Neuronal hyperexcitability is a DLK-dependent trigger of herpes simplex virus reactivation that can be induced by IL-1
Figures
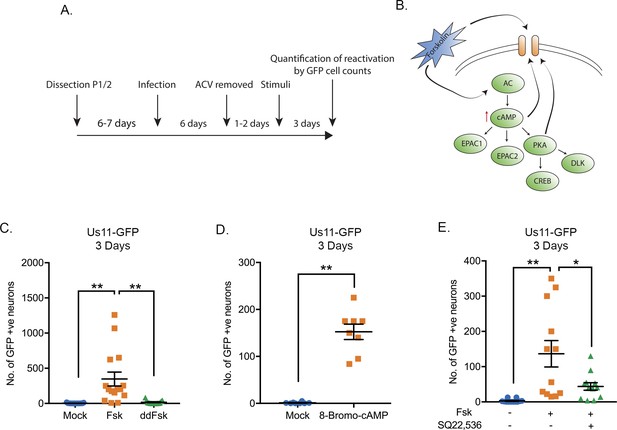
HSV-1 Reactivation from sympathetic neurons is induced by adenylate cyclase activation.
(A) Schematic of the primary sympathetic superior cervical ganglia (SCG)-derived model of HSV latency. Reactivation was quantified based on Us11-GFP-positive neurons in presence of WAY-150168, which prevents cell-to-cell spread. (B) Schematic of the cellular pathways activated by forskolin treatment. Forskolin can act both intracellularly to activate adenylate cyclase (AC) and increasing the levels of cAMP or extracellularly on ion channels. (C) Numbers of Us11-GFP-positive neurons following addition of either forskolin (60 μM) or cell-impermeable dideoxy-forskolin (60 μM) treatment of latently-infected sympathetic neurons. (D) Numbers of Us11-GFP-positive neurons following treatment with a cAMP mimetic 8-Bromo-cAMP (125 μM). (E) Reactivation, quantified by Us11-GFP-positive neurons, was induced by forskolin in the presence or absence of the adenylate cyclase inhibitor SQ22,536 (50 μM). In C-E each point represents a single biological replicate, and the mean and standard errors of the mean (SEM) are also shown. In D statistical comparisons were made using an unpaired t-test. In C and E statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey's multiple comparisons test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Quantification of GFP-positive neurons for Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig1-data1-v3.xlsx
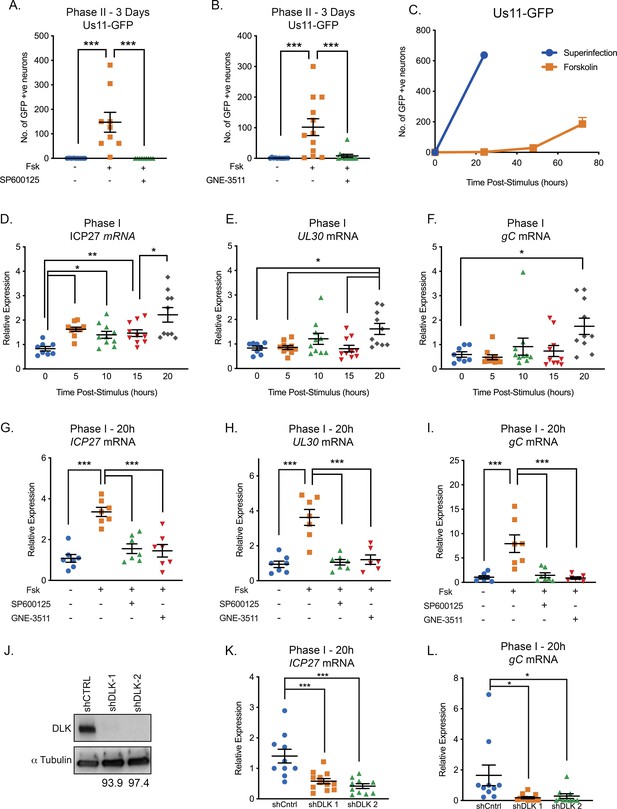
Reactivation triggered by forskolin involves a DLK/JNK-dependent phase I of viral gene expression.
(A) Reactivation was induced by forskolin in the presence of JNK inhibitor SP600125 (20 μM). (B) Reactivation was induced by forskolin in the presence of the DLK inhibitor GNE-3511 (4 μM). In A and B each experimental replicate is shown. (C) Reactivation was induced by forskolin or superinfection with a wild-type (F strain) HSV-1 (MOI of 10 PFU/cell) and qualified based on Us11-GFP-positive neurons (n = 3). (D–F) RT-qPCR for viral mRNA transcripts following forskolin treatment of latently infected SCGs. (G–I) RT-qPCR for viral lytic transcripts at 20 hr post-forskolin treatment and in presence of the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (20 μM) and the DLK inhibitor GNE-3511 (4 μM). (J) Neurons were transduced with a non-targeting shRNA control lentivirus or two independent lentiviruses expressing shRNAs that target DLK (shDLK-1, shDLK-2). Western-blotting for DLK or β-III tubulin was carried out 3 days post transduction. The percentage knock-down of DLK normalized to β-III tubulin is shown. (K and L) RT-qPCR for viral mRNA transcripts following forskolin treatment of latently infected SCGs that were either transduced with the shRNA control or shRNA DLK lentiviruses. In D-I, K, and L, each experimental replicate is represented. Statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. The mean and SEM are shown.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Quantification of GFP-positive neurons, RT-qPCR and western blot band densities for Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig2-data1-v3.xlsx
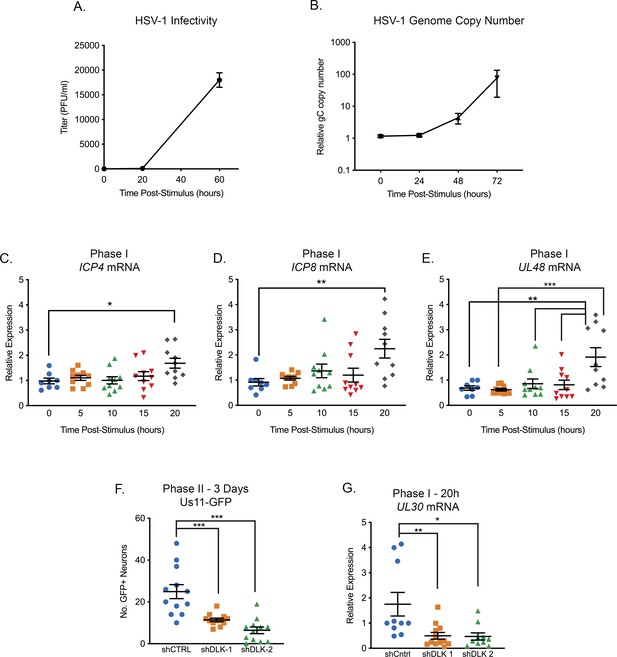
Reactivation triggered by forskolin triggers a wave of lytic gene expression that precedes DNA Replication and infectious virus production.
(A) Titers of infectious virus detected from reactivating neurons induced with forskolin (n = 4). (B) Quantification of the relative viral genome copy number following forskolin-mediated reactivation based on gC copy number normalized to cellular GAPDH and expressed relative to the 0 hr time-point (n = 7). (C–E) RT-qPCR for viral mRNA transcripts following forskolin treatment of latently infected SCGs. (F) Quantification of Us11-GFP neurons and (G) RT-qPCR for UL30 mRNA transcript following forskolin treatment of latently infected SCGs that were either transduced with the shRNA control or shRNA DLK lentiviruses. Statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (C–E) In C-G each biological replicate is represented. The means and SEMs are shown.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantification of HSV titer, GFP-positive neurons and RT-qPCR for Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v3.xlsx
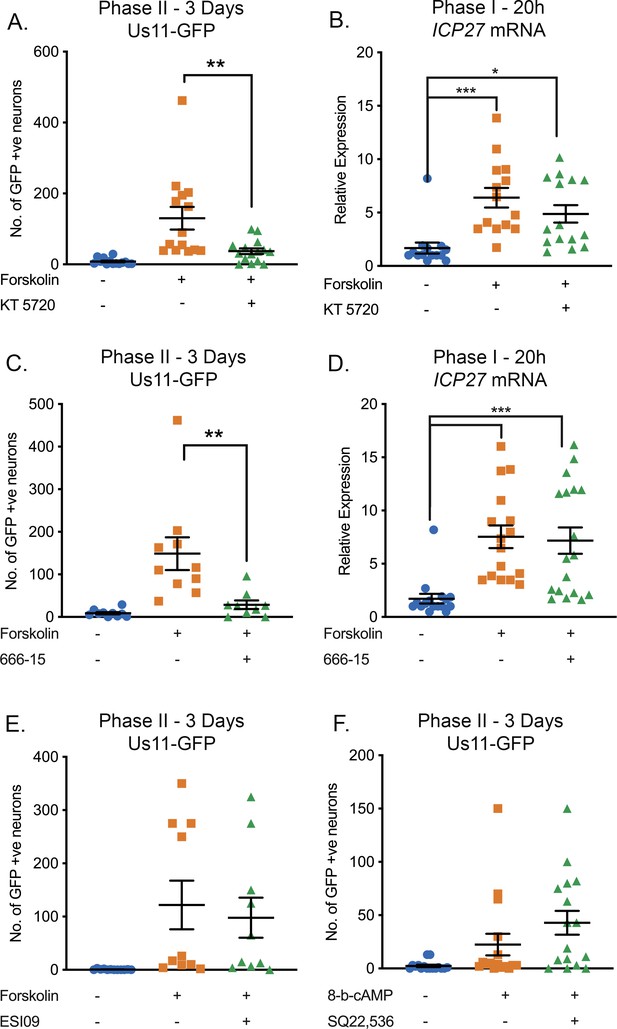
Effect of PKA, CREB, Rapgef2 and EPAC Inhibition on HSV-1 Reactivation.
(A) Latently infected cultures were reactivated with forskolin (60 μM) in the presence of the PKA inhibitor KT 5720 (3 µM) and the number of Us11-GFP-positive neurons quantified at 3 days post-reactivation. (B) RT-qPCR for the viral lytic transcript ICP27 at 20 hr post-forskolin treatment and in the presence of KT 5720. (C) Latently infected cultures were reactivated with forskolin in the presence of the CREB inhibitor 666–15 (2 µM). (D) RT-qPCR for ICP27 at 20 hr post-forskolin treatment and in the presence of 666–15. (E) Latently infected cultures were reactivated with forskolin (60 μM) in the presence of the EPAC inhibitor ESI09 (10 µM). (F) Latently infected cultures were reactivated with 8-Bromo-cAMP (125 μM) in the presence of the Rapgef2 inhibitor SQ22,536 (50 µM). Individual experimental replicates are represented along with the means and SEMs. Statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Quantification of GFP-positive neurons and RT-qPCR for Figure 2—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig2-figsupp2-data1-v3.xlsx
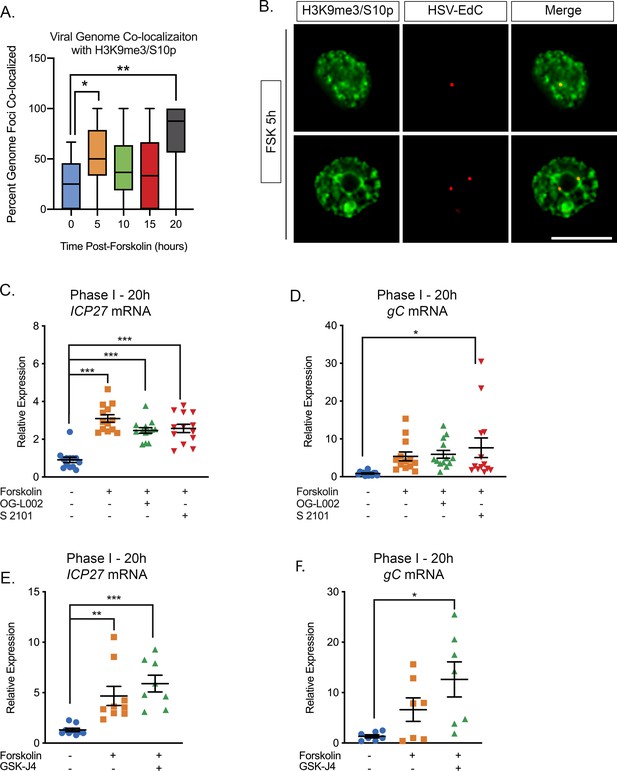
The Initial wave of viral lytic gene expression during forskolin-mediated reactivation is independent on histone demethylase activity.
(A) Quantification of the percentage of genome foci stained using click-chemistry that co-localize with H3K9me3/S10p. At least 15 fields of view with 1–8 genomes per field of view were blindly scored from two independent experiments. Data are plotted around the median, with the boxes representing the 25th–75th percentiles and the whiskers the 1st-99th percentiles. (B) Representative images of click-chemistry based staining of HSV-EdC genomes and H3K9me3/S10p staining at 5 hr post-forskolin treatment. (C and D). Effect of the LSD1 inhibitors OG-L002 and S 2101 on forskolin-mediated Phase I of reactivation determined by RT-qPCR for ICP27 (C) and gC (D) viral lytic transcripts at 20 hr post-forskolin treatment and in the presence of 15 μM OG-L002 and 20 μM S 2102. (E) Effect of the JMJD3 and UTX inhibitor GSK-J4 (2 μM) on forskolin-mediated Phase I measured by RT-qPCR for viral lytic transcripts ICP27 (E) and gC (F) at 20 hr post-forskolin treatment and in the presence of GSK-J4. For C-F each experimental replicate along with the mean and SEM is represented. (C–F). Statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Quantification of genome co-localization and RT-qPCR for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig3-data1-v3.xlsx
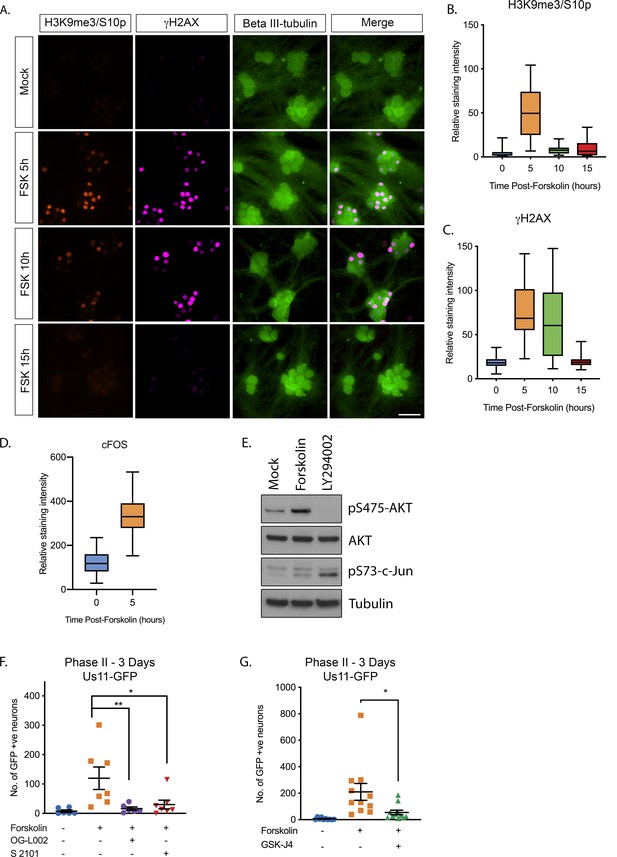
Forskolin induces hyperexcitability-associated chromatin changes, and hsv reactivation that requires histone demethylase.
(A) SCG neurons were treated with forskolin and immunofluorescence staining was carried out for H3K9me3/S10p, the DNA damage marker γH2AX and the neuronal marker beta III-tubulin. (B) Quantification of neuronal nuclear staining intensity for H3K9me3 (>150 cells/condition). (C) Quantification of neuronal nuclear staining for γH2AX. In B and C data are plotted around the median and whiskers represent the 2.5–97.5 percentile range. (D). Western blotting for pS475-AKT, total AKT, pS73-c-Jun and tubulin at 15 hr post-treatment with the PI3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 (20 µM) or forskolin (60 µM) (E). Effect of the LSD1 inhibitors OG-L002 (15 μM) and S 2101 (20μM) on forskolin-mediated reactivation measured by Us11-GFP-positive neurons (F). Effect of the JMJD3 and UTX inhibitor GSK-J4 (2 μM) on forskolin-mediated reactivation measured by Us11-GFP-positive neurons (G). Statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (E, F). In E and F individual experimental replicates are shown along with the mean and SEM.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantification of nuclear staining intensity and GFP-positive neurons Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v3.xlsx
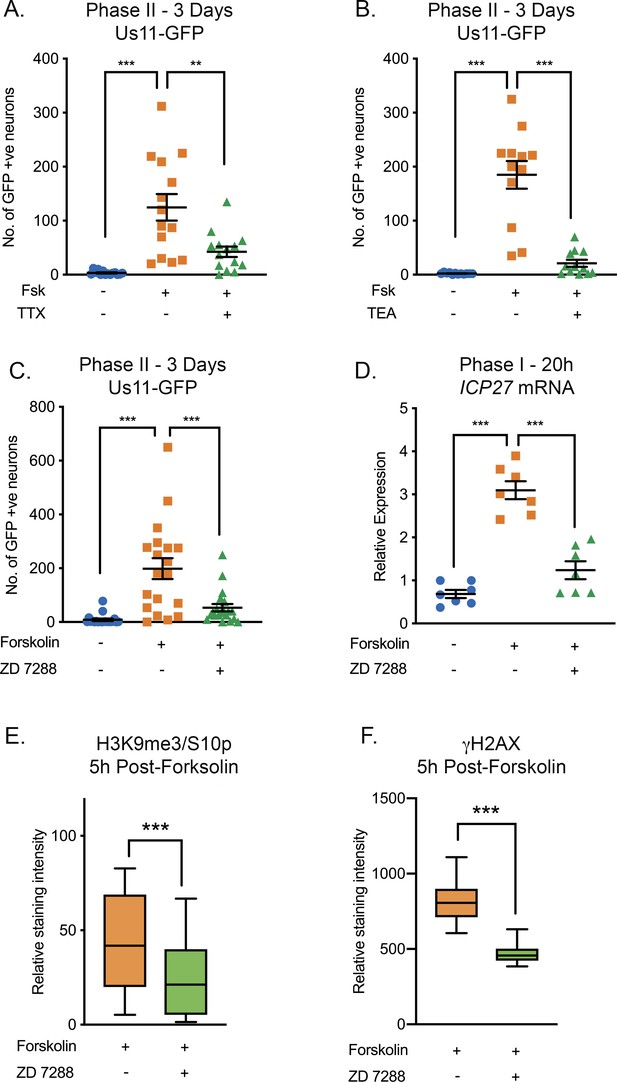
HSV Reactivation Mediated by Forskolin Requires Neuronal Excitability.
(A) Latently infected cultures were reactivated with forskolin in the presence of the voltage-gated sodium channel blocker tetrodotoxin (TTX; 1 µM) and the number of Us11-GFP-positive neurons quantified at 3 days post-reactivation. (B) Latently infected cultures were reactivated with forskolin in the presence of the voltage-gated potassium channel blocker tetraethylammonium (TEA; 10 mM) and the number of Us11-GFP-positive neurons quantified at 3 days post-reactivation. (C) Forskolin-mediated reactivation in the presence of the HCN channel blockers ZD 7288 (10μM) quantified as the numbers of Us11-GFP-positive neurons at 3 days post-reactivation. (D) The effect of ZD 7288 on the HSV lytic gene transcript ICP27 during Phase I reactivation measured at 20 hr post-forskolin treatment by RT-qPCR. In A-D individual experimental replicates are represented along with the mean and SEM. (E and F) Quantification of the relative nuclear staining for H3K9me3/S10p and γH2AX in SCG neurons at 5 hr post-forskolin treatment and in the presence of ZD 7288 from >800 cells/condition from two independent experiments. Data are plotted around the mean, with the boxes representing the 25th-75th percentiles and the whiskers the 5st-95th percentiles. Statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison (A–D) or two-tailed unpaired t-test (E–F). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. In A-D individual experimental replicates are represented.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Quantification of GFP-positive neurons, RT-qPCR and nuclear staining intensity for Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig4-data1-v3.xlsx

HSV Reactivation Mediated by Forskolin Requires Neuronal Excitability.
(A and B) Latently infected cultures were reactivated with forskolin in the presence of the HCN channel inhibitors ivabradine (20 µM; A) and CsCl (3 mM; B). Latently infected cultures were reactivated with forskolin in the presence of the HCN inhibitor ZD 7288 (10 µM) and viral lytic transcripts measured at 20 hr post-reactivation (C and D). Individual experimental replicates are represented in addition to the mean and SEM. Statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantification of GFP-positive neurons and RT-qPCR for Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v3.xlsx
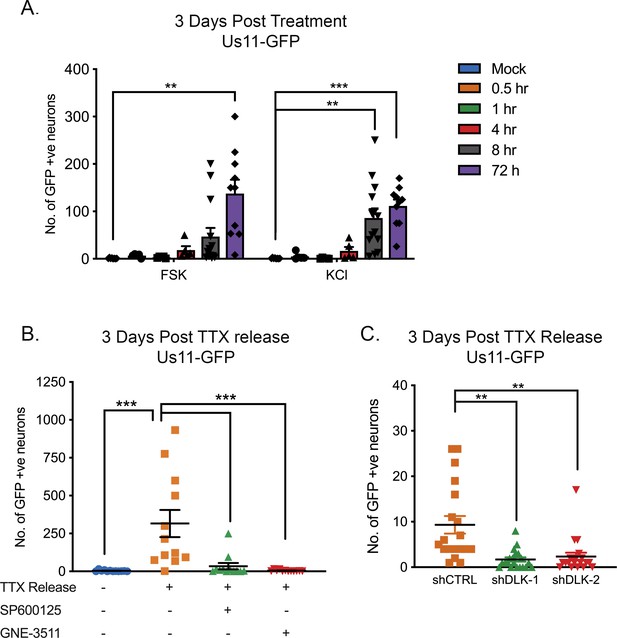
HSV Reactivation triggered by prolonged neuronal hyperexcitability is DLK/JNK-dependent.
(A) Latently infected SCG cultures were treated with forskolin or KCl (55 mM) for the indicated times followed by wash-out. Reactivation was quantified by number of Us11-GFP-positive neurons at 3 days after the initial stimulus was added. (B) Latently infected neurons were placed in tetrodotoxin (TTX; 1 μM) for 2 days and the TTX was then washed out. At the time of wash-out the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (20 μM) or DLK inhibitor GNE-3511 (4 μM) was added. (C) Latently infected neurons were transduced with either control non-targeting shRNA or shRNA targeting DLK for 3 days, then placed in tetrodotoxin (TTX; 1 μM) for 2 days and the TTX was then washed out. Reactivation was quantified at 3 days post-wash-out. Individual experimental replicates, the mean and SEMs are represented. Statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Quantification of GFP-positive neurons for Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig5-data1-v3.xlsx
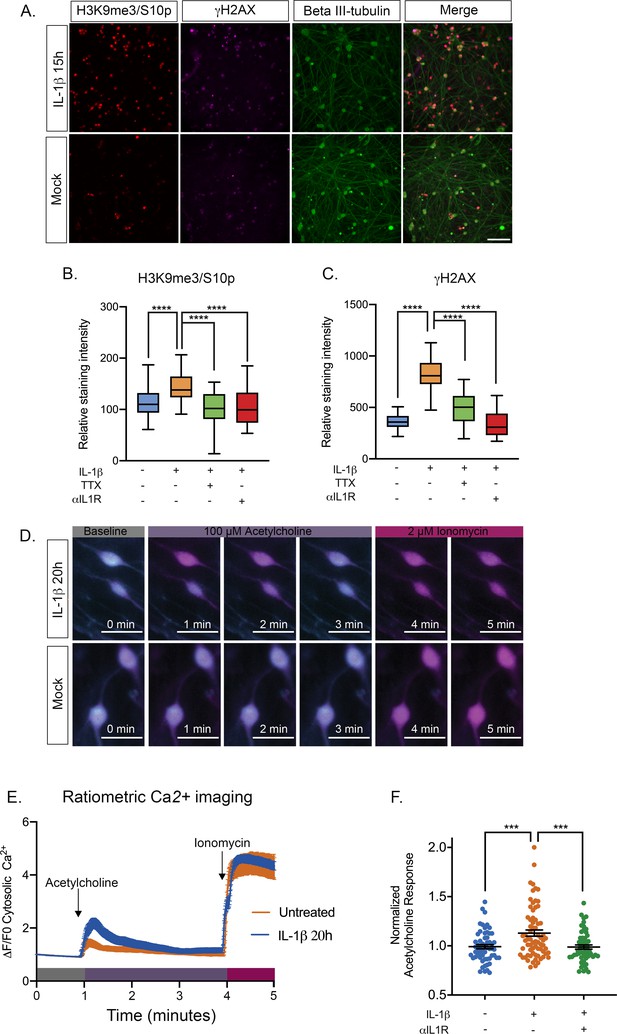
IL-1β Treatment of sympathetic neurons results in changes consistent with heightened neuronal excitability.
(A) Adult P36 SCG neurons were treated with IL-1β (30 ng/mL) for 15 hr and stained for H3K9me3/S10p, γH2AX and beta II-tubulin to mark neurons. (B and C) Quantification of the intensity of H3K9me3/S10p (B) and γH2AX (C) staining following 15 of IL-1β treatment and in the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX; 1 μM) or anti-IL1 receptor (IL-1R) blocking antibody (2 μg/mL). Data are plotted around the median and whiskers represent the 5th-95th percentiles. (D) Representative images of cytosolic Ca2+ elevations measured using Fura-2-AM in neurons stimulated with 100 µM acetylcholine either pre-treated with IL-1β for 20 hr or mock treated. As a control the neurons were also treated with Ionomycin at the end of the protocol. Bar = 100 μm. (E) Representative experiment for cytosolic Ca2+ elevations in neurons stimulated with 100 µM acetylcholine. Cells were pretreated with IL-1β or vehicle for 20 hr prior to imaging. The plotted values were calculated as a change in fluorescence/initial fluorescence (ΔF/F0). Error bars represent SEM (IL-1β treatment, n = 58 cells and vehicle control, n = 25 cells). (F) Peak cytosolic Ca2+ elevations normalized to untreated controls in neurons stimulated with 100 µM acetylcholine. Cells were pretreated with IL-1β (n = 70, wells) or vehicle (n = 58, wells) for 20 hr prior to imaging. IL-1R blocking antibody (n = 54, wells) was also added. Data points represent individual wells, horizontal line represents mean. Statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison (B–D). ***p<0.001 ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Quantification of nuclear staining intensity and ratiometric calcium imaging for Figure 6.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig6-data1-v3.xlsx
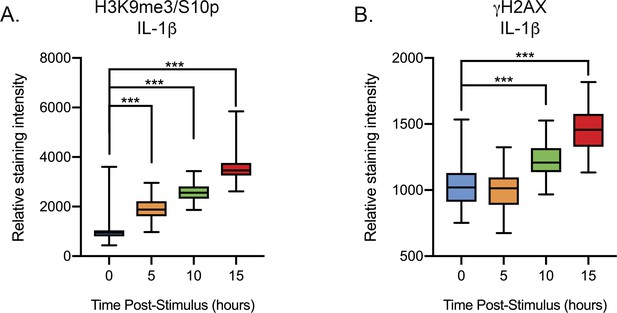
IL-1β Treatment of mature scg neurons induces excitability-associated histone post-translational modifications (supplement to Figure 6).
Quantification of the nuclear staining intensity in P36 sympathetic neurons for H3K9me3/S10 (A) and γH2AX (B) following treatment with IL-1β (30 ng/mL) from 150 nuclei from two independent experiments. Data are plotted around the median and whiskers represent the 5th-95th percentile.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantification of nuclear staining intensity for Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v3.xlsx
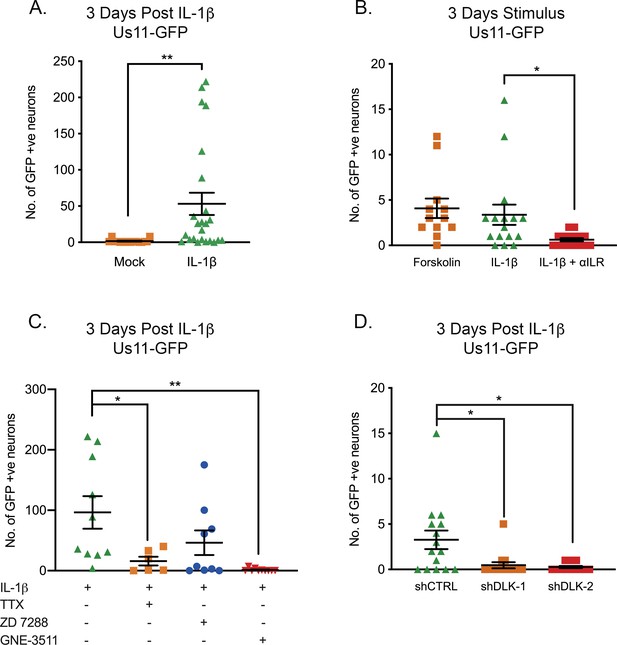
IL-1β-Induced HSV Reactivation is linked to heightened neuronal excitability and dlk activation.
(A) Quantification of Us11-GFP expressing neurons following addition of IL-1β to latently infected cultures of mature SCG neurons. (B) Numbers of Us11-GFP-positive neurons following addition of forskolin or IL-1β to mature SCG neurons, and in the presence of an IL-1R-blocking antibody (2 μg/mL). (C) Quantification of IL-1β induced reactivation in the presence of the voltage-gated sodium channel blocker TTX (1 μM), the HCN-channel blocker ZD 7288 (10 μM) and the DLK inhibitor GNE-3511 (4 μM). (D) Latently infected SCG neurons were transduced with an shRNA control lentivirus or lentiviruses expressing shRNA against DLK. Three days later IL-1β was added to the cultures and the numbers of GFP-positive neurons quantified at 3 days later. Individual experimental replicates, means and SEMs are represented. Statistical comparisons were made using two-tailed unpaired t-test (A) or a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison (B–D). *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Quantification of GFP-positive neurons for Figure 7.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-fig7-data1-v3.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus, M/F) | CD1 | Charles River | Crl:CD1(ICR) | |
| Strain, strain background (Human herpesvirus 1) | HSV Us11-GFP | I gift from Ian Mohr, NYU. PMID:12915535 | ||
| Strain, strain background (Human herpesvirus 1) | HSV-1 17syn+ | A gift from Roger Everett, MRC Virology Unit Glasgow | ||
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | 293LTV | Cell Biolabs | Cat # LTV-100 RRID:CVCL_JZ09 | |
| Cell line (Cercopithecus aethiops) | Vero | ATCC | Cat # CCCL-81 RRID:CVCL_0059 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCMV-VSV-G | A gift from Bob Weinberg/Addgene PMID:12649500 | Cat # 8454 RRID:Addgene_8454 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | psPax2 | A gift from Didier Trono/Addgene | Cat # 12260 RRID:Addgene_12260 | |
| Antibody | Anti-phospho-Akt (S473) (Rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signalling Technologies | Cat # 4060 RRID:AB_2315049 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-Akt (pan) (Rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signalling Technologies | Cat # C67E7 RRID:AB_915783 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-phopsho-c-Jun (Rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signalling Technologies | Cat # 3270 RRID:AB_2129575 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-DLK/MAP3K12 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher | PA5-32173 RRID:AB_2549646 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-a-tubulin (Mouse monoclonal) | Millipore sigma | Cat # T9026 RRID:AB_477593 | WB (1:2500) |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit IgG Antibody (H+L), Peroxidase (Goat polyclonal) | Vector Labs | Cat # PI-1000 RRID:AB_2336198 | WB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG Antibody (H+L), Peroxidase (Horse polyclonal) | Vector Labs | Cat # PI-2000 RRID:AB_2336177 | WB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | Anti- H3K9me3S10P (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat # Ab5819 RRID:AB_305135 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-Beta-III Tubulin (Chicken polyclonal) | Millipore Sigma | Cat # AB9354 RRID:AB_570918 | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-γH2A.X (Mouse monoclonal) | Cell Signalling Technologies | Cat # 80312 RRID:AB_2799949 | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-c-Fos (Rabbit polyclonal) | Novus | Cat # NB110-75039 RRID:AB_1048550 | IF (1:125) |
| Antibody | F(ab’)2 Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Alexa Fluor 647, (Goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher | Cat # A21237 RRID:AB_2535806 | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | F(ab’)2 Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Alexa Fluor 555 (Goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher | Cat # A21425 RRID:AB_2535846 | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Chicken IgY (H+L) Alexa Fluor 647 (Goat pAb) | Abcam | Cat # Ab150175 RRID:AB_2732800 | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Chicken IgY (H+L) Alexa Fluor 488 (Goat polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat # Ab150173 RRID:AB_2827653 | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | F(ab’)2 Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Alexa Fluor 488 (Goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher | Cat # A-11070 RRID:AB_2534114 | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Mouse IL-1R (Goat polyclonal) | Leinco Technologies | Cat # I-736 RRID:AB_2830857 | Blocking (2 ug/mL) |
| Sequence-based reagent | mGAP F | PMID:19515781 | PCR primers | CATGGCCTTCCGTGTGTTCCTA |
| Sequence-based reagent | mGAP R | PMID:19515781 | PCR primers | GCGGCACGTCAGATCCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | ICP27 F | PMID:21285374 | PCR primers | GCATCCTTCGTGTTTGTCATTCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ICP27 R | PMID:21285374 | PCR primers | GCATCTTCTCTCCGACCCCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ICP8 F | PMID:23322639 | PCR primers | GGAGGTGCACCGCATACC |
| Sequence-based reagent | ICP8 R | PMID:23322639 | PCR primers | GGCTTAAATCCGGCATGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | ICP4 F | This paper | PCR primers | TGCTGCTGCTGTCCACGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | ICP4 R | This paper | PCR primers | CGGTGTTGACCACGATGAGCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UL30 F | PMID:22383875 | PCR primers | CGCGCTTGGCGGGTATTAACAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | UL30 R | PMID:22383875 | PCR primers | TGGGTGTCCGGCAGAATAAAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UL48 F | This paper | PCR primers | TGCTCGCGAATGTGGTTTAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | UL48 R | This paper | PCR primers | CTGTTCCAGCCCTTGATGTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | gC F | This paper | PCR primers | CAGTTTGTCTGGTTCGAGGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | gC R | This paper | PCR primers | ACGGTAGAGACTGTGGTGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA: DLK-1 | Broad Institute: Genetic Perturbation Platform/Millipore Sigma | TRCN0000022573 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA: DLK-2 | Broad Institute: Genetic Perturbation Platform/Millipore Sigma | TRCN0000022572 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA: non-targeting control | PMID:16873256 | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | Quick-RNA Miniprep | Zymo Research | R1054 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SuperScript IV First-Strand Synthesis System | ThermoFisher | 18091050 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SYBR Green PCR Master Mix | ThermoFisher | 4309155 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Acycloguanosine | Millipore Sigma | A4669 | 10 µM, 50 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | FUDR | Millipore Sigma | F-0503 | 20 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | Uridine | Millipore Sigma | U-3003 | 20 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | SP600125 | Millipore Sigma | S5567 | 20 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | GNE-3511 | Millipore Sigma | 533168 | 4 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | GSK-J4 | Millipore Sigma | SML0701 | 2 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | L-Glutamic Acid | Millipore Sigma | G5638 | 3.7 µg/mL |
| Chemical compound, drug | Forskolin | Tocris | 1099 | 60 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | LY 294002 | Tocris | 1130 | 20 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | 666–15 | Tocris | 5661 | 2 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | SQ 22,536 | Tocris | 1435 | 50 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | KT 5720 | Tocris | 1288 | 3 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | TEA | Tocris | 3068 | 10 mM |
| Chemical compound, drug | CsCl | Tocris | 4739 | 3 mM |
| Chemical compound, drug | OG-L002 | Tocris | 6244 | 30 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | S2101 | Tocris | 5714 | 20 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tetrodotoxin | Tocris | 1069 | 1 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | ESI-09 | Tocris | 4773 | 10 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | ZD 7288 | Cayman | 15228 | 20 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | 8-bromo-cyclic AMP | Cayman | 14431 | 125 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | NGF 2.5S | Alomone Labs | N-100 | 50 ng/mL |
| Chemical compound, drug | Primocin | Invivogen | ant-pm-1 | 100 µg/mL |
| Chemical compound, drug | Aphidicolin | AG Scientific | A-1026 | 3.3 µg/mL |
| Chemical compound, drug | IL-1β | Shenendoah Bio. | 100–167 | 30 ng/mL |
| Chemical compound, drug | WAY-150138 | Pfizer, gift from Lynn Enquist and Jay Brown. | NA | 10 µg/mL |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fura-2 AM | Thermo Fisher | F1221 | 5 µM |
| Other | Hoescht Stain | Thermo | 62249 | 2 µM |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Table 1.
Cell Body Score for Neuronal Health and Degeneration IndexScoring system used to determine neuronal health based on morphology of the soma following treatment with compounds used in this study. Table 2. Axon Score for Neuronal Health and Degeneration IndexScoring system used to determine neuronal health based on morphology of the axons following treatment with compounds used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-supp1-v3.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58037/elife-58037-transrepform-v3.pdf





