Transposase-assisted tagmentation of RNA/DNA hybrid duplexes
Figures
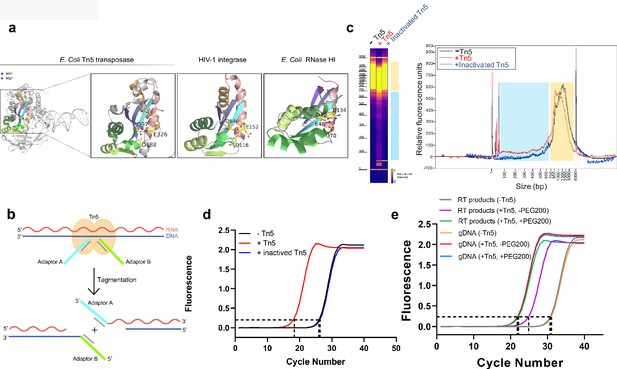
Tn5 transposome has direct tagmentation activity on RNA/DNA hybrid duplexes.
(a) Crystal structure of a single subunit of E. coli Tn5 Transposase (PDB code 1MM8) complexed with ME DNA duplex, and zoom-in views of the conserved catalytic core of Tn5 transposase, HIV-1 integrase (PDB code 1BIU), and E. coli RNase HI (PDB code 1G15), all of which are from the retroviral integrase superfamily. Active-site residues are shown as sticks, and the Mn2+ and Mg2+ ions are shown as deep blue and magenta spheres. (b) Schematic of Tn5-assisted tagmentation of RNA/DNA hybrids. (c) Gel pictures (left) and peak pictures (right) represent size distributions of HEK293T mRNA-derived RNA/DNA hybrid fragments after incubation without Tn5 transposome, with Tn5 transposome, and with inactivated Tn5 transposome. The blue and orange patches denote small and large fragments, respectively. (d) qPCR amplification curve of tagmentation products of HEK293T mRNA-derived RT samples with Tn5 treatment, with inactivated Tn5 treatment, or without Tn5 treatment. Average Ct values of two technical replicates are 18.06, 26.25 and 26.41, respectively. (e) qPCR amplification curve of tagmentation products of HEK293T mRNA-derived RT products samples and gDNA samples under different conditions. (Average Ct values of three technical replicates: RT products sample without Tn5 treatment = 30.38; RT products sample with PEG200 = 21.94; RT products sample without PEG200 = 25.23; gDNA sample without Tn5 treatment = 30.71; gDNA sample with PEG200 = 21.15; gDNA sample without PEG200 = 21.19).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
qPCR Ct values of tagmentation products of samples under different conditions in Figure 1d and e.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54919/elife-54919-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
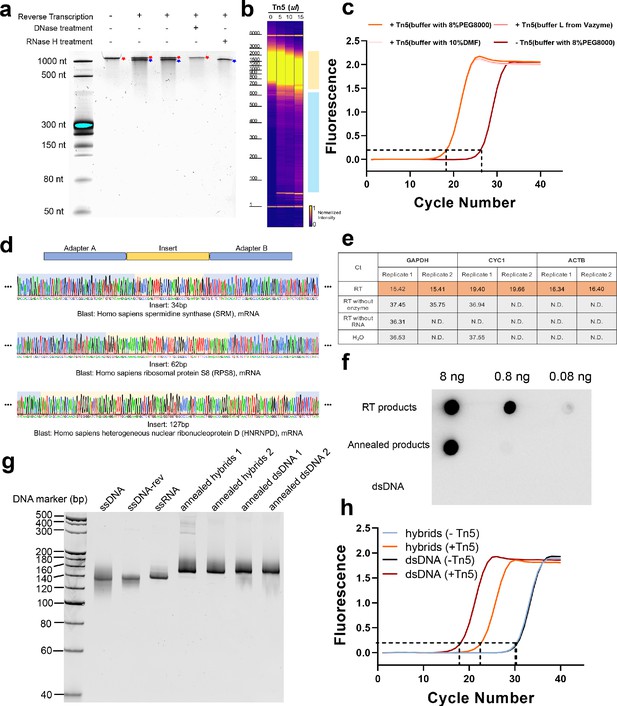
Tagmentation activity of Tn5 transposome on RNA/DNA hybrids.
(a) Denaturing (8 M urea) polyacrylamide gel analysis of reverse transcription products of an in vitro transcribed mRNA (IRF9). Lane 1: ssRNA marker. Lane 2: in vitro transcribed mRNA (IRF9). Lane 3 and 4: reverse transcription products of an in vitro transcribed mRNA (IRF9). Lane 5: reverse transcription product treated with DNase I. Lane 6: reverse transcription product treated with RNase H. ssRNA and ssDNA is marked with a red asterisk and a blue pound sign, respectively. (b) Gel picture showing size distribution of RNA/DNA hybrids products of 50 μl reaction systems without Tn5 transposome, and with 5 μl, 10 μl, and 15 μl Tn5 transposome, respectively. The blue and orange patches denote small and large fragments, respectively. (c) qPCR amplification curve of tagmentation products without Tn5 treatment or with Tn5 treatment in three different buffers (see Methods). Average Ct values of two technical replicates are 26.41, 18.39, 18.33 and 18.34, respectively. (d) Sanger sequencing chromatograms of PCR products following RNA/DNA hybrid tagmentation and strand extension. Adaptor A and B sequences are highlighted with blue background color and insert sequences are highlighted with yellow background. (e) Assessment of gDNA contamination by qPCR of represented genes. (f) Dot blot analysis of a series of diluted samples using the anti-hybrid S9.6 antibody. S9.6 antibody showed no cross-reactivity with dsDNA and the successful hybrids productions were confirmed in CLuc annealed products and mRNA RT products. (g) Native PAGE analysis of 150 bp CLuc annealed products under different annealing conditions. (Annealed hybrids 1: RNA:DNA = 2:1; Annealed hybrids 2: RNA:DNA = 1.2:1; Annealed dsDNA 1: ssDNA:ssDNA-rev = 2:1; Annealed dsDNA 2: ssDNA:ssDNA-rev = 1.2:1; See Methods). (h) qPCR amplification curve of tagmentation products of CLuc annealed RNA/DNA hybrid and dsDNA products with Tn5 treatment or without Tn5 treatment. Average Ct values of three technical replicates of annealed hybrid products are 22.68 and 30.4, respectively. Average Ct values of three technical replicates of annealed dsDNA products are 18.08 and 30.83, respectively.
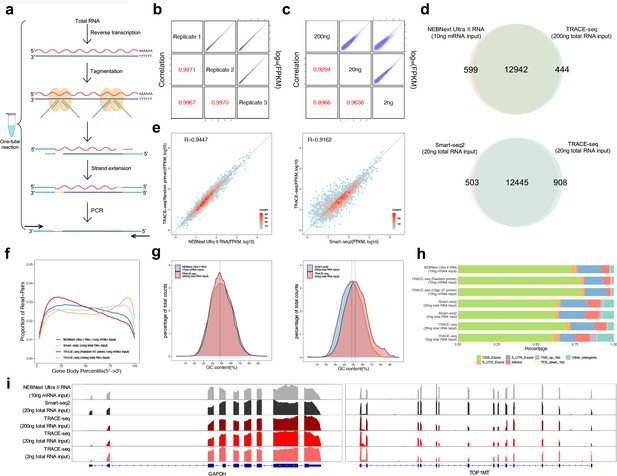
Workflow and evaluation of TRACE-seq.
(a) Workflow of TRACE-seq. (b) Gene expression, measured by three technical replicates of TRACE-seq with 200 ng total RNA as input, are shown as scatter plots in the upper right half. Pearson's product-moment correlations are displayed in the lower left half. (c) Gene expression, measured by TRACE-seq using 200 ng, 20 ng and 2 ng total RNA as input, are shown as scatter plots in the upper right half. Pearson's product-moment correlations are displayed in the lower left half. (d) Venn diagrams of gene numbers detected by TRACE-seq with 200 ng total RNA as input and NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit with 200 ng mRNA as input (top) and by TRACE-seq with 20 ng total RNA as input and Smart-seq2 with 20 ng mRNA as input (below). (e) Scatterplots showing a set of housekeeping gene expression values for TRACE-seq and NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit with 10 ng mRNA as input (left), and for TRACE-seq with 10 ng mRNA as input and Smart-seq2 with 20 ng total RNA as input (right). Pearson's product-moment correlation is displayed in the upper left corner. (f) Comparison of read coverage over gene body for NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit, Smart-seq2 and TRACE-seq with different amount of RNA as input. The read coverage over gene body is displayed along with gene body percentile from 5’ to 3’ end. (g) Distribution of GC content of all mapped reads from TRACE-seq library with 200 ng total RNA as input and NEBNext Ultra II RNA library with 10 ng mRNA as input (left) or Smart-seq2 library with 20 ng total RNA as input (right). The vertical dashed lines indicate 48% (left) and 48% and 51% respectively (right). (h) Comparison of the distribution of reads across known genome features for NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit, Smart-seq2 and TRACE-seq with different amount of RNA as input. (i) IGV tracks showing the coverage of two representative transcripts (GAPDH and TOP1MT). The data come from NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit, Smart-seq2 and three sets of TRACE-seq with different amount of total RNA as input.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Distribution of reads across known genome features for NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit, Smart-seq2 and TRACE-seq with different amount of RNA as input.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54919/elife-54919-fig2-data1-v2.xls
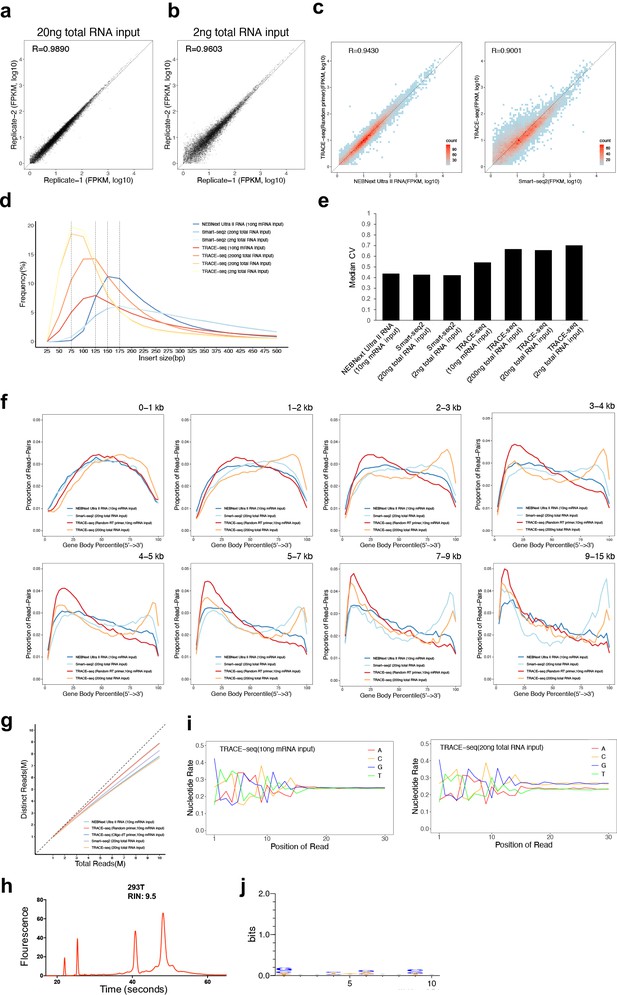
Quality assessment of TRACE-seq.
(a) Gene expression measured by two technical replicates of TRACE-seq with 20 ng total RNA as input are shown as scatter plots. Pearson's product-moment correlations are displayed in the upper left corner. (b) Gene expression measured by two technical replicates of TRACE-seq with 2 ng total RNA as input are shown as scatter plots. Pearson's product-moment correlations are displayed in the upper left corner. (c) Scatterplots showing gene expression values for TRACE-seq and NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit with 10 ng mRNA as input (left), and for TRACE-seq with 10 ng mRNA as input and Smart-seq2 with 20 ng total RNA as input (right). All expressed genes (FPKM >0.5) are included. Pearson's product-moment correlation is displayed in the upper left corner. (d) Distribution of the insert size in NEBNext Ultra II RNA library, Smart-seq2 libraries and TRACE-seq libraries with different amount of RNA as input, respectively. (e) Median coefficient of variation of gene coverage over the 1000 most highly expressed transcripts in NEBNext Ultra II RNA library, Smart-seq2 libraries and TRACE-seq libraries with different amount of RNA as input, respectively. (f) Comparison of read coverage over gene body for NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit, Smart-seq2 and TRACE-seq with different amount of RNA as input. Transcripts were grouped according to annotated lengths and analyzed separately, with the transcript length ranges indicated (top right). The read coverage over gene body is displayed along with gene body percentile from 5’ to 3’ end. (g) Library complexity for each library shown by plotting the number of uniquely occurring read-pairs with respect to total number of sampled read-pairs. (h) Assessment of RNA Integrity number (RIN). RNA of high RIN score (9.5) was used as input, which allows us to rule out the possibility that the 3’ end bias of gene body coverage is due to RNA degradation. (i) Nucleotide versus cycle (NVC) plots showing percentage of observed bases at each position of the first 30 bases of each sequencing read from TRACE-seq library with 10 ng mRNA and 20 ng total RNA as input. (j) WebLogo plot of sequence conservations of the first 10 bases of all sequencing reads from TRACE-seq library with 10 ng mRNA as input. The overall height of the stack indicates the sequence conservation at that position (measured in bits), while the height of symbols within the stack indicates the relative frequency of each nucleic acid at that position.
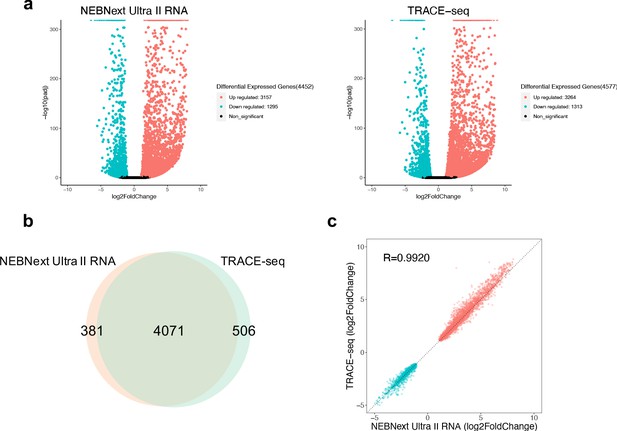
Performance of TRACE-seq in differential expression analysis.
(a) Volcano plot showing differential expressed genes between undifferentiated and differentiated mESCs detected by NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit and TRACE-seq. Significantly up-regulated and down-regulated expressed genes (padj <0.05, |log2FoldChage| > 1) are highlighted in red and blue, respectively. (b) Venn diagram of differentially expressed gene numbers detected by TRACE-seq and NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit. (c) Correlation between the fold change of the 4071 differentially expressed genes that overlap between NEBNext Ultra II RNA and TRACE-seq library.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HEK293T | American Type Culture Collection | Cat#: CRL-11268, RRID:CVCL_1926 | |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-DNA-RNA Hybrid [S9.6] Antibody | Kerafast | Cat#: ENH001, RRID:AB_2687463 | 1:2000 |
| Antibody | Antibody Anti-mouse-IgG-HRP | CWBiotech | Cat#: CW0102, RRID:AB_2736997 | 1:3000 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CLuc Control Template | NEB | Cat#: E2060S | |
| Sequence-based reagent | CLuc Control_F | This paper | PCR primers | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | CLuc Control_R | This paper | PCR primers | TTAGCTTCACAGGAAGTTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | GAPDH-qFWD | This paper | PCR primers | GCATCCTGGGCTACACTGAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | GAPDH-qRVS | This paper | PCR primers | AAAGTGGTCGTTGAGGGCAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | ACTB-qFWD | This paper | PCR primers | AGTCATTCCAAATATGAGATGCGTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | ACTB-qRVS | This paper | PCR primers | TGCTATCACCTCCCCTGTGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | CYC1-qFWD | This paper | PCR primers | CACCATAAAGCGGCACAAGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | CYC1-qRVS | This paper | PCR primers | CAGGATGGCAAGCAGACACT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Tn5ME-A | doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-12-r119 | Transposon adaptor oligonucleotides | TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Tn5ME-B | doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-12-r119 | Transposon adaptor oligonucleotides | GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Tn5MErev | doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-12-r119 | Transposon adaptor oligonucleotides | CTGTCTCTTATACACATCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Tn5_qFWD | This paper | PCR primers | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCGTCGGCAGCGTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Tn5_qRVS | This paper | PCR primers | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | TSO | doi:10.1038/nprot.2014.006 | Template switch primer | AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGTACATrGrG+G |
| Sequence-based reagent | ISPCR oligo | doi:10.1038/nprot.2014.006 | PCR primers | AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | oligo dT(23)VN primer | NEB | Cat#: S1327S | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Random primer mix | NEB | Cat#: S1330S | |
| Sequence-based reagent | N501 primer | Illumina | PCR primers for sequencing | |
| Sequence-based reagent | N701-N712 primers | Illumina | PCR primers for sequencing | |
| Commercial assay or kit | TRIzol | Invitrogen | Cat#: 15596018 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Blood & Cell Culture DNA Midi Kit | Qiagen | Cat#: 13343 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | MAXIscript T7 Transcription Kit | Invitrogen | Cat#: AM1314M | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SUPERase-In RNase Inhibitor | Invitrogen | Cat#: AM2696 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit | Invitrogen | Cat#: P11496 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | AceQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix | Vazyme | Cat#: Q511-02 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | pEASY-Blunt Zero Cloning Kit | TransGen | Cat#: CB501-01 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NEBNext Q5 Hot Start HiFi PCR Master Mix | NEB | Cat#: M0544 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Agencourt AMPure XP beads | Beckman Coulter | Cat#: A63882 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNAClean XP beads | Beckman Coulter | Cat#: A63987 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Qubit dsDNA HS Assay kit | Invitrogen | Cat#: Q33230 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | DNF-474 High Sensitivity NGS Fragment Analysis Kit | Agilent | Cat#: DNF-473-1000 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NEBNext Ultra II RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina | NEB | Cat#: E7770S | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Dynabeads Oligo(dT)25 | Invitrogen | Cat#: 61005 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix | KAPA Biosystems | Cat#: KK2601 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | TransDetect PCR Mycoplasma Detection Kit | TransGen | Cat#: FM311-01 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNA 6000 Pico kits (Agilent Technologies | Agilent | Cat#: 5067-1513 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | DNase I | NEB | Cat#: M0303S | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | SuperScript IV reverse transcriptase | Invitrogen | Cat#: 12594100 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | SuperScript II reverse transcriptase | Invitrogen | Cat#: 18064022 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | RNase H | NEB | Cat#: M0297 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | TruePrep Tagment Enzyme | Vazyme | Cat#: S601-01 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Bst 3.0 DNA Polymerase | NEB | Cat#: M0374S | |
| Chemical compound, drug | PEG200 | Sigma | Cat#: 88440 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | PEG8000 | Sigma | Cat#: 89510 | |
| Software, algorithm | Trim Galore | http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/trim_galore/ | RRID:SCR_011847 | v0.6.4_dev |
| Software, algorithm | STAR | PMID:23104886 | RRID:SCR_015899 | v2.7.1a |
| Software, algorithm | bowtie2 | https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923 | RRID:SCR_005476 | v2.2.9 |
| Software, algorithm | Samtools | http://samtools.sourceforge.net/ | RRID:SCR_002105 | v1.9 |
| Software, algorithm | cuffnorm | PMID:20436464 | RRID:SCR_014597 | v2.2.1 |
| Software, algorithm | QoRTs | https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-015-0670-5 | RRID:SCR_018665 | v1.1.6 |
| Software, algorithm | RseQC | PMID:22743226 | RRID:SCR_005275 | v2.6.4 |
| Software, algorithm | Picard Tools | http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/ | RRID:SCR_006525 | v2.20.6 |
| Software, algorithm | Preseq | PMID:23435259 | RRID:SCR_018664 | v2.0.0 |
| Software, algorithm | RStudio | https://rstudio.com/ | RRID:SCR_000432 | 1.2.5033 |
| Software, algorithm | Integrative Genomics Viewer | http://software.broadinstitute.org/software/igv/ | RRID:SCR_011793 | v2.4.16 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Quality control of the sequencing results using different enzymes for strand extension and PCR in TRACE-seq library construction procedure.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54919/elife-54919-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Quality control of the sequencing results using NEBNext kit and TRACE-seq.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54919/elife-54919-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Quality control of the sequencing results using Smart-seq2 and TRACE-seq.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54919/elife-54919-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Costs of RNA-seq constructed by NEBNext Ultra II RNA kit, TRACE-seq and Smart-seq2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54919/elife-54919-supp4-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
List of housekeeping genes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54919/elife-54919-supp5-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54919/elife-54919-transrepform-v2.pdf





