A conserved function for pericentromeric satellite DNA
Figures
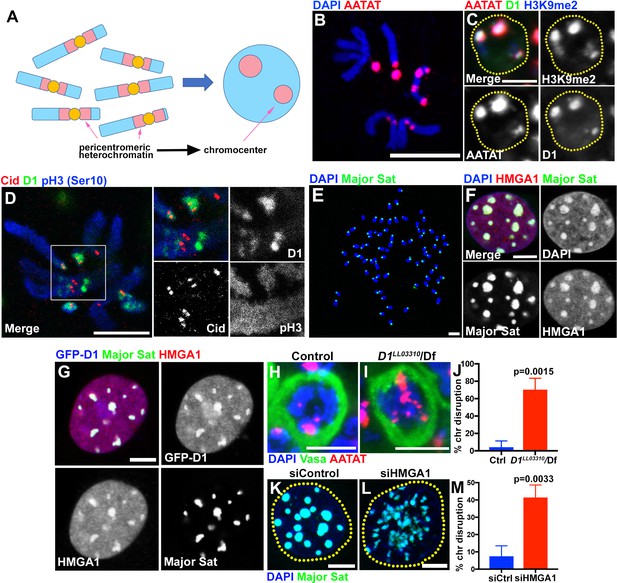
Multi-AT-hook proteins, D1 and HMGA1, are required for chromocenter formation in Drosophila and mouse cells.
(A) Schematic of pericentromeric heterochromatin being organized into the chromocenter. (B) FISH against {AATAT}n satellite (red) on the Drosophila neuroblast mitotic chromosomes co-stained with DAPI (blue) indicating the location of {AATAT}n in the Drosophila genome. (C) FISH against {AATAT}n satellite (red) in spermatogonial cells immunostained for H3K9me2 (blue) and D1 (green). Dotted lines indicate nucleus. Bars: 5 µm. (D) Drosophila neuroblast mitotic chromosomes stained for D1 (green), phospho-histone H3 Serine 10 (pH3-S10) (blue) and Cid/CENP-A (red). (E–G) FISH against the mouse major satellite (green) on C2C12 mitotic chromosomes co-stained with DAPI (blue) (E), in interphase MOVAS cells co-stained for DAPI (blue) and HMGA1 (red) (F) and in MOVAS cells expressing GFP-D1 (blue) stained for HMGA1 (red) (G). (H, I) FISH against {AATAT}n satellite (red) in control (D1LL03310/+) (H) and D1LL03310/Df (I) spermatogonial cells stained for DAPI (blue) and Vasa (green). (J) Quantification of spermatogonial cells with disrupted chromocenters (+/+ control n = 117, D1LL03310/Df n = 89) from three independent experiments. p-Value from student’s t-test is shown. Error bars: SD. (K, L) FISH against the major satellite (green) in siControl (K) and siHMGA1 (L) transfected MOVAS cells co-stained with DAPI (blue). (M) Quantification of cells with disrupted chromocenters from siControl (n = 304) and siHMGA1 (n = 329) from three independent experiments.
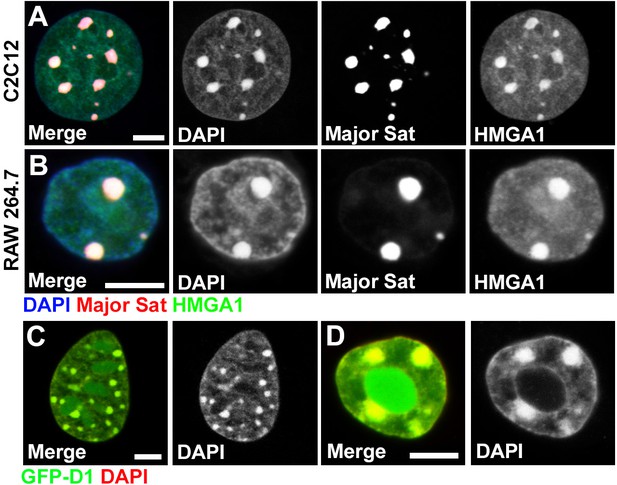
Multi-AT-hook proteins, Drosophila D1 and mouse HMGA1, localize to chromocenters in various mouse cell types.
(A, B) FISH against the mouse major satellite (red) in C2C12 (A) and RAW 264.7 (B) cells stained for HMGA1 (green) and DAPI (blue). (C, D) Colocalization of GFP-D1 (green) with DAPI-dense chromocenters in C2C12 (C) and RAW 264.7(D) cells. DAPI (red). Scale bars: 5 μm.
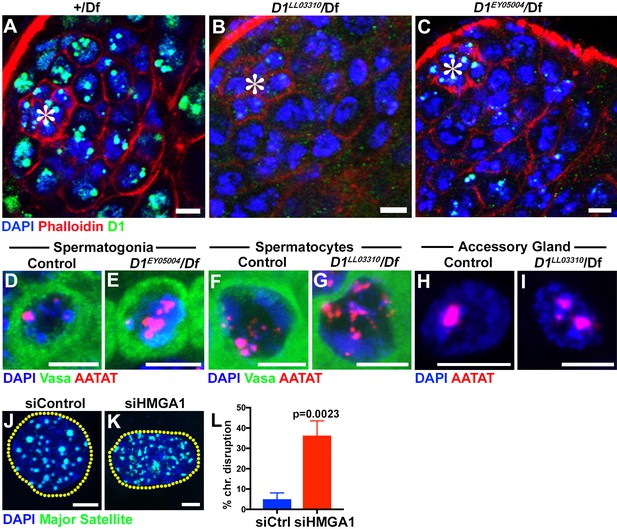
Drosophila D1 and mouse HMGA1 are required for chromocenter formation.
(A–C) Testes from control (+/Df) (A) and two D1 mutant (D1LL03310/Df (B) and D1EY05004/Df (C)) flies were stained for DAPI (blue), Phalloidin (red) and D1 (green). Asterisks indicate the apical tip of the testis. Bars: 5 μm. (D, E) FISH against {AATAT}n (red) in control (D1EY05004/+) (D) and D1EY05004/Df (E) spermatogonial cells stained for DAPI (blue) and Vasa (green). Bars: 2.5 μm. (F, G) FISH against {AATAT}n (red) in control (D1LL03310/+) (F) and D1LL03310/Df (G) spermatocytes stained for DAPI (blue) and Vasa (green). (H, I) FISH against {AATAT}n (red) in control (D1LL03310/+) (H) and D1LL03310/Df (I) accessory gland cells stained for DAPI (blue). Bars: 5 μm. (J, K) FISH against the major satellite (green) in siControl (J) and siHMGA1 transfected (K) C2C12 cells. Dotted lines indicate nucleus. (L) Quantification of cells with disrupted chromocenters in siControl (n = 304) and siHMGA1 (n = 298) transfected C2C12 cells from three independent experiments. p-Value from student’s t-test is shown. Error bars: SD.
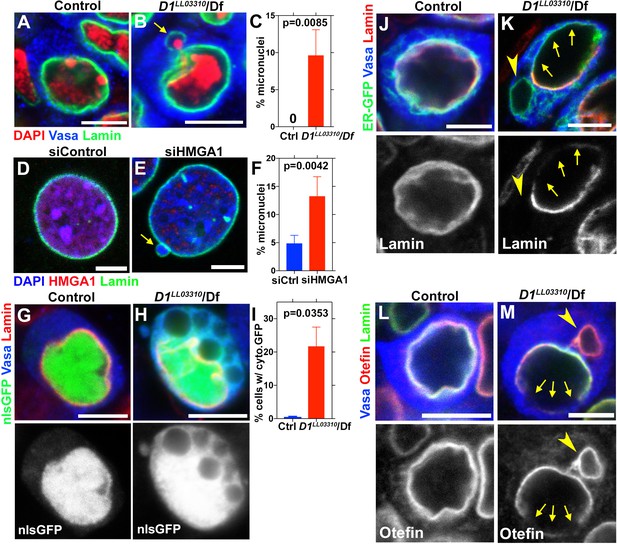
D1/HMGA1 loss-of-function results in micronuclei formation, and defective nuclear envelope integrity.
(A, B) Control (D1LL03310/+) (A) and D1LL03310/Df mutant (B) spermatogonial cells stained for DAPI (red), Vasa (blue) and LaminDm0 (green). Arrow indicates micronucleus. Bars: 5 μm. (C) Quantification of micronuclei-containing cells from +/+ control (n = 269) and D1LL03310/Df (n = 334) from three independent experiments. p-Value from student’s t-test is shown. Error bars: SD. (D, E) siControl (D) and siHMGA1 transfected (E) MOVAS cells stained for DAPI (blue), HMGA1 (red) and Lamin (green). Arrow indicates micronucleus. (F) Quantification of micronuclei-containing cells in siControl (n = 518) and siHMGA1 (n = 588) transfected cells from four independent experiments. (G, H) Control (D1LL03310/+) (G) and D1LL03310/Df (H) spermatogonia expressing nls-GFP (green) stained for Vasa (blue) and LaminDm0 (red). nlsGFP was observed in cytoplasm in D1LL03310/Df spermatogonia. (I) Quantification of spermatogonia with cytoplasmic GFP (>1 μm exclusions or pan-cytoplasmic) in D1LL03310/+ (n = 810) and D1LL03310/Df (n = 780) testes from two independent experiments. (J, K) D1LL03310/+ (J) and D1LL03310/Df (K) spermatogonia expressing ER-GFP marker (green) stained for Vasa (blue) and LaminDm0 (red). Arrowhead points to ER marker-positive micronucleus. Arrows point to site of weak nuclear LaminDm0 staining. (L, M) Control (D1LL03310/+) (L) and D1LL03310/Df (M) spermatogonia stained for Vasa (blue) and LaminDm0 (green) and Otefin (red). Arrowhead points to Otefin-containing micronucleus. Arrows point to site of weak nuclear LaminDm0 staining.
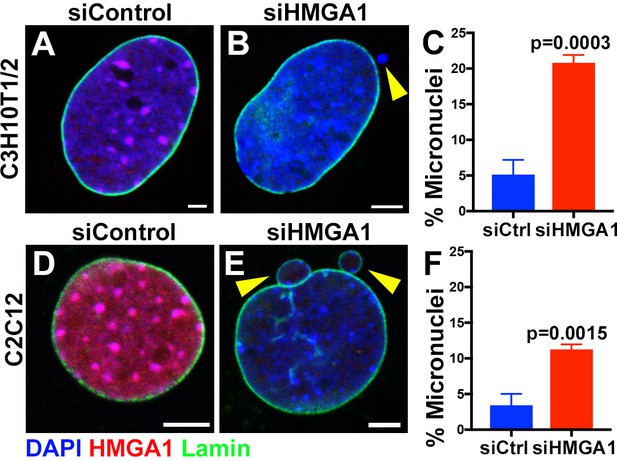
Formation of micronuclei upon chromocenter disruption in C3H10T1/2 and C2C12 mouse cells.
(A, B) siControl (A) and siHMGA1 (B) transfected C3H10T1/2 cells stained for DAPI (blue), HMGA1 (red) and LaminB (green). Arrowhead indicates micronuclei. Bars: 5 μm. (C) Quantification of micronuclei containing cells from siControl (n = 291) and siHMGA1 (n = 303) transfected cells from three independent experiments. p-Value from student’s t-test is shown. Error bars are SD. (D, E) siControl (D) and siHMGA1 (E) transfected C2C12 cells stained for DAPI (blue), HMGA1 (red) and LaminB (green). Arrowhead indicates micronuclei. Bars: 5 μm. (F) Quantification of micronuclei containing cells from siControl (n = 953) and siHMGA1 (n = 699) transfected cells from three independent experiments. p-Value from student’s t-test is shown. Error bars are SD.
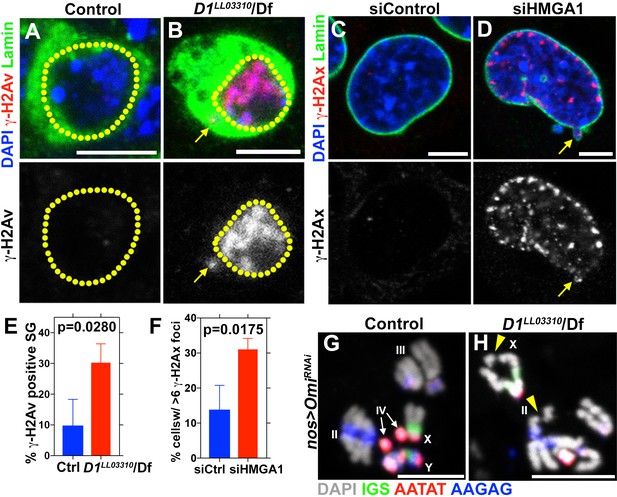
D1 mutation/HMGA1 depletion leads to an increase in DNA damage.
(A, B) Control (D1LL03310/+) (A) and D1LL03310/Df (B) spermatogonia stained for DAPI (blue), Vasa (green) and γ-H2Av (red). Dotted lines indicate nucleus and arrow points to DNA damage in micronuclei. (C, D) siControl (C) and siHMGA1 (D) transfected MOVAS cells stained for DAPI (blue), γ-H2Av (red) and LaminDm0 (green). Arrow points to DNA damage in micronuclei. (E) Quantification of γ-H2Av positive cells in D1LL03310/+ (n = 317) and D1LL03310/Df (n = 242) spermatogonia from three independent experiments. (F) Quantification of cells containing >6 γ-H2Ax foci in siControl (n = 304) and siHMGA1 (n = 309) transfected cells from three independent experiments. (G, H) FISH against the rDNA intergenic spacer (IGS) (green), {AATAT}n (red) and {AAGAG}n (blue) on chromosome spreads from meiotic spermatocytes from control (nos > OmiRNAi, n = 27) and D1 mutant (nos >Omi RNAi; D1LL03310/Df, n = 57) testes co-stained for DAPI (grey). OmiRNAi was used to block DNA damage-induced cell death. Arrowheads point to chromosome breaks.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Quantification of g-H2Ax foci in mouse cells.
g-H2Ax foci were scored in siControl and siHMGA1 transfected MOVAs cells. At least 100 cells were scored from three biological replicates. Percentage of cells containing the indicated number of g-H2Ax foci is listed in the table.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34122.010
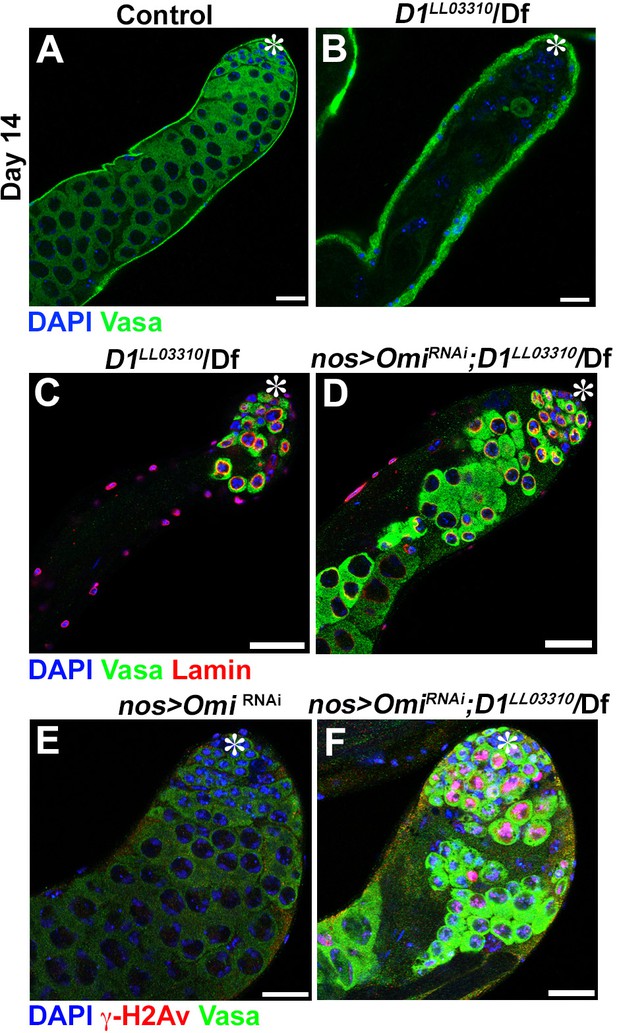
Chromocenter disruption results in germ cell death in Drosophila in an Omi-dependent manner.
(A, B) Representative images of 14-day-old control (D1LL03310/+, n = 18) and D1LL03310/Df (n = 12) testes stained for DAPI (blue) and the germ cell marker, Vasa (green). Asterisk indicates apical tip. Bars: 25 μm (C, D) Representative images of D1 mutant testes (D1LL03310/Df) without (C) and with (D) germ cell death suppression by Omi knockdown (nos > OmiRNAi), stained for DAPI (blue), Vasa (green) and LaminDm0 (red) at 7 days post eclosion. (E, F) Representative images of control (nos > OmiRNAi, D1LL033010/+, n = 10) and D1 mutant (nos > OmiRNAi; D1LL03310/Df, n = 13) testes stained for DAPI (blue), Vasa (green) and γ-H2Av (red).
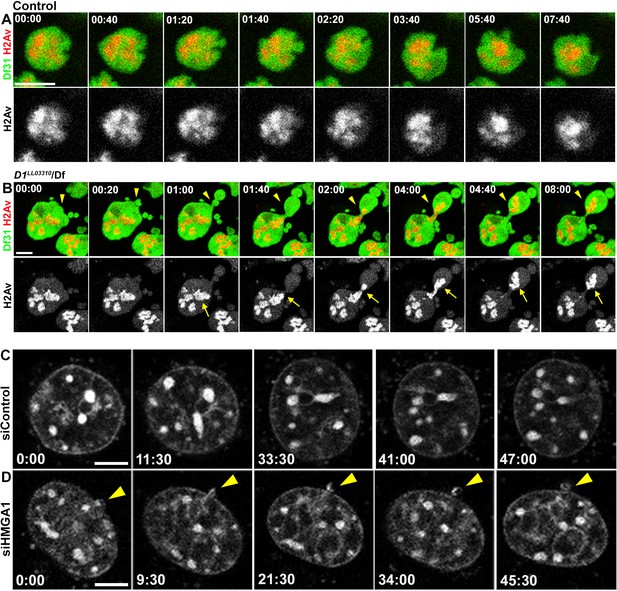
D1/HMGA1 loss of function results in micronuclei formation due to nuclear budding during interphase.
(A, B) Time-lapse live imaging of control (+/+) (A) and D1LL03310/Df (B) spermatogonial cells expressing Df31-GFP as a nuclear marker and H2Av-RFP as a DNA marker. (C, D) Time-lapse live imaging of siControl (C) and siHMGA1 (D) MOVAS cells stained with Hoechst 33342. Arrowheads indicate site of micronucleus budding. Time is indicated in mm:ss. Scale bars: 5 μm.
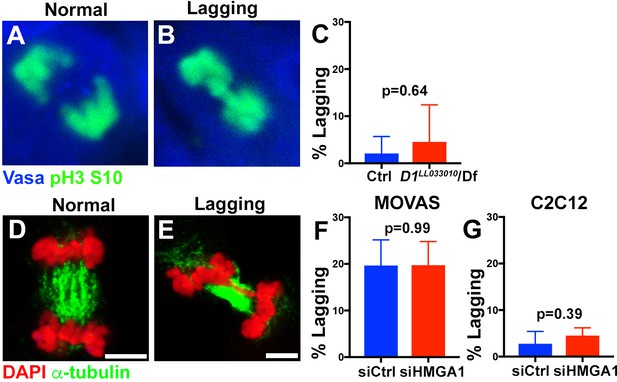
Micronuclei formation upon chromocenter disruption is not a result of mitotic lagging chromosomes.
(A, B) Examples of normal and lagging mitotic chromosomes in Drosophila spermatogonia stained for Vasa (blue) and pH3-S10 (green). (C) Quantification of spermatogonia with lagging chromosomes from control (D1LL033010/+, n = 43) and D1LL03310/Df (n = 47) from three independent experiments. P value from student’s t test is shown. Error bars are SD. (D, E) Examples of normal and lagging mitotic chromosomes in mouse cells stained for DAPI (red) and α-tubulin (green). Bars: 5 μm. (F) Quantification of mitotic cells with lagging chromosomes from siControl (n = 149) and siHMGA1 (n = 174) transfected MOVAS cells from three independent experiments. (G) Quantification of mitotic cells with lagging chromosomes from siControl (n = 110) and siHMGA1 (n = 129) transfected C2C12 cells from three independent experiments.
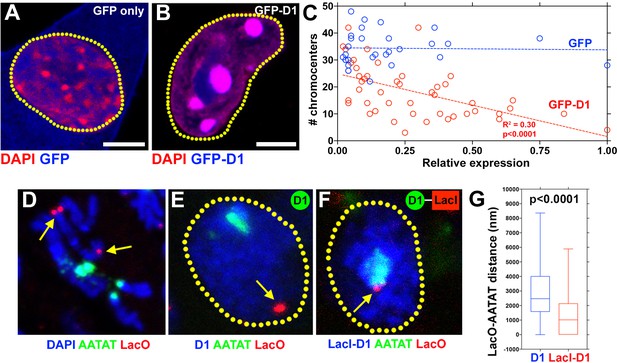
D1 bundles satellite DNA from heterologous chromosomes to form chromocenter.
(A, B) C2C12 cells expressing GFP only (blue) (A) or GFP-D1 (blue) (B) stained for DAPI (red). Dotted lines indicate nucleus. (C) Quantification of chromocenter number relative to expression level of GFP (n = 29) or GFP-D1 (n = 47). P value and R2 value are indicated from linear regression analysis. (D) FISH against LacO (red) and {AATAT}n (green) on mitotic neuroblast chromosomes from the LacO strain stained for DAPI (blue), indicating the sites of LacO insertion (arrows). (E, F) FISH against LacO (red) and {AATAT}n (green) in spermatogonia expressing GFP-D1 (blue) (E) or GFP-LacI-D1 (blue) (F). Arrows indicate location of LacO sequence. (G) AATAT-LacO distance (nm) in GFP-D1 (n = 97) and GFP-LacI-D1 (n = 69) expressing spermatogonia. P value from student’s t-test is shown. Error bars: SD. All scale bars: 5 μm.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Quantification of the relative expression of GFP/GFP-D1 and number of chromocenters in mouse cells.
Images of cells expressing GFP (n=27) or GFP-D1 (n=47) were acquired from a single slide/transfection with all image acquisition parameters held constant and care taken to avoid pixel oversaturation. Total GFP fluorescence per cell was quantified using ImageJ software. Relative expression was calculated by dividing each individual fluorescence value over the maximum fluorescence value obtained over the course of the experiment. DAPI staining was used to calculate number of chromocenters per cell.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34122.014
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Quantification of LacO-AATAT distance (nm) in cells expressing GFP-D1 and GFP-LacI-D1.
LacO-AATAT distance (nm) was measured in spermatogonial cells expressing GFP-D1 (n=97) and GFP-LacI-D1 (n=69) using Leica LAS X software.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34122.015
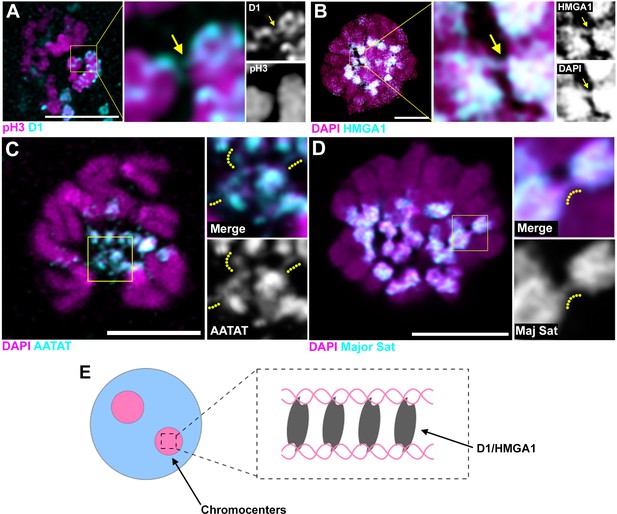
D1/HMGA1 and satellite DNA form chromatin threads that link chromosomes.
(A) Deconvolution microscopy performed on Drosophila mitotic neuroblasts stained for D1 (cyan) and pH3-S10 (magenta). Arrows in magnified images indicate D1-positive thread connecting two chromosomes. (B) Deconvolution microscopy performed on CSK-extracted RAW 264.7 macrophages stained for HMGA1 (cyan) and DAPI (magenta). Arrows in magnified images indicate HMGA1-positive thread connecting two chromosomes. (C) Deconvolution microscopy performed on neuroblast mitotic chromosomes stained for DAPI (magenta) and FISH against {AATAT}n (cyan) from a Drosophila strain containing AATAT-rich B chromosomes (Bauerly et al., 2014). Dotted lines in magnified images indicate AATAT-positive threads connecting heterologous chromosomes. (D) Deconvolution microscopy performed on RAW 264.7 macrophages stained for DAPI (magenta) and FISH against major satellite (cyan). Dotted lines in magnified images indicate major satellite-positive threads connecting two chromosomes. (E) The model of chromosome bundling by D1/HMGA1 and satellite DNA.
Tables
| Reagent type (species ) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | D1EY05004 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | ID_BDSC:17340 | |
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | Df(3R)BSC666 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | ID_BDSC:26518 | |
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-OmiRNAi | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | ID_BDSC:55165 | |
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-GFP-nls | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | ID_BDSC:4776 | |
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-GFP-ER-SR | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | ID_BDSC:59042 | |
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | D1LL03310 | Kyoto Stock Center | ID_DGRC:140754 | |
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | Df31-GFP | Kyoto Stock Center | ID_DGRC:110806 | |
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | nos-gal4 | PMID: 9501989 | ||
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | hs-flp;nos-FRT-stop-FRT-gal4,UAS-GFP | PMID: 24465278 | ||
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-H2A-YFP | PMID: 11146626 | ||
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | B1 LacO | PMID: 12225662 | ||
| Genetic Reagent (D. melanogaster) | mtrm126 + B | PMID: 24478336 | Gift of Dr. Scott Hawley | |
| Recombinant DNA Reagent | pUASt-GFP-attB | PMID: 24465278 | ||
| Recombinant DNA Reagent | pUASt-GFP-D1-attB | This Paper | ||
| RecombinantDNA Reagent | pUASt-GFP-LacI-D1-attB | This Paper | ||
| Recombinant DNA Reagent | pCDNA3 | Gift of Dr. Cheng-Yu Lee | ||
| Cell Line | MOVAS | Gift of Dr. Daniel Eitzman | ||
| Cell Line | C2C12 | Gift of Dr. David Bridges | ||
| Cell Line | RAW264.7 | Gift of Dr. Harry Mobley | ||
| Cell Line | C3H10T1/2 | Gift of Dr. Stephen Weiss | ||
| siRNA | ON-TARGET plus Mouse HMGA1 siRNA SMARTpool | Dharmacon/GE Healthcare | ID_Dharmacon: L-049293–01 | |
| siRNA | ON-TARGET plus Non-targeting pool | Dharmacon/GE Healthcare | ID_Dharmacon: L-001810–10 | |
| Antibody | anti-Vasa | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | ID_SCB: d-26 | |
| Antibody | anti-H3K9 dimethyl | Abcam | ID_abcam: ab32521 | |
| Antibody | anti-Otefin | Gift of Dr. Georg Krohne | ||
| Antibody | anti-D1 | This Paper | Peptide - CDGENDANDGYVSDNYNDSESVAA | |
| Antibody | anti-LaminDm0 | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | ID_DSHB: ADL84.12 | |
| Antibody | anti-γ-H2Av | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | ID_DSHB: UNC93-5.2.1 | |
| Antibody | Phalloidin-Alexa546 | ThermoFisher | ID_ThermoFisher: a22283 | |
| Antibody | anti-HMGA1 | Abcam | ID_abcam: ab129153 | |
| Antibody | anti-LaminB (C20) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | ID_SCB: 2616 | |
| Antibody | anti-α-tubulin | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | ID_DSHB: 4.3 | |
| Antibody | anti-γ-H2Ax S139 | Cell Signaling Technologies | ID_CST: 2577 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34122.017





