Arginine-vasopressin mediates counter-regulatory glucagon release and is diminished in type 1 diabetes
Figures
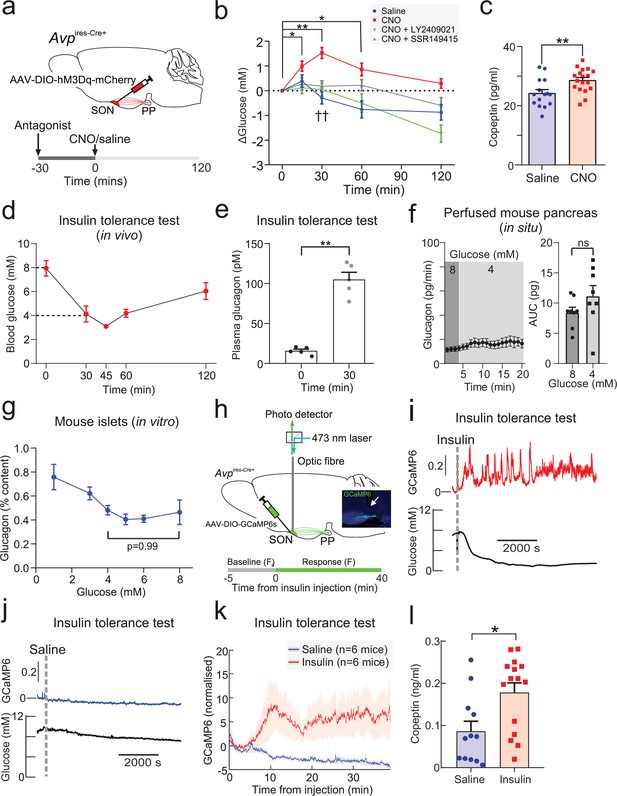
Insulin-induced hypoglycemia enhances population activity of AVP neurons in the supraoptic nucleus (SON), driving glucagon secretion AAV-DIO-hM3Dq-mCherry was injected bilaterally into the SON of Avpires-Cre/+ mice.
CNO (3 mg/kg) or vehicle was injected i.p. In the same cohort (different trial), LY2409021 (5 mg/kg) or SSR149415 (30 mg/kg) was injected (i.p.) 30 min prior to CNO. See Figure 1—figure supplement 1. (a) Blood glucose measurements from (a). Two-way RM ANOVA (Tukey’s). CNO 0 min versus CNO at 15, 30, and 60 min; p<0.05=*, p<0.01=**. Comparison of CNO versus Saline, CNO+LY2409021 or CNO+SSR149415 at 30 min; p<0.01=††. Time, p<0.0001; Treatment, p=0.0006; Interaction, p<0.0001. n=6 mice. (b) Terminal plasma copeptin 30 min following saline or CNO injection. Mann-Whitney t-test (p=0.0025, **). n=15–18 mice. (c) Plasma glucose during an insulin tolerance test (ITT; 0.75 U/kg) in n=5 wild-type mice. (d) Plasma glucagon following an ITT. n=5 wild-type mice. Paired t-test, p<0.01=**. (e) Glucagon secretion from the perfused mouse pancreas. Glucagon released during all time points in 8 mM glucose was not significantly different from 4 mM glucose (all p>0.8). Right: area under curve. Paired t-test, ns=not significant. (f) Glucagon secretion from isolated mouse islets during 60 min static incubation at indicated glucose concentrations. n=7 wild-type mice. One-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc. 4 mM versus 8 mM glucose, p=0.99. (g) Measurements of population GCaMP6s activity in pituitary-projecting AVP neurons in the SON. Inset: Expression of GCaMP6s in AVP neurons in the SON. Arrow=tip of the optic fiber. (h) Simultaneous in vivo fiber photometry of AVP neuron activity (GCaMP6) and continuous glucose monitoring (black line) in response to an ITT (1 U/kg). Dashed gray line indicates the time of insulin injection. (i) Same animal as in (j), but for saline vehicle injection (dashed gray line). (j) GCaMP6s signal (normalized) in response to insulin (n=6 mice) or saline vehicle (n=6). Plasma copeptin at 30 min following saline or insulin. Mann-Whitney U-test, p=0.021. n=15–18 mice. AVP, arginine-vasopressin.
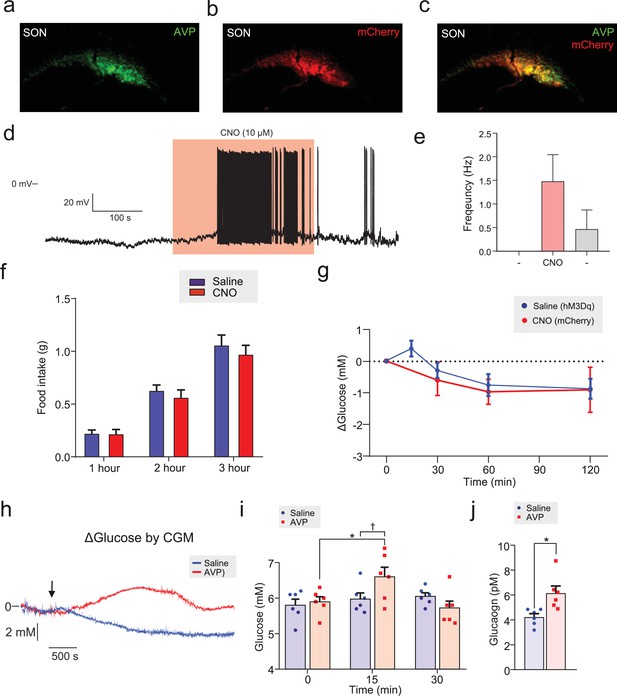
Effects of CNO in animals expressing mCherry in supraoptic nucleus (SON) AVP neurons (a) AAV-DIO-hM3Dq-mCherry was injected into the SON of Avpires-Cre/+ mice.
Immunostaining for AVP. See Figure 1. (b) Staining for mCherry; same brain sample as (a). (c) Merge of (a) and (b). (d) Patch-clamp recording from mCherry+ neuron in the SON in response to CNO. Firing frequency was increased in response to CNO. (e) Grouped data for firing frequency response to CNO in 3 mCherry+ neurons from SON of n=2 mice, as described in (a). One-way ANOVA; before treatment (−) versus CNO, p=0.11. CNO concentration applied was 5–10 µM. (f) Food intake in response to CNO in Avpires-Cre/+ mice expressing hM3Dq in the SON. Two-way RM (both factors) ANOVA (Time, p<0.001; Treatment, p=0.52). n=11 mice. (g) AAV-DIO-mCherry was injected into the SON of Avpires-Cre/+ mice, yielding mCherry expression in AVP neurons. CNO (3 mg/kg; i.p.) was injected and blood glucose was measured (control experiments for Figure 1b). One-way RM ANOVA (Time, p=0.26). n=7 mice. For comparison, the saline injections from Figure 1b are also shown, wherein saline was injected i.p. into mice expressing hM3Dq in AVP neurons in the SON. (h) Response of blood glucose to exogenous AVP (5 µg/kg) during continuous glucose monitoring. Representative of six trials from n=2 mice. (i) AVP (10 µg/kg, i.p.) was injected into wild-type mice and blood glucose was measured with glucose test strips. Two-way RM ANOVA with Tukey’s (within treatments) and Sidak’s (between treatments) multiple comparison. AVP injection, 0 min versus 15 min, p<0.05=*. Vehicle, 0 min versus 15 min, p>0.2. Between treatments at t=15 min; p=0.038, †. (j) Same cohort as in (e), but plasma glucagon measurements. Two-way RM ANOVA; p<0.05=*. AVP, arginine-vasopressin.

Simultaneous continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and in vivo fiber photometry of AVP neurons Grouped analysis of the glucose value at which the GCaMP6 signal crosses >2 SD from baseline, >3 SD from baseline and first exhibits a peak.
Six trials, two mice. One-way repeated measures ANOVA (Sidak), p<0.05=*. AVP, arginine-vasopressin.
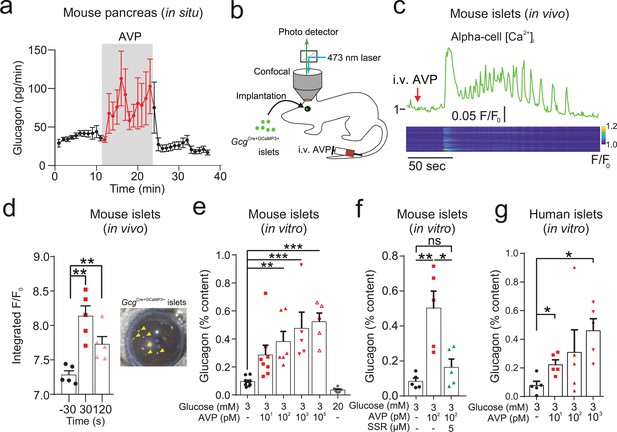
AVP increases glucagon release and alpha-cell activity ex vivo, in situ, and in vivo.
(a) Glucagon secretion from the perfused mouse pancreas in response AVP (10 nM). All data are represented as mean ± SEM. n=5 mice. Extracellular glucose of 3 mM. (b) Islets from GcgCre/+:GCaMP3/+ mice were injected into the anterior chamber of the eye (ACE) of recipient mice (n=5 islets in 5 mice). After >4 weeks, GCaMP3 was imaged in vivo in response to i.v. AVP (10 µg/kg) or saline administration. Saline did not change the GCaMP3 signal. Signal is GCaMP3 fluorescence (F) divided by baseline signal (F0). AVP evoked an increase in calcium activity, typically starting with a large transient. Below: Raster plot of response (normalized F/F0) in different cells (ROIs) with a single islet. (c) Response of alpha-cell to i.v. AVP. Lower panel shows raster plot of response in different cells. (d) Integrated F/F0 (area under curve) response for all alpha-cells in recorded islets (five islets, N=3 mice). The area under the curve was calculated 30 sec before i.v. injection, 30 sec after and 120 sec after. One-way RM ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test; p<0.01=**. Right: Image of islets (arrows) engrafted in the ACE. (e) Glucagon secretion from isolated mouse islets in response to AVP. One-way ANOVA (p<0.05=*; p<0.01=**; p<0.001=***). n=5–10 wild-type mice in each condition. (f) Glucagon secretion from isolated mouse islets in response to AVP in the presence and absence of the V1bR antagonist SSR149415. One-way ANOVA (p<0.05=*; p<0.01=**). n=5 wild-type mice per condition. (g) Glucagon secretion from islets isolated from human donors, in response to AVP. Paired t-tests, p<0.05=*. n=5 human donors. AVP, arginine-vasopressin; ROIs, regions of interest.

Expression of the vasopressin 1b receptor in mouse and human.
(a) mRNA expression of Avpr family in mouse heart, kidney, islets and adrenal glands. Samples from n=3 wild-type mice, each run in triplicate. Calculated with the Pfaffl method, using Actb as the reference gene. (b) mRNA expression in sorted islet cells. Fractions were sorted from mice with a fluorescent reporter (RFP) in alpha-cells (GcgCre/+-RFP mice) into an alpha-cell fraction (RFP(+)) and non-alpha-cell fraction (RFP(−)). Data from four sorts from n=4 GcgCre/+-RFP mice. Ratio paired t-test; p<0.05=*, p<0.01=**. (c) Same data as in (b). mRNA expression in alpha-cells (RFP(+) fraction) represented as fold of RFP(−) expression. Scale=log10. All data represented as mean ± SEM. (d) mRNA expression of AVPR1A, AVPR1B, AVPR2, and OXTR in human islets. Human islet samples n=7–8 donors. Calculated with the Pfaffl method, using Actb as the reference gene.
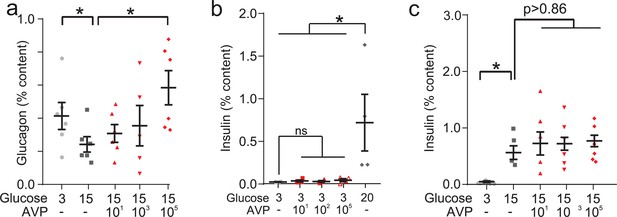
AVP and beta-cell function.
(a) Glucagon secretion (% content) from isolated mouse islets in response to AVP. One-way ANOVA (p<0.05=*). n=5–6 wild-type mice per condition. AVP was applied in high (15 mM glucose). (b) Insulin secretion from isolated mouse islets in response to physiological (10–100 pM) and supra-physiological (100 nM) concentrations of AVP. One-way ANOVA, p<0.01=**. n=5 wild-type mice per condition. (c) Insulin secretion (% content) from isolated mouse islets in response to AVP. One-way ANOVA, p<0.01=**. n=4–6 wild-type mice per condition. AVP was applied in high (15 mM glucose). AVP, arginine-vasopressin.
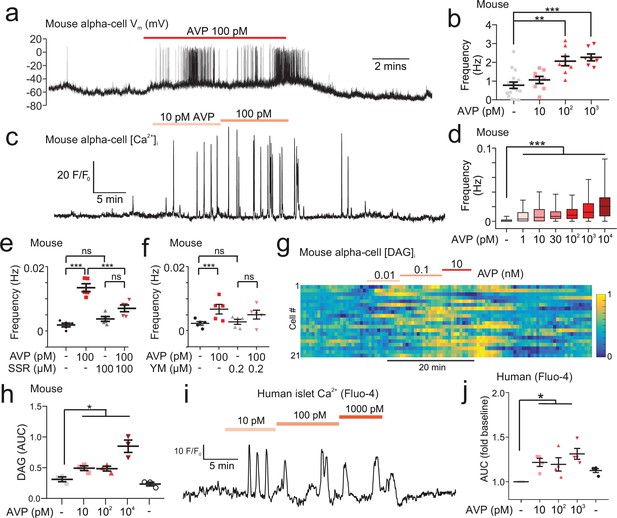
AVP increases action potential firing, Ca2+ activity, and intracellular DAG in alpha-cells in intact islets.
(a) Membrane potential (Vm) recording (perforated patch-clamp) of an alpha-cell in response to 100 pM AVP. (b) Frequency-response curve for varying concentrations of AVP (17 alpha-cells, 10 Gcg-GCaMP3 mice). Mixed-effects analysis of variance, Holm-Sidak’s post-hoc (p<0.01=**; p<0.001=***; p=0.073 for 3 mM glucose vs. 10 pM AVP). (c) GCaMP3 signal from an alpha-cell in response to AVP. (d) Box and whisker plot of the frequency of GCaMP3 oscillations in response to AVP. 142–170 alpha-cells, 7 islets, n=7 Gcg-GCaMP3 mice. Recordings in 3 mM glucose. One-way RM ANOVA, p<0.001=***. (e) Frequency of GCaMP3 oscillations in response to 100 pM AVP in the presence and absence of SSR149415 (10 µM). 75–90 alpha-cells, 6 islets, n=5 Gcg-GCaMP3 mice. Recordings in 3 mM glucose. One-way ANOVA (Tukey), p<0.001=***, ns=not significant (p>0.2). (f) Frequency of GCaMP3 oscillations in response to 100 pM AVP in the absence and presence of YM-254890 (0.2 µM). 75–90 alpha-cells, 6 islets, n=5 GcgCre/+:GCaMP3/+ mice. Recordings in 3 mM glucose. One-way RM ANOVA (Tukey’s multiple comparisons test), p<0.05=*, ns=not significant (p>0.3). AVP versus AVP+YM-254890; p=0.99. (g) Heatmap of intracellular diacylglycerol (DAG; upward DAG) signal from single islet cells (dispersed into clusters) in response to AVP. The signal was median filtered and normalized to largest signal in the recording. (h) Area under curve (AUC, normalized to duration) for DAG signal for each experimental condition. 10 recordings, 152 cells, n=3 wild-type mice. One-way RM ANOVA, p<0.05=* (Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (i) Fluo4 signal from a putative alpha-cell in a human islet in response to AVP (10, 100, and 1000 pM). Recording in 3 mM glucose. (j) Area under curve (AUC, normalized to duration) for Fluo4 signal in each human islet, for each experimental condition. 26 islets, n=4 human donors. One-way ANOVA, p<0.05=* (Sidak). AVP, arginine-vasopressin.
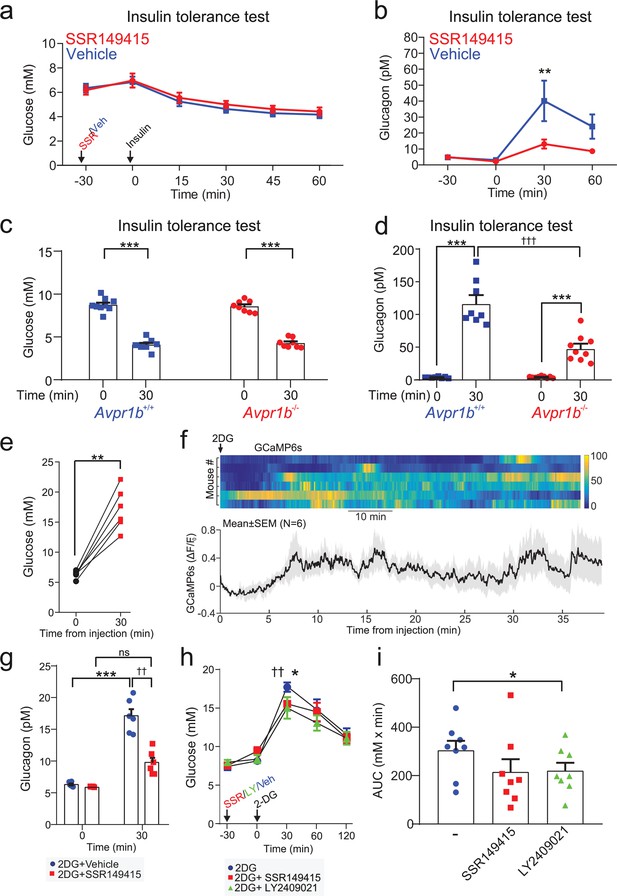
The vasopressin 1b receptor mediates hypoglycemia-induced glucagon secretion.
(a) Blood glucose during an ITT (0.75 U/kg; injection at 30 min). 30 min prior to the commencement of the ITT (t=0 min), either the V1bR antagonist SSR149415 (30 mg/kg) or vehicle was administered i.p. n=7 wild-type mice. (b) Plasma glucagon for (a). Two-way RM ANOVA with Sidak’s (between conditions) and Tukey’s (within condition) multiple comparisons test. Vehicle versus SSR149415; p<0.01=†† (30 min) and p<0.05=† (60 min). Glucagon was increased in response to an ITT in both treatment groups (p<0.01=** vs. 0 min). n=6–7 wild-type mice. (c) Plasma glucose during an ITT (0.75 U/kg; injection at 0 min) in Avpr1b−/− mice and littermate controls (Avpr1b+/+). Two-way RM ANOVA (Tukey), p<0.001=***. n=8–9 mice. (d) Plasma glucagon for (c). Two-way RM ANOVA (Sidak). Avpr1b−/− versus Avpr1b+/+; p<0.001=††† (30 min). 0 min versus 30 min; p<0.001=***. n=8–9 mice. (e) Population GCaMP6s activity in pituitary-projecting AVP neurons in the supraoptic nucleus (SON). GCaMP6s was imaged in response to 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2DG, 500 mg/kg) injection (i.p.). Plasma glucose at baseline (0 min) and 30 min after 2DG injection. Paired t-test, p<0.01=**. n=6 mice. (f) Upper: heatmap of population activity (GCaMP6s) response to 2DG for each mouse (n=6). Lower: mean ± SEM GCaMP6s signal for all mice (n=6) in response to 2DG. GCaMP6s data represented as (F–F0)/F0. (g) Plasma glucagon following 2DG injection (at 0 min). Prior to 2DG, either SSR149415 or vehicle was administered i.p. Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors (Bonferroni). Vehicle versus SSR149415; p<0.01=†† (30 min); p>0.99 (0 min). 0 min versus 30 min; p=0.009 (Vehicle); p=0.093 (SSR149415). Time, p<0.0001; Treatment, p=0.002; Interaction, p=0.005. n=6 mice. (h) Blood glucose response to 2DG, with or without pretreatment with SSR149415 (30 mg/kg), LY2409021 (5 mg/kg), or saline vehicle. Antagonists/vehicle injected 30 min prior to 2DG. Two-way RM ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test; 2DG versus 2DG+SSR149415, p=0.0103 (*); 2DG versus 2DG+LY024091, p=0.0047 (††). (i) Area under the (glucose) curve (AUC). One way ANOVA; 2DG versus 2DG+LY024091, p<0.05 (*). ITT, insulin tolerance test.
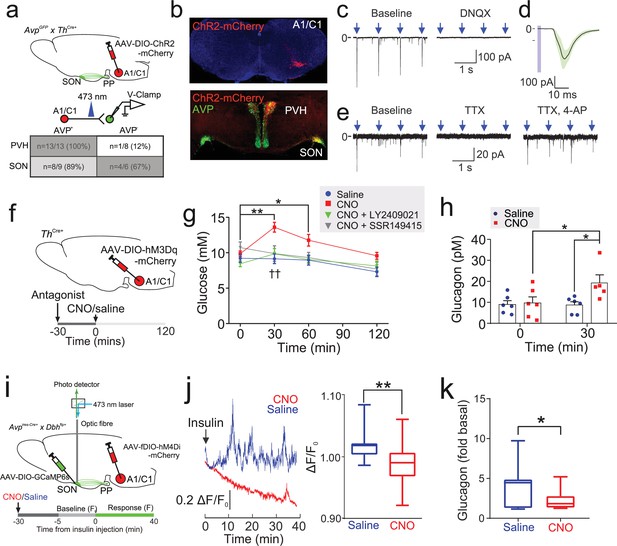
Insulin-induced AVP secretion is mediated by A1/C1 neurons.
(a) Upper: AAV-DIO-ChR2-mCherry was injected into the VLM of ThCre/+ mice or AvpGFP/+::ThCre/+ mice, targeting A1/C1 neurons. Lower: CRACM. Excitatory post-synaptic currents (EPSCs) were recorded in voltage-clamp mode in GFP+ (AVP) and GFP− neurons in the SON and PVH. The number (n) of neurons that responded to opto-activating A1/C1 terminals. Total of 36 neurons recorded from five mice. See Figure 5—figure supplement 1a. (b) Upper: Viral expression of ChR2-mCherry in A1/C1 neurons. Lower: A1/C1 neuron terminals co-localize with AVP-immunoreactive neurons. Representative from three mice. (c) Left: EPSCs evoked by opto-activation of A1/C1 terminals with 473 nm light pulses (arrows). Right: Light-evoked EPSCs following application of DNQX (20 µM). Representative of five recordings from three mice. (d) EPSC waveforms in a single GFP+ (AVP) neuron in response to repeated opto-activation of A1/C1 neuron terminals. Black line and shaded are=Mean ± SD of EPSCs. Light pulse=blue bar. Representative of three recordings from three mice. (e) EPSCs evoked by opto-activating A1/C1 terminals at baseline (left) and following addition of TTX (1 µM; middle) and 4-AP (1 mM; right). Representative of three recordings from three mice. (f) AAV-DIO-hM3Dq was injected into ThCre/+ mice, targeting A1/C1 neurons. CNO (1 mg/kg) was then injected (i.p.). Antagonists (or vehicle) for the V1bR (SSR149415, 30 mg/kg) or glucagon receptor (GCGR; LY2409021, 5 mg/kg) were injected 30 min prior to CNO. Plasma glucose and glucagon were then measured. See Figure 5—figure supplement 1b,c. (g) Plasma glucose in response to CNO and pretreatment with antagonists. n=8 mice. Two-way RM ANOVA (Sidak’s multiple comparison’s test). Time (p<0.0001), Treatment (p=0.03), and Interaction (p=0.0002). (h) Plasma glucagon at 30 min post-CNO (or vehicle) injection. Two-way RM ANOVA with Tukey’s (within treatment) and Sidak’s (between treatments) multiple comparisons. p<0.05=*, ns=not significant. Within treatment, CNO increased glucagon at 30 min versus 0 min (p=0.022). Saline did not (p=0.96). Between treatments, CNO increased glucagon at 30 min versus saline (p=0.001). n=6 mice. (i) In vivo fiber photometry measurements of population GCaMP6 activity in pituitary-projecting SON AVP neurons during A1/C1 neuron inhibition. AAV-DIO-GCaMP6s was injected into the SON and AAV-fDIO-hM4Di-mCherry into the VLM of Avpires-Cre/+::Dbhflp/+ mice. GCaMP6s was then imaged in response to an insulin tolerance test (ITT), following inhibition of the A1/C1 neuron (with CNO at 1 mg/kg), as indicated by the protocol in the lower horizontal bar. See Figure 5—figure supplement 2c. (j) Left: Example population activity in one mouse (as described in (i)) in response to an ITT, following saline or CNO treatment (on different trials). CNO strongly inhibited the response to insulin. Right: Average GCaMP6 signal ((F–F0)/F0) during response to insulin with either saline or CNO pretreatment (n=9 mice). CNO reduces the AVP GCaMP6 signal. t-test, p<0.01=**. (k) Plasma glucagon in response to an ITT in mice described in (i). 30 min before the insulin injection, either saline or CNO was given i.p. Glucagon is represented as fold of basal, where basal is 0 min (just prior to insulin) and the sample was taken at 30 min post-insulin. t-test, p=0.023 (*). n=8 mice. AVP, arginine-vasopressin; SON, supraoptic nucleus.
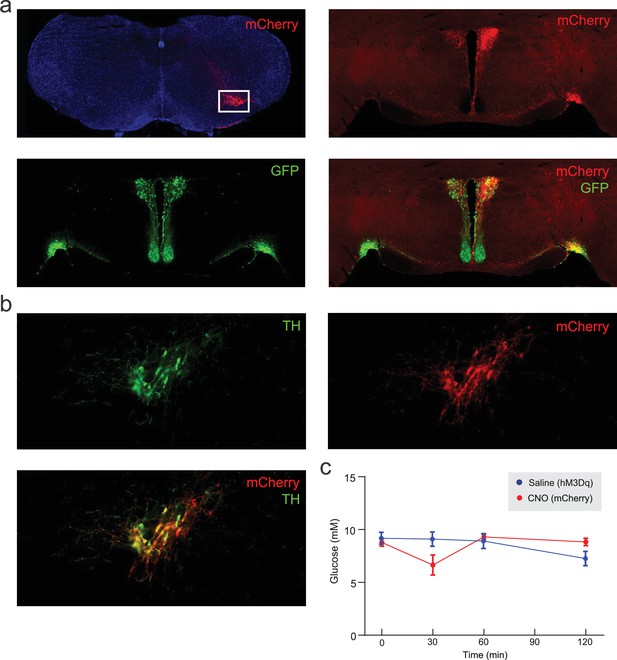
Viral tracing of A1/C1 terminals.
(a) Injection of a Cre-dependent viral vector containing the light-gated ion channel Channelrhodopsin-2 (AAV-DIO-ChR2-mCherry) into A1/C1 neurons of ThCre/+ mice. Top left: mCherry expression in A1/C1 neurons (white box). Top right: mCherry expression in the PVH and SON. Bottom left: AVP-immunoreactive neurons (green) expression in the PVH and SON. Bottom right: A1/C1 terminals (mCherry) co-localizing with AVP neurons (green) in the PVH and SON. (b) Expression of hM3Dq in A1/C1 neurons, following AAV-DIO-hM3Dq-mCherry injection into the A1/C1 region of ThCre/+ mice (i). TH=tyrosine hydroxylase. (c) CNO administration (i.p.) into ThCre/+ mice expressing mCherry (and not hM3Dq) in A1/C1 neurons (control experiments for Figure 5f–h). The saline injections in mice expressing hM3Dq in A1/C1 neurons (from Figure 5f–h) are also shown for comparison. AVP, arginine-vasopressin; SON, supraoptic nucleus.
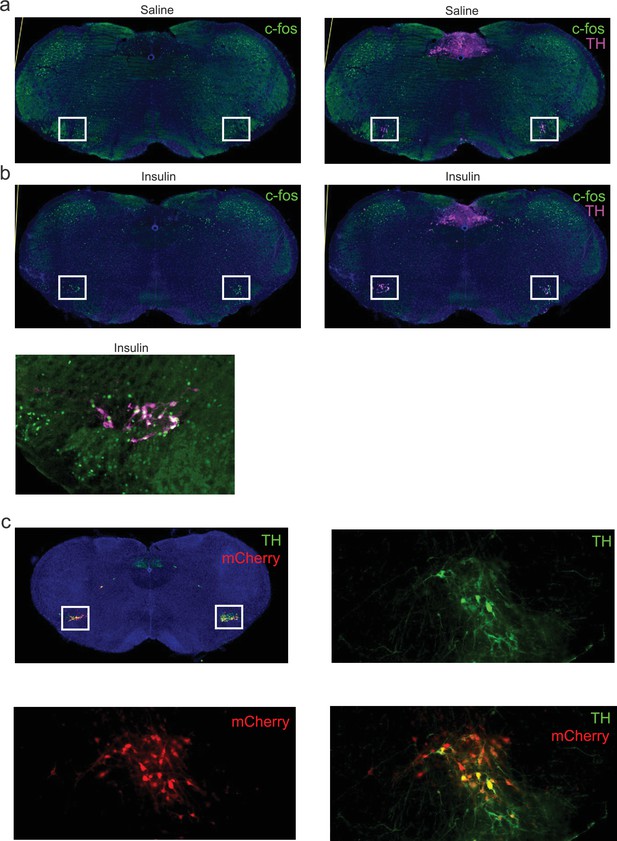
c-Fos expression in A1/C1 neurons during an ITT.
(a) Left: c-Fos expression 30 min following i.p. saline injection. Right: Same animal, but merge of Th and c-Fos. Note the Th+ immunoreactive neurons in the A1/C1 region (white box). (b) Left: c-Fos expression in ThCre/+ mice following an 30 min following i.p. insulin injection. Right: Same animal, but merge of Th and c-Fos. Note the Th+ immunoreactive neurons in the A1/C1 region (white box) co-expressing c-Fos. Lower panel: Magnified view of c-Fos and Th in A1/C1 neurons 30 min following insulin injection. Images representative of experiments in n=1+1 mice. See Figure 5. (c) Top left: Expression of mCherry and TH (green) in A1/C1 neurons (white box) of Dbhflp/+ mice, following viral injection of AAV-fDIO-hM4Di-mCherry into the VLM, targeting A1/C1 neurons. Top right: Magnified view of the A1/C1 region, TH expression. Bottom left: Magnified view, mCherry expression. Bottom right: merge. ITT, insulin tolerance test; TH. tyrosine hydroxylase.
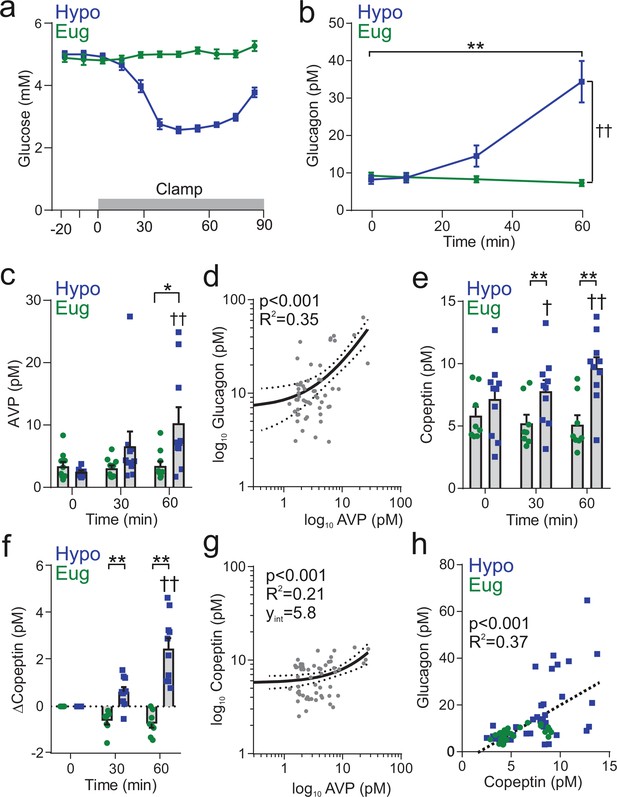
Insulin-induced hypoglycemia evokes copeptin and glucagon secretion in human participants.
(a) Blood glucose was clamped at euglycemia (Eug) and followed during insulin-induced hypoglycemia (Hypo). n=10 healthy human subjects. The clamp was initiated at time 0 min and terminated at 60 min. (b) Plasma glucagon measurement during insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors. Time point versus 0 min; p<0.01=**. Between treatments; p<0.01=††. (c) Plasma AVP measurement during and following clamping period. Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors. Hypoglycemia 0 min versus 60 min; p<0.01=††. Hypoglycemia 0 min versus 30 min; p=0.07. Between treatments; p<0.05=*. (d) Log-log plot of plasma AVP and plasma glucagon. Data points are 0, 30, and 60 min during hypoglycemic clamp. Linear regression (solid line) with 95% CI (dashed line). (e) Plasma copeptin measurement during hypoglycemic or euglycemic clamp. Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors. Indicated time point versus 0 min; p<0.05=†, p<0.01=††. For hypoglycemic clamp 0 min versus 30 min, p=0.07. Between treatments; p<0.01=**. (f) Change in plasma copeptin from baseline (time=0 min). Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors. Indicated time point versus 0 min; p<0.01=††. For hypoglycemic clamp 0 min versus 30 min, p=0.07. Between treatments; p<0.01=**. (g) Log-log plot of plasma AVP and plasma copeptin (as plotted in Roussel et al., 2014). Data points are 0, 30, and 60 min during hypoglycemic clamp. Linear regression (solid line) with 95% CI (dashed line). (h) Correlation of change in copeptin and glucagon, with a linear regression (dashed line). Data points are from both euglycemia and hypoglycemia at 0, 10, 30, and 60 min.
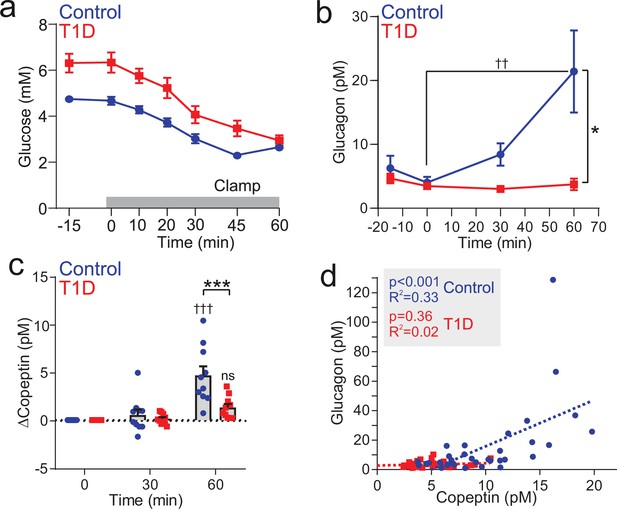
Insulin-induced copeptin and glucagon secretion is diminished in people with type 1 diabetes.
(a) Hypoglycemia was induced by an insulin infusion in patients with T1D (n=10) and non-diabetic individuals (Controls; n=10). The insulin infusion was initiated at 0 min. (b) Plasma glucagon during the clamping period. Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors. Indicated time point versus 0 min; p<0.01=††. Between groups; p<0.05=*. Data from n=10 Control and n=10 T1D. (c) Plasma copeptin measurement during and following clamping period. Change in copeptin from baseline (time=0 min). Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors. Time point versus 0 min; p<0.001=†††; ns = not significant (p>0.05). Between groups; p<0.001=***. Data from n=10 Control and n=10 T1D. (d) Correlation of copeptin and glucagon following hypoglycemic clamping for control participants (n=10, circle) and T1D (n=10, square). Linear regressions (dashed lines) for Control and T1D data sets.
Tables
Participant characteristics for Figure 7.
| Christensen et al., 2011 | Christensen et al., 2015 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | Control (n=10) | T1D (n=10) | |
| Age (years) | 23±1 | 26±1 | 0.06 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23±0.5 | 24±0.5 | 0.1744 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.5±0.1 | 7.3±0.2 | <0.0001 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72919/elife-72919-transrepform1-v2.docx
-
Source data 1
Data for figures.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72919/elife-72919-supp1-v2.xlsx





