Ciliary Hedgehog signaling regulates cell survival to build the facial midline
Figures
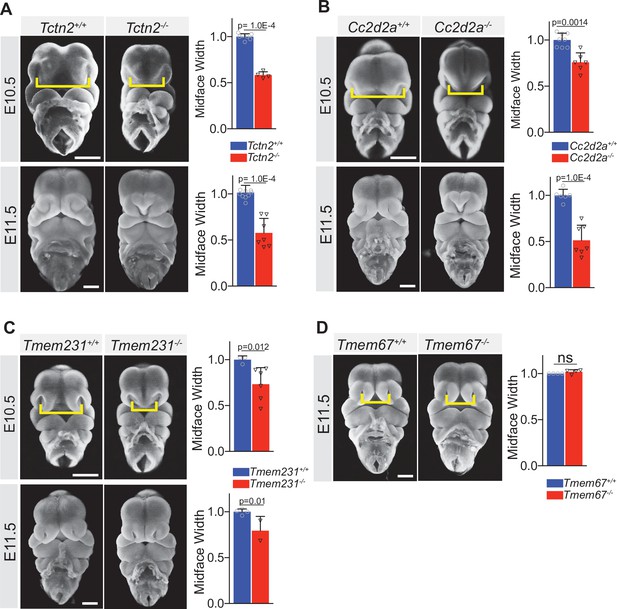
The ciliary Meckel syndrome (MKS) transition zone complex is essential for midline facial development.
Frontal view images of Tctn2 (A), Cc2d2a (B), Tmem231 (C) wild-type and null embryos at embryonic day (E)10.5 and E11.5. Tmem67 null embryos (D) display normal midface width at E11.5. Quantification of midface width (denoted by yellow brackets) at respective timepoints was measured via one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Data are expressed as mean, and error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) with individual data points (N) representing biological replicates (biologically distinct samples). Scale bar indicates 500 μm. ns = not significant.
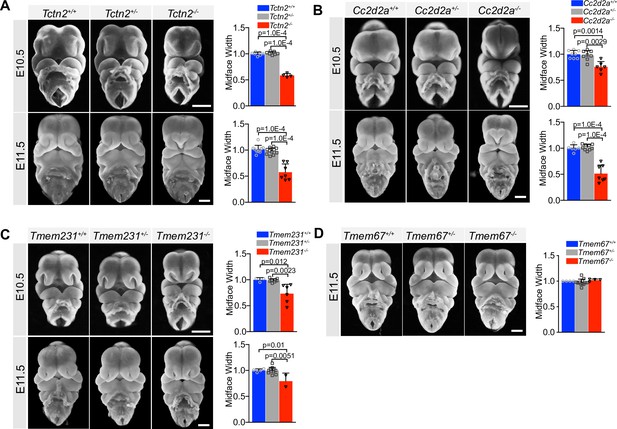
The ciliary Meckel syndrome (MKS) transition zone complex is essential for midline facial development.
Reproduced frontal view images from Figure 1 of Tctn2 (A), Cc2d2a (B), Tmem231 (C), wild-type and null embryos at embryonic day (E)10.5 and E11.5 with the addition of heterozygous embryos. (D) Tmem67 null and wild-type E11.5 embryos reproduced from Figure 1 with addition of heterozygous embryos. Quantification of midface width at respective timepoints measured via one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) and each data point indicates a biological replicate. Scale bar indicates 500 μm.

Removing TCTN2 in the neural crest does not result in hypotelorism.
(A) Frontal view images of embryonic day (E)11.5 Tctn2 control (Tctn2lox/-) and neural crest deletion (Wnt1Cre;Tctn2fl/-) embryos with corresponding midface width quantification. (B) Brightfield and fluorescent images of E11.5 Wnt1Cre;R26EYFP/+ embryos show expected pattern of Cre recombination (embryo outlined with white dotted line in B). (C) Immunofluorescence staining of E10.5 medial nasal prominence sections for ciliary membrane protein ARL13B, GFP, and epithelial marker E-cadherin (E-Cad). Dotted white line in (C) represents boundary separating epithelia and neural crest mesenchyme. Quantified data in A represents the mean with error bars indicating standard deviation (SD) and each individual data point indicates a biological replicate. Student’s t test performed for statistical analysis of (A), ns = not significant. Scale bars indicate 500 μm (A) and 10 μm (C).
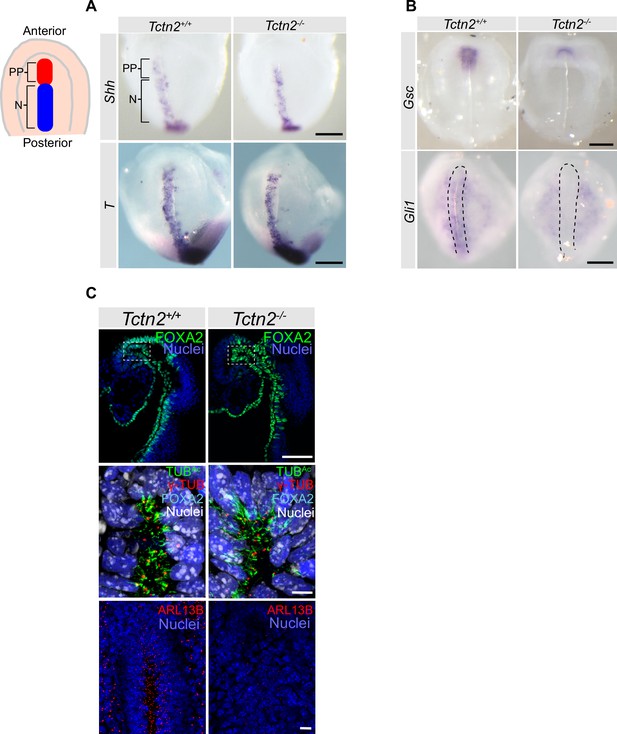
Tctn2 mutants exhibit defects in prechordal plate differentiation soon after gastrulation.
(A) Whole mount in situ hybridization (WM-ISH) of embryonic day (E)8.0 embryos for axial mesendoderm markers Shh and Brachyury (T). (B) WM-ISH of E8.0 embryos for prechordal plate marker Goosecoid (Gsc) and Hedgehog (HH) pathway target Gli1. (C) Whole mount immunofluorecence staining for the prechordal plate transcription factor FOXA2, cilia marker acetylated tubulin (TUBAc), basal body marker gamma tubulin (γ-TUB), and ciliary membrane protein ARL13B in E8.0 embryos. Middle panel in C is magnified region in top panel highlighted by dotted rectangle and rotated 90 degrees. Scale bar in A–B indicates 0.2 mm, C (top panel) is 100 μm, C (middle and bottom panels) is 10 μm.
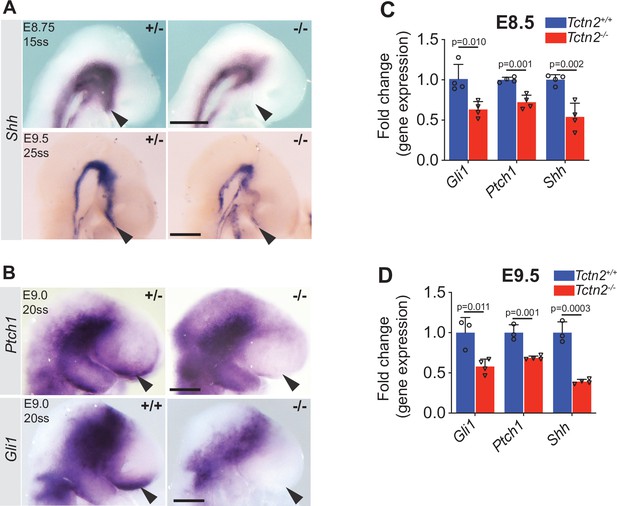
Tctn2 mutants display decreased Hedgehog (HH) signaling in the ventral telencephalon.
Whole mount in situ hybridization (WM-ISH) for Shh in Tctn2 control and mutant embryos at embryonic day (E)8.75 and E9.5 (A) show reduced expression in the ventral telencephalons (arrowheads) of mutant embryos . WM-ISH for HH pathway targets Ptch1 and Gli1 also show reduced expression in the ventral telencephalon in Tctn2 mutants (B, arrowheads). Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis of RNA transcripts isolated from E8.5 and E9.5 Tctn2 control and mutant heads (C and D, respectively) show reduced levels of Gli1, Ptch1, and Shh transcripts in the absence of TCTN2, consistent with WM-ISH results. Data in C, D represent mean, and error bar represents the standard deviation (SD). Sample size in C and D indicated with 3-4 biological replicates per assay. Student’s t test performed for statistical analysis. Scale bar indicates 0.5 mm.
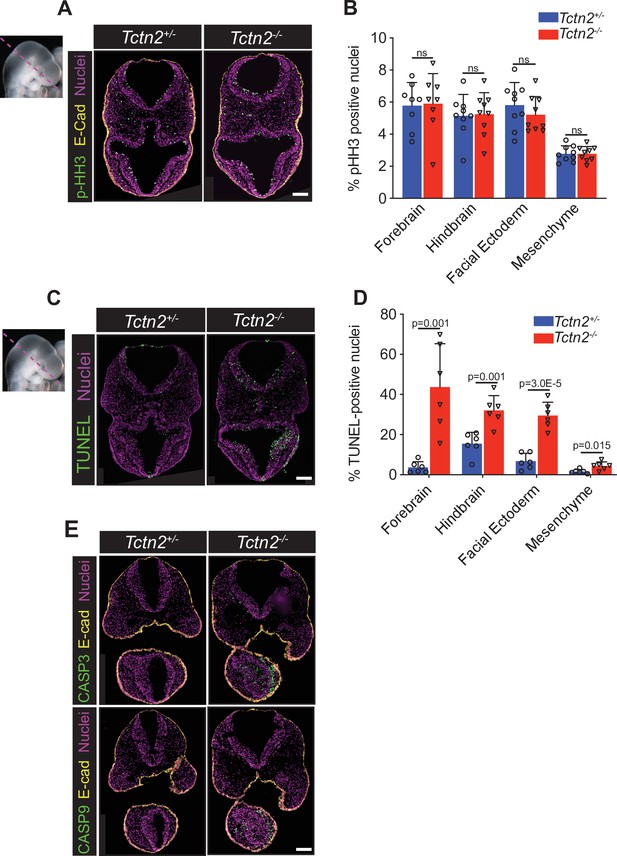
TCTN2 protects the neurectoderm and facial ectoderm from apoptosis.
Immunostaining for proliferation marker phospho-histone H3 (pHH3) in transverse sections of Tctn2 control and mutant embryonic day (E9.5) embryos (A) with corresponding quantification (B). (C) TUNEL staining for analysis of apoptosis in Tctn2 E9.5 embryos with corresponding quantification (D). (E) Immunostaining for intrinsic apoptotic pathway components cleaved-caspase-3 and cleaved-caspase-9 in Tctn2 control and mutant E9.5 embryos. Quantified data represent N = 3 biological replicates (biologically distinct samples) with a minimum of two sections analyzed per sample. Student’s t test performed for statistical analysis. Data in B, D represent the mean, and error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). Scale bar indicates 100 μm. ns = not significant.
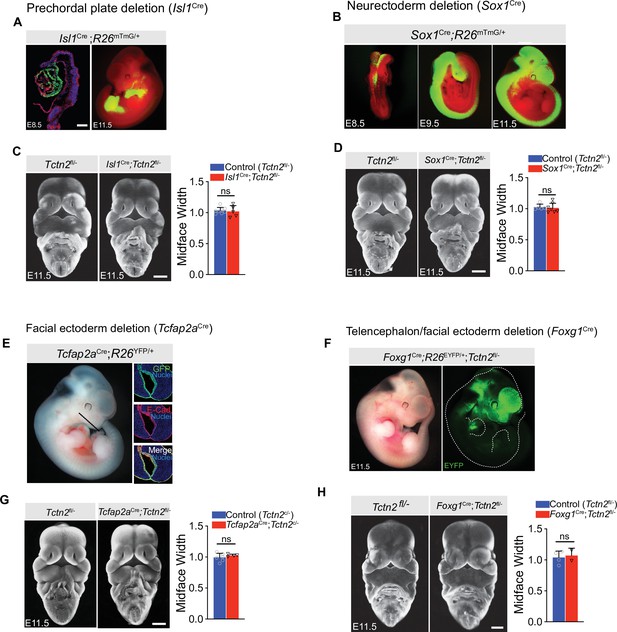
Deletion of Tctn2 in the prechordal plate by Isl1Cre, neurectoderm by Sox1Cre, facial ectoderm by Tcfap2aCre, or forebrain and facial ectoderm by Foxg1Cre does not result in hypotelorism.
(A) Analysis of Isl1Cre recombination pattern at E8.5 and E11.5 using the R26mTmG reporter shows robust recombination in the prechordal plate and endodermal derivatives at respective timepoints. (B) Analysis of Sox1Cre recombination pattern at E8.5, E9.5, and E11.5 using the R26mTmG reporter shows early recombination in the neural folds at E8.5 followed by robust recombination throughout the neurectoderm at E9.5 and E11.5. (C) Frontal view images of E11.5 control (Tctn2fl/-) and mutant (Isl1Cre;Tctn2fl/-) embryos with corresponding midface width quantification. (D) Frontal view images of E11.5 control (Tctn2fl/-) and neurectoderm-specific Tctn2 mutant (Sox1Cre;Tctn2fl/-) embryos with corresponding midface width quantification. (E) Analysis of Tcfap2aCre recombination pattern at E11.5 using the R26EYFP reporter shows robust recombination in the facial ectoderm as evidenced by colocalization with epithelial marker E-cadherin (E-Cad). (F) Analysis of Foxg1Cre recombination pattern at E11.5 using the R26EYFP reporter shows expected robust recombination in the forebrain and facial ectoderm at E11.5. (G) Frontal view images of E11.5 control (Tctn2fl/-) and facial ectoderm deletion (Tcfap2aCre;Tctn2fl/-) embryos with corresponding midface width quantification. (H) Frontal view images of E11.5 control (Tctn2fl/-) and forebrain/facial ectoderm-specific Tctn2 deletion (Foxg1Cre;Tctn2fl/-) embryos with corresponding midface width quantification. Dotted line in E indicates approximate section through midface for immunofluorescence images in E. Dotted white line in F indicates embryo outline. Quantified data in C, D, G, and H represent the mean with error bars indicating standard deviation (SD) and each individual data point indicates a biological replicate. Student’s t test performed for statistical analysis of C, D, G, and H. Scale bars indicate 100 μm in B, 500 μm in C, D, G, and H. ns = not significant.
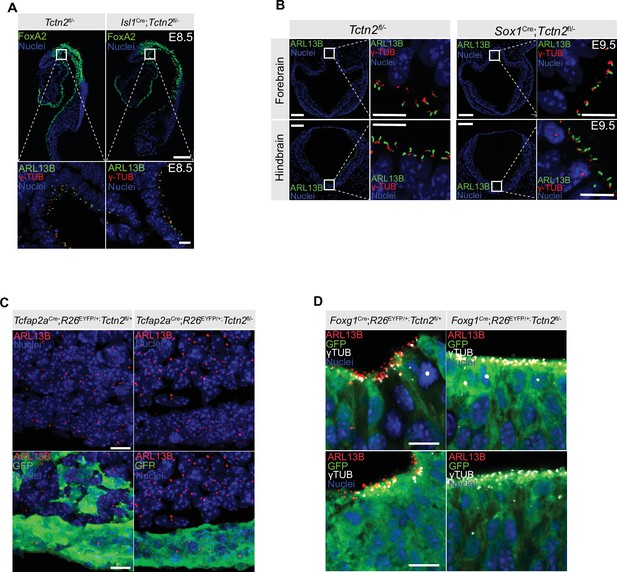
Residual TCTN2 function through persistent ARL13B ciliary localization in TCTN2 conditional mutants.
(A) Analysis of Tctn2 deletion in the prechordal plate of embryonic day (E)8.5 Isl1Cre;Tctn2fl/- embryos through ciliary localization of ARL13B indicates residual TCTN2 function remains at this early timepoint despite reporter recombination. (B) Analysis of Tctn2 deletion in the neurectoderm of E9.5 Sox1Cre;Tctn2fl/- embryos through ciliary localization of ARL13B in the forebrain (top panels) and hindbrain (bottom panels) indicates residual TCTN2 function remains at this early timepoint despite robust reporter recombination. (C) Analysis of Tctn2 deletion in the facial ectoderm of E11.5 Tcfap2aCre;Tctn2fl/- embryos through ciliary localization of ARL13B indicates residual TCTN2 function remains at this timepoint as ARL13B accumulation in cilia persists in the facial ectoderm of Tcfap2aCre;Tctn2fl/- mutants. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of E11.5 neural tube sections for ciliary membrane protein ARL13B, basal body marker gamma tubulin (γTUB), and α-GFP for readout of reporter recombination shows loss of TCTN2 function in Foxg1Cre;Tctn2fl/- embryos through loss of ARL13B ciliary accumulation. Low-magnification images in A and B indicate 100 μm, and high-magnification images in A (bottom panels), B (right panels), C, and D indicate 10 μm. ns = not significant.
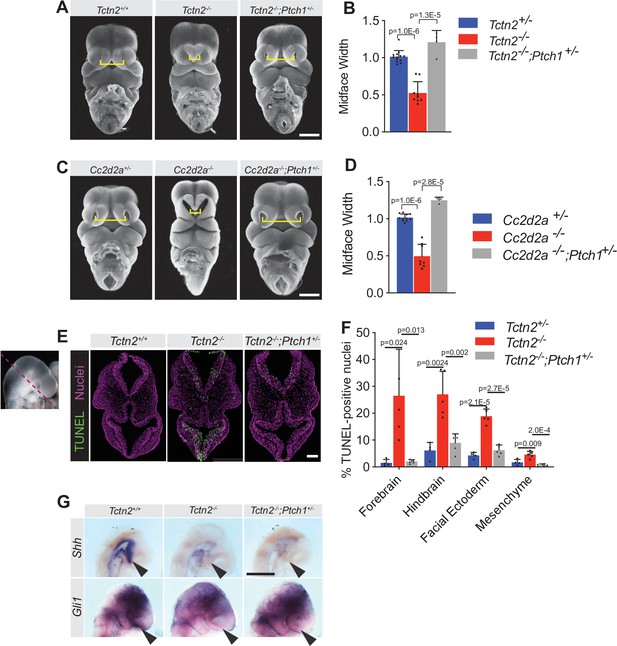
Reducing Ptch1 gene dosage rescues the facial midline defect in transition zone mutants.
(A) Frontal images of Tctn2 wild-type, mutant, and Ptch1+/- rescue embryonic day (E)11.5 embryos with corresponding midline width quantification (B). (C) Frontal images of Cc2d2a wild-type, mutant, and Ptch1+/- rescue E11.5 embryos with corresponding midline width quantification (D). (E) TUNEL assay sections of E9.5 Tctn2 wild-type, mutant, and Ptch1+/- rescue with corresponding quantification (F). (G) Whole mount in situ hybridization (WM-ISH) of E9.5 Tctn2 wild-type, mutant, and Ptch1+/- rescue embryos for Shh and Gli1. Quantified data represent N = 3 biological replicates (biologically distinct samples) with a minimum of two sections analyzed per sample. Data in B, D, F represent the mean, and error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). For statistical analysis, one-way ANOVA was performed with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Scale bars indicate 500 μm (A, C, G) and 100 μm (E).
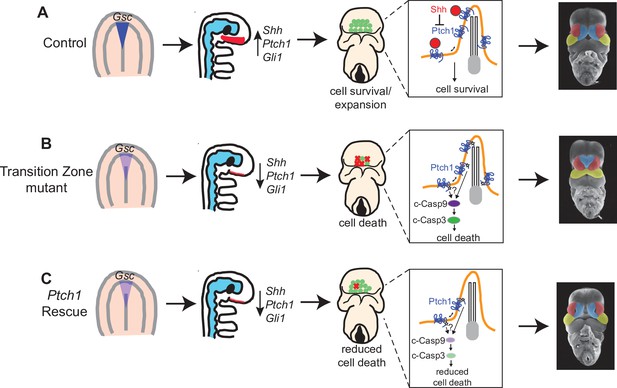
Model for transition zone coordination of facial midline development.
(A) In wild-type embryos, the transition zone complex mediates signaling in the prechordal plate and Hedgehog (HH) pathway activation in the adjacent neurectoderm to at allow for cell survival and normal midline development. (B) In transition zone mutants, disrupted signaling in the prechordal plate results in reduced Shh and HH pathway activation in the neurectoderm resulting in increased cell death and corresponding collapse of the facial midline. (C) In transition zone mutants with Ptch1 haploinsufficiency (Ptch1 rescue), reduced cell death allows for normal midface development despite persistent reduction of Shh and HH pathway activation in the neurectoderm.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Anti-Arl13b (rabbit polyclonal) | Proteintech | 17711–1-AP | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-cleaved-caspase-3 (Asp175) (rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | #9664 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Anti-cleaved-caspase-9 (Asp353) | Cell Signaling | #9509 | (1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-phospho-histone H3 (Ser28) (rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | #9713 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Anti-acetylated tubulin (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | T6793 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-FoxA2 (rabbit monoclonal) | abcam | Ab108422 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Anti-Gamma tubulin (goat polyclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Sc-7396 | (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (chicken polyclonal) | Aves Labs | GFP-1020 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-E-cadherin (rat monoclonal) | Invitrogen | 13–1900 | (1:1000) |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNAeasy Micro Kit | QIAGEN | 74004 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit | Roche | 11684795910 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | iScript cDNA synthesis kit | BioRad | 1708891 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Tctn2tm1.1Reit | PMID:21565611 | MGI:5292130;RRID:MGI:5292219 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Cc2d2aGt(AA0274)Wtsi | PMID:21725307 | MGI:4344514;RRID:MGI:5292228 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Tmem231Gt(OST335874)Lex | PMID:22179047 | MGI:4284576;RRID:MGI:5301844 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Tmem67tm1Dgen | PMID:21725307 | MGI:5292220;RRID:MGI:5292226 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Wnt1Cre: H2az2Tg(Wnt1-cre)11Rth | PMID:9843687 | MGI:2386570;RRIDSupplemental:IMSR_JAX:003829 | Gift from Brian Black |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Isl1tm1(cre)Sev | PMID:16556916 | MGI:3623159;RRID:IMSR_HAR:3351 | Gift from Brian Black |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Sox1tm1(cre)Take | PMID:17604725 | MGI:3807952;RRID:IMSR_RBRC05065 | Gift from Jeff Bush |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Foxg1tm1(cre)Skm | PMID:10837119 | MGI:1932522;RRID:IMSR_JAX:004337 | Gift from Stavros Lomvardas |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Tg(Tcfap2a-cre)1Will | PMID:21087601 | MGI:4887352;RRID:MGI:4887452 | Gift from Trevor Williams |
| Sequence-based reagent | Shh in situ probe | PMID:7916661 | Gift from Andrew McMahon | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gsc in situ probe | PMID:1352187 | Gift from Edward De Robertis | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Ptch1 in situ probe | PMID:10395791 | Gift from Lisa Goodrich | |
| Sequence-based reagent | RT-qPCR primers | This paper | *See Supplementary file 1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Genotyping primers | This paper | *See Supplementary file 1 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Prism (https://graphpad.com) | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | ImageJ (http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/) | RRID:SCR_003070 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Primer sets used for genotyping and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR).
File contains all sequencing primer pairs used for genotyping of all mouse strains used in this study. In addition, file contains primer sets used for RT-qPCR experiments. Inquiries regarding primers should be sent to Jeremy Reiter.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68558/elife-68558-supp1-v2.pdf
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68558/elife-68558-transrepform1-v2.docx





