Taar1 gene variants have a causal role in methamphetamine intake and response and interact with Oprm1
Figures
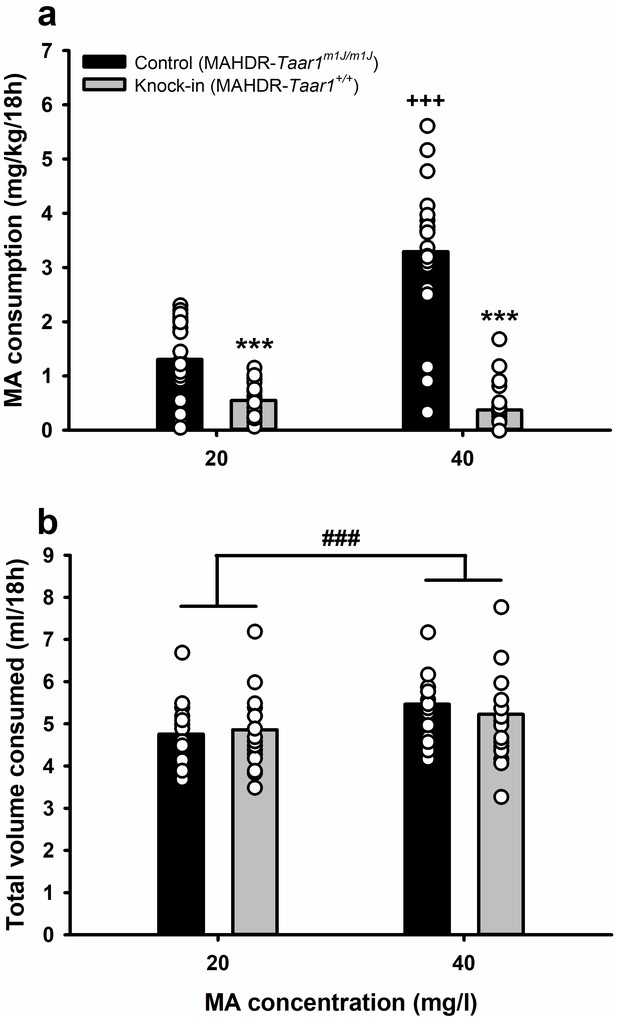
Knock-in of Taar1+ converts high MA intake to low MA intake, but does not impact total volume of fluid consumed.
(a) MA consumption and (b) total volume consumed, when MA was offered vs. water for 18h/day at a concentration of 20 or 40 mg/l for control and knock-in mice. Presented are means (represented by bars) and individual data points (represented by circles) for data collapsed on sex. n = 20/genotype tested in a single cohort. Repeated measures ANOVA followed by simple main effects analysis, ***p<0.001 vs. control (MAHDR-Taar1m1J/m1J) at the same MA concentration; +++p < 0.001 vs. control (MAHDR-Taar1m1J/m1J) at 20 mg/l MA. Repeated measures ANOVA, ###p<0.001 for the main effect of 20 mg/l vs. 40 mg/l MA. MA, methamphetamine; MAHDR, MA high drinking mice; Taar1, trace amine-associated receptor 1 gene; Taar1+/+, homozygous for reference Taar1+ allele; Taar1m1J/m1J, homozygous for mutant Taar1m1J allele. The raw data represented in the graphs are available in Figure 1—source data 1.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
MA consumption (mg/kg/18h) and total volume consumed (ml/18h) data for male and female, control MAHDR-Taar1m1J/m1J and knock-in MAHDR-Taar1+/+ mice.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46472.004
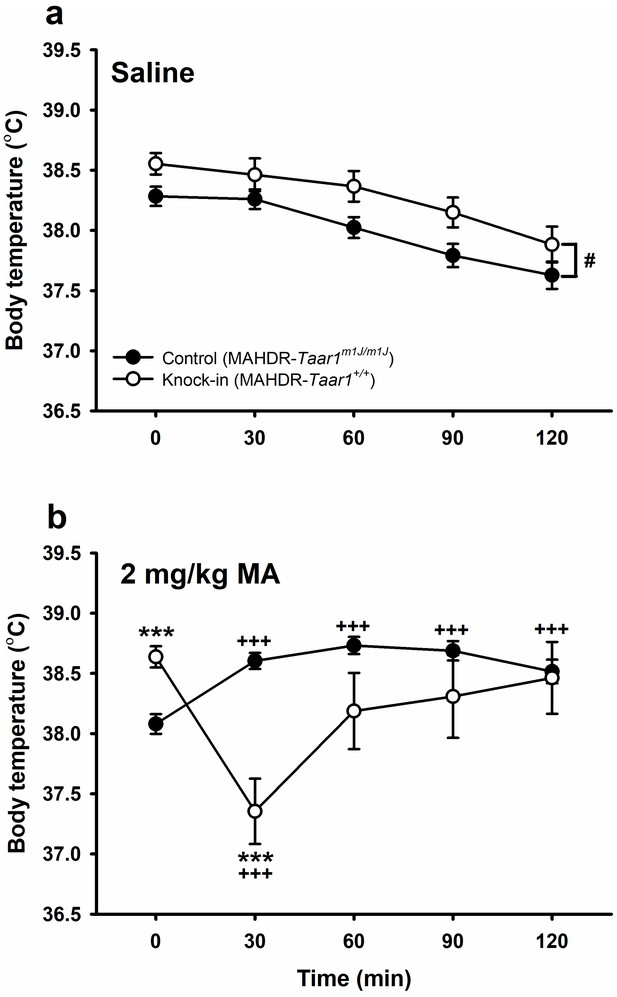
Knock-in of Taar1+ restores a hypothermic response to MA.
Body temperatures obtained immediately before (T0) or 30–120 min (T30-120) after (a) saline or (b) 2 mg/kg MA treatment for control and knock-in mice. Presented are means ± SEM for data collapsed on sex. n = 24–25/genotype/MA dose tested in 3 cohorts of 25–46 mice. Repeated measures ANOVA, #p<0.05 for the main effect of genotype. Repeated measures ANOVA followed by simple main effects analysis, ***p<0.001 for the effect of genotype at the indicated time point; Dunnett’s post hoc test,+++p < 0.001 compared to T0. MA, methamphetamine; MAHDR, MA high drinking mice; Taar1, trace amine-associated receptor 1 gene; Taar1+/+, homozygous for reference Taar1+ allele; Taar1m1J/m1J, homozygous for mutant Taar1m1J allele. The raw data represented in the graphs are available in Figure 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Core body temperature (°C) data across time for saline and 2 mg/kg MA-treated male and female, control MAHDR-Taar1m1J/m1J and knock-in MAHDR-Taar1+/+ mice.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46472.006
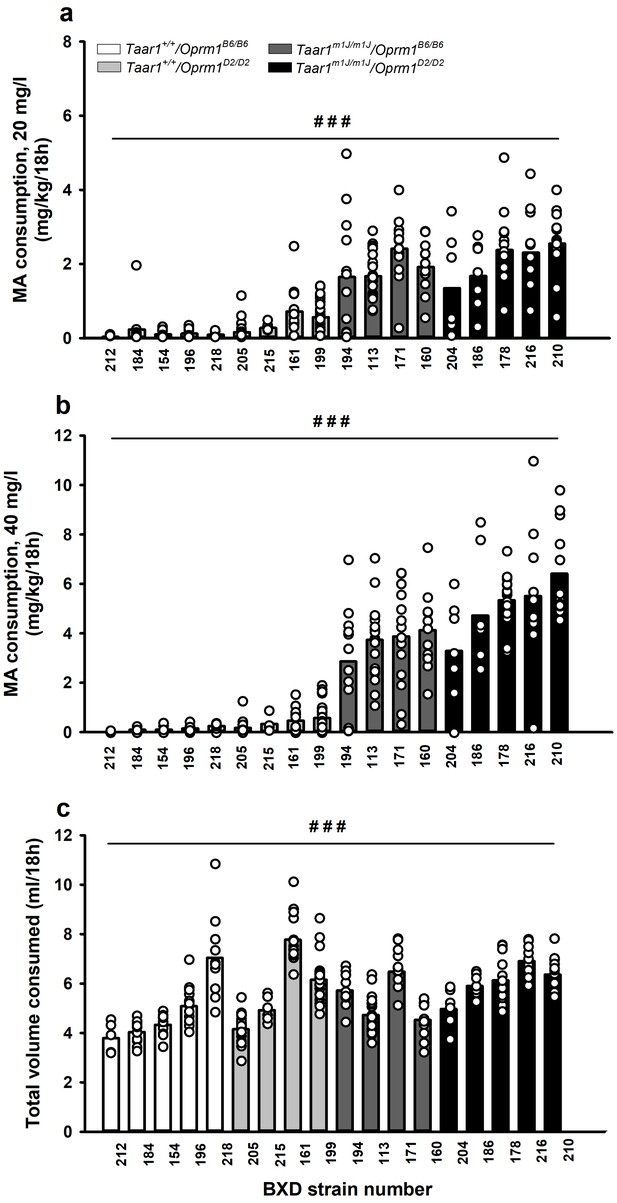
MA consumption and total volume consumed among BXD strains are strain-dependent.
MA consumption when MA was offered vs. water for 18h/day at a concentration of (a) 20 mg/l or (b) 40 mg/l. (c) Total volume consumed from the water and MA tubes during the 18h period when MA was offered vs. water, collapsed on MA concentration, because there was no concentration-dependent effect. Presented are means (represented by bars) and individual data points (represented by circles) for data collapsed on sex. n = 5–28/strain tested in 4 cohorts of 27–97 mice. Repeated measures ANOVA, ###p<0.001 for the main effect of strain. BXD, C57BL/6J (B6) x DBA2/J (D2); MA, methamphetamine; Oprm1, mu opioid receptor gene; Oprm1B6/B6, homozygous for B6 Oprm1 allele; Oprm1D2/D2, homozygous for D2 Oprm1 allele; Taar1, trace amine-associated receptor 1 gene; Taar1+/+, homozygous for reference Taar1+ allele; Taar1m1J/m1J, homozygous for mutant Taar1m1J allele. The raw data represented in the graphs are available in Figure 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
MA consumption (mg/kg/18h) and total volume consumed (ml/18h) data for male and female, BXD mice, according to Taar1 and Oprm1 genotype.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46472.008
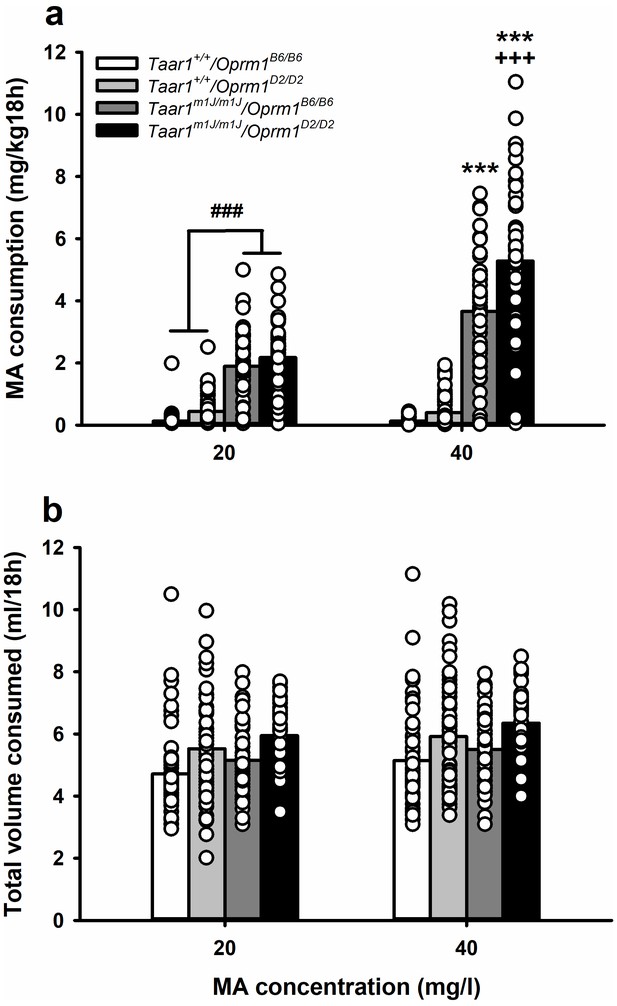
MA consumption is impacted in BXD mice by a Taar1 x Oprm1 interaction.
(a) MA consumption and (b) total volume consumed, when MA was offered vs. water for 18h/day at a concentration of 20 or 40 mg/l for BXD strain mice with different combined Taar1/Oprm1 genotypes. Presented are means (represented by bars) and individual data points (represented by circles) for data collapsed on sex. n = 52–71/ genotype tested in 4 cohorts of 27–97 mice. Repeated measures ANOVA, ###p<0.001 for the main effect of Taar1+/+ vs. Taar1m1J/m1J. Repeated measures ANOVA followed by simple main effects analysis, ***p<0.001 compared to Taar1+/+ with the same Oprm1 genotype; +++p < 0.001 compared to Taar1m1J/m1J/Oprm1B6/B6 at 40 mg/l MA. BXD, C57BL/6J (B6) x DBA2/J (D2); MA, methamphetamine; Oprm1, mu-opioid receptor gene; Oprm1B6/B6, homozygous for B6 Oprm1 allele; Oprm1D2/D2, homozygous for D2 Oprm1 allele; Taar1, trace amine-associated receptor 1 gene; Taar1+/+, homozygous for reference Taar1+ allele; Taar1m1J/m1J, homozygous for mutant Taar1m1J allele. The raw data represented in the graphs are available in Figure 4—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
MA consumption (mg/kg/18h) and total volume consumed (ml/18h) data for male and female BXD mice, according to Taar1 and Oprm1 genotype.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46472.010
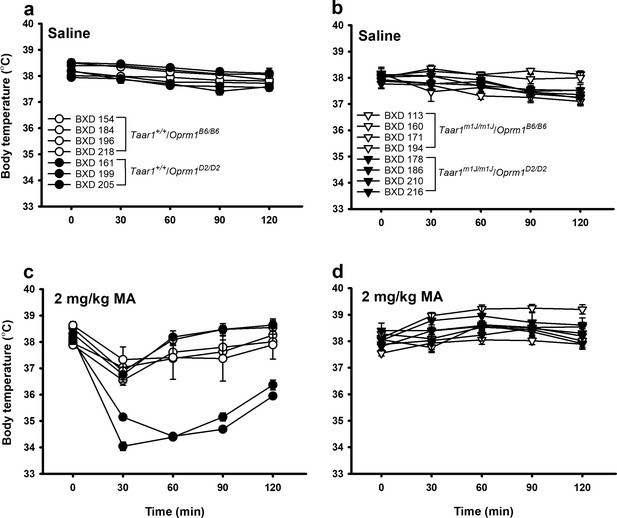
Body temperature among BXD strains treated with saline or MA is strain-dependent.
Body temperatures obtained just before (T0) or 30–120 min (T30-120) after injection for (a) saline-treated Taar1+/+ mice of either Oprm1 genotype, (b) saline-treated Taar1m1J/m1J mice of either Oprm1 genotype, (c) 2 mg/kg MA-treated Taar1+/+ mice of either Oprm1 genotype, and (d) 2 mg/kg MA-treated Taar1m1J/m1J mice of either Oprm1 genotype. Presented are means ± SEM for data collapsed on sex. n = 4–15/strain/dose tested in 16 cohorts of 8–36 mice. For clarity, significant findings are discussed in the text. BXD, C57BL/6J (B6) x DBA2/J (D2); MA, methamphetamine; Oprm1, mu-opioid receptor gene; Oprm1B6/B6, homozygous for B6 Oprm1 allele; Oprm1D2/D2, homozygous for D2 Oprm1 allele; Taar1, trace amine-associated receptor 1 gene; Taar1+/+, homozygous for reference Taar1+ allele; Taar1m1J/m1J, homozygous for mutant Taar1m1J allele. The raw data represented in the graphs are available in Figure 5—source data 1.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Core body temperature (°C) data across time for saline and 2 mg/kg MA-treated male and female, BXD mice, according to Taar1 and Oprm1 genotype.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46472.013
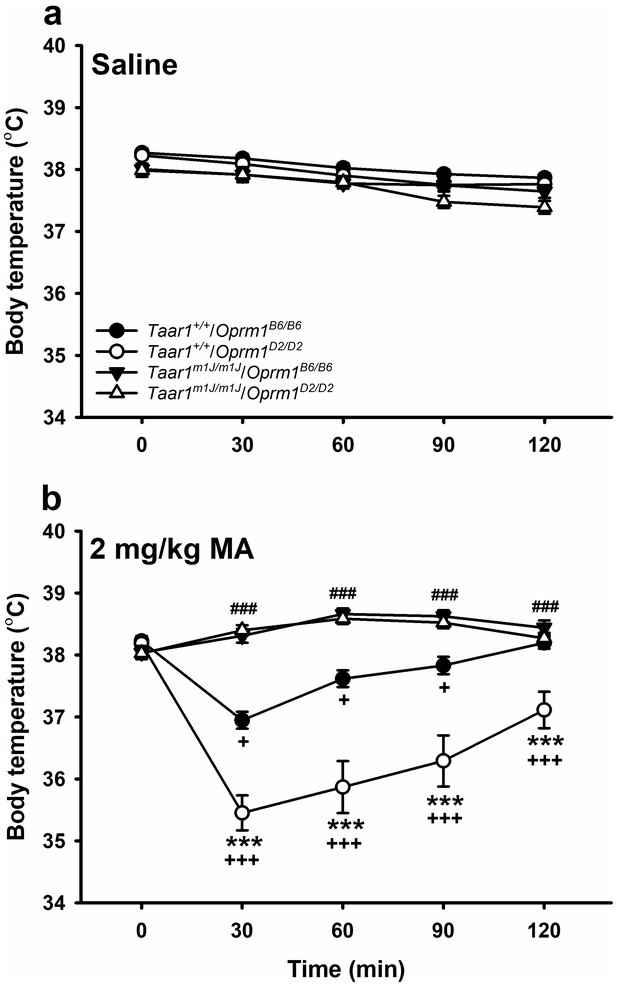
MA-induced hypothermia is impacted in BXD mice by a Taar1 x Oprm1 interaction.
Body temperatures obtained just before (T0) or 30–120 min (T30-120) after (a) saline or (b) 2 mg/kg MA treatment for BXD strain mice with different combined Taar1/Oprm1 genotypes. Presented are means ± SEM for data collapsed on sex. n = 30–47/genotype/MA dose tested in 16 cohorts of 8–36 mice. Repeated measures ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test,+p < 0.05 compared to T0 of same genotype; +++p < 0.001 compared to T0 of same genotype. Repeated measures ANOVA followed by simple main effects analysis, ***p<0.001 compared to Taar1+/+/Oprm1B6/B6. Repeated measures ANOVA collapsed on Oprm1 genotype followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test, ###p<0.001 compared to T0 of Taar1m1J/m1J mice. BXD, C57BL/6J (B6) x DBA2/J (D2); MA, methamphetamine; Oprm1, mu-opioid receptor gene; Oprm1B6/B6, homozygous for B6 Oprm1 allele; Oprm1D2/D2, homozygous for D2 Oprm1 allele; Taar1, trace amine-associated receptor 1 gene; Taar1+/+, homozygous for reference Taar1+ allele; Taar1m1J/m1J, homozygous for mutant Taar1m1J allele. The raw data represented in the graphs are available in Figure 6—source data 1.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Core body temperature (°C) data across time for saline and 2 mg/kg MA-treated male and female, BXD mice, according to Taar1 and Oprm1 genotype.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46472.015
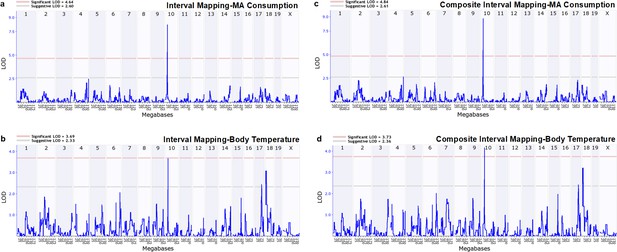
Genome-wide QTL scans identify a significant QTL on mouse chromosome 10 for both MA consumption and MA effect on body temperature.
Means for 18 BXD strains were used for mapping of (a) consumption of MA from a 40 mg/l solution, and 15 strains for mapping of (b) body temperature response to 2 mg/kg MA at 30 min post-treatment. Composite interval mapping for MA consumption (c) and body temperature response (d) included Oprm1 genotype as a co-factor. Chromosome number and megabase position are represented along the x-axis (chromosome indicated at top of plot). The y-axis represents the LOD ratio, a measure of the strength of association between variation in the phenotype and genetic differences (alleles) at a particular chromosomal locus. The horizontal pink and gray lines indicate the significant and suggestive threshold levels, respectively. Mapping results were generated using the QTL mapping module of GeneNetwork (www.genenetwork.org). BXD, C57BL/6J (B6) x DBA2/J (D2); LOD, logarithm of the odds; MA, methamphetamine; QTL, quantitative trait locus. The raw data represented in the graphs are available in Figure 7—source data 1.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
BXD means for QTL mapping of MA consumption (mg/kg/18h) from the 40 mg/l concentration and for QTL mapping of 2 mg/kg MA-induced body temperature change.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46472.017
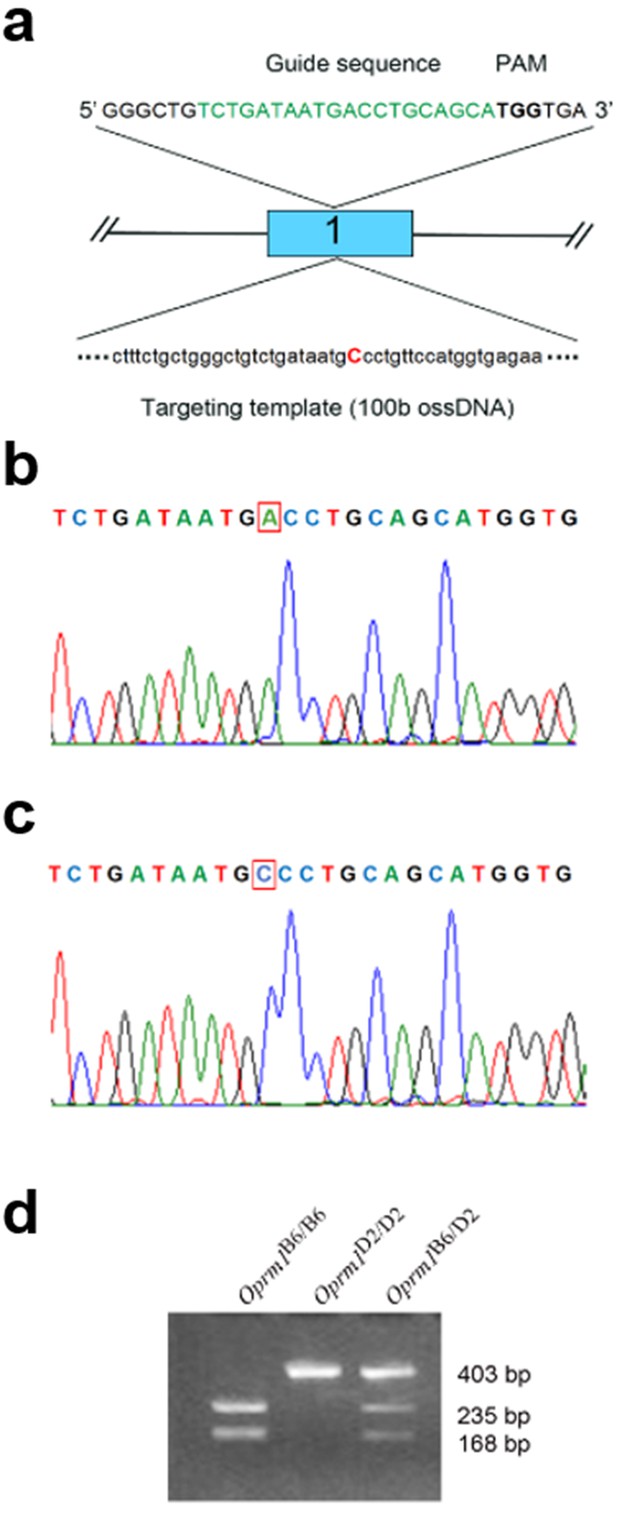
Generation of MAHDR-Taar1+/+ knock-in and MAHDR-Taar1m1J/m1J control mice, and genotyping of Taar1 and Oprm1.
(a) Strategy for insertion of a point mutation into mouse Taar1 exon 1. The guide sequence is indicated in green text and the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) is indicated by bold black text. The targeting template is indicated in black text, except for the single base pair to be inserted during the CRISPR-Cas9 process, which is indicated in red text. (b) A sequencing chromatograph of a homozygous Taar1m1J/m1J mouse that is representative of all MAHDR mice. The red box indicates the single nucleotide targeted for replacement during the CRISPR-Cas9 process. (c) A sequencing chromatograph of a homozygous MAHDR-Taar1+/+ edited knock-in mouse. The nucleotide that was successfully inserted during the CRISPR-Cas9 procedure is indicated by a red square. (d) An agarose genotyping gel example of Oprm1 genotypes for Oprm1B6/B6, Oprm1D2/D2 and Oprm1B6/D2 (from a B6 x D2 cross). All BXD mice were either homozygous Oprm1B6/B6 or Oprm1D2/D2, as well as homozygous for one or the other Taar1 allele. BXD, C57BL/6J (B6) x DBA2/J (D2); Oprm1, mu-opioid receptor gene; Oprm1B6/B6, homozygous for B6 Oprm1 allele; Oprm1D2/D2, homozygous for D2 Oprm1 allele; Oprm1B6/D2, heterozygous for B6 and D2 Oprm1 alleles; PAM, protospacer adjacent motif; Taar1, trace amine-associated receptor 1 gene; Taar1+/+, homozygous for reference Taar1+ allele; Taar1m1J/m1J, homozygous for mutant Taar1m1J allele.
Tables
Taar1/Oprm1 genotype combinations for the BXD strains.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46472.011| Taar1/Oprm1 genotype combination | MA intake | MA-induced change in body temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Taar1+/+/Oprm1B6/B6 | BXD 154, 184, 196, 212, 218 | BXD 154, 184, 196, 218 |
| Taar1m1J/m1J/Oprm1B6/B6 | BXD 113, 160, 171, 194 | BXD 113, 160, 171, 194 |
| Taar1+/+/Oprm1D2/D2 | BXD 161, 199, 205, 215 | BXD 161, 199, 205 |
| Taar1m1J/m1J/Oprm1D2/D2 | BXD 178, 186, 204, 210, 216 | BXD 178, 186, 210, 216 |
-
Abbreviations: BXD, C57BL/6J (B6) x DBA2/J (D2); MA, methamphetamine; Oprm1, mu-opioid receptor gene; Oprm1B6/B6, homozygous for B6 Oprm1 allele; Oprm1D2/D2, homozygous for D2 Oprm1 allele; Taar1, trace-amine associated receptor 1 gene; Taar1+/+, homozygous for reference Taar1+ allele; Taar1m1J/m1J, homozygous for mutant Taar1m1J allele.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus, females) | CD1/NCrl | Charles River | Strain code: 022 | foster dams for generation of knock-in mice |
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus, females and males) | BXD recombinant inbred strains | University of Tennessee Health Sciences Center | original breeders from Dr. Robert Williams; offspring for research produced by Dr. Tamara Phillips at VA Portland Health Care System (VAPORHCS) | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus, females) | MAHDR | VAPORHCS | methamphetamine high drinking mice; created by Dr. Tamara Phillips; all are homozygous for SNP rs33645709 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus, females and males) | MAHDR-Taar1m1J/m1J control | this paper | created by Oregon Health & Science University Transgenic Mouse Models Shared Resource; offspring for research produced by Dr. Tamara Phillips at VAPORHCS | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus, females and males) | MAHDR-Taar1+/+ knock-in | this paper | created by Oregon Health & Science University Transgenic Mouse Models Shared Resource; offspring for research produced by Dr. Tamara Phillips at VAPORHCS | |
| Biological sample (Mus musculus) | tail snip | other | obtained from breeders and research animals to determine genotype | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Taar1 gRNA | this paper | designed by ThermoFisher Scientific; reagent for generation of knock-in mice (Mus musculus) | |
| Sequence-based reagent | 100b oligo single strand DNA for Taar1+ (ossDNA) | this paper | MGI:MGI2148258 | synthesized by ThermoFisher Scientific; reagent for generation of knock-in mice (Mus musculus) |
| Sequence-based reagent | Cas9 mRNA | TriLink | Catalog number: L-7606 | reagent for generation of knock-in mice (Mus musculus) |
| Sequence-based reagent | primers for genotyping Oprm1 | this paper | original reference for these primers: Ferraro et al. (2005); based on Oprm1 sequence NM_001304955 (Mus musculus) | |
| Sequence-based reagent | DdeI restriction enzyme | ThermoFisher Scientific | Catalog number: ER1882 | reagent for Oprm1 genotyping (Helicobacter pylori, RFL3) |
| Commercial assay or kit | QuickExtract DNA Extraction Solution | Lucigen | Catalog number: QE09050 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Hotstart DNA Polymerase Kit | Qiagen | Catalog number: 203205 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Taqman kit for determining Taar1 alleles | ThermoFisher Scientific | Custom order | probes based on Taar1 sequence: NM_053205.1; SNP rs33645709 |
| Chemical compound, drug | ethidium bromide | Sigma Aldrich | Catalog number: E1510 | reagent for Oprm1 genotyping |
| Chemical compound, drug | (+)-methamphetamine hydrochloride | Sigma Aldrich | Catalog number: M8750 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | sterile 0.9% saline | Baxter Healthcare Corporation | Catalog number: 2F7124 | vehicle for methamphetamine |
| Software, algorithm | Statistica | TIBCO Software Inc | ||
| Software, algorithm | GeneNetwork | University of Tennessee | RRID:SCR_002388 | www.genenetwork.org |
| Software, algorithm | R | The R Foundation for Statistical Computing | RRID:SCR_001905 | www.r-project.org |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46472.019





