Drug Discovery: From worms to fish to mice
Muscle contraction is a complicated process that starts with an electrical signal called an action potential entering a muscle cell, and ends with thin filaments sliding past thick filaments to make the cell shorter. A central part of this process involves the action potential activating a protein called a dihydropyridine (DHP) receptor, which then activates a calcium-ion channel called a ryanodine receptor. The activation of this channel in an organelle called the sarcoplasmic reticulum results in the release of calcium ions (Ca2+) into the cytoplasm of the cell. These ions go on to activate muscle contraction through a mechanism that involves promoting the interaction between thick and thin filaments (see Figure 1A).
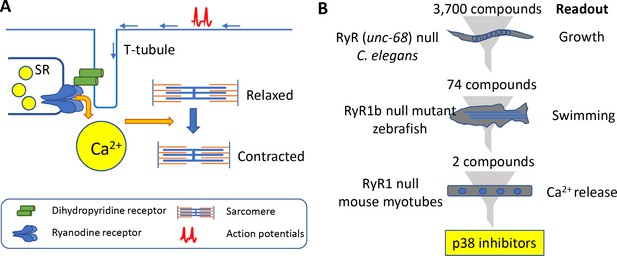
Muscle contraction and a 'multi-species discovery pipeline' for drug screening.
(A) Ryanodine receptor 1 (RyR1; blue) is a channel protein that releases calcium ions (yellow) from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) when activated by a dihydropyridine receptor (DHP; green). Muscle tissue contains thick filaments (blue) and thin filaments (orange) arranged in units called sarcomeres. The calcium ions cause structures on the thick filaments called myosin heads (not shown) to bind to the thin filaments and pull them so that the muscle contracts. The DHP receptor is activated by action potentials (red spikes) travelling along a structure called a T-tubule (blue). (B) Drug screening was performed sequentially using null mutants in C. elegans (top), zebrafish (middle), and mouse myotubes (bottom). A screen of 3700 compounds in C. elegans identified 74 compounds that enabled the mutants to grow. Testing many of these 74 compounds on zebrafish revealed two compounds that improved the swimming performance of the mutant animals. Both compounds were known to be inhibitors of a protein kinase called p38, and both were found to induce the release of calcium ions in mutant mouse muscle cells.
Congenital muscle diseases in humans can result from mutations in at least 20 genes, but mutations in the gene for ryanodine receptor 1 (RyR1) are the most common cause of such myopathies (Jungbluth et al., 2018; Robinson et al., 2006). Mutations in this gene cause malignant hyperthermia (a rare severe reaction that can occur during anesthesia), central core disease and a range of other myopathies that can result in severe disabilities and early mortality. There are currently no effective therapies for any of these conditions. Now, in eLife, James Dowling (Hospital for Sick Children and the University of Toronto) and colleagues – including Jonathan Volpatti as first author – report how they have used a 'multi-species discovery pipeline' to identify two compounds that might be effective in treating these patients (Volpatti et al., 2020).
The pipeline involved three species: the worm C. elegans, the zebrafish and mouse cells (see Figure 1B). C. elegans has just one type of ryanodine receptor (humans have three) and mutants that lack unc-68, the gene for this receptor, move much less than wild-type worms (Maryon et al., 1996). To make the phenotype more robust, Volpatti et al. exposed the mutant animals to a DHP inhibitor called nemadipine-A that induces larval growth arrest in mutant animals but not in wild-type animals. The researchers screened 3700 compounds to identify those that permitted mutant worms that had been exposed to nemadipine-A to reach adulthood. Initially, the screen revealed 278 compounds, but this number dropped to 74 after additional testing. Compounds that inhibited a protein kinase called p38 were over-represented in this sample. To explore if off-target effects might be responsible for their results, Volpatti et al. used RNAi to knock-down orthologs of p38 in worms. Again the mutant worms reached adulthood, confirming that the results were likely due to p38 being inhibited and not due to off-target effects.
Many of the 74 compounds identified from the worm screen were then tested for their ability to improve the movement of zebrafish that lacked a gene called ryr1b that encodes one of the ryanodine receptors: these mutants are normally poor swimmers (Hirata et al., 2007). Two of the p38 inhibitors were successful.
Volpatti et al. then moved to a mouse cell line called C2C12. These cells are myoblasts that can be differentiated into mature functional muscle cells, and the researchers used CRISPR/Cas9 to create mutants in which the gene Ryr1 had been knocked out. When caffeine is administered to wild-type C2C12 cells they release calcium ions, but this does not happen with the mutant cells. However, when the mutant cells were treated with either of the p38 inhibitors, they released calcium ions. The researchers verified that the two compounds were likely specifically inhibiting p38 by observing the release of calcium ions from the knockout cells when any one of the three isoforms of p38 were knocked down by siRNA.
The role of p38 during the formation of muscle tissue has been studied intensively. p38 activates various factors that regulate muscle formation (Keren et al., 2006); it also activates adult muscle stem cells and promotes their self-renewal (Jones et al., 2005). Thus, p38 has been proposed as a potential therapeutic target for muscular dystrophies. Activation of p38 has been detected in mouse models of two forms of muscular dystrophy (Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy R6). Moreover, deletion of the gene for the alpha isoform of p38 results in reduced myopathy in both muscular dystrophy models via the inhibition of apoptosis (Wissing et al., 2014). Although the role of p38 in the pathology of the various myopathies related to RyR1 is not explored by Volpatti et al., the inhibition of apoptosis or the regulation of muscle formation may not be relevant, since their results were obtained on fully differentiated muscle cells. A more likely explanation is that p38 inhibition results in increased expression or activity of other Ca2+ channels.
A weakness of this study is that the screens were conducted on models that completely lack expression of RyR1, whereas none of the patients with malignant hyperthermia or RyR1-related myopathies are nulls. Recognizing this problem, Volpatti et al. plan to re-do their screens on mice or cells carrying missense mutations analogous to those found in malignant hyperthermia (Lopez et al., 2018), or the more complex mutations found in patients with RyR1-related myopathies (see, for example, Brennan et al., 2019). An intriguing question is how can the inhibition of p38 result in the release of more Ca2+ in animals or cells that have no RyR1 expression? As mentioned in the previous paragraph, it is possible that the inhibition of p38 increases the release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum through other Ca2+channels such as the IP3R and STIM1/ORAI1 channels (which are found in both C. elegans and C2C12 cells), and RyR3 channel, which is also found in C2C12 cells.
Volpatti et al. conducted their drug screens rapidly and in mutant animals displaying phenotypes relevant to those found in human patients. For example, the screen of 3700 compounds in C. elegans was completed in just two weeks.
It is likely that their strategy of screening in C. elegans first, followed by zebrafish and cultured cells, could be used to screen drugs for many human genetic diseases that are due to mutations in proteins with orthologs in C. elegans. (About 40% of C. elegans proteins have human orthologs). This is particularly true for human diseases that display developmental or neuromuscular defects, as development is fast (fertilized egg to adult in three days) and occurs in distinct stages (embryo, four larval stages and adult), and there are powerful methods for studying the locomotion of these animals (see, for example, Restif et al., 2014). This presages another case in which worms will lead the way!
References
-
Mouse model of severe recessive RYR1-related myopathyHuman Molecular Genetics 28:3024–3036.https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddz105
-
The p38α/ß MAPK functions as a molecular switch to activate the quiescent satellite cellJournal of Cell Biology 169:105–116.https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200408066
-
Congenital myopathies: disorders of excitation-contraction coupling and muscle contractionNature Reviews Neurology 14:151–167.https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.191
-
The p38 MAPK signaling pathway: a major regulator of skeletal muscle developmentMolecular and Cellular Endocrinology 252:224–230.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2006.03.017
-
unc-68 encodes a ryanodine receptor involved in regulating C. elegans body-wall muscle contractionJournal of Cell Biology 134:885–893.https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.134.4.885
-
P38α MAPK underlies muscular dystrophy and myofiber death through a Bax-dependent mechanismHuman Molecular Genetics 23:5452–5463.https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu270
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: May 6, 2020 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2020, Benian and Choo
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 1,047
- views
-
- 113
- downloads
-
- 2
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Medicine
Irisin, released from exercised muscle, has been shown to have beneficial effects on numerous tissues but its effects on bone are unclear. We found significant sex and genotype differences in bone from wildtype (WT) mice compared to mice lacking Fndc5 (knockout [KO]), with and without calcium deficiency. Despite their bone being indistinguishable from WT females, KO female mice were partially protected from osteocytic osteolysis and osteoclastic bone resorption when allowed to lactate or when placed on a low-calcium diet. Male KO mice have more but weaker bone compared to WT males, and when challenged with a low-calcium diet lost more bone than WT males. To begin to understand responsible molecular mechanisms, osteocyte transcriptomics was performed. Osteocytes from WT females had greater expression of genes associated with osteocytic osteolysis and osteoclastic bone resorption compared to WT males which had greater expression of genes associated with steroid and fatty acid metabolism. Few differences were observed between female KO and WT osteocytes, but with a low-calcium diet, the KO females had lower expression of genes responsible for osteocytic osteolysis and osteoclastic resorption than the WT females. Male KO osteocytes had lower expression of genes associated with steroid and fatty acid metabolism, but higher expression of genes associated with bone resorption compared to male WT. In conclusion, irisin plays a critical role in the development of the male but not the female skeleton and protects male but not female bone from calcium deficiency. We propose irisin ensures the survival of offspring by targeting the osteocyte to provide calcium in lactating females, a novel function for this myokine.
-
- Medicine
- Microbiology and Infectious Disease
Background:
End-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients experience immune compromise characterized by complex alterations of both innate and adaptive immunity, and results in higher susceptibility to infection and lower response to vaccination. This immune compromise, coupled with greater risk of exposure to infectious disease at hemodialysis (HD) centers, underscores the need for examination of the immune response to the COVID-19 mRNA-based vaccines.
Methods:
The immune response to the COVID-19 BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine was assessed in 20 HD patients and cohort-matched controls. RNA sequencing of peripheral blood mononuclear cells was performed longitudinally before and after each vaccination dose for a total of six time points per subject. Anti-spike antibody levels were quantified prior to the first vaccination dose (V1D0) and 7 d after the second dose (V2D7) using anti-spike IgG titers and antibody neutralization assays. Anti-spike IgG titers were additionally quantified 6 mo after initial vaccination. Clinical history and lab values in HD patients were obtained to identify predictors of vaccination response.
Results:
Transcriptomic analyses demonstrated differing time courses of immune responses, with prolonged myeloid cell activity in HD at 1 wk after the first vaccination dose. HD also demonstrated decreased metabolic activity and decreased antigen presentation compared to controls after the second vaccination dose. Anti-spike IgG titers and neutralizing function were substantially elevated in both controls and HD at V2D7, with a small but significant reduction in titers in HD groups (p<0.05). Anti-spike IgG remained elevated above baseline at 6 mo in both subject groups. Anti-spike IgG titers at V2D7 were highly predictive of 6-month titer levels. Transcriptomic biomarkers after the second vaccination dose and clinical biomarkers including ferritin levels were found to be predictive of antibody development.
Conclusions:
Overall, we demonstrate differing time courses of immune responses to the BTN162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in maintenance HD subjects comparable to healthy controls and identify transcriptomic and clinical predictors of anti-spike IgG titers in HD. Analyzing vaccination as an in vivo perturbation, our results warrant further characterization of the immune dysregulation of ESRD.
Funding:
F30HD102093, F30HL151182, T32HL144909, R01HL138628. This research has been funded by the University of Illinois at Chicago Center for Clinical and Translational Science (CCTS) award UL1TR002003.






