The presence and absence of periplasmic rings in bacterial flagellar motors correlates with stator type
Figures
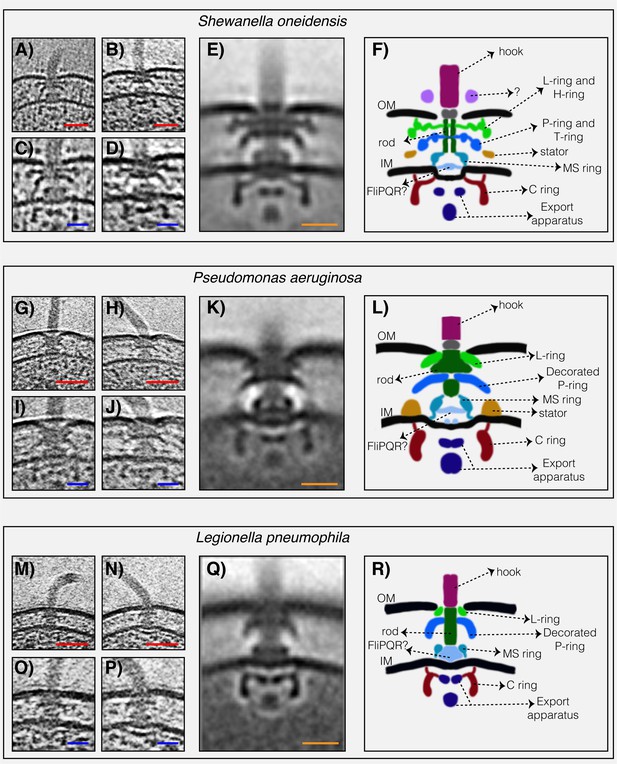
The structures of three dual-stator Gammaproteobacteria flagellar motors revealed by ECT.
(A and B) slices through Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 electron cryo-tomograms showing single polar flagella. (C and D) zoomed-in views of the slices shown in (A) and (B) highlighting the flagellar motors. (E) central slice through a sub-tomogram average of the S. oneidensis MR-1 flagellar motor. (F) schematic representation of the sub-tomogram average shown in (E) with the major parts of the motor labeled. (G–L) flagellar motor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Panels follow the same scheme as in (A–F) above. (M–R) flagellar motor of Legionella pneumophila. Panels follow the same scheme as above. Scale bars 50 nm (red) and 20 nm (blue and orange).
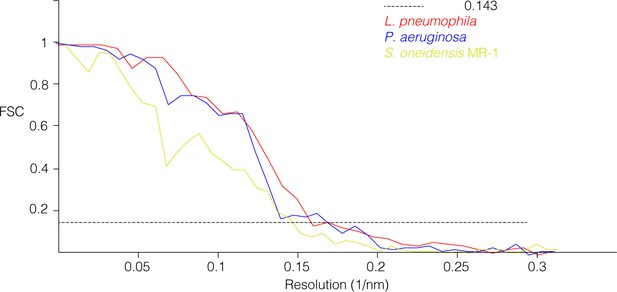
Gold-standard FSC curves of sub-tomogram averages.
Resolutions at a 0.143 cutoff (dashed line) are: L. pneumophila, 6.4 nm; P. aeruginosa, 5.9 nm; S. oneidensis MR-1, 6.9 nm.
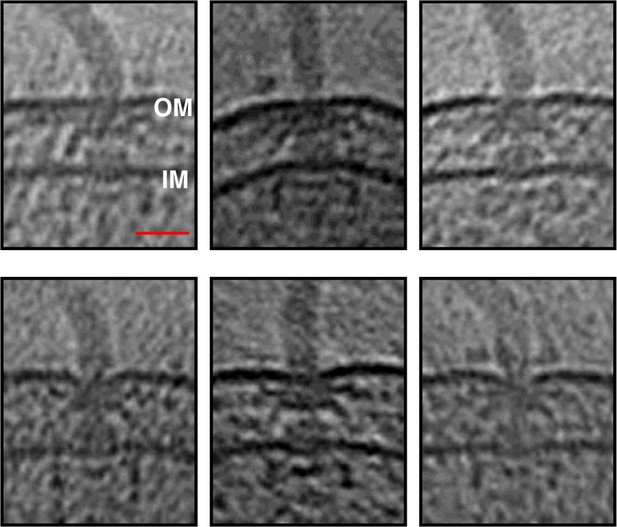
Slices through electron cryo-tomograms of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 cells illustrating the presence of flagellar motors.
OM = outer membrane, IM = inner membrane. Scale bar = 25 nm.
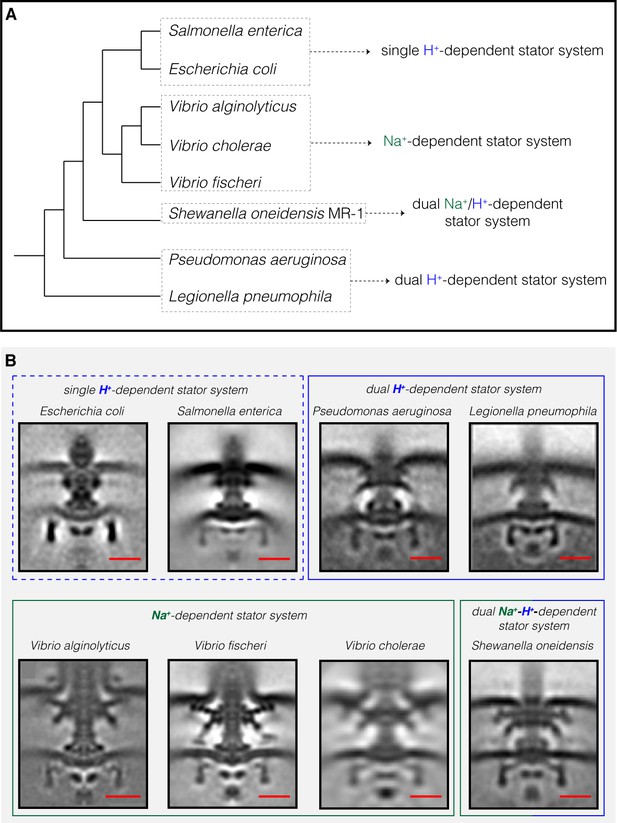
Compilation of all Gammaproteobacteria flagellar motors imaged to date by ECT.
(A) A phylogenetic tree of the eight Gammaproteobacteria species with available ECT structures of their flagellar motors. This tree was made based on (Williams et al., 2010). (B) Central slices of sub-tomogram averages are shown for the eight Gammaproteobacteria flagellar motors revealed by ECT, including the three structures solved in this study (P. aeruginosa, L. pneumophila and S. oneidensis). The motors are classified based on their stator system: single H+-driven (dashed blue box), dual H+-driven (blue box), Na+-driven (green box) or dual Na+-H+-driven (green-blue box). E. coli EMDB 5311, S. enterica EMDB 3154, V. fischeri EMDB 3155, V. cholerae EMDB 5308, V. alginolyticus is adapted from Zhu et al., 2017. Scale bars are 20 nm.
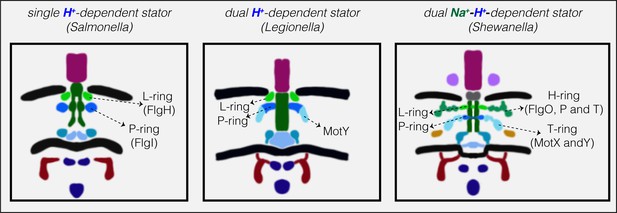
Models showing correlation between structural elaboration of the flagellar motor and its stator type.
Flagellar motors with single H+-driven stator systems (e.g. Salmonella) have P- and L-rings alone. Motors with dual H+-driven stator systems have an extra ring surrounding the P-ring formed by the MotY protein alone. Motors with Na+-driven motors have two periplasmic rings, the T-ring (MotX and MotY) and H-ring (FlgO, FlgP and FlgT), decorating the P- and L-rings, respectively. Note that the boundaries between the P- and L-rings and their decorations are tentative in these schematics.
Tables
Candidate homologs of H- and T-ring components in species imaged in this study.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43487.007| Species | MotX candidate | MotY candidate | FlgO candidate | FlgP candidate | FlgT candidate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (dual H+-driven stator) | - | + 2e-37 (PA3526) | - | - | - |
| Legionella pneumophila (dual H+-driven stator) | - | + 3e-35 (lpg2962) | - | - | - |
| Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 (dual Na+-H+-driven stator) | + 2e-46 (SO_3936) | + 2e-80 (SO_2754) | + 2e-19 (SO_3257) | + 6e-31 (SO_3256) | + 3e-36 (SO_3258) |
Candidate homologs of H- and T-ring components in single H+-dependent stator systems of Gammaproteobacteria.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43487.008| Species | MotX candidate | MotY candidate | FlgO candidate | FlgP candidate | FlgT candidate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | - | - | - | - | - |
| Salmonella enterica | - | - | - | - | - |
| Sodalis glossinidius | - | - | - | - | - |
| Photorhabdus laumondii subsp. laumondii TTO1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Serratia proteomaculans | - | + 7e-13 (Spro_1787) | - | - | - |
| Psychromonas ingrahamii | - | + 3e-14 (Ping_3567) | - | - | - |
Candidate homologs of H- and T-ring components in dual H+-dependent stator systems of Gammaproteobacteria.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43487.009| Species | MotX candidate | MotY candidate | FlgO candidate | FlgP candidate | FlgT candidate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azotobacter vinelandii DJ | - | + 8e-14 (Avin_48650) | - | - | - |
| Cellvibrio japonicas Ueda107 | - | + 9e-28 (CJA_2588) | - | - | - |
| Chromohalobacter salexigens DSM 3043 | - | + 6e-13 (Csal_3309) | + 9e-16 (Csal_2511) | - | - |
| Pseudomonas entomophila | - | + 2e-31 (PSEEN1209) | - | - | - |
| Saccharophagus degradans 2–40 | - | + 1e-37 (Sde_2427) | - | - | - |
| Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris | - | + 1e-13 (XCC1436) | - | - | - |
| Pseudomonas putida | - | + 7e-31 (PP_1087) | - | - | - |
| Yersinia pestis CO92 | - | + 6e-11 (YPO0448) | - | - | - |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf0-1 | - | + 2e-30 (Pfl01_4518) | - | - | - |
| Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citrumelo F1 | - | + 1e-14 (XACM_1468) | - | - | - |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia R551-3 | - | + 4e-10 (Smal_1563) | - | - | - |
Candidate homologs of H- and T-ring components in Na+-dependent stator systems of Gammaproteobacteria.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43487.010| Species | MotX candidate | MotY candidate | FlgO candidate | FlgP candidate | FlgT candidate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colwellia psychrerythraea 34H | + 2e-63 (CPS_4618) | + 1e-73 (CPS_3471) | + 2e-59 (CPS_1469) | + 6e-28 (CPS_1470) | + 5e-38 (CPS_1468) |
| Vibrio fischeri | + 1e-113 (VF_2317) | + 3e-141 (VF_0926) | + 3e-113 (VF_1884) | + 1e-60 (VF_1883) | + 2e-166 (VF_1885) |
| Vibrio vulnificus YJ016 | + 4e-136 (VV3065) | + 9e-177 (VV1183) | + 8e-140 (VV0953) | + 1e-77 (VV0954) | + 0.0 (VV0952) |
| Photobacterium profundum | + 1e-110 (PBPRA3344) | + 3e-146 (PBPRA2571) | + 5e-101 (PBPRA0894) | + 5e-60 (PBPRA0895) | + 6e-145 (PBPRA0893) |
| Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis | + 3e-76 (PSHAa0276) | + 6e-73 (PSHAa2115) | + 3e-37 (PSHAa0755) | + 2e-26 (PSHAa0762) | + 5e-40 (PSHAa0761) |
| Pseudoalteromonas tunicata | + 4e-71 (PTUN_a0699) | + 1e-68 (PTUN_a1296) | + 2e-32 (PTUN_a3193) | + 2e-28 (PTUN_a3178) | + 4e-34 (PTUN_a3179) |
| Idiomarina loihiensis L2TR | + 5e-67 (IL2001) | + 4e-78 (IL1801) | + 4e-18 (IL1169) | + 9e-32 (IL1153) | + 1e-30 (IL1154) |
| Alteromonas macleodii ATCC 27126 | + 8e-73 (MASE_16945) | + 3e-74 (MASE_05600) | + 2e-34 (MASE_11745) | + 7e-29 (MASE_04615) | + 3e-35 (MASE_04610) |
| Pseudoalteromonas atlantica | + 2e-71 (Patl_0993) | + 1e-79 (Patl_1400) | + 1e-30 (Patl_1308) | + 1e-26 (Patl_3106) | + 1e-31 (Patl_3107) |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Raw T- and H-rings proteins Blast results for all species in Tables 1–4.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43487.012
-
Supplementary file 2
Raw stator proteins Blast results for all species in Tables 1–4.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43487.013
-
Supplementary file 3
S. oneidensis strains used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43487.014
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43487.015





