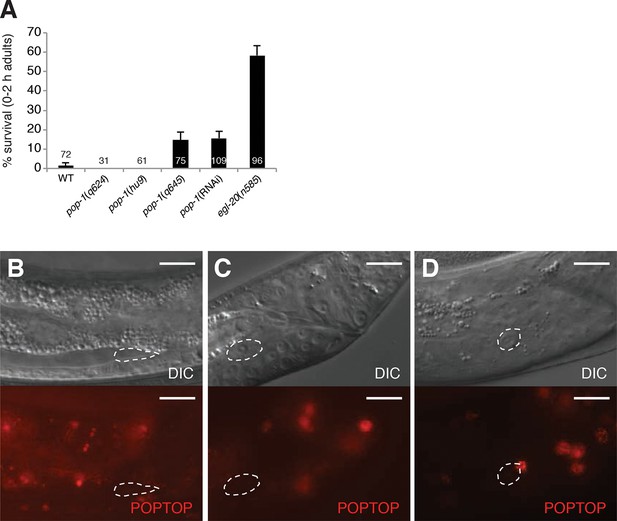
pop-1 does not play a significant role in linker cell death.
(A) Linker cell survival in 0-2h adults of the indicated genotypes. All strains also contain the qIs56 reporter transgene to visualize the linker cell and him-5(e1490) to increase the incidence of males. pop-1(RNAi) performed with RNAi-sensitizing rrf-3(pk1426) allele. (B-D) All panels are images of strain unc-119(ed4); him-5(e1490); syIs187[POPTOP::HIS-24-mCherry]. Linker cell outlined in dashed white. (B) Late L3/early L4 male. (C) Mid-L4 male. Note the already-apparent linker cell cytoplasmic changes in the DIC image. (D) Late L4 male. mCherry-staining nucleus at the top right of the linker cell in (D), belongs to a neighboring overlying cell. Scale bars, 10 μm.
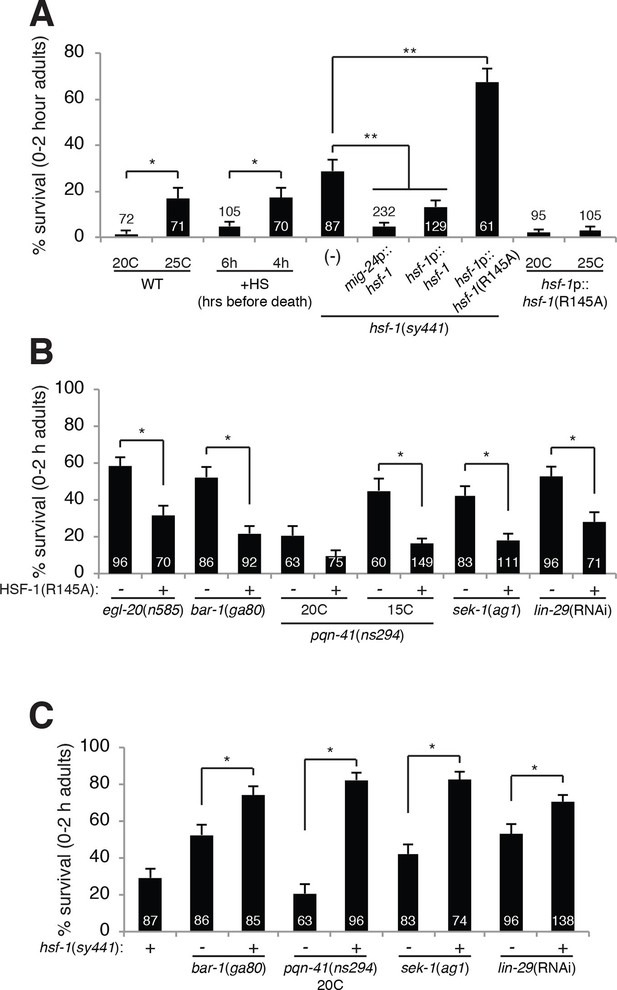
HSF-1 promotes linker cell death.
(A) Linker cell survival in indicated genotypes. In (A-C), strains also contain qIs56 and him-5(e1490). *p<10–2;**p<10–3; Fisher’s exact test. hsf-1p::hsf-1(WT/R145A) transgenes are fused to GFP. WT: animals raised at indicated temperature after hatching. +HS: WT animals heat shocked at 37°C for 15 min at 6 hr or 4 hr before the L4-adult molt. hsf-1(sy441): mig-24p::hsf-1 bar is average of three independent extrachromosomal array lines. hsf-1p::hsf-1(R145A) bar is average of two independent single-copy integrated lines. hsf-1p::hsf-1(R145A): animals were raised at the indicated temperature after hatching. (B) Linker cell survival in indicated genotypes. HSF-1(R145), hsf-1p::hsf-1(R145A). The drSi28[hsf-1p::hsf-1(R145A)] transgene was used. For hsf-1p::hsf-1(R145A); bar-1(ga80), two other independent single-copy integrated lines gave similar results. (C) Linker cell survival in indicated genotypes.
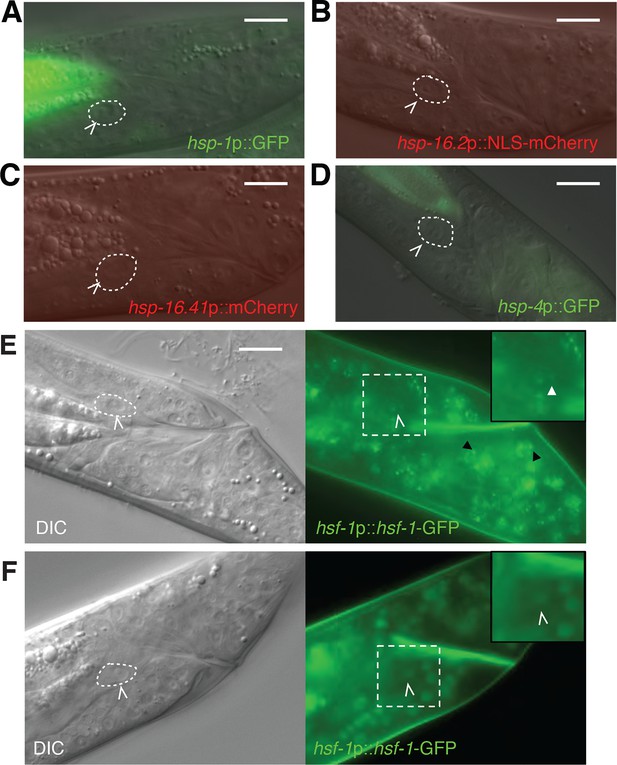
Markers of the heat-shock response are not induced during linker cell death.
(A-D) Shown are L4 males harboring reporters for (A) hsp-1; (B) hsp-16.2; (C) hsp-16.41; (D) hsp-4. At least 20 animals were examined for each reporter. hsp-4 is not a typical heat-shock hsf-1 target but harbors cryptic heat-shock elements in its proximal promoter. (E) DIC (left) and fluorescence (right) images of an L4 male treated with NaN3 to induce HSF-1 nuclear stress granules. Dashed square magnified 1.5x in inset. White carets, LC. White arrowheads in inset, nuclear stress granules in the LC. Black arrowhead, stress granule in another cell. Scale bars, 10 μm. (F) Same as (E) except animal treated with tetramisole, which does not induce HSF-1 granules.
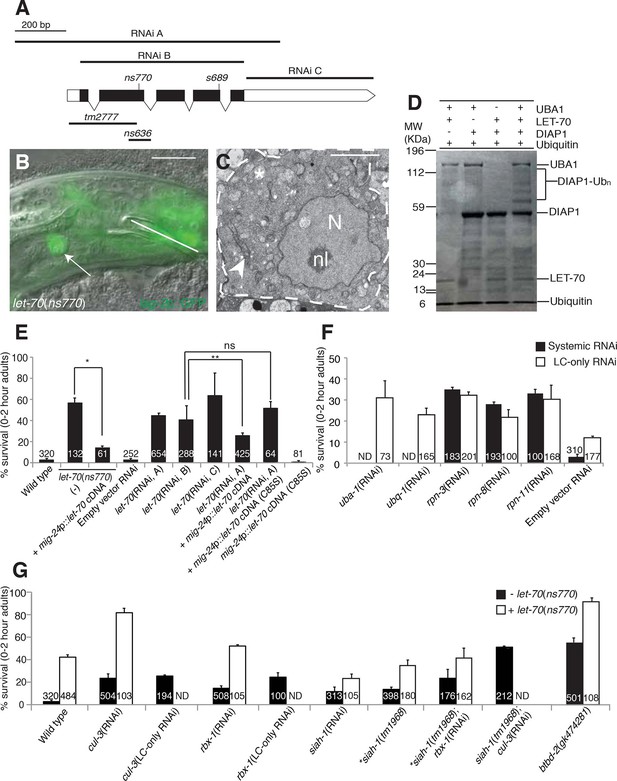
let-70 promotes linker cell death.
(A) let-70 gene structure and mutations/RNAi clones used in our studies. Black boxes, exons; white boxes, 5’ or 3’ untranslated regions. Scale bar, 200 bp. (B) Combined DIC and fluorescent images of let-70(RNAi) adult male. lag-2p::GFP marks the linker cell. Arrow, linker cell. White line, cloaca. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) EM of surviving let-70(RNAi) linker cell. Scale bar, 2 μm. Asterisk, mitochondria, Arrowhead, ER, N, nucleus, nl, nucleolus. (D) Purified 6xHis-LET-70, Drosophila UBA1, DIAP1 and ubiquitin. causes DIAP1 auto-ubiquitination. (E-H) Linker cell survival in indicated genotypes. No. animals scored, inside bars. Error bars, SEM. *p<0.001; **p<0.0001; Fisher’s Exact Test; ns, not significant. Animals contained qIs56 and him-5(e1490). In (F) animals also contained rrf-3(pk1426) for increased RNAi efficiency. In LC-only experiments, mig-24p was used to drive rde-1 cDNA in rde-1(ne219); him-8(e1489); qIs56 mutants. ND, not determined.
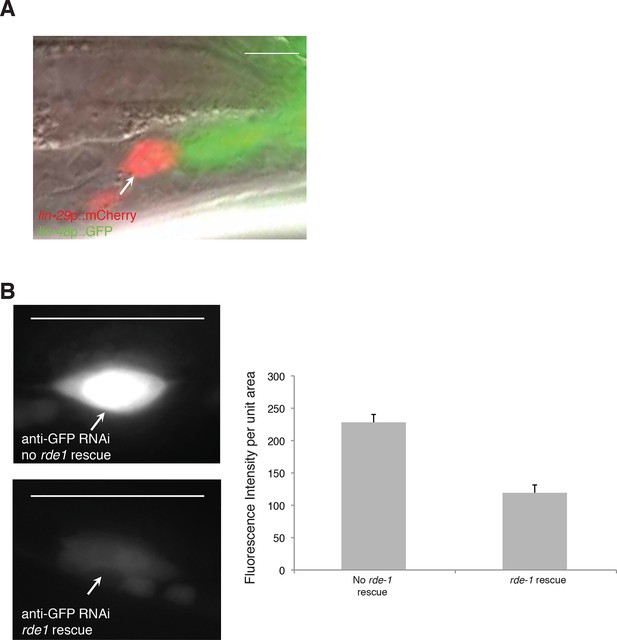
let-70(RNAi) animals have unengulfed linker cells.
(A) Surviving let-70(RNAi) linker cell fail is not engulfed. Scalebar, 5 μm. Arrow/red cell, linker cell. Green cells, engulfing U.l/rp cells. (B) Cell-specific linker cell RNAi by restoring rde-1 expression in rde-1 mutants only to the linker cell using a mig-24 promoter::rde-1 cDNA transgene. lag-2::GFP is used to mark the linker cell. Top left: GFP is expression in animals with RNAi against GFP without rde-1 rescue in the linker cell. Bottom left: GFP expression is reduced in animals with rde-1 rescued in the linker cell subjected to GFP RNAi. Right: Quantification of fluorescence intensity. n=16 for each genotype. Error bars, SD. p<0.0001, Student’s t-test. Scalebar = 10 μm.
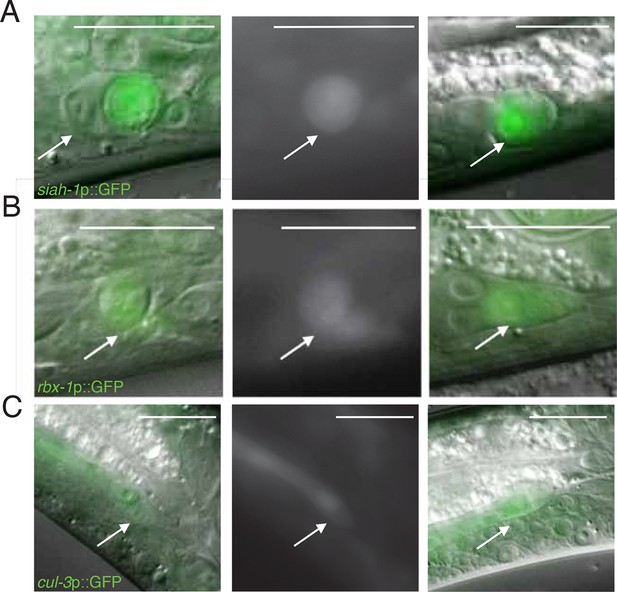
Expression of siah-1, rbx-1, and cul-3 in migrating and dying linker cells.
(A) siah-1p::GFP. Left, merged DIC/fluorescent image of a dying linker cell at the cloaca; middle, fluorescent image of the linker cell at left; right, merged DIC/fluoresent image of a migrating linker cell. Scalebar, 10 μm. Arrow, linker cell. (B) Same as (A) except rbx-1p::GFP. (C) Same as (A) except cul-3p::GFP.
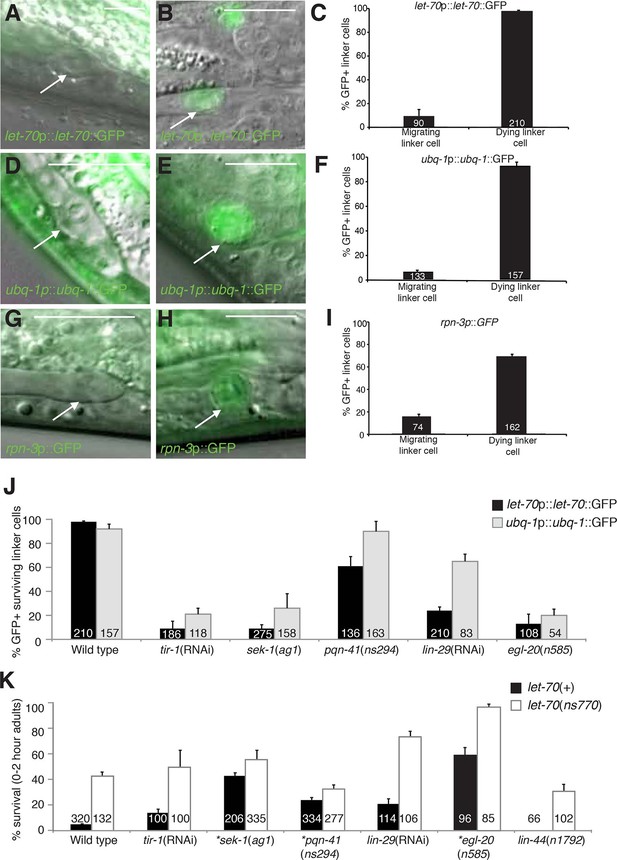
let-70, ubq-1, and rpn-3 expression is induced just before linker cell death onset.
(A-C) let-70p::let-70::GFP expression in migrating (A) or dying (B) linker cell. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Expression quantification in (A,B). Error bars, SEM. Number inside bar, no. animals scored. (D-F) Same as (A-C) for ubq-1p::ubq-1::GFP. (G-I) Same as (A-C) for rpn-3p::GFP. (J) Expression of indicated GFP reporters in surviving linker cells in him-8(e1489) animals of indicated genotype. (K) All animals contained qIs56 and him-5(e1490). *let-70(RNAi) instead of let-70(ns770).
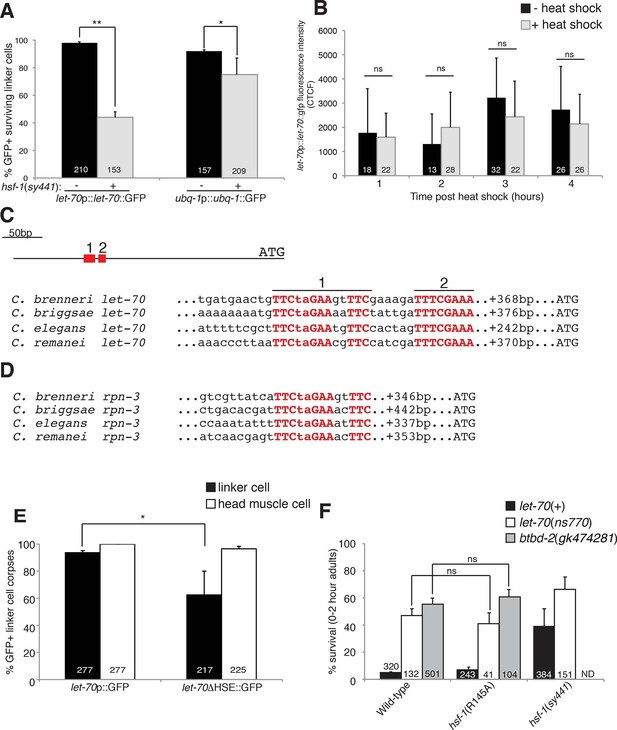
HSF-1 controls LET-70 expression.
(A) Expression of indicated GFP reporter in surviving linker cells in him-8(e1489) animals of indicated genotype. **p<0.0001, *p<0.005, Fisher’s exact test. Error bars, SEM. (B) let-70p::let-70::gfp expression in head region after heat shock. Error bars, SD. ns, not significant, Student’s t-test. (C) let-70 promoter sequence alignment across indicated nematodes. Red, conserved nucleotides. (D) Same as (C) but for rpn-3. (E) let-70p::GFP and let-70∆HSE::GFP expression. Error bar, SEM. *p<0.0001, Fisher’s exact test. (F) let-70 and btbd-2 interactions with hsf-1. Error bars, SEM. Number within bars, no. of animals scored. Animals contained qIs56 and him-5(e1490). ND= not determined.

∆HSE reduces let-70 promoter::let-70::GFP expression in the linker cell.
(A) Male containing an integrated wild-type let-70p::let-70::GFP transgene; inset: higher magnification image of linker cell. Scale bar, 10 μm. Arrow, linker cell. (B) Same as (A) except with ∆HSE.
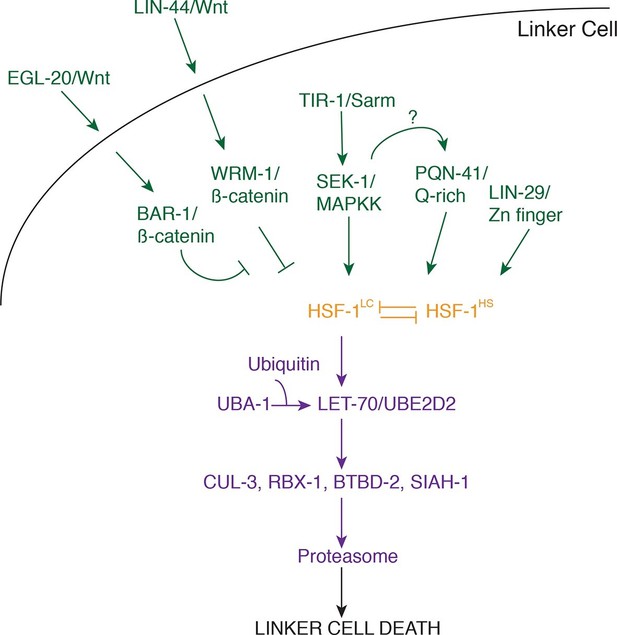
Model for linker cell death.
Green, upstream regulators. Orange, HSF-1. Purple, proteolytic components.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Wnt pathway genes, UPS components, and SCF/BTB genes screened for linker cell death defects.
(A) Wnt pathway genes and their effects on linker cell death. *All strains also contain the qIs56 reporter transgene to visualize the linker cell, except for the mom-2(ne834) and daf-21(p673) strains which contained the nsIs64 transgene. Allele numbers are in parentheses. † ± SEM. ‡Number of animals scored. ¶This strain also contained the unc-13(e1091) allele. §This strain had a severe migration defect which precluded accurate scoring of a survival phenotype. (B) RNAi against UPS components and effects on linker cell survival.*All animals contained rrf-3(pk1426); him-8(e1489) mutations and a qIs56 reporter transgene to visualize the linker cell. †LC, linker cell. ± SEM. ‡Number of animals scored. (C) RNAi against SCF components/BTB domain proteins and linker cell survival. *All animals contained rrf-3(pk1426); him-8(e1489) mutations and a qIs56 reporter transgene to visualize the linker cell. †LC, linker cell. ± SEM. ‡Number of animals scored.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.12821.017
-
Supplementary file 2
Transgenic strains and plasmids used.
(A) Transgenic strain allele number and relevant plasmids. (B) Plasmid names, descriptions, and construction.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.12821.018





