Trisomy 21: Signaling a link between interferon and the traits of Down syndrome
Most people have two copies of every chromosome in their cells. However, Down syndrome, one of the most complex human genetic disorders, is caused by the presence of a third copy of chromosome 21 in some or all of an individual’s cells. Also known as trisomy 21, Down syndrome occurs in approximately 1 in 700 births in the United States. Traits that are commonly seen in individuals with Down syndrome include intellectual disability, heart defects, Alzheimer’s disease, susceptibility to leukemia, and a decreased likelihood of developing other tumors (Alexander et al., 2016; Hasle et al., 2016).
Despite much research, the genetic mechanisms that link trisomy 21 to specific Down syndrome traits are poorly understood, in part due to the large number of genes involved. Additionally, genetic modifiers affect how common and severe the traits that result from trisomy 21 will be in different individuals. This complexity has made it difficult to identify the molecules that could be therapeutically targeted to improve the quality of life for individuals with Down syndrome.
Now, in eLife, Joaquín Espinosa and colleagues at the University of Colorado – including Kelly Sullivan as first author – shed new light on the link between the multiple traits associated with Down syndrome and the extra chromosome 21 genes inside cells affected by trisomy 21 (Sullivan et al., 2016). Their results suggest that interferons – signaling molecules that are normally released by cells in response to nearby pathogens – may underlie many of the features associated with Down syndrome.
By sequencing the RNA of human fibroblast cells taken from age- and gender-matched individuals with and without Down syndrome, Sullivan et al. identified a consistent core pattern of gene expression in cells affected by trisomy 21. As expected, these cells contained approximately 1.5 times as much of the gene products for chromosome 21 genes as normal cells. Unexpectedly though, Sullivan et al. also found that the core gene expression pattern associated with trisomy 21 was associated with an interferon-stimulated transcriptional response. It is worth noting that four of the six interferon receptors are encoded on chromosome 21, which partially explains why the interferon pathway is activated.
Next, Sullivan et al. performed several studies to verify the relevance of the interferon pathway to Down syndrome traits. First, they showed that interferon stimulation produced a stronger response in Down syndrome fibroblasts than in control cells. Second, using an shRNA screen of the protein kinases encoded in the genome of the fibroblasts, they identified two interferon-activated kinases, which strongly reduce the viability of Down syndrome fibroblasts (Figure 1). Treating the trisomy 21 cells with a drug that inhibits the kinases recovered their viability.
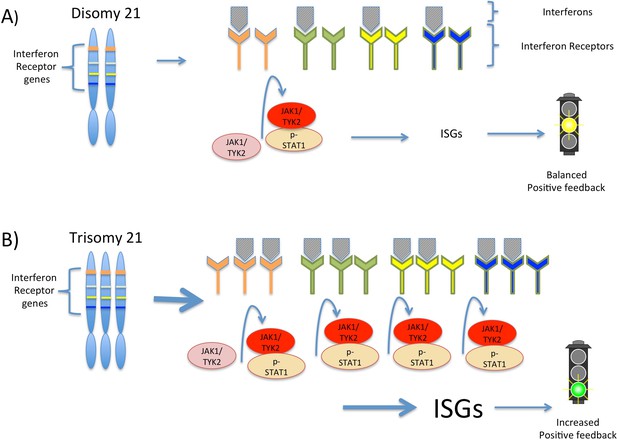
Interferon signaling is amplified by trisomy 21.
(A) Chromosome 21 encodes four types of interferon receptors. In cells with two copies of this chromosome (disomy 21), the binding of interferons to the receptors activates two kinases, JAK1and TYK2. These kinases activate the transcription factor STAT1, which then transcribes a set of genes known as interferon stimulated genes (ISGs). (B) In cells with three copies of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21), as in Down syndrome, the increased abundance of interferon receptors increases the transcription of ISGs, including the genes that encode interferons themselves. This ultimately leads to increased positive feedback and hyperactivated interferon signaling, which can damage the cell.
Sullivan et al. next confirmed their findings in multiple types of blood cells from individuals with and without Down syndrome. While gene expression analysis showed that all cells with trisomy 21 had activated an interferon response, the specific genes stimulated by interferon signaling varied by cell type. Sullivan et al. then examined gene expression in a mouse model of trisomy 21 (Li et al., 2007) and found interferon activation in multiple blood cell types.
By distinguishing between chromosome 21 genes and non-chromosome 21 genes in their data, Sullivan et al. have developed a model that suggests how the extra copy of chromosome 21 produces the traits of Down syndrome. In the model, the increased expression of the four interferon receptors encoded on chromosome 21 increases interferon signaling in Down syndrome cells, leading to positive feedback and greater amplification of interferon signaling than would be expected from the increased number of gene copies alone (Figure 1). This increased signaling, in turn, increases the expression of different interferon response genes in different cell types, which potentially explains the variability observed in the traits associated with trisomy 21.
While interferon sensitivity in Down syndrome has previously been reported (Tan et al., 1974), the study by Sullivan et al. establishes a broad foundation of RNA, protein and functional data that provide insights into how interferon signaling contributes to the distinct characteristics of Down syndrome. Furthermore, the study highlights the potential of targeting interferons as a way of treating these symptoms.
Intriguingly, a number of Down syndrome traits resemble the symptoms of hyperactive interferon signaling disorders, termed “interferonopathies” (Crow and Manel, 2015). In a mouse model of Down syndrome, both anti-interferon therapy and genetic methods that reduce the number of interferon receptors on the surface of cells have been shown to improve growth and brain development (Maroun et al., 2000). Moreover, the drug memantine, which can improve cognition in individuals with Down syndrome (Costa, 2014), works by blocking NMDA receptor signaling. Interferons are known to amplify signaling via NMDA receptors (Sonekatsu et al., 2016), which correlates with amplified interferon signaling in Down syndrome and may suggest a strategy for combined therapy.
The next step will be to determine whether specific targets of interferon signaling can be linked to Down syndrome traits. It also remains to be discovered whether interferon therapy might be useful to individuals with Down syndrome – either alone, or in combination with other treatments – and whether there are developmentally sensitive time-points for potential intervention.
Finally, interferon signaling has well-established functions in regulating tumor development. Individuals with Down syndrome experience a unique cancer risk profile: although they have a dramatically increased risk of developing childhood leukemia, they are far less likely to develop solid tumors than individuals with just two copies of chromosome 21 (Hasle et al., 2016). It remains to be seen whether the cell-type specific effects of interferon signal amplification underlie these differences in tumor susceptibility. In any case, insights into the correlation between hyperactive interferon signaling in Down syndrome and cancer development may provide opportunities for treating both Down syndrome-associated malignancies and cancer in the general population.
References
-
Morbidity and medication in a large population of individuals with Down syndrome compared to the general populationDevelopmental Medicine & Child Neurology 58:246–254.https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.12868
-
The glutamatergic hypothesis for Down syndrome: the potential use of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists to enhance cognition and decelerate neurodegenerationCNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets 13:16–25.https://doi.org/10.2174/18715273113126660183
-
Aicardi-Goutières syndrome and the type I interferonopathiesNature Reviews Immunology 15:429–440.https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3850
-
Partial IFN-alpha/beta and IFN-gamma receptor knockout trisomy 16 mouse fetuses show improved growth and cultured neuron viabilityJournal of Interferon & Cytokine Research 20:197–203.https://doi.org/10.1089/107999000312612
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
Copyright
© 2016, Kirsammer et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 2,295
- views
-
- 330
- downloads
-
- 7
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Chromosomes and Gene Expression
- Developmental Biology
Differentiation of female germline stem cells into a mature oocyte includes the expression of RNAs and proteins that drive early embryonic development in Drosophila. We have little insight into what activates the expression of these maternal factors. One candidate is the zinc-finger protein OVO. OVO is required for female germline viability and has been shown to positively regulate its own expression, as well as a downstream target, ovarian tumor, by binding to the transcriptional start site (TSS). To find additional OVO targets in the female germline and further elucidate OVO’s role in oocyte development, we performed ChIP-seq to determine genome-wide OVO occupancy, as well as RNA-seq comparing hypomorphic and wild type rescue ovo alleles. OVO preferentially binds in close proximity to target TSSs genome-wide, is associated with open chromatin, transcriptionally active histone marks, and OVO-dependent expression. Motif enrichment analysis on OVO ChIP peaks identified a 5’-TAACNGT-3’ OVO DNA binding motif spatially enriched near TSSs. However, the OVO DNA binding motif does not exhibit precise motif spacing relative to the TSS characteristic of RNA polymerase II complex binding core promoter elements. Integrated genomics analysis showed that 525 genes that are bound and increase in expression downstream of OVO are known to be essential maternally expressed genes. These include genes involved in anterior/posterior/germ plasm specification (bcd, exu, swa, osk, nos, aub, pgc, gcl), egg activation (png, plu, gnu, wisp, C(3)g, mtrm), translational regulation (cup, orb, bru1, me31B), and vitelline membrane formation (fs(1)N, fs(1)M3, clos). This suggests that OVO is a master transcriptional regulator of oocyte development and is responsible for the expression of structural components of the egg as well as maternally provided RNAs that are required for early embryonic development.
-
- Chromosomes and Gene Expression
- Genetics and Genomics
The preservation of genome integrity during sperm and egg development is vital for reproductive success. During meiosis, the tumor suppressor BRCA1/BRC-1 and structural maintenance of chromosomes 5/6 (SMC-5/6) complex genetically interact to promote high fidelity DNA double strand break (DSB) repair, but the specific DSB repair outcomes these proteins regulate remain unknown. Using genetic and cytological methods to monitor resolution of DSBs with different repair partners in Caenorhabditis elegans, we demonstrate that both BRC-1 and SMC-5 repress intersister crossover recombination events. Sequencing analysis of conversion tracts from homolog-independent DSB repair events further indicates that BRC-1 regulates intersister/intrachromatid noncrossover conversion tract length. Moreover, we find that BRC-1 specifically inhibits error prone repair of DSBs induced at mid-pachytene. Finally, we reveal functional interactions of BRC-1 and SMC-5/6 in regulating repair pathway engagement: BRC-1 is required for localization of recombinase proteins to DSBs in smc-5 mutants and enhances DSB repair defects in smc-5 mutants by repressing theta-mediated end joining (TMEJ). These results are consistent with a model in which some functions of BRC-1 act upstream of SMC-5/6 to promote recombination and inhibit error-prone DSB repair, while SMC-5/6 acts downstream of BRC-1 to regulate the formation or resolution of recombination intermediates. Taken together, our study illuminates the coordinated interplay of BRC-1 and SMC-5/6 to regulate DSB repair outcomes in the germline.





