Par protein localization during the early development of Mnemiopsis leidyi suggests different modes of epithelial organization in the metazoa
Figures
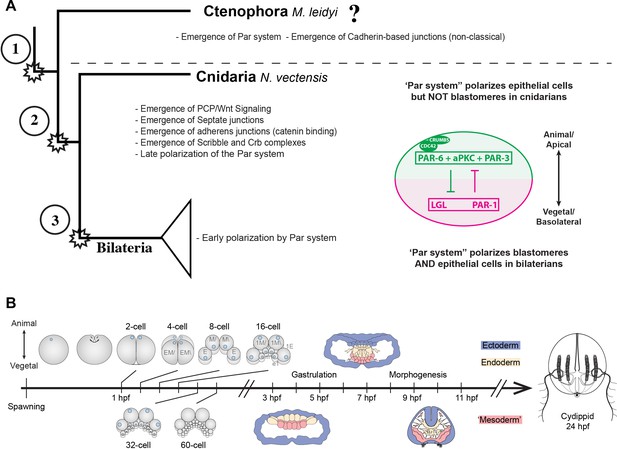
Evolution of cell polarity components during animal evolution.
(A) Three major evolutionary steps (left side) that might have changed the organization of cell polarity in the Metazoa. The diagram (right side) depicts the subcellular asymmetric localization of Par proteins in Cnidaria and Bilateria. However, there are no previous descriptions available for ctenophore cells. (B) The stereotyped early development of M. leidyi.
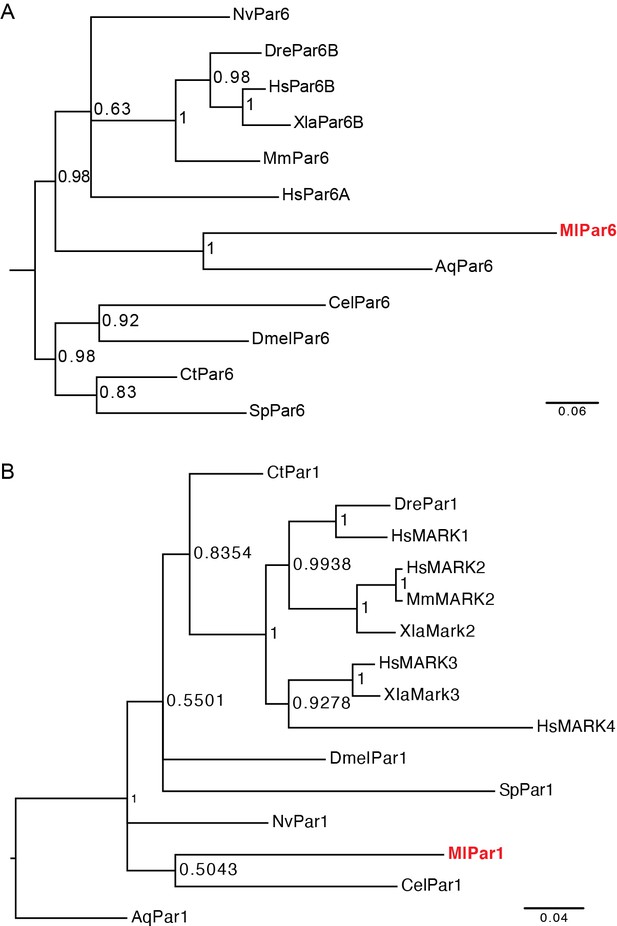
Phylogenetic analysis for (A) MlPar-6 and (B) MlPar-1.
Trees were constructed using MrBayes (v3.2.6 × 64) and consisted of 2,000,000 generations using ‘mixed’ models. Maximum-likelihood tree bootstraps were based on 100 replicates. Aq: Amphimedon queenslandica; Cel: Caenorhabditis elegans; Ct: Capitella teleta; Dmel: Drosophila melanogaster; Dre: Danio rerio; Hs: Homo sapiens; Ml: Mnemiopsis leidyi; Mm: Mus musculus; Nv: Nematostella Vectensis; Sp: Strongylocentrotus purpuratus; Xla: Xenopus laevis. See also Fahey and Degnan, 2010 and Belahbib et al., 2018.
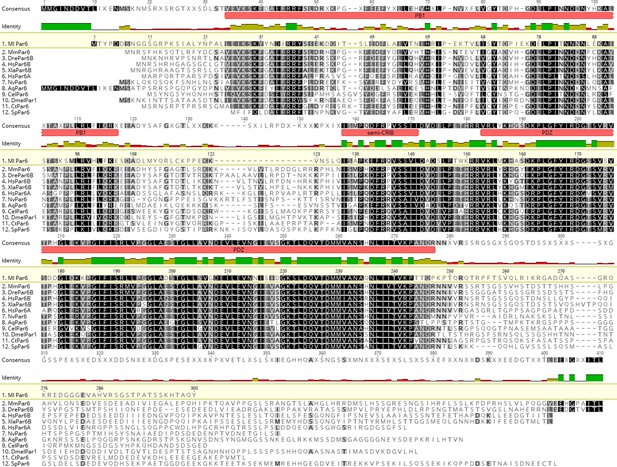
Protein sequence alignment for MlPar-6.
Protein domains were predicted by Geneious software using Pfam and SMART databases. Aq: Amphimedon queenslandica; Cel: Caenorhabditis elegans; Ct: Capitella teleta; Dmel: Drosophila melanogaster; Dre: Danio rerio; Hs: Homo sapiens; Ml: Mnemiopsis leidyi; Mm: Mus musculus; Nv: Nematostella Vectensis; Sp: Strongylocentrotus purpuratus; Xla: Xenopus laevis. See also references Belahbib et al., 2018 and Fahey and Degnan, 2010 .
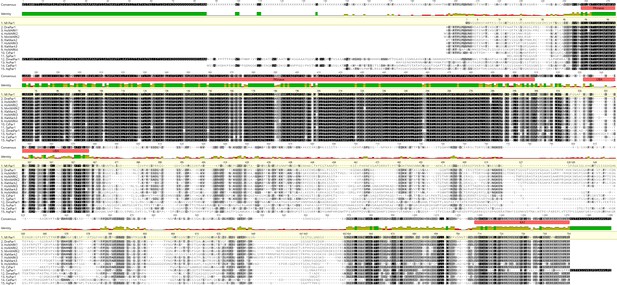
Protein sequence alignment for MlPar-1.
Protein domains were predicted by Geneious software using Pfam and SMART databases. Aq: Amphimedon queenslandica; Cel: Caenorhabditis elegans; Ct: Capitella teleta; Dmel: Drosophila melanogaster; Dre: Danio rerio; Hs: Homo sapiens; Ml: Mnemiopsis leidyi; Mm: Mus musculus; Nv: Nematostella Vectensis; Sp: Strongylocentrotus purpuratus; Xla: Xenopus laevis. See also references Fahey and Degnan, 2010 and Belahbib et al., 2018.
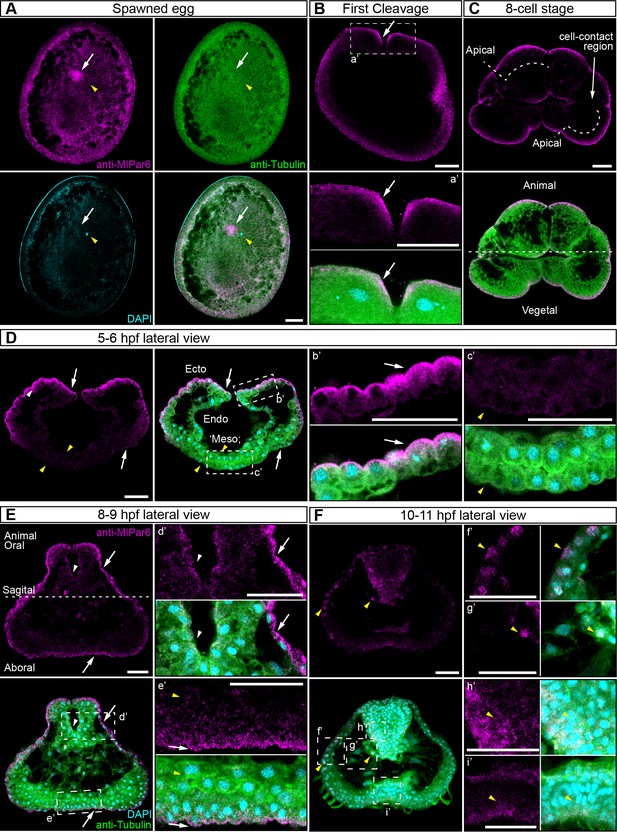
MlPar-6 protein subcellular localization during the early development of M. leidyi.
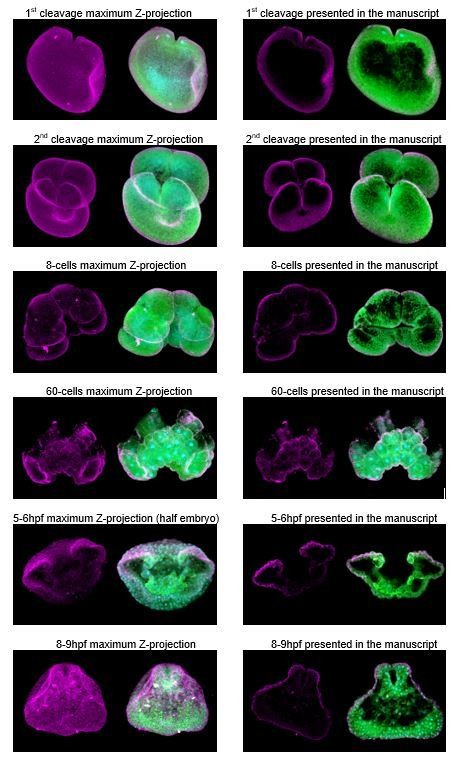
Immunostaining against MlPar-6 protein shows that this protein localizes asymmetrically in the cell cortex of the eggs (A) and in the cell-contact-free regions of cleavage stages (B–C; white arrows). White circle in C indicates the lack of signal in the cell-contact region. Yellow arrowhead indicates the zygotic nucleus in A. a’ is a magnification of the section depicted in (B) the first cleavage. (D–F): b’ to i’ correspond to magnifications of the regions depicted for each stage. (D) 5–6 hpf, MlPar-6 protein localizes to the apical cortex of the ectodermal cells (Ecto) but is absent from endodermal (Endo) and ‘mesodermal’ (‘Meso’) cells. White arrowhead indicates MlPar-6 protein in regions of cell-contact. Yellow arrowheads indicate the absence of cortical localization. (E) Until 9 hpf, MlPar-6 protein localizes to the apical cortex of the ectoderm (white arrows) and pharynx (white arrowhead) but it is not cortically localized after 10 hpf (F; Yellow arrowheads indicate nuclear localization). Images are maximum projections from a z-stack confocal series. The 8 cell stage corresponds to a single optical section. Orientation axes are depicted in the Figure: Animal/oral pole is to the top. Morphology is shown by DAPI and Tubulin immunostainings. See Figure 2—figure supplements 1–11 for expanded developmental stages. Scale bars: 20 µm.
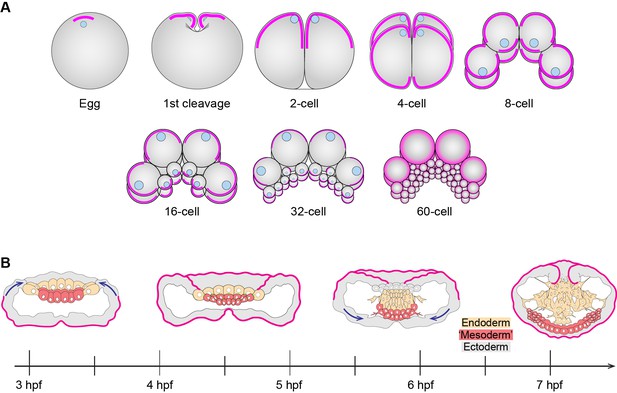
Diagram depicting the cortical localization of MlPar-6 (magenta).
(A) Cleavage stages and (B) gastrulation. Animal pole is to the top. Ectoderm is colored in grey. Endoderm and ‘mesoderm’ are colored in yellow and red, respectively. Blue arrows depict gastrulation movements in (B). For simplicity, most of the cell boundaries are not depicted.
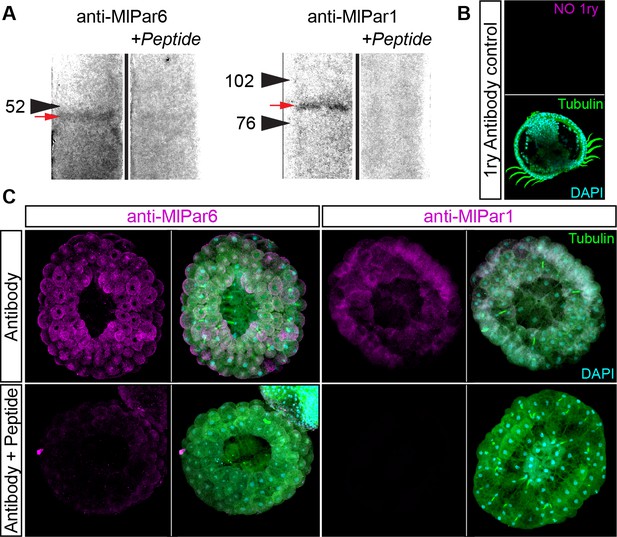
Specificity of M. leidyi antibodies as tested by pre-adsorption experiments.
Genome searches of M. leidyi showed that there is only a single copy for both Par-6 (MlPar-6) and Par-1 (MlPar-1) genes and they express through development in the transcriptome of M. leidyi (Babonis, 2018; Levin et al., 2016). (A) Western blots of M. leidyi adult tissue extracts using specific antibodies (rabbit polyclonal affinity-purified; Bethyl labs, Inc) against MlPar-6 and MlPar-1. Pre-adsorption of the antibodies with a tenfold excess of the antigen peptide resulted in the elimination of the staining of the appropriate-sized single band for MlPar-6 and MlPar-1. Arrowheads indicate the molecular weight in KD (MlPar-6: predicted size 33.3 KD and MlPar-1: predicted size 84.7 KD). A red arrow indicates the single band recognized by the antibody for each protein. See Figure 2—figure supplement 12 for the full lanes and input lysate staining. (B) Negative control without the rabbit primary antibody shows that there is no inherent autofluorescence. (C) Whole-mount immunohistochemistry pre-adsorption experiments show that the staining pattern was strongly mitigated in early embryos when pre-incubated antibodies against MlPar-6 and MlPar-1 with the respective peptide. Thus, both antibodies are specific to their intended targets and provide robust reagents to determine the subcellular localization of these proteins during M. leidyi embryogenesis.
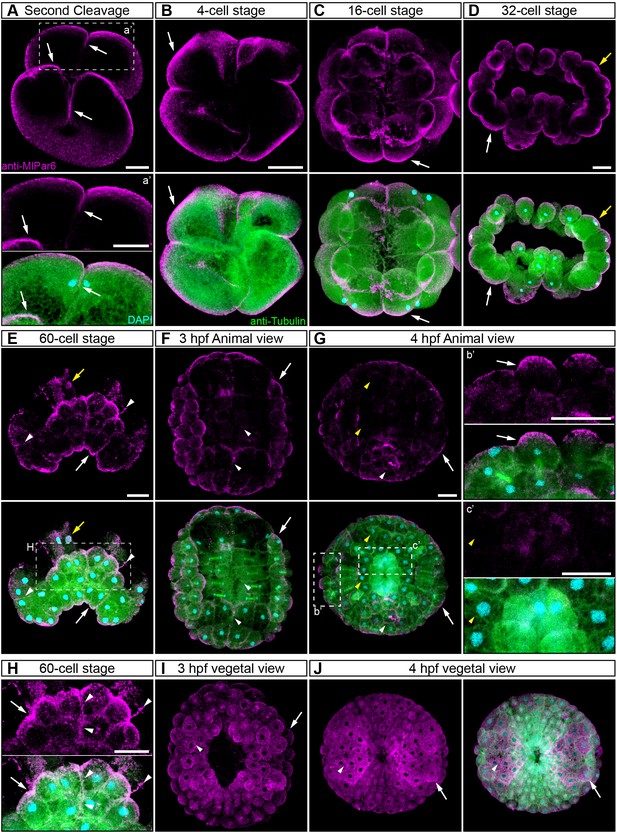
MlPar-6 localization during early developmental stages.
(A–E) Immunostaining against MlPar-6 during cleavage stages of M. leidyi development complimentary to Figure 2. (A–D) MlPar-6 protein localizes to the apical cortex (white arrows) until the 60 cell-stage (E) where its signal was detected in regions of cell-cell contact (white arrowhead). During 3 to 4 hpf (F–G), MlPar-6 protein localizes to the apical cortex (white arrows) but it is not localized in cells undergoing cellular movements. (H) Magnification of the region H depicted in 60 cell-stage. (I–J) Vegetal views of MlPar-6 localization during 3 and 4 hpf. Morphology is shown by DAPI and Tubulin immunostainings. Yellow arrows indicate nuclear localization. Yellow arrowheads indicate the absence of cortical localization. Images are maximum projections from a z-stack confocal series. Scale bars: 20 µm.
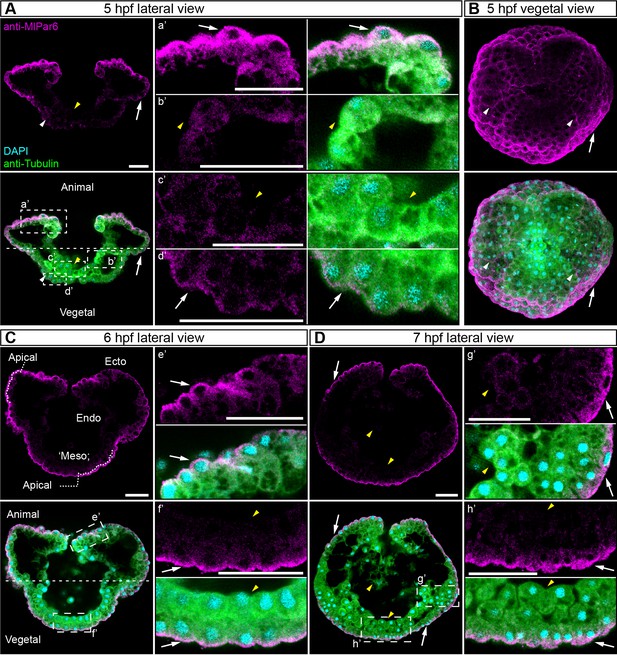
MlPar-6 localization during late gastrulation stages.
Complimentary to Figure 2. MlPar-6 protein localizes to the apical cortex of the ectodermal cells (Ecto) but is absent from endodermal (Endo) and ‘mesodermal’ (‘Meso’) cells. 5 to 7 hpf (A–D): MlPar-6 protein localizes to the apical cortex of the ectoderm (white arrows). Images are maximum projections from a z-stack confocal series. 6 hpf embryo (C) corresponds to a single optical section from a z-stack confocal series. a’ to h’ correspond to the magnifications of the regions depicted for each stage. The axial orientation in each panel is animal pole up. Morphology is shown by DAPI and Tubulin immunostainings. Scale bars: 20 µm.
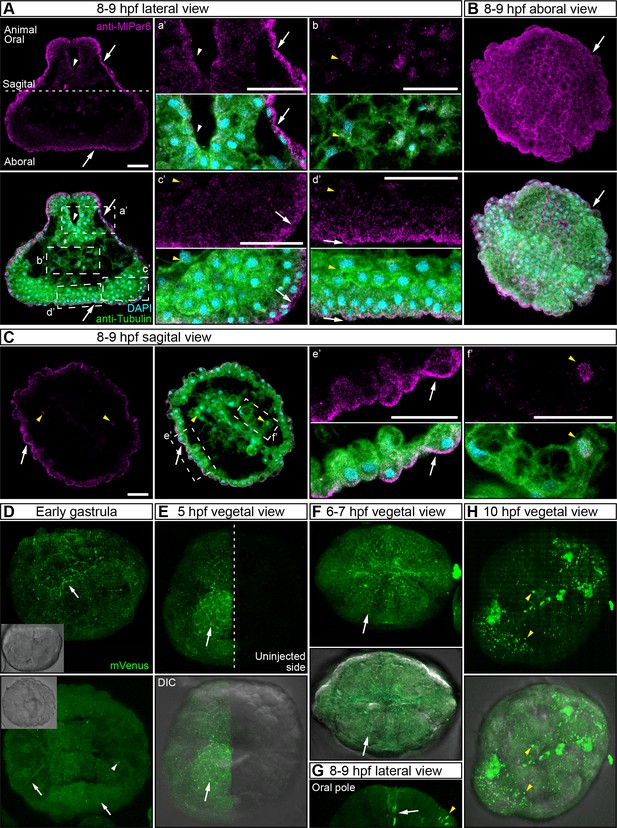
MlPar-6 localization during late developmental stages.
Complimentary to Figure 2. (A–C) Immunostaining against MlPar-6 shows that MlPar-6 protein localizes to the apical cortex (white arrows) until nine hpf. 8–9 hpf images in (A) and (C) are single optical sections from a z-stack confocal series. a’ to f’ correspond to the magnifications of the regions depicted for each stage. Orientation is depicted in (A): Animal/oral pole is to the top. Morphology is shown by DAPI and tubulin immunostainings. Yellow arrowheads indicate the absence of cortical localization in (A) and nuclear localization (C). (D–H) in vivo localization of MlPar6-mVenus during different stages of M. leidyi development. The overexpression of MlPar6-mVenus protein displays similar patterns observed with the antibody staining against the same protein; no cortical localization was observed after 10 hpf (H). All images are maximum projections from a z-stack confocal series. Orientation is animal/oral pole to the top. Morphology is shown by DIC microscopy. White arrows indicate MlPar6-mVenus protein cortical localization. Yellow arrowheads indicate the absence of cortical localization and cytosolic aggregation. Scale bars: 20 µm.
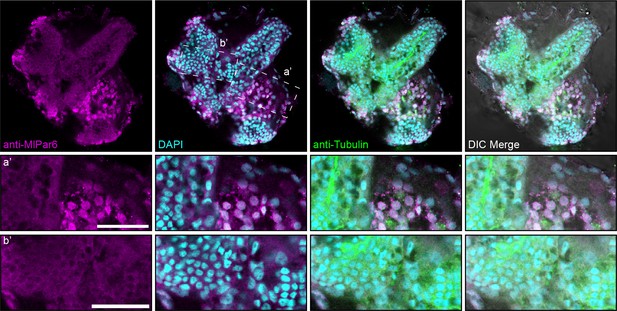
Immunofluorescent staining against MlPar-6 after 20 hpf.
The distribution of MlPar-6 in juvenile epithelium is nuclear and cytosolic during later stages. Neither asymmetrical nor cortical localization was observed. a’ and b’ correspond to the magnifications of the regions depicted. Morphology is shown by DIC, DAPI, and tubulin immunostainings. Scale bars: 20 µm.
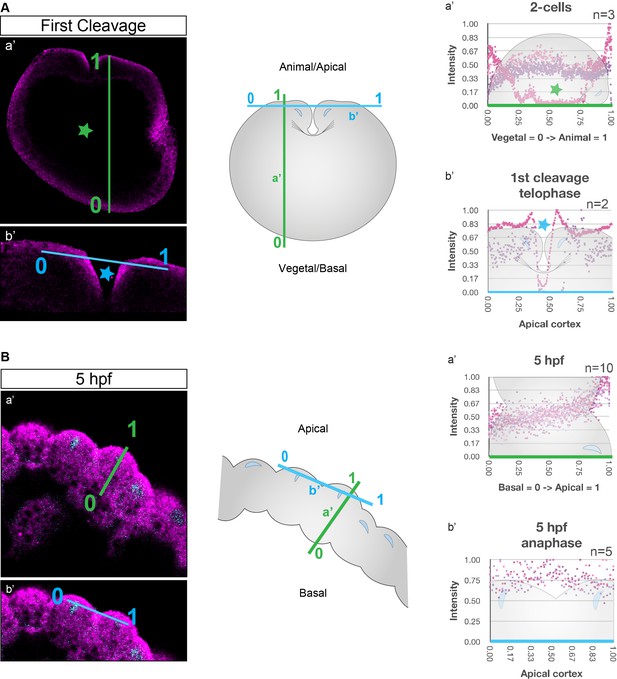
Schematic depiction of fluorescent intensity measurements correspondent to Figure 2.
(A) Depiction of the measurement direction during early stages. 0 is the vegetal pole and one is the animal pole in a’ (Figure 2—figure supplements 8–10). 0 and 1 in b’ are arbitrary along the apical cortex (Figure 2—figure supplement 11). The drop in the signal observed for earliest stages in Figure 2—figure supplements 8 and 11 corresponds to the space outside of the focal plane (green star; a’) and the space between cleavage furrow (blue star; b’), respectively. (B) Depiction of the measurement direction during later stages. 0 is basal and 1 is the apical in a’. 0 and 1 in b’ are arbitrary along the apical cortex.
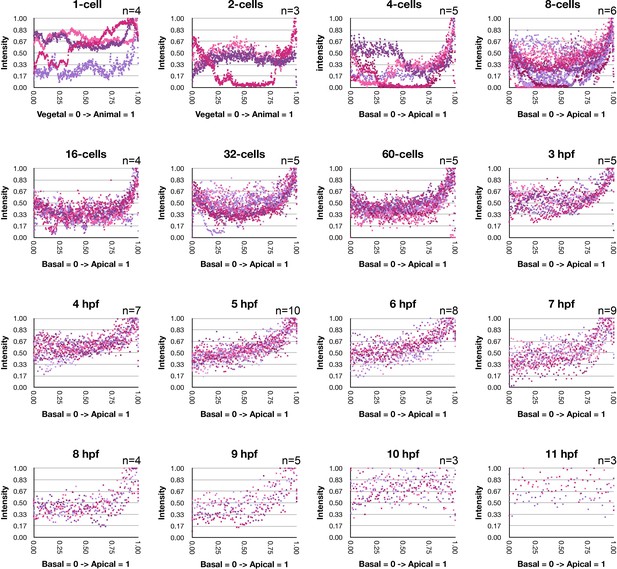
Fluorescent intensity measurements of immunofluorescent staining against MlPar-6.
Fluorescent intensity (Y axis) was measured along the vegetal/animal and basal/apical axes (X axis) for the developmental stages reported in Figure 2 and Figure 2—figure supplements 1–6. All measured cells display apical localization of MlPar-6 until 10hpf where its intensity is uniform (Figure 2—figure supplement 10). These measurements correspond to cells in undergoing through interphase and metaphase. Numerical data can be found in Figure 2—figure supplement 8—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 8—source data 1
Numerical data that are represented as a graph in Figure 2—figure supplement 8.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54927/elife-54927-fig2-figsupp8-data1-v3.xlsx
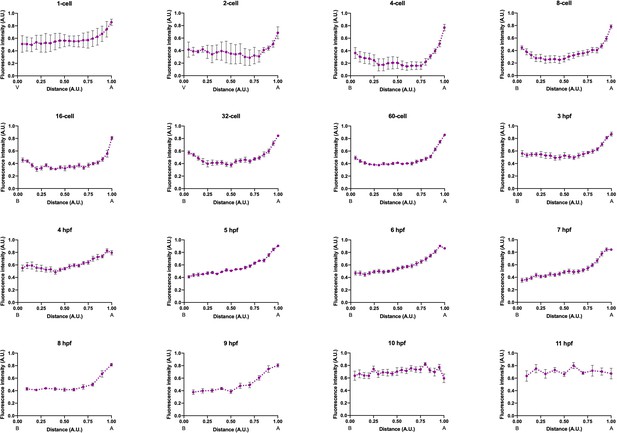
Fluorescent intensity distribution of immunofluorescent staining against MlPar-6.
The distribution of the MlPar-6 antibody signal was obtained by plotting Fluorescent intensity data from Figure 2—figure supplement 8 (Y axis) in intervals along the vegetal/animal and basal/apical axes (X axis) for the developmental stages reported. Means and SEM are depicted in the figure. Numerical data can be found in Figure 2—figure supplement 9—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 9—source data 1
Numerical data that are represented as a graph in Figure 2—figure supplement 9.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54927/elife-54927-fig2-figsupp9-data1-v3.pzfx
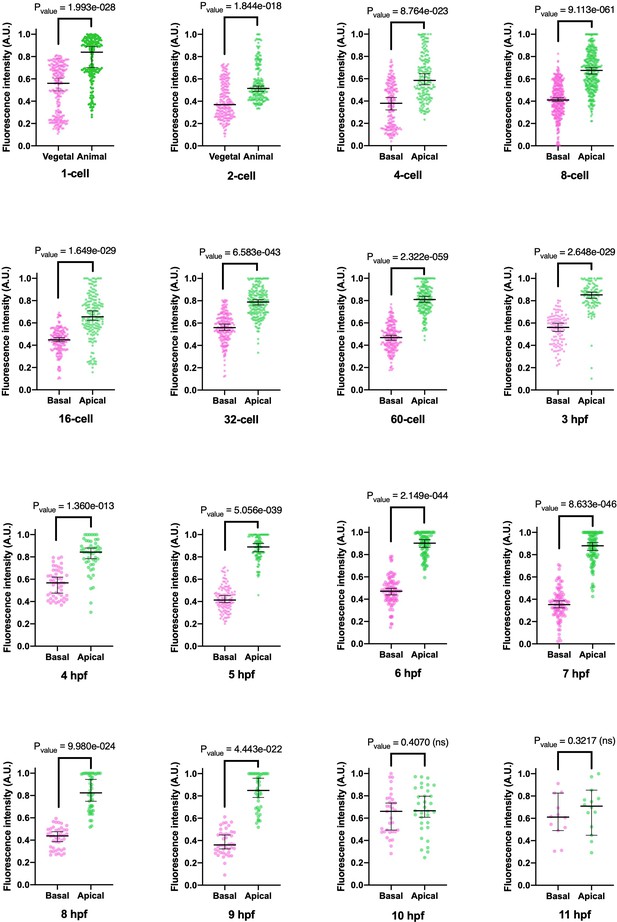
Graphical depiction of fluorescence intensity measurements between basal and apical cortex.
Different MlPar-6 localization between basal and apical cortex for each stage represented in Figure 2 and Figure 2—figure supplement 8. Median, 95% CI, and P values are depicted in the figure. Numerical and statistical data can be found in Figure 2—figure supplement 10—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 10—source data 1
Numerical and statistical data that are represented as graphs in Figure 2—figure supplement 10.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54927/elife-54927-fig2-figsupp10-data1-v3.pzfx
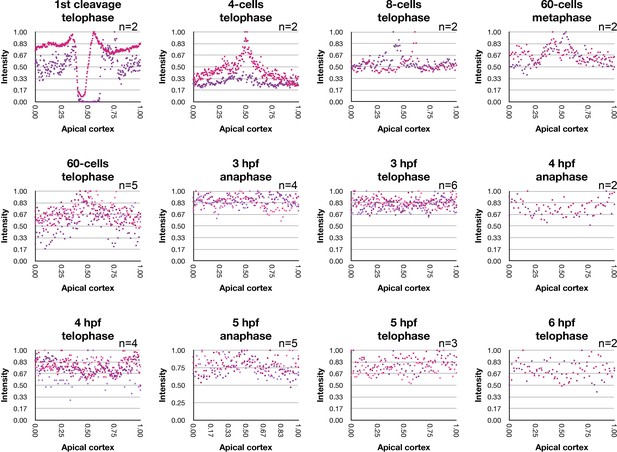
Fluorescent intensity measurements of immunofluorescent staining against MlPar-6 during cell cycle.
Fluorescent intensity (Y axis) was measured along the apical axis (X axis) for cells undergoing through anaphase and telophase, during the developmental stages reported in Figure 2 and Figure 2—figure supplements 1–6. All measured cells display uniform apical localization of MlPar-6. During cleavage stages MlPar-6 signal display higher intensity in the cleavage furrow and cell-cell contact region of 60 cell-stage (middle points along the X axis). Unfortunately, we did not have enough telophase replicates to show statistical significance of these observations. Numerical data can be found in Figure 2—figure supplement 11—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 11—source data 1
Numerical data that are represented as a graph in Figure 2—figure supplement 11.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54927/elife-54927-fig2-figsupp11-data1-v3.xlsx
Western blot analyses for the tested antibodies.
(A) Coomassie stained gel of the full input lysate. (B) Full Western blot lanes for the MlPar-6 and MlPar-1 antibodies sections shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 2.
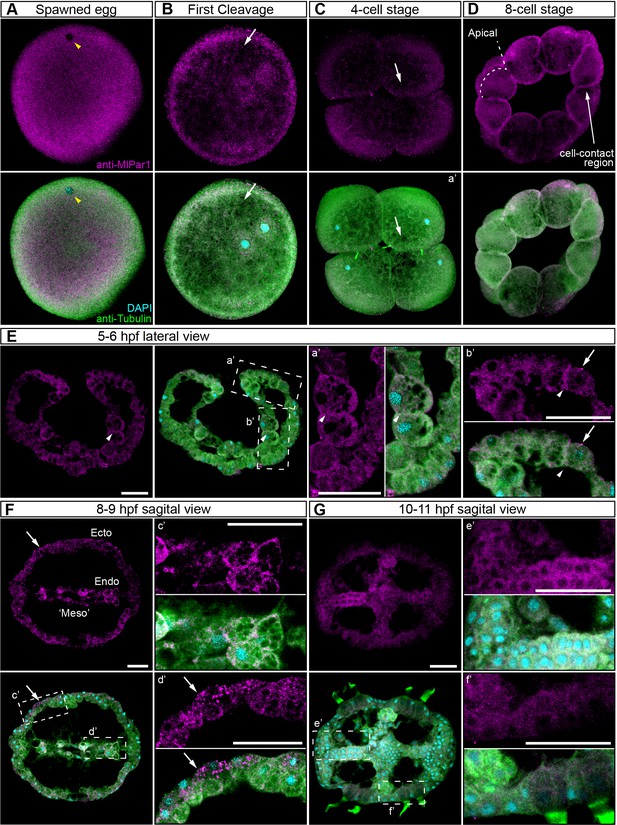
MlPar-1 protein subcellular localization during the early development of M. leidyi.
Immunostaining against MlPar-1 protein shows that this protein remains cytoplasmic during early cleavage stages (A–D). MlPar-1 protein appears as punctate aggregations distributed uniformly in the cytosol (white arrows). Yellow arrowhead indicates the zygote nucleus in (A). 8 cell-stage (D): A single optical section from a z-stack confocal series. MlPar-1 appears to be localized in the cortex at the cell-contact regions but this antibody signal was similar to its cytosolic distribution. (E–G) Between 5 and 11 hpf, MlPar-1 protein remains as punctate aggregations distributed uniformly in the cytosol (white arrows). a’ to f’ correspond to the magnifications of the regions depicted for each stage. (E) MlPar-1 appears to be localized in the cortex at the cell-contact regions (white arrowheads) but this antibody signal was similar to its cytosolic distribution. (F) MlPar-1 protein remains cytoplasmic in ectodermal cells (Ecto; c’), endodermal (Endo; d’), and ‘mesodermal’ (‘Meso’) cells. Images are maximum projections from a z-stack confocal series. Sagittal view of an 8–9 hpf embryo corresponds to a single optical section from a z-stack confocal series. Orientation axes are depicted in the figure. Morphology is shown by DAPI and tubulin immunostainings. The animal pole is towards the top. Scale bars: 20 µm.
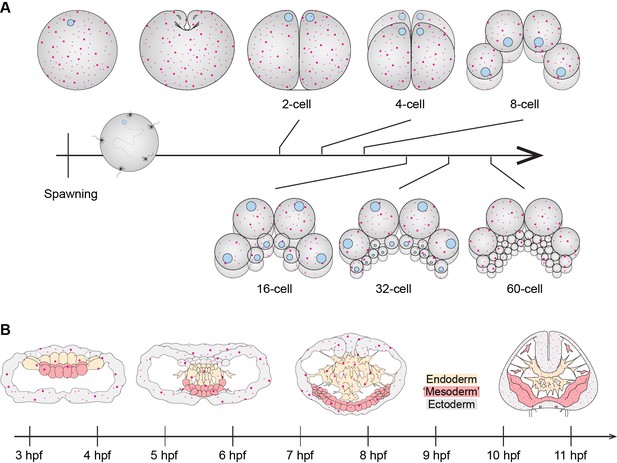
Diagram depicting the cortical localization of MlPar-1 (magenta).
(A) Cleavage stages and (B) gastrulation. (B) Ectoderm is colored in grey. Endoderm and ‘mesoderm’ are colored in yellow and red, respectively. Animal pole is to the top. For simplicity, most of the cell boundaries are not depicted.
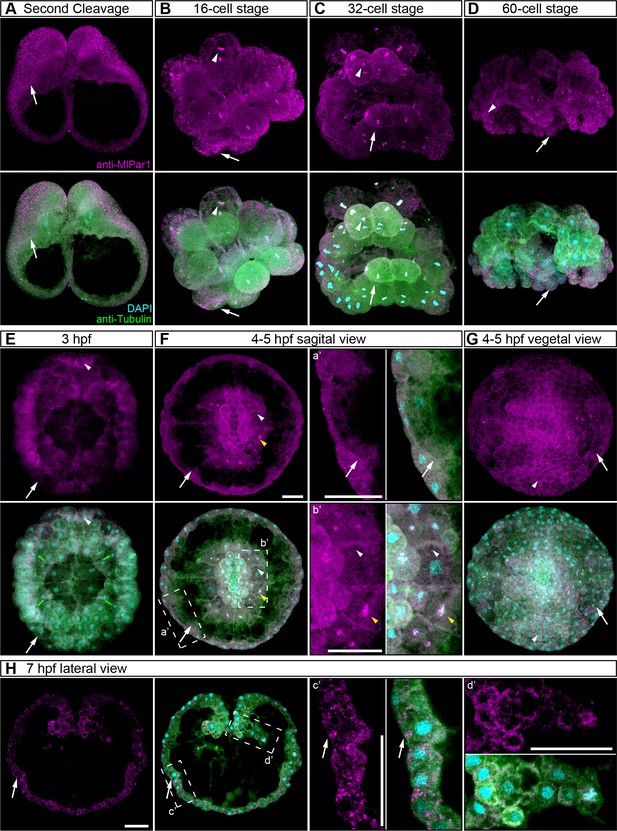
MlPar-1 localization during developmental stages complementary to Figure 3.
(A–D) Immunostaining against MlPar-1 during cleavage stages of M. leidyi development shows that MlPar-1 protein appears as punctate aggregations distributed uniformly in the cytosol (white arrows). White arrowheads indicate nuclear localization. (E–H) Between 3 hpf and 7 hpf, MlPar-1 protein remains as punctate aggregations distributed uniformly in the cytosol (white arrows). (E–G) MlPar-1 appears to be localized in the cortex at the cell-contact regions (white arrowheads) but this antibody signal was similar to its cytosolic distribution. Images are maximum projections from a z-stack confocal series. (E–H): a’ to d’ correspond to the magnifications of the regions depicted for each stage. Morphology is shown by DAPI and tubulin immunostainings. Yellow arrowheads indicate nuclear localization in (F). The animal pole is towards the top. Scale bars: 20 µm.
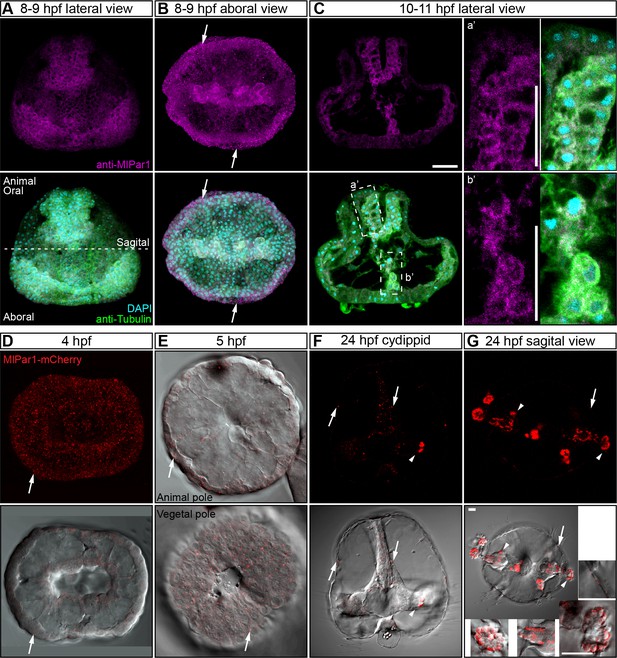
MlPar-1 protein remains cytoplasmic during M. leidyi development between 8 hpf and 11 hpf.
(A–C) MlPar-1 protein remains as punctate aggregations distributed uniformly in the cytosol (white arrows). Images are maximum projections from a z-stack confocal series. a’ and b’ correspond to the magnifications of the regions depicted for each stage. Morphology is shown by DAPI and tubulin immunostainings. The animal pole is to the top. Scale bars: 20 µm. (D–G) The overexpression of MlPar1-mCherry protein displays similar patterns observed with the antibody staining against the same protein, with no cortical localization observed after four hpf. White arrows indicate MlPar-1-mCherry protein cytosolic aggregates. White arrowhead indicates MlPar-1-mCherry protein aggregates in the tentacle apparatus. All images are maximum projections from a z-stack confocal series. Orientation of axes are depicted in the Figure.
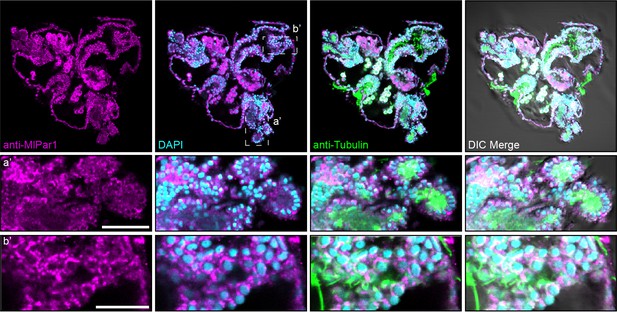
Immunofluorescent staining against MlPar-1 after 20 hpf.
The distribution of MlPar-1 in juvenile epithelium is cytosolic during later stages, similar to Figure 3—figure supplement 3F–G. Neither asymmetrical nor cortical localization was observed. a’ and b’ correspond to the magnifications of the regions depicted Morphology is shown by DIC, DAPI, and tubulin immunostainings. Scale bars: 20 µm.
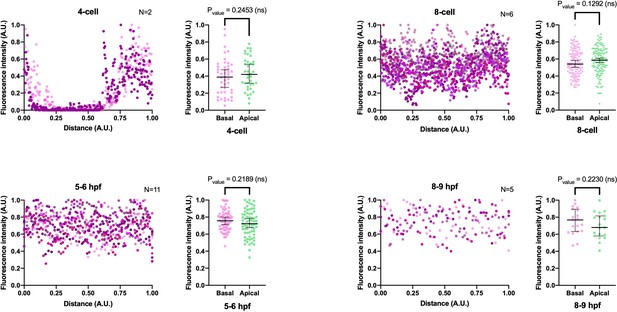
Fluorescent intensity measurements correspondent to Figure 3.
Fluorescent intensity (Y axis) was measured along the basal/apical axes (X axis) for the developmental stages reported in Figure 3. Numerical data can be found in Figure 3—figure supplement 5—source data 1 and 2. Median, 95% CI, and P values are depicted in the figure.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 5—source data 1
Numerical data that are represented as graphs in Figure 3—figure supplement 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54927/elife-54927-fig3-figsupp5-data1-v3.xlsx
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 5—source data 2
Numerical and statistical data that are represented as graphs in Figure 3—figure supplement 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54927/elife-54927-fig3-figsupp5-data2-v3.pzfx
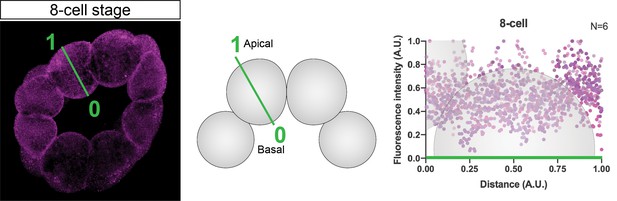
Schematic depiction of fluorescent intensity measurements correspondent to Figure 3.
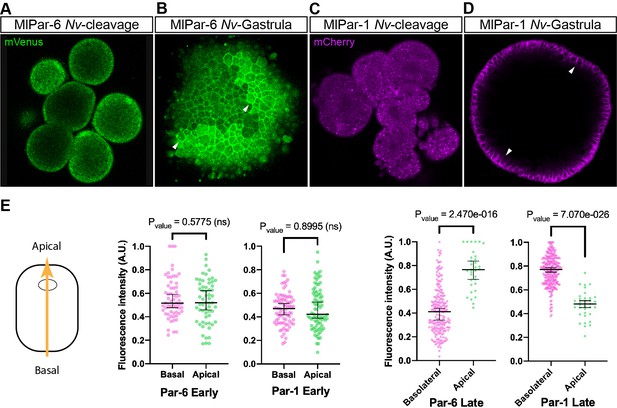
Expression of ctenophore MlPar6-mVenus and MlPar1-mCherry in embryos of the cnidarian N. vectensis.
The translated exogenous proteins display the same pattern than the previously described for endogenous N. vectensis proteins (A–D). White arrowheads indicate MlPar6-mVenus and MlPar1-mCherry cortical localization (B and D). All images are a single slice from a z-stack confocal series. (E) Graphical depiction of fluorescence intensity measurements between basal and apical cortex. The diagram at the left shows the direction of the measurements represented in this figure and in Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Median, 95% CI, and P values are depicted in the figure.
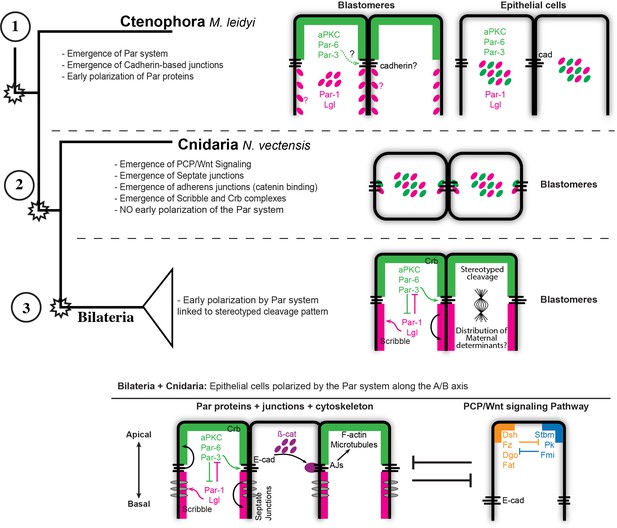
Evolution of cell polarity in Metazoa.
Diagram depicting the evolution of different interactions between known signaling pathways that organize cell polarity in animal cells (see references), including the new information obtained by this study during the early development of the ctenophore M. leidyi. Our results challenge the conception of a deep homology of the epithelial organization and the establishment of the apicobasal cell polarity in Metazoa.
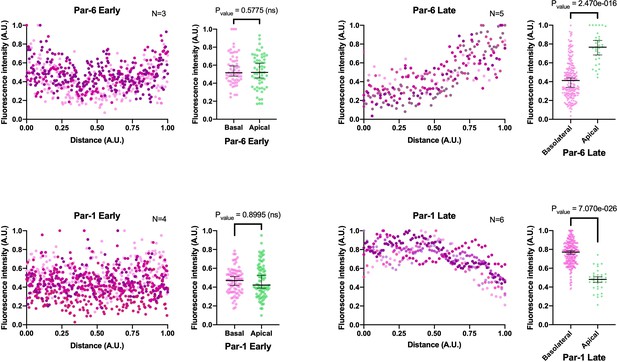
Fluorescent intensity measurements correspondent to Figure 4.
Fluorescent intensity (Y axis) was measured along the basal/apical axes (X axis) for the developmental stages reported in Figure 4. All measured cells display asymmetric localization of MlPar-6-mVenus and MlPar-1-mCherry during later stages. Median, 95% CI, and P values are depicted in the figure. Numerical data can be found in Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1 and 2.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Numerical data that are represented as graphs in Figure 4—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54927/elife-54927-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v3.xlsx
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 2
Numerical and statistical data that are represented as graphs in Figure 4—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54927/elife-54927-fig4-figsupp2-data2-v3.pzfx
Videos
Punctuate aggregates of MlPar-1-mCherry are highly dynamic.
2.5 min in vivo recording of a gastrula embryo at 40x.
Z-stack of MlPar-1-mCherry expression at 24 hpf at 40X.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Mouse Anti-alpha-Tubulin Monoclonal Antibody, Unconjugated, Clone DM1A | Sigma-Aldrich | T9026; RRID:AB_477593 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-MlPar-6 custom peptide antibody produced in rabbit | Bethyl labs; This study | Stored at MQ Martindale's lab; (1:100) | |
| Antibody | anti-MlPar-1 custom peptide antibody produced in rabbit | Bethyl labs; This study | Stored at MQ Martindale's lab; (1:100) | |
| Antibody | Goat anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 568 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11004; RRID:AB_2534072 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 647 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-21245; RRID:AB_2535813 | (1:250) |
| Other | DAPI (4',6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole, Dihydrochloride) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | D1306; RRID:AB_2629482 | (0.1 µg/µl) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dextran, Alexa Fluor 488; 10,000 MW, Anionic, Fixable | Thermo Fisher Scientific | D22910 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dextran, Alexa Fluor 555; 10,000 MW, Anionic, Fixable | Thermo Fisher Scientific | D34679 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dextran, Alexa Fluor 647; 10,000 MW, Anionic, Fixable | Thermo Fisher Scientific | D22914 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dextran, Cascade Blue, 10,000 MW, Anionic, Lysine Fixable | Thermo Fisher Scientific | D1976 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mlpar-6: F-GTACTGTGCTGTGTGTTTGGA; R- GTACTGTGCTGTGTGTTTGGA | Mnemiopsis Genome Project - NIH-NHGRI | MLRB351777 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mlpar-1: F- ATGTCAAATTCTCAACACCAC; R- CAGTCTTAATTCATTAGCTATGTTA | Mnemiopsis Genome Project - NIH-NHGRI | MLRB182569 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pSPE3-mVenus | Roure et al., 2007 | Gateway vector | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pSPE3-mCherry | Roure et al., 2007 | Gateway vector | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji (ImageJ) | NIH | http://fiji.sc | |
| Software, algorithm | Imaris 7.6.4 | Bitplane Inc |