Genetic timestamping of plasma cells in vivo reveals tissue-specific homeostatic population turnover
Abstract
Plasma cells (PCs) are essential for protection from infection, and at the origin of incurable cancers. Current studies do not circumvent the limitations of removing PCs from their microenvironment and confound formation and maintenance. Also, the investigation of PC population dynamics has mostly relied on nucleotide analog incorporation that does not label quiescent cells, a property of most PCs. The main impediment is the lack of tools to perform specific genetic manipulation in vivo. Here we characterize a genetic tool (JchaincreERT2) in the mouse that permits first-ever specific genetic manipulation in PCs in vivo, across immunoglobulin isotypes. Using this tool, we found that splenic and bone marrow PC numbers remained constant over-time with the decay in genetically labeled PCs being compensated by unlabeled PCs, supporting homeostatic population turnover in these tissues. The JchaincreERT2 tool paves the way for an in-depth mechanistic understanding of PC biology and pathology in vivo, in their microenvironment.
Introduction
Antibodies produced by plasma cells (PCs) are crucial for immune protection against infection and for vaccination success (Nutt et al., 2015). Upon activation, B cells terminally differentiate into PCs, a process initiated by the downregulation of the B cell transcription factor PAX5 (Kallies et al., 2007). This event allows the expression of multiple factors normally repressed by PAX5, including Xbp1 and Jchain (Castro and Flajnik, 2014; Nutt et al., 2015; Rinkenberger et al., 1996; Shaffer et al., 2004). PAX5 downregulation is also followed by the expression of the transcription factors IRF4 and BLIMP1 that play essential roles in the establishment of the PC program (Kallies et al., 2007; Klein et al., 2006; Sciammas et al., 2006; Shapiro-Shelef et al., 2003). Beyond physiology, multiple cancers have a PC as cell of origin, including multiple myeloma, the second most frequent hematological malignancy overall, and for which a cure remains to be found (Palumbo and Anderson, 2011). As a consequence, the study of gene function in PC biology and pathology is a subject of intense investigation.
However, at least in part because of technical limitations most PC studies make use of in vitro and cell transfer systems that remove PCs from their microenvironment. Currently, genetic manipulation of PCs is not specific and targets other cell populations such as B cells, confounding PC formation, and maintenance. Also, studies on the turnover of the PC population are lacking, as investigation of the regulation of PC maintenance has mostly relied on the use of nucleotide analogs that do not track the vast majority of PCs due to their quiescent nature.
We found amongst well-known PC-associated genes, that Jchain (Igj) had the highest level and most specific expression in PC populations. JCHAIN is a small polypeptide required to multimerize IgM and IgA, and necessary for the transport of these Ig classes across the mucosal epithelium in a poly-Ig receptor-mediated process (Brandtzaeg and Prydz, 1984; Castro and Flajnik, 2014; Max and Korsmeyer, 1985). Here we characterized in detail a GFP-tagged creERT2 allele at the Jchain endogenous locus: IgjcreERT2, hereafter termed JchaincreERT2. We found at the single cell level that GFP as a reporter of Jchain expression occurred in PCs across immunoglobulin isotypes, including IgG1. Using the JchaincreERT2 allele we performed the first-ever highly specific cre-loxP genetic manipulation in PCs residing in their natural microenvironment in vivo. This system allowed inclusive genetic timestamping of PCs, independently of their cell cycle status. We uncovered that the number of PCs in the spleen and bone marrow remained constant over-time with the decay in numbers of genetically labeled PCs being compensated by that of unlabeled PCs, supporting homeostatic population turnover in these tissues. The JchaincreERT2 is thus a validated PC specific genetic tool that paves the way for an in-depth mechanistic understanding of PC biology and pathology in vivo, in their microenvironment.
Results
Jchain transcripts are highly enriched in plasma cells
B-to-PC differentiation is a process that involves a complex network of factors (Figure 1A; Nutt et al., 2015). We investigated the level and specificity of the expression of genes associated with PCs (Xbp1, Jchain, Scd1, Irf4, and Prdm1) through the analysis of a publicly available RNA sequencing dataset for immune cell populations (ImmGen, [Heng et al., 2008]). We first determined the cell populations with the highest transcript level for each factor. Xbp1 and Irf4 were primarily expressed in PCs, however, the expression in bone marrow PCs (B_PC_BM) was less than two-fold greater than that of non-PC populations (Figure 1B). The expression of Sdc1 and Prdm1 was not specific to PCs (Figure 1C). Notably, peritoneal cavity macrophages (MF_226+II+480lo_PC) expressed more Sdc1 than bone marrow PCs (B_PC_BM), and a subset of FOXP3+ T cells (Treg_4_FP3+_Nrplo_Co) expressed higher levels of Prdm1 than that observed in splenic plasmablasts (B_PB_Sp) and bone marrow PCs (B_PC_BM; Figure 1C). By contrast, Jchain had the highest level of transcript expression in PCs compared to non-PCs and was the most PC specific amongst all factors, with a forty-fold enrichment over germinal center (GC) B cells (B_GC_CB_Sp; Figure 1D). We concluded that the Jchain locus was a suitable candidate for the generation of PC specific genetic tools.
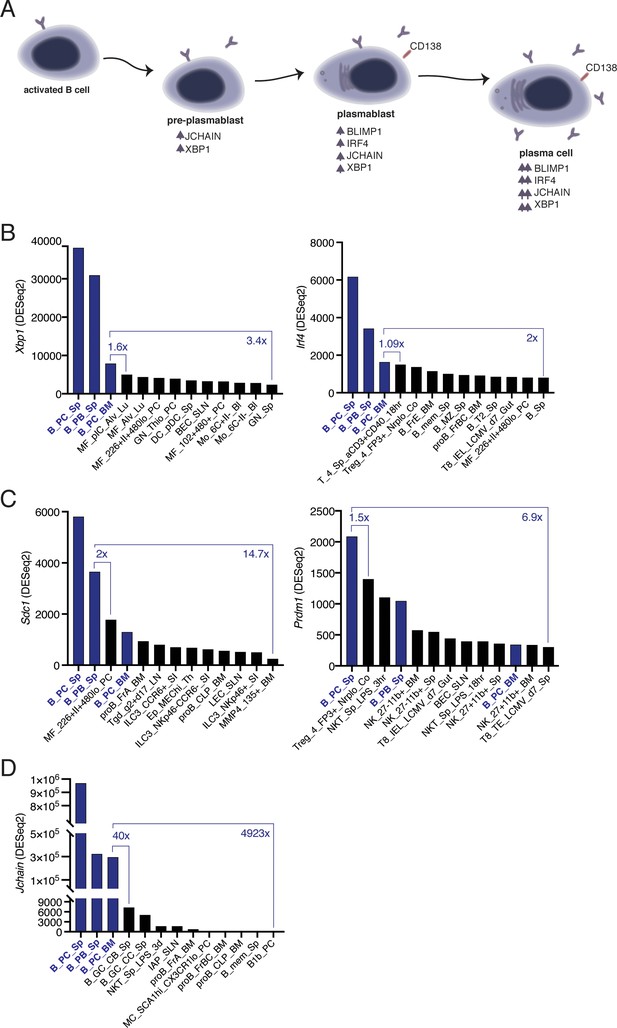
Jchain transcripts are highly enriched in plasma cells.
(A) Schematic of the network of factors associated with plasma cell differentiation. Upward arrows indicate increased expression compared to the precursor population. (B–D) Differential gene expression analysis using RNA sequencing data (ImmGen, Heng et al., 2008). (B) Analysis of Xbp1 and Irf4, which encode for XBP1 and IRF4, respectively. (C) Analysis of Sdc1 and Prdm1, which encode for CD138 and BLIMP1, respectively. (D) Analysis for Jchain (Igj) that encodes for JCHAIN. ‘x’ indicates fold change. Expression Value Normalized by DESeq2. http://rstats.immgen.org/Skyline/skyline.html.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Gene expression values normalised by DESeq2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59850/elife-59850-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
Jchain is expressed in a small fraction of GC B cells and in most plasma cells
We searched alleles produced by the EUCOMMTools consortium (Koscielny et al., 2014) and identified a genetically engineered Jchain allele produced by the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute: MGI:5633773, hereafter termed JchaincreERT2. The genetically engineered Jchain allele contained an FRT site between exons 1 and 2 followed by an engrailed two splice acceptor sequence and an EGFP.2A.creERT2 expression cassette (Figure 2A). In this design, the expression of the EGFP (GFP) and of creERT2 is linked by a self-cleaving 2A peptide under the transcriptional control of the Jchain promoter (Figure 2A). To determine cells with GFP expression, we initially analyzed the spleen from mice heterozygous for the JchaincreERT2 allele that had been immunized with sheep red blood cells (SRBC) 12 days earlier (Figure 2B). B220 is expressed on the surface of B cells and downregulated during PC differentiation (Pracht et al., 2017). We, therefore, defined three cell populations based on the levels of GFP fluorescence and B220 surface expression: GFPlowB220high, GFPintB220int, GFPhighB220low, and a population negative for both markers (GFPnegB220neg; Figure 2C). Next, we determined the fraction of cells within these populations that expressed surface CD138, a commonly used marker to define PCs by flow-cytometry (Pracht et al., 2017). The GFPnegB220neg population did not contain CD138+ cells, however, the fraction of CD138+ cells increased in the remaining populations in agreement with the reduction of B220 expression during PC differentiation, and the GFPintB220int and GFPhighB220low populations were mostly composed of CD138+ cells (Figure 2D,E). Identical results were found when defining PCs using in addition surface expression of CXCR4, a chemokine receptor that facilitates homing of PCs to the bone marrow (Figure 2D,E; Hargreaves et al., 2001). Thus, increased GFP expression from the JchaincreERT2 allele associates with the loss of B220 and increased expression of PC-associated surface markers.
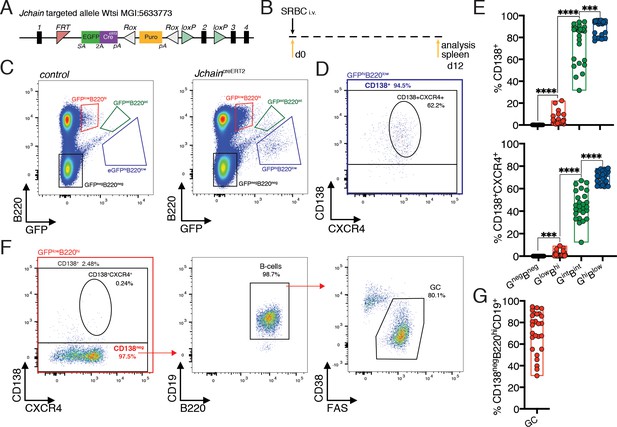
Jchain is expressed in a small fraction of GC B cells and in most plasma cells.
(A) Schematic of Jchain targeted allele Wtsi MGI:5633773. Rectangular boxes indicate exons, and exon number is on top; pink triangle indicates an FRT sequence; EGFPcreERT2 cassette contains a splice acceptor site (SA)-led EGFP-2A-creERT2 expression cassette followed by a poly-A tail inserted in the intron between exons 1 and 2; white triangle indicates a ROX sequence; orange rectangle indicates a promoter-driven puromycin resistance cassette; green triangle indicates loxP sequence. (B) Schematic of experimental procedure protocol. Mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 allele were immunized with sheep red blood cells (SRBC) intravenously (i.v.) on day 0 and spleens of mice were analyzed at day 12 post-immunization. (C) Gating strategy of populations by flow-cytometry according to the expression of GFP and B220 in mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 allele and wild-type B6 mice for a negative control of GFP expression. (D) Gating strategy by flow-cytometry for plasma cells within the GFPhiB220low population using CD138+ and CD138+CXCR4+ markers. (E) Cumulative data for CD138+ and CD138+CXCR4+plasma cells analyzed as in (D). Top: fraction of CD138+plasma cells; bottom: fraction of CD138+CXCR4+plasma cells within the four populations defined by flow-cytometry according to the expression of GFP and B220 in mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 allele. (F) Gating strategy by flow-cytometry for total CD138+ and CD138+CXCR4+plasma cells within GFPlowB220hi population. The CD138neg cell fraction within the GFPlowB220hi population was analyzed for the CD19 B cell marker and stained for CD38 and FAS to determine germinal center (GC) B cells. (G) Cumulative data for the frequency of GC B cells within the CD138negGFPlowB220hi population. Each symbol (E: n = 26, G: n = 26) represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate median, minimum, and maximum values. ***=p ≤ 0.001, ****=p ≤ 0.0001 (unpaired Student’s t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments (E, G).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Frequency of plasma cells or B cells within the populations defined by GFP and B220 expression.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59850/elife-59850-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
We further investigated the cellular composition of the GFPlowB220high population that contained the fewest CD138+ cells (1% to 20%; Figure 2E). The gate defining this population was designed to not disregard the occurrence of cells with a low-level of GFP expression in mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 allele. However, such strategy inevitably led to the inclusion of a small fraction of ‘false’ GFP positive cells as indicated by the analysis of control mice (wild-type C57BL/6) that are GFP negative (Figure 2C). Still, the fraction of cells within the GFPloB220hi population was significantly enriched in JchaincreERT2 mice compared to control (Figure 2—figure supplement 1). Also above background, we found that virtually all CD138neg cells within the GFPlowB220high population of mice with the JchaincreERT2 allele expressed the B cell marker CD19 (Figure 2F), and in agreement with Jchain gene expression analysis (Figure 1D) these cells mostly represented germinal center (GC) B cells (CD38lowFAShigh; Figure 2F,G and Figure 2—figure supplement 1). By contrast, only 30% of JchaincreERT2 mice had above background enrichment for CD138+ and CD138+CXCR4+ expressing cells within the GFPlowB220high population (Figure 2—figure supplement 1). These data prompts caution when using the gate defining the GFPlowB220high population to study enrichment for PC markers in mice carrying JchaincreERT2 allele, as it may contain an unacceptable level of contamination by non-GFP positive cells.
We further performed analyses in the spleen and bone marrow of 12 day SRBC immunized mice heterozygous for the JchaincreERT2 allele in which precursors and mature B cells, and non-B cell populations were first defined using surface markers and the fraction of GFP expressing cells within those populations determined (Figure 2—figure supplement 2). We found that most PCs in the spleen and bone marrow expressed GFP (CD138+CXCR4+, 60 to 90%; Figure 2—figure supplement 2). We also observed that a minor fraction of B1b cells (0 to 6%) in the spleen expressed GFP (Figure 2—figure supplement 2), possibly in agreement with the knowledge that B1b cells are prone to differentiate into PCs and are a source of IgM antibodies during T cell independent responses (Alugupalli et al., 2004). Collectively these data confirmed at the single cell level the gene expression analysis using bulk populations (Figure 1D) and suggested that Jchain expression is highly enriched in PCs.
Jchain expression correlates with that of IRF4 and BLIMP1
IRF4 and BLIMP1 transcription factors play an essential role in PC differentiation (Kallies et al., 2007; Klein et al., 2006; Sciammas et al., 2006; Shapiro-Shelef et al., 2003). We analyzed the spleen of 12 day SRBC immunized mice heterozygous for the JchaincreERT2 allele and determined the expression pattern of IRF4 and BLIMP1 in the populations defined by varied GFP and B220 expression (Figures 2C and 3A,B). The GFPnegB220neg population was virtually devoid of cells with BLIMP1 and IRF4 expression (Figure 3C). In 30% of mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 allele we found above background enrichment for BLIMP1+IRF4+ cells within the GFPlowB220high population (Figure 3D,E and Figure 3—figure supplement 1). However, most GFPlowB220high cells were negative for BLIMP1 and IRF4, suggesting that Jchain expression precedes that of IRF4 and BLIMP1, as previously observed in in vitro cultures of Blimp1 deficient B cells (Kallies et al., 2007). Still, Jchain expression as measured by GFP strongly correlated with that of IRF4 and BLIMP1 given that the vast majority of cells within the GFPintB220int and GFPhighB220low populations were BLIMP1+IRF4+ (Figure 3D and E). Overall, we identified an in vivo population of cells in which Jchain expression preceded that of IRF4 and BLIMP1, possibly representing PC precursors. As PC differentiation ensued, Jchain expression correlated highly with the expression of the transcription factors BLIMP1 and IRF4 that are critical for the establishment of the PC program.
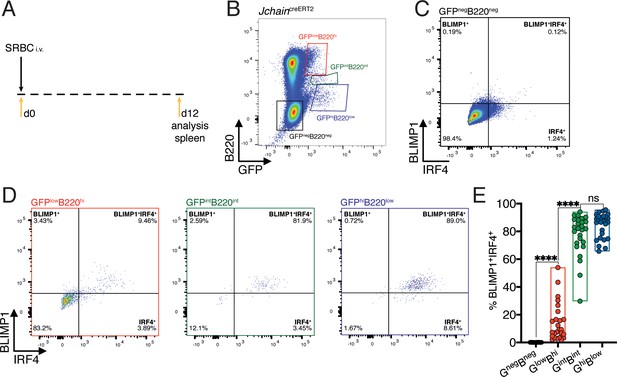
Jchain expression correlates with that of IRF4 and BLIMP1.
(A) Schematic of experimental procedure protocol. Mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 allele were immunized with sheep red blood cells (SRBC) intravenously (i.v.) on day 0 and spleens of mice were analyzed at day 12 post-immunization. (B) Gating strategy of populations by flow-cytometry according to the expression of GFP and B220 in mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 allele. (C) Gating strategy for IRF4 and BLIMP1 expression by flow-cytometry within the GFPnegB220neg population. (D) Gating strategy for IRF4 and BLIMP1 expression by flow-cytometry within GFPlowB220hi, GFPintB220int, and GFPhiB220low populations, defined as in (B). (E) Cumulative data for the frequency of BLIMP1+IRF4+ cells within the four populations defined as in (B). Each symbol in (E: n = 26) represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate median, minimum, and maximum values. ns = not significant, ***=p ≤ 0.001, ****=p ≤ 0.0001 (unpaired Student’s t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments (E).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Frequency of BLIMP1+IRF4+ cells within the populations defined by GFP and B220 expression.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59850/elife-59850-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
JchaincreERT2 mediated genetic manipulation is effective only in plasma cells
Next, we sought to determine whether the JchaincreERT2 allele could be used to perform genetic manipulation in PCs. For that we generated compound mutant mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 allele and a Rosa 26 allele in which RFP expression is conditional to cre-mediated recombination of a loxP-STOP-loxP cassette (R26lslRFP; Luche et al., 2007). In the JchaincreERT2 allele, cre is fused to an estrogen binding domain (ERT2) that sequesters cre in the cytoplasm through the binding to HSP90 (Feil et al., 2009). Addition of tamoxifen displaces the creERT2-HSP90 complex allowing effective nuclear import of creERT2 and its access to loxP flanked DNA sequences (Figure 4A; Feil et al., 2009). We first performed an in vitro experiment using a classical plasmablast (B220lowCD138+) differentiation assay in which B cells purified from mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 and R26lslRFP alleles were cultured with LPS (Andersson et al., 1972) in the presence or absence of 4-OH tamoxifen. GFP expression was highly enriched in plasmablasts compared to B cells and RFP expression was only observed upon addition of 4-OH tamoxifen to the cell culture, and that occurred virtually only in plasmablasts (Figure 4—figure supplement 1). This data suggested that creERT2 was specifically expressed by plasmablasts and effectively retained in the cytoplasm in the absence of 4-OH tamoxifen.
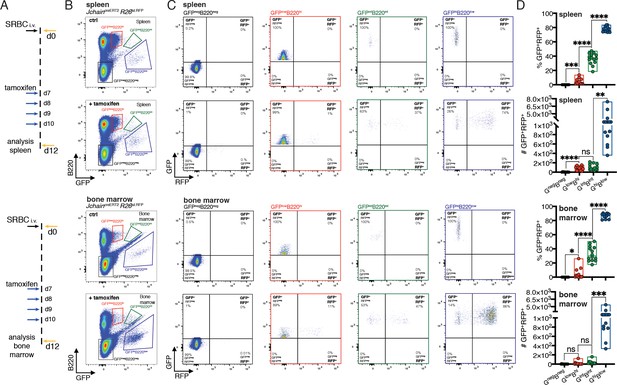
JchaincreERT2 mediated genetic manipulation is effective only in plasma cells.
(A) Schematic of experimental procedure protocol. Mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 and R26lslRFP alleles were immunized with sheep red blood cells (SRBC) intravenously (i.v.) on day 0 and spleens (top) and bone marrow (bottom) of mice were analyzed at day 12 post-immunization. A group of mice received tamoxifen treatment for four consecutive days from day 7 to day 10 after immunization. (B) Gating strategy of populations by flow-cytometry in the spleen (top) and bone marrow (bottom) according to the expression of GFP and B220 in mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 allele. (C) Gating strategy for GFP and RFP expression by flow-cytometry in the four populations defined as in (B). Top: spleen; bottom: bone marrow. (D) Cumulative data for the frequency and number of GFP+RFP+ cells within GFPnegB220neg, GFPlowB220hi, GFPintB220int, and GFPhiB220low populations, defined as in (B). Top: spleen; bottom: bone marrow. Each symbol (D: n = 14) represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate median, minimum, and maximum values. ns = not significant, *=p ≤ 0.05, **=p ≤ 0.01, ***=p ≤ 0.001, ****=p ≤ 0.0001 (unpaired Student’s t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments (D).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Frequency and number of GFP+RFP+ cells within the populations defined by GFP and B220 expression.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59850/elife-59850-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
Similar observations were made in mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 and R26lslRFP alleles in vivo. In the absence of tamoxifen administration RFP expressing cells were not detected, confirming the in vitro results and supporting that the JchaincreERT2 allele was not ‘leaky’ in the control of cre activity (Figure 4—figure supplement 2). Next, we immunized mice carrying JchaincreERT2 and R26lslRFP alleles and administered tamoxifen on days 7, 8, 9, and 10 followed by analysis of the spleen and bone marrow at day 12 (Figure 4A). Analyses of the populations defined by varied GFP and B220 surface expression (Figures 2 and 4B) revealed that a small fraction of GFPlowB220high cells were positive for RFP in the spleen (median ~2%) and in the bone marrow (median ~1.2%; Figure 4C,D). In contrast, cre mediated recombination and as consequence RFP expression occurred in ~37% and~31% of GFPintB220int in the spleen and bone marrow, respectively, and the vast majority of cells within the GFPhighB220low population had undergone cre mediated recombination and were RFP positive (~76% in the spleen, and ~88% in the bone marrow, median; Figure 4C,D). These data showed that JchaincreERT2 mediated cre-recombination was only effective in PC populations validating it as a tool to specifically perform genetic manipulation of PCs.
Genetic manipulation using JchaincreERT2 occurs across immunoglobulin isotypes
IgG1 does not multimerize, and due to differences in its secretory tail to that of IgA and IgM, JCHAIN does not associate with IgG1 (Johansen et al., 2000). Currently it is suggested that Jchain expression occurs in all PCs regardless of isotype (Castro and Flajnik, 2014; Johansen et al., 2000; Mather et al., 1981). However, this has not been demonstrated at the single cell level. We performed experiments that investigated whether JchaincreERT2 allele GFP expression and cre-mediated loxP recombination occurred in PCs across immunoglobulin isotypes. For that we analyzed the spleen, mesenteric lymph node (mLN), Peyer’s patches and bone marrow of younger (15 weeks) and older (30 weeks) mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 and R26lslRFP alleles. These mice were immunized with SRBC and administered with tamoxifen on days 7, 8, 9, and 10 followed by analysis at day 12 (Figure 5A). We first analyzed total PCs (B220lowCD138+), and within these cells those that expressed GFP (RFP+ and RFPneg) and GFP+RFP+ cells (cre recombined) to determine the proportions of IgA, IgM, and IgG1 expressing cells using intracellular stain (Figure 5B–D). Overall, we found only small differences. Analysis of spleens of 15-week-old mice revealed a slight increase in the percentage of IgA+ cells within the GFP+RFP+ PCs only when compared to total PCs (Figure 5E). A similar trend was observed when analyzing Peyer’s patches of 15-week-old mice (Figure 5E). However, in the other analyzed tissues of these mice we did not observe differences in the proportion of IgA, nor for IgM and IgG1 in any of the tissues analyzed (Figure 5E). 30-week-old mice showed a slight increase in the percentage of splenic IgM+ cells within the GFP+RFP+ PCs only when compared to total PCs, and for IgA+ in the mLN (Figure 5F). No significant difference was observed in 30-week-old mice for the proportion of IgM or IgA in any of the other analyzed tissues, and in none of the analyzed tissues for IgG1 (Figure 5F). Taken together, these data suggested that Jchain expression is not overly represented in IgA or IgM expressing PCs compared to IgG1+ PCs. We concluded that JchaincreERT2 mediated cre-loxP recombination occurs across immunoglobulin isotypes and thus that the JchaincreERT2 allele is a useful tool for genetic manipulation also of IgG1 expressing PCs.
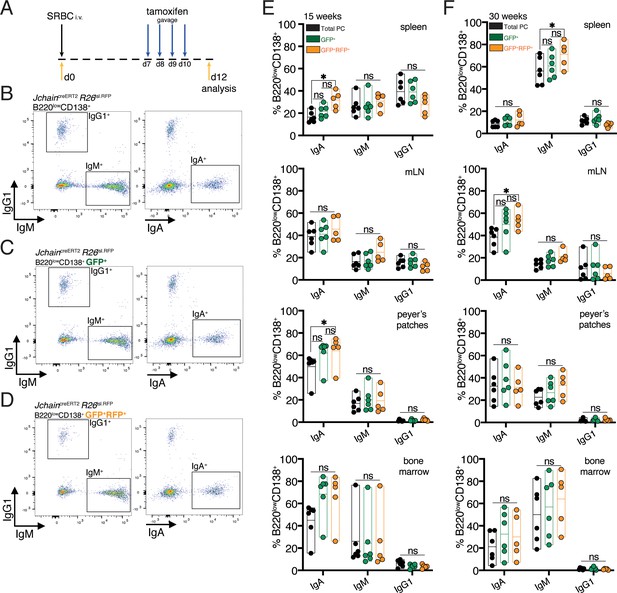
Genetic manipulation using JchaincreERT2 occurs across immunoglobulin isotypes.
(A) Schematic of experimental procedure protocol. Mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 and R26lslRFP alleles were immunized with sheep red blood cells (SRBC) intravenously (i.v.) on day 0 and spleens, mesenteric lymph nodes (mLN), Peyer’s patches, and bone marrows of mice were analyzed at day 12 post-immunization. Mice received tamoxifen treatment for four consecutive days from day 7 to day 10 after immunization. (B) Gating strategy by flow-cytometry for intracellular and extracellular expression of IgG1, IgM and IgA within total B220lowCD138+plasma cells. Analysis in the spleen is provided as example. (C) Gating strategy by flow-cytometry for intracellular and extracellular expression of IgG1, IgM, and IgA within B220lowCD138+GFP+ (RFP+ and RFPneg) plasma cells. Analysis in the spleen is provided as example. (D) Gating strategy by flow-cytometry for intracellular and extracellular expression of IgG1, IgM, and IgA within B220lowCD138+GFP+RFP+plasma cells. Analysis in the spleen is provided as example. (E) Cumulative data for the fractions of IgA, IgM or IgG1 expressing cells within total plasma cells (PC) (black, B220lowCD138+), GFP+ (RFP+ and RFPneg) plasma cells (green, B220lowCD138+GFP+), and GFP+RFP+plasma cells (orange, B220lowCD138+GFP+RFP+) at 15 weeks of age. (F) Cumulative data for the fractions of IgA, IgM, or IgG1 expressing cells within total plasma cells (PC) (black, B220lowCD138+), GFP+ (RFP+ and RFPneg) plasma cells (green, B220lowCD138+GFP+), and GFP+RFP+plasma cells (orange, B220lowCD138+GFP+RFP+) at 30 weeks of age. Each symbol (E: n = 5–6, F: n = 5–6) represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate median, minimum, and maximum values. ns = not significant, *=p ≤ 0.05 (unpaired Student’s t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments (E, F).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Fractions of IgA, IgM or IgG1-expressing cells within populations of plasma cells defined by GFP and RFP expression at various immune sites.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59850/elife-59850-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
Inclusive analysis of plasma cell dynamics reveals tissue-specific homeostatic population turnover
Understanding of the PC population turnover is lacking. Multiple investigations have been performed to determine the PC lifespan using primarily nucleotide analog incorporation into the DNA. These studies have provided fundamental insights on PC maintenance and currently it is accepted that a fraction of PCs in the mouse survives for periods longer than 3 months (Ho et al., 1986; Lemke et al., 2016; Manz et al., 1998; Manz et al., 1997; Slifka et al., 1998). However, given the quiescent nature of PCs and that nucleotide analog methodology requires cell division, these methods are not appropriate to study global population turnover in tissues. We investigated the suitability of the JchaincreERT2 allele to determine the turnover of the PC population in the spleen and bone marrow. We immunized mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 and R26lslRFP alleles at two time-points spaced by a period of 21 days (Figure 6A; Calado et al., 2010). Thirty days after the secondary immunization (day 51) we administered tamoxifen for five consecutive days to genetically label PCs (Figure 6A). Next, we determined the absolute cell number of total PCs, of GFP+ cells (RFP+ and RFPneg), GFP+RFP+ cells (cre recombined), and GFP+RFPneg cells (not cre recombined). We found that over a period of 5 months the cell number of total and GFP+ PCs remained constant over time (Figure 6B,C). By contrast, the cell number of GFP+RFP+ cells decayed (Figure 6B,C) in both the spleen (t1/2 ~31.63d) and bone marrow (t1/2 ~251.93d; Figure 6D,E). These results may agree with the knowledge that the half-life of PC residence differs between spleen and the bone marrow (Sze et al., 2000). Notably, analysis of the GFP+RFPneg cell numbers revealed that the emergence of these cells paralleled that observed for the decay in cell numbers of GFP+RFP+ cells (Figure 6B,C) both in the spleen (t1/2 ~20.20d) and bone marrow (t1/2 ~190.19d; Figure 6F,G). These data indicated that the turnover of the PC population is homeostatically regulated in a tissue-specific manner.
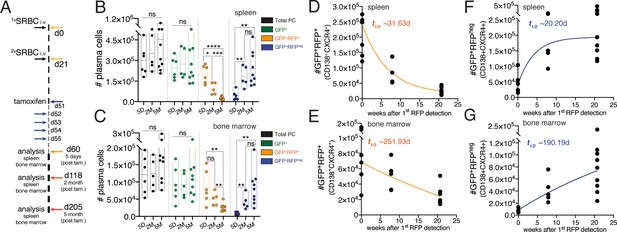
Inclusive analysis of plasma cell dynamics reveals tissue-specific homeostatic population turnover.
(A) Schematic of the experimental procedure protocol. Mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 and R26lslRFP alleles were immunized twice with sheep red blood cells (SRBC) intravenously (i.v.) on day 0 and day 21. Mice received tamoxifen treatment for five consecutive days from day 51 to 55 after the first immunization. Spleens and bone marrow of mice were analyzed at day 5, 2-month, and 5-month timepoints after the last tamoxifen administration. (B) Cumulative data for the absolute cell numbers of total PCs, of GFP+ cells (RFP+ and RFPneg), GFP+RFP+ cells (cre recombined), and GFP+RFPneg cells (not cre recombined) in the spleen. (C) Cumulative data for the absolute cell numbers of total PCs, of GFP+ cells (RFP+ and RFPneg), GFP+RFP+ cells (cre recombined), and GFP+RFPneg cells (not cre recombined) in the bone marrow. (D) Graphical representation of half-life (t1/2) of GFP+RFP+CD138+CXCR4+plasma cells in the spleen using the data presented in (B). Graphing of the best-fit curve was performed using the GraphPad Prism eight software. (E) Graphical representation of half-life (t1/2) of GFP+RFP+CD138+CXCR4+plasma cells in the bone marrow using the data presented in (C). Graphing of the best-fit curve was performed using the GraphPad Prism eight software. (F) Graphical representation of half-life (t1/2) of GFP+RFPnegCD138+CXCR4+plasma cells in the spleen using the data presented in (B). Graphing of the best-fit curve was performed using the GraphPad Prism eight software. (G) Graphical representation of half-life (t1/2) of GFP+RFPnegCD138+CXCR4+plasma cells in the bone marrow using the data presented in (C). Graphing of the best-fit curve was performed using the GraphPad Prism eight software. Each symbol (B-G: 5D n = 6; 2M n = 5; 5M n = 9) represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate median, minimum, and maximum values. ns = not significant, *=p ≤ 0.05 **=p ≤ 0.01, ***=p ≤ 0.001, ****=p ≤ 0.0001 (unpaired Student’s t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments (B, C).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Absolute cell numbers of plasma cell populations defined by GFP and RFP expression in the spleen and bone marrow over time.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59850/elife-59850-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
Discussion
Plasma cells (PC)s are an essential component of the adaptive immune system. However, compared to other B cell lineage populations the molecular analysis of PC gene function in vivo has lagged behind. One underlying cause is the lack of tools for specific genetic manipulation of PCs, something available for B cells since 1997, more than 20 years ago (Rickert et al., 1997), and more recently for B cells at multiple stages of development (Boross et al., 2009; Casola et al., 2006; Croker et al., 2004; Crouch et al., 2007; de Boer et al., 2003; Dogan et al., 2009; Düber et al., 2009; Georgiades et al., 2002; Hobeika et al., 2006; Kraus et al., 2004; Kwon et al., 2008; Moriyama et al., 2014; Robbiani et al., 2008; Schweighoffer et al., 2013; Shinnakasu et al., 2016; Weber et al., 2019; Yasuda et al., 2013).
Here we used a systematic analysis of PC-associated factors for which expression is increased during PC differentiation (Xbp1, Jchain, Scd1, Irf4, and Prdm1) with the aim of identifying suitable candidates for the generation of PC-specific tools. Blimp1, a critical transcription factor for the establishment of the PC program, displayed an expression pattern unspecific to PCs. This was unsurprising given the knowledge that Blimp1 is expressed by other hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells (John and Garrett-Sinha, 2009), including germ cells (Ohinata et al., 2005). Among the analyzed factors we found that Jchain displayed the highest RNA expression level in PCs and had the most PC-specific expression pattern. We considered Jchain to be the most suitable candidate for the generation of PC-specific tools. Next, we searched among alleles generated by the EUCOMMTools consortium and identified a JchaincreERT2 allele which through a comprehensive series of experiments we validated for specific genetic manipulation of PCs.
GFP expression as a reporter for Jchain was expressed in a very small subset of B cells (<2%, primarily GC B cells) and in most plasma cells. The GFP expressing B cells were mostly negative for BLIMP1 and IRF4 expression. This data agrees with previous work using in vitro cultures of Blimp1 deficient B cells suggesting that the initiation of Jchain expression does not require BLIMP1 (Kallies et al., 2007). Thus, the identified population of cells in vivo marked by low GFP expression and high surface expression of B220 (GFPlowB220hi), possibly contains PC precursor cells and future analysis may provide information on the mechanisms underlying the very first steps of PC differentiation. It is important to note, however, that the analysis of the GFPlowB220hi population requires caution as it contains false GFP positive cells (i.e. background cells). If the underlying reason for the false GFP positivity within the GFPlowB220hi population is autofluorescence; a common issue when GFP is weakly expressed because autofluorescence typically displays similar excitation and emission characteristics to GFP (Shapiro, 1995; approaches that quench autofluorescence may reduce or abrogate background; Shilova et al., 2017). Alternatively, the experimenter may design a more stringent gate, possibly increasing specificity and thus reducing contamination as long as the loss of a fraction of lowly expressing GFP cells is acceptable and consideration is taken that such stringency may itself introduce bias in the analysis.
JchaincreERT2 mediated genetic manipulation was only effective in PCs and data of others deposited in bioRxiv during the revision of this work supports this finding (Ayala et al., 2020). In the JchaincreERT2 allele GFP and creERT2 are linked by a self-cleaving 2A peptide that ensures a near equitable co-expression of the proteins (Szymczak et al., 2004). As consequence, it is likely that the effectiveness of cre recombination correlates with the level of creERT2 expression because PCs expressed the highest level of Jchain, as suggested by GFP expression. Of note, the JchaincreERT2 allele analyzed in this work retained the puromycin selection cassette that is flanked by rox recombination sites. This knowledge should be taken in consideration in future experiments involving compound mutant mice that make use of dre recombinase (Anastassiadis et al., 2009). On occasion it has been observed that retention of the selection cassette reduces gene expression of the targeted locus (Meyers et al., 1998; Nagy et al., 1998). Thus, inadvertent or intentional removal of the puromycin selection cassette may increase creERT2 expression, including in B cells, possibly reducing the PC specificity of JchaincreERT2 mediated genetic manipulation. Finally, in the JchaincreERT2 allele the expression of Jchain is interrupted by a GFP-2A-creERT2 cassette and induction of cre-mediated recombination deletes Jchain exon two that is loxP-flanked. It was previously shown that heterozygous deletion of Jchain displayed an intermediate phenotype to that of knockout mice (Lycke et al., 1999). This knowledge must be considered when performing JchaincreERT2 mediated genetic manipulation, including the need to use the JchaincreERT2 allele without the targeted manipulation as control, and the utility of the JchaincreERT2 allele in homozygosity. Future iterations of JchaincreERT2 alleles in which JCHAIN protein expression is preserved should be considered.
It is currently thought that Jchain expression occurs in all PCs regardless of their isotype (Castro and Flajnik, 2014; Johansen et al., 2000; Mather et al., 1981). The characterization of the JchaincreERT2 allele demonstrated at the single cell level that Jchain expression indeed occurs in PCs across immunoglobulin isotypes. However, we observed the occurrence of both GFP+ PCs and of a smaller fraction of GFPneg PCs, which in a first approximation suggested that Jchainneg PCs exist. Nevertheless, it is important to consider that although GFP is driven by the endogenous Jchain promoter, it does not directly measure JCHAIN itself at the transcriptional and translational level. Further investigation of GFP+ and GFPneg PCs in mice carrying the JchaincreERT2 allele is required.
Using the JchaincreERT2 allele we performed inclusive genetic timestamping of PCs, independent of the time at which cells were generated, cell cycle status, and localization. We uncovered that the numbers of total PCs in the spleen and bone marrow remained constant for at least 5 months. Notably, within the GFP+ PC population, the decay in numbers of genetically labeled PCs (GFP+RFP+) was compensated by that of unlabeled PCs (GFP+RFPneg), supporting that PC turnover is homeostatically regulated in these tissues. Homeostatic control of mature B cell numbers is widely accepted (Crowley et al., 2009). In mature B cells, the expression of a B cell receptor is crucial for cell survival (Srinivasan et al., 2009; however, BAFF is the limited resource that defines the boundaries of the biological ‘space’; Crowley et al., 2009; Srinivasan et al., 2009). On other hand, the regulation of PC numbers remains unclear. PCs express the BCMA receptor that allows the sensing of both BAFF and APRIL, and BCMA deficient mice have reduced PC numbers (O'Connor et al., 2004). However, because BCMA is expressed in B cells committed to PC differentiation further studies are required to disentangle formation and maintenance (Mackay et al., 2003). The JchaincreERT2 allele is therefore ideally suited to tackle these questions. PC homeostatic regulation could also be the reflection of a limited number of niches in a given organ which would then limit the number of PCs (Höfer et al., 2006; Khodadadi et al., 2019; Lightman et al., 2019; Lindquist et al., 2019; Wilmore and Allman, 2017).
In this work, we have not determined if the decay in numbers of genetically labeled PCs (GFP+RFP+) was the reflection of cell death and/or migration away from the tissue analyzed. A possible strategy to determine the latter would be the use of a photoactivatable fluorescent reporter (Patterson and Lippincott-Schwartz, 2002) in combination with the JchaincreERT2 allele to label through photoactivation PCs in a specific tissue and investigate their migratory patterns. Knowledge on the mechanisms underlying PC homeostasis and turnover is important as these are directly related to long-term protection from infection, vaccination, and cancer pathogenesis. The JchaincreERT2 allele is highly suited to perform these investigations as it allows genetic manipulation of PCs in vivo in their microenvironment, and to retrieve live time-stamped PCs for downstream analysis.
Materials and methods
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus, C57BL/6) | JchaincreERT2; Jchaintm1(EGFP/cre/ERT2)Wtsi | Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute (WTSI) | MGI: 5633773 | The allele was purchased from EMMA mouse repository in agreement with WTSI, mice were rederived at the Francis Crick Institute. |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse Blimp1(host species: rat, clone: 6D3) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 565002 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD16/32 Fc Block (host species: rat, clone: 2.4G2) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 553141 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD19 (host species: rat, clone: 1D3) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 563557 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD23 (host species: rat, clone: B3B4) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 563986 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD38 (host species: rat, clone: 90) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 760361 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD95 (host species: hamster, clone: Jo2) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 562633 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG1 (host species: rat, clone: A85-1) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 560089 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD138 (host species: rat, clone: 281–2) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 740880 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse B220 (host species: rat, clone: RA3-6B2) | BioLegend | Cat#: 103247 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD11c (host species: hamster, clone: N418) | BioLegend | Cat#: 117333 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD19 (host species: rat, clone: 6D5) | BioLegend | Cat#: 115543 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD21/35 (host species: Rat, clone: 7E9) | BioLegend | Cat#: 123421 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD43 (host species: rat, clone: 1B11) | BioLegend | Cat#: 121223 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD86 (host species: rat, clone: GL1) | BioLegend | Cat#: 105013 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse BP1 (host species: rat, clone: 6C3) | Ebioscience | Cat#: 13–5891 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CD5 (host species: rat, clone: 53–7.3) | Ebioscience | Cat#: 13-0051-82 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse CXCR4 (host species: rat, clone: 2B11) | Ebioscience | Cat#: 46-9991-82 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgA (host species: rat, clone: 11-44-2) | Ebioscience | Cat#: 13–5994 | FACS (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgM (host species: rat, clone: II/41) | Ebioscience | Cat#: 25–5790 | FACS (1:300) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IRF4 (host species: rat, clone: 3E4) | Ebioscience | Cat#: 25-9858-80 | FACS (1:200) |
| Commercial assay or kit | BD Cytofix/CytoPerm Fixation/Permeabilization Kit | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 554714 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Zombie NIR Fixable Viability Kit | BioLegend | Cat#: 423106 | (1:200) |
| Commercial assay or kit | CD43 (Ly-48) MicroBeads, mouse | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat#: 130-049-801 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | (Z) 4-hydroxytamoxifen | Sigma-Aldrich | CAS: 68047-06-3 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tamoxifen | Sigma | Cat#: T5648-5G | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sunflower seed oil from Helianthus annuus | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: S5007-250ml | |
| Software, algorithm | FACSDiva software | BD | V9.0 | |
| Software, algorithm | FlowJo | BD | V10 | |
| Software, algorithm | Prism | GraphPad | V7, V8 | |
| Other | Sheep red blood cells (SRBCs) | TCS Biosciences Ltd | Cat#: SB054 |
Mice
The JchaincreERT2 allele was purchased from EMMA in agreement with the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute (Jchain targeted allele Wtsi MGI:5633773, genebank https://www.i-dcc.org/imits/targ_rep/alleles/43805/escell-clone-genbank-file) and mice were rederived at the The Francis Crick Institute. The allele contains a splice acceptor site (SA), an EGFP-2A-creERT2 expression cassette and a poly-A tail in the intron between exons 1 and 2 under the Jchain promoter. In addition, exon 2 is loxP-flanked and the allele also contains a rox-flanked puromycin resistance cassette. These mice were crossed to carry a Rosa26lslRFP cre recombination reporter allele (R26lsl.RFP) allele that expresses a non-toxic tandem-dimer red fluorescent protein upon cre-mediated deletion of a floxed STOP cassette (Luche et al., 2007). Mice were maintained on the C57BL/6 background and bred at The Francis Crick Institute biological resources facility under specific pathogen-free conditions. Animal experiments were carried out in accordance with national and institutional guidelines for animal care and were approved by The Francis Crick Institute biological resources facility strategic oversight committee (incorporating the Animal Welfare and Ethical Review Body) and by the Home Office, UK. All animal care and procedures followed guidelines of the UK Home Office according to the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 and were approved by Biological Research Facility at the Francis Crick Institute. The age of mice ranged between 15–30 weeks as specified.
Immunization and in vivo induction of cre activity
Request a detailed protocolMice were injected intravenously with 1 × 109 sheep red blood cells (SRBCs, TCS Biosciences Ltd) in PBS. For the induction of cre activity, 4 mg tamoxifen (SIGMA T5648) dissolved in sunflower seed oil were administered by oral gavage to mice once per day for multiple days depending on experimental design.
In vitro B cell culture and induction of cre activity
Request a detailed protocolSplenic cells were harvested, and B cells were isolated using CD43 (Ly-48) MicroBeads, mouse (Miltenyi Biotec). The purity of B cells was determined by flow-cytometry (>95%). B cells were cultured in 96-well round-bottom plates (Falcon) in B cell media (DMEM high glucose/Glutamax from Thermo Fisher Scientific supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum F7524 from Sigma, 100 U/mL Penicillin, 100 µg/mL Streptomycin from Life Technologies, 10 mM HEPES buffer solution from Life Technologies, 100 µM MEM non-essential amino acids from Thermo Fisher Scientific, 1 mM sodium pyruvate from Life Technologies, and 50 uM β-mercaptoethanol from Sigma) at 1 million/mL concentration (200,000 cells/well) with 10 ug/mL LPS and varied concentrations of (Z) 4-hydroxytamoxifen (Sigma-Aldrich). Analysis was performed using flow-cytometry at 48, 72, or 96 hr of culture.
Flow cytometry
Request a detailed protocolSingle cell suspensions were stained with antibodies. We used Zombie NIR Fixable Viability Kit (BioLegend) for live/dead discrimination. For intracellular staining, we fixed cells using the BD CytoFix/Cytoperm (BD Biosciences) kit as per manufacturer instructions. Samples were acquired on a BD LSRFortessa analyzer using FACSDiva software (BD) and analyzed on FlowJo software.
Quantification and statistical analysis
Request a detailed protocolData were analyzed with unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test; a p-value=p ≤ 0.05 was considered significant. Prism (v7 and v8, GraphPad) was used for statistical analysis. A single asterisk (∗) in the graphs of figures represents a p-value≤0.05, double asterisks (∗∗) a p-value≤0.01, triple asterisks (∗∗∗) a p-value≤0.001, quadruple asterisks (∗∗∗∗) a p-value≤0.0001, and ‘ns’ stands for not statistically significant (i.e. a p-value>0.05). Nonlinear regression (curve fit) using (v8, GraphPad) was used to calculate half-life (t1/2) of the population and followed a one-phase decay model, with no special handling of outliers, robust regression and strict convergence criteria and no weighting with a 1000 maximum number of iterations.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in the manuscript and supporting files.
-
NCBI Gene Expression OmnibusID GSE127267. ImmGen ULI RNA-seq data.
References
-
Dre recombinase, like cre, is a highly efficient site-specific recombinase in E. coli, mammalian cells and miceDisease Models & Mechanisms 2:508–515.https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.003087
-
Induction of immunoglobulin and antibody synthesis in vitro by lipopolysaccharidesEuropean Journal of Immunology 2:349–353.https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830020410
-
NFATc2 (NFAT1) assists BCR-mediated anergy in anti-insulin B cellsMolecular Immunology 62:321–328.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2014.01.003
-
Putting J chain back on the map: how might its expression define plasma cell development?The Journal of Immunology 193:3248–3255.https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1400531
-
Regulation of AID expression in the immune responseJournal of Experimental Medicine 204:1145–1156.https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20061952
-
Transgenic mice with hematopoietic and lymphoid specific expression of creEuropean Journal of Immunology 33:314–325.https://doi.org/10.1002/immu.200310005
-
Multiple layers of B cell memory with different effector functionsNature Immunology 10:1292–1299.https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1814
-
Inducible cre miceMethods in Molecular Biology 530:343–363.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-471-1_18
-
A coordinated change in chemokine responsiveness guides plasma cell movementsJournal of Experimental Medicine 194:45–56.https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.194.1.45
-
The immunological genome project: networks of gene expression in immune cellsNature Immunology 9:1091–1094.https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1008-1091
-
Distinct short-lived and long-lived antibody-producing cell populationsEuropean Journal of Immunology 16:1297–1301.https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830161018
-
Adaptation of humoral memoryImmunological Reviews 211:295–302.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00380.x
-
Role of J chain in secretory immunoglobulin formationScandinavian Journal of Immunology 52:240–248.https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3083.2000.00790.x
-
Blimp1: a conserved transcriptional repressor critical for differentiation of many tissuesExperimental Cell Research 315:1077–1084.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.11.015
-
The maintenance of memory plasma cellsFrontiers in Immunology 10:721.https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00721
-
Survival of Long-Lived plasma cells (LLPC): Piecing together the puzzleFrontiers in Immunology 10:965.https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00965
-
Lack of J chain inhibits the transport of gut IgA and abrogates the development of intestinal antitoxic protectionJournal of Immunology 163:913–919.
-
BAFF AND APRIL: a tutorial on B cell survivalAnnual Review of Immunology 21:231–264.https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141152
-
Survival of long-lived plasma cells is independent of antigenInternational Immunology 10:1703–1711.https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/10.11.1703
-
Human J chain gene. structure and expression in B lymphoid cellsJournal of Experimental Medicine 161:832–849.https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.161.4.832
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 is critical for follicular helper T cell retention in germinal centersJournal of Experimental Medicine 211:1297–1305.https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20131666
-
The generation of antibody-secreting plasma cellsNature Reviews Immunology 15:160–171.https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3795
-
BCMA is essential for the survival of long-lived bone marrow plasma cellsJournal of Experimental Medicine 199:91–98.https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20031330
-
Multiple myelomaNew England Journal of Medicine 364:1046–1060.https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1011442
-
A new staining protocol for detection of murine antibody-secreting plasma cell subsets by flow cytometryEuropean Journal of Immunology 47:1389–1392.https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201747019
-
B lymphocyte-specific, Cre-mediated mutagenesis in miceNucleic Acids Research 25:1317–1318.https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.6.1317
-
BookPractical Flow CytometryNew York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.https://doi.org/10.1002/0471722731
-
The effect of trypan blue treatment on autofluorescence of fixed cellsCytometry Part A 91:917–925.https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.23199
-
Regulated selection of germinal-center cells into the memory B cell compartmentNature Immunology 17:861–869.https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3460
-
Intrinsic constraint on plasmablast growth and extrinsic limits of plasma cell survivalThe Journal of Experimental Medicine 192:813–822.https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.192.6.813
-
A novel allele for inducible cre expression in germinal center B cellsEuropean Journal of Immunology 49:192–194.https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201847863
-
Here, there, and anywhere? arguments for and against the physical plasma cell survival nicheThe Journal of Immunology 199:839–845.https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1700461
-
ConferenceStudying Epstein-Barr virus pathologies and immune surveillance by reconstructing EBV infection in miceCold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. pp. 259–263.https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.2013.78.020222
Article and author information
Author details
Funding
Cancer Research UK (FC001057)
- Dinis Pedro Calado
Medical Research Council (FC001057)
- Dinis Pedro Calado
Wellcome Trust (FC001057)
- Dinis Pedro Calado
Cancer Research UK ([C355/A26819])
- Dinis Pedro Calado
FC AECC ([C355/A26819])
- Dinis Pedro Calado
AIRC ([C355/A26819])
- Dinis Pedro Calado
Medical Research Council (MR/J008060/1)
- Dinis Pedro Calado
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the Immunity and Cancer laboratory (FCI, London) for critical discussions and review of the manuscript; the FCI BRF and Flow-cytometry platforms for expert advice and technical support. This work was supported by The Francis Crick Institute which receives its core funding from Cancer Research UK (FC001057), the UK Medical Research Council (FC001057), the Wellcome Trust (FC001057) to DPC, by CRUK [C355/A26819], FC AECC [C355/A26819], AIRC [C355/A26819] under the Accelerator Award Program to DPC, and an MRC career development award MR/J008060/1 to DPC.
Ethics
Animal experimentation: Animal experiments were carried out in accordance with national and institutional guidelines for animal care and were approved by The Francis Crick Institute biological resources facility strategic oversight committee (incorporating the Animal Welfare and Ethical Review Body) and by the Home Office, UK licence number PCE886633. All animal care and procedures followed guidelines of the UK Home Office according to the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 and were approved by Biological Research Facility at the Francis Crick Institute.
Copyright
© 2020, Xu et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 4,473
- views
-
- 555
- downloads
-
- 43
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Citations by DOI
-
- 43
- citations for umbrella DOI https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.59850






