MCPH1 inhibits Condensin II during interphase by regulating its SMC2-Kleisin interface
Figures
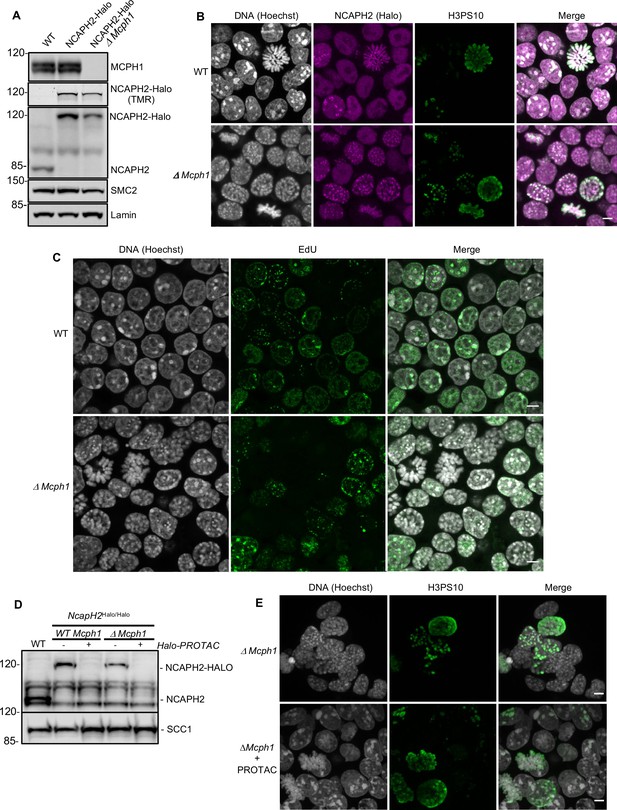
The deletion of Mcph1 in E14 cells induces condensin II-dependent chromosome condensation in both G1 and G2 phases of the cell cycle.
(A) In gel TMR-Halo detection and western blot analysis of E14 cells wild type, Ncaph2Halo/Halo and Ncaph2Halo/Halo Mcph1Δ/Δ. TMR signal detects NCAPH2-Halo tagged. The anti-NCAPH2 antibody shows that all the NCAPH2 protein expressed is fused to the Halo-tag and that the expression levels are similar to wild type but reduced after Mcph1 deletion. The anti-SMC2 detection shows similar levels of condensin in the three cell lines. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of Histone H3 phosphorylated on serine 10 (green) combined with TMR detection of NCAPH2-Halo (Red) in Mcph1wt/wt and Mcph1Δ/Δ cells. The DNA organisation was analysed using Hoechst. (C) EdU incorporation in Mcph1wt/wt or Mcph1Δ/Δ cells.(D) Western blot analysis of Halo-PROTAC induced NCAPH2-Halo degradation in wild-type, Ncaph2Halo/Halo Mcph1wt/wt and Ncaph2Halo/Halo Mcph1Δ/Δ cells using an anti-NCAPH2 antibody. Anti-SCC1 was used as a loading control. (E) Immunofluorescence analysis of the chromosome decompaction induced by 16 hr treatment of Mcph1Δ/Δ cells with Halo-PROTAC. Immunofluorescence analysis of Histone H3 phosphorylated on serine 10 (green) was used to compare similar cell cycle stages. All the cells showed a diffuse chromatin organisation (150 cells counted). Scale bar, 5 μm.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Raw data uncropped blots corresponding to Figure 1A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Raw data uncropped blots corresponding to Figure 1D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig1-data2-v2.zip

The cell cycle parameters are unchanged in Mcph1-deleted cells.
FACS analysis of the cell cycle parameters of Mcph1 deleted cells compared to wild type: (A) Analysis of the DNA content using propidium Iodide (repeated twice). (B) EdU incorporation (repeated twice). (C) H3 Phosphorylation on serine 10 (repeated twice). All FACS experiments where repeated twice with two independent clones. (D) Western blot analysis of the amount of γH2AX and H3 phosphorylation on serine 10 in wild-type cells compared to Mcph1 deleted cells. Scale bar, 5 μm.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data uncropped blots corresponding to Figure 1A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
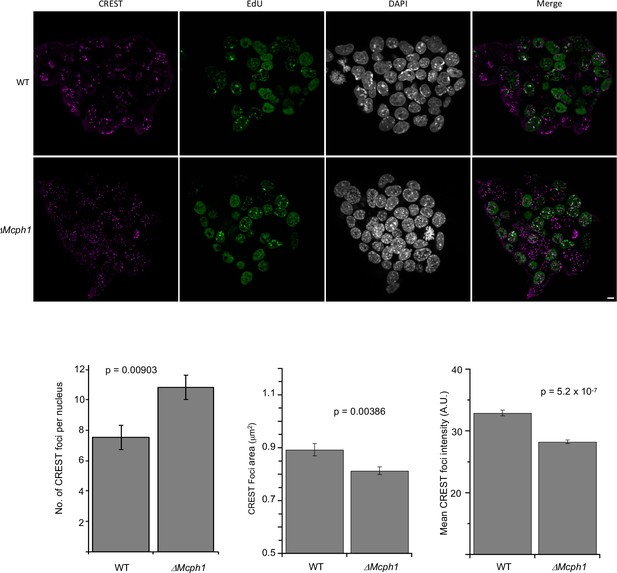
Chromocenters disruption in Mcph1 deleted cells.
Top: Immunofluorescence analysis of centromere clustering using CREST antibody showing that in Mcph1-deleted cells, the centromeres are scattered in the nucleus even in replicating, EdU-positive cells. Bottom: Image J quantification of the number of CREST foci, their area and their intensity. The number of CREST foci was counted in 30 nuclei in each condition. The area and intensity of the foci was analysed in 369 foci for the wild-type condition and 488 foci for the Mcph1-deleted condition. In each graph, the two tailed T-test p values are indicated is indicated.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw data of foci quantification.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig1-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
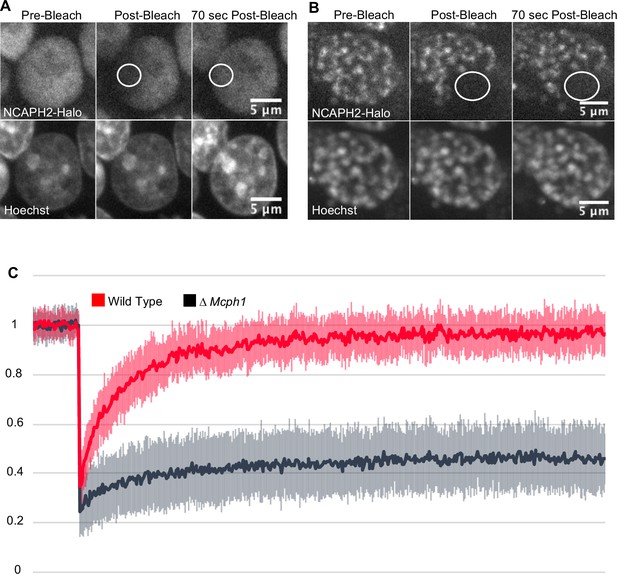
Mcph1 deletion induces the stable binding of condensin II to the condensed chromosomes in interphase.
FRAP analysis of NCAPH2-Halo turn-over on chromatin in Mcph1wt/wt (A) and Mcph1Δ/Δ cells (B). Top row: NCAPH2-Halo signal pre-bleach, post bleach and after 70 s recovery. The region bleached correspond to the white circle. Scale bar, 5 μm. (C) Quantification of the fluorescence recovery after photobleaching over a 10 min post-bleach period. (Average of three experiments, total number of cells analysed: WT 28 cells, Mcph1Δ/Δ 30 cells, standard deviation is represented for every time point).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Microsoft excel of FRAP measurements.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
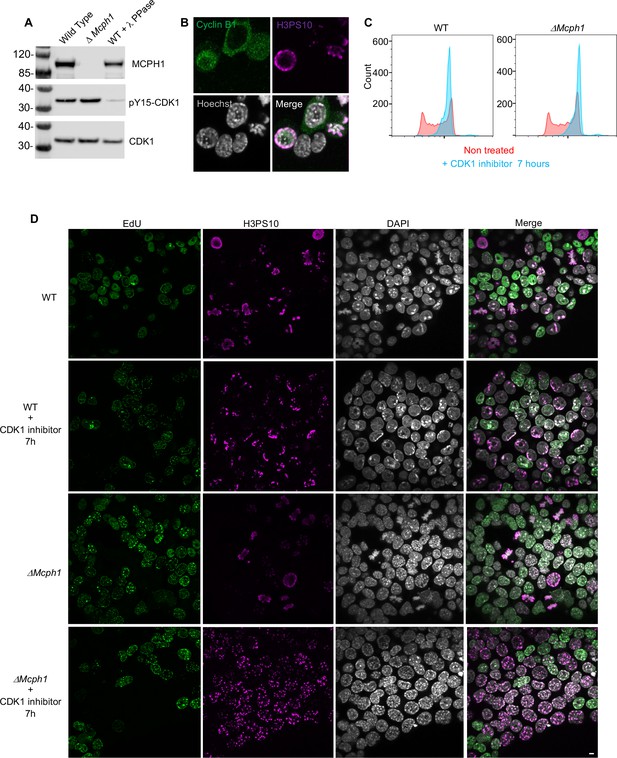
CDK1 activity is not required for the condensation phenotype induced by Mcph1 deletion.
(A) Western blot analysis of CDK1 phosphorylation on tyrosine 15 in wild-type cells compared to Mcph1-deleted cells. Wild-type protein extracts were treated by λ phosphatase as a control of antibody specificity. An anti-CDK1 protein was used as a loading control. (B) Immunolocalisation of Cyclin B in Mcph1-deleted cells. (C) CDK1 activity was inhibited by incubating wild-type or Mcph1 deleted cells to RO-3306 for 7 hr. The cell cycle profile was analysed by FACS for both wild-type and Mcph1-deleted cells without treatment or after 7 hr incubation with 9 μM R0-3306. (D) All the G2 cells in Mcph1-deleted cells present the condensed phenotype after CDK1 inhibition (150 cells counted). No condensation was observed in wild-type G2 cells (200 cells counted). Scale bar, 5 μm.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Raw data uncropped blots corresponding to Figure 3A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig3-data1-v2.zip
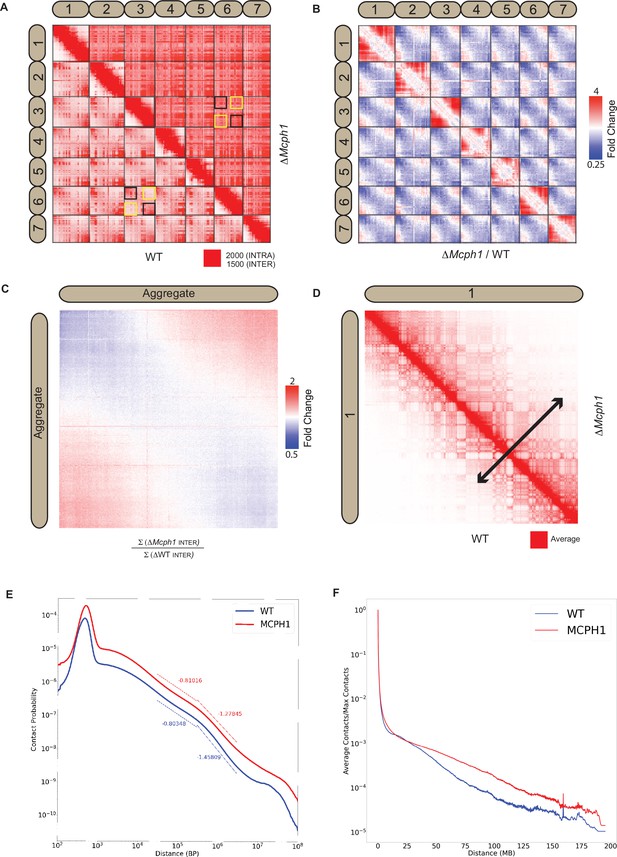
Mcph1 deletion causes chromosome compaction and loss of chromocenters.
(A) Representative subset of interactions between chromosomes 1–7 for wild-type and Mcph1 deletion maps (wild-type below diagonal) shows loss of chromocenters in the Mcph1 deletion maps. The intensity of color in the Hi-C maps show the frequency of contacts between pairs of loci (row and column), with the upper bound cutoff for interaction frequency in red and zero interaction frequency in white (different upper bound cutoffs for intrachromosomal vs interchromosomal interactions are indicated in the legend). In the wild-type map, the p-termini of different chromosomes show increased contact frequency with one another, as do the q-termini of different chromosomes with each other; examples of such interactions are highlighted by the black squares. The wild-type map also shows that the p-termini of one chromosome show less contact frequency with the q-termini of other chromosomes; examples of such interactions are highlighted by the yellow squares. Such differential interactions in the wild-type map are contrasted with the same regions highlighted by the black and yellow squares in the Mcph1 deletion maps, where no significant difference of interaction is seen. (B) Log fold change for Mcph1 deletion over wild-type for chromosomes 1–7. Red indicates genomic loci pairs that enriched contact in the Mcph1 deletion maps relative to wild-type, and blue indicates genomic loci pairs that have depleted contacts in the Mcph1 deletion maps relative to wild-type. (C) Log fold enrichment of the Mcph1 deletion map over wild-type map for the aggregated inter-chromosomal matrix. (D) Balanced KR-normalised Hi-C Maps for wild-type and Mcph1 deletion maps for the intrachromosomal region of chromosome 1 (wild-type below diagonal). Increased interactions between distant loci in the intrachromosomal Mcph1 deletion maps is seen. Color scale threshold is at the average value of each respective Hi-C map. Black arrows indicate the genomic distance at which loci show a greater than average level of contact frequency for the respective maps. (E) Intrachromosomal contact probability for all chromosomes shows increased long-range interactions and diminished contact drop-off for Mcph1 deletion. (F) Average intrachromosomal contact frequency for all chromosomes shows increased long-range interactions with Mcph1 deletion.
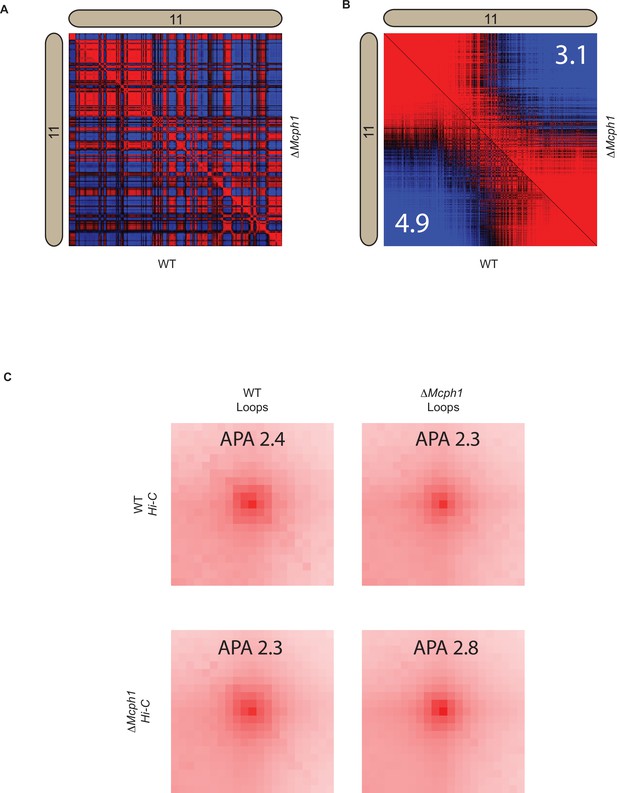
Mcph1 deletion decreases intra-compartment strength and does not affect looping.
(A) Pearson correlation map at 250 kB for wildtype and Mcph1 deletion maps for the intrachromosomal region of chromosome 11 (wildtype below diagonal). (B) Pearson correlation map at 250 kB for wildtype and Mcph1 deletion maps for the intrachromosomal region of chromosome 11 sorted by values of the principal eigenvector (wildtype below diagonal). Intra-compartmental interactions (A–A and B–B) vs inter-compartment interactions (A–B) show a relative decrease in the Mcph1 deletion maps. The top 50 % of A compartment loci and top 50 % of B compartment loci were computed from the magnitude of the principal eigenvector; the distance-normalised frequency of interactions was then calculated between loci in the same compartment (A-A and B-B interactions) vs interactions where one locus is in the A compartment, and one locus is in the B compartment (A-B interactions). The number in the upper right and lower left corners is the relative enrichment of A-A and B-B interactions vs A-B interactions in the respective maps. (C) Aggregate peak analysis using the loop lists for both wildtype and Mcph1 deletion on both Hi-C maps shows no significant global change to chromatin looping, which is also verified by direct observation of the maps.
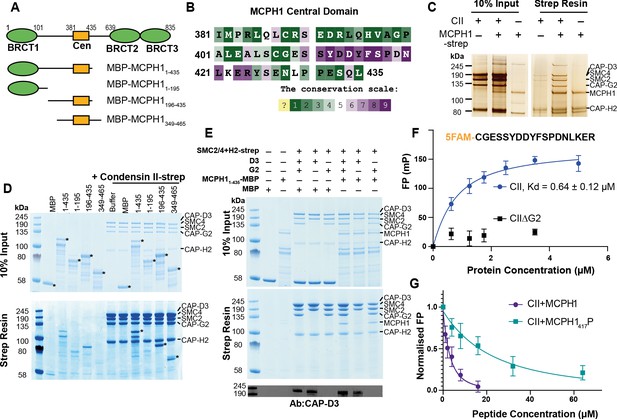
Human condensin II interaction with MCPH1.
(A) Domain structure of MCPH1 and MBP fusion constructs that were expressed in E. coli and used in binding assays. BRCT domains are indicated in green and the central domain in yellow. (B) Conservation analysis of the MCPH1 central domain with the ConSurf server. (C) Strep tag pull-down indicating full-length MCPH1 binds condensin II. Full-length MCPH1 and condensin II were expressed in insect cells and separately purified, before being mixed on strep-tactin sepharose. Samples of input and resin after run on SDS page and visualised with silver stain. (D) Strep-tag pull-down assay indicating strep tagged condensin II pulls down MBP-MCPH1 constructs that contain the central domain, but not MBP-MCPH11-195 or MBP alone. SDS page gel visualised with Coomassie stain, (*) indicates the running position of the MBP/MCPH1 construct used. (E) Strep pull-down assay showing strep-tagged pentameric condensin II or tetrameric condensin II lacking NCAPD3 can pull down MBP-MCPH11-435, while tetrameric condensin lacking NCAPG2 does not pull down MCPH1. The lower panel shows a western blot performed using strep-resin samples, blotted using an anti-NCAPD3 antibody. (F) Fluorescence polarisation binding assay using 5-FAM-labelled MCPH1407-424 peptide and increasing concentration of either pentameric condensin or tetrameric condensin II lacking MCPH1 binding subunit NCAPG2 (CIIΔG2). (G) Peptide competition assay using a fixed concentration of 5-FAM labelled MCPH1407-424 and condensin II with an increasing amount of MCPH1407-424 wild-type or phosphorylated at serine 417. All error bars indicate standard deviation from three replicates.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Microsoft excel data corresponding to Figure 5F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Microsoft excel data corresponding to Figure 5G.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig5-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Raw data uncropped gels corresponding to Figure 5C, D and E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig5-data3-v2.zip

Condensin I does not interact with MCPH1.
(A) Strep-tag pull-down assay indicating strep tagged condensin I does not pull-down any MBP-MCPH1 construct. SDS page visualised with Coomassie stain for input samples and silver stain for resin samples, (*) indicates the running position of the MBP/MCPH1 construct used. (B) Condensin II and MBP-MCPH1196-435 form a stable complex and co-elute in size exclusion chromatography. Elution profiles of condensin II + MBP-MCPH1196-435, condensin II alone and MBP-MCPH1196-435 alone are shown in green, blue and red, respectively. Fractions from void, condensin II and MCPH1 peak were run on an SDS page and stained with Coomassie. (C) Sequence conservation map of MCPH11-435 generated using the ConSurf server (Ashkenazy et al., 2016; Berezin et al., 2004), with the central motif indicated. Colours range from non-conserved (green) to conserved (purple), ‘b’ indicates residues predicted to be buried and ‘e’ indicates residues predicted to be solvent-exposed.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data uncropped gels corresponding to Figure 5—figure supplement 1B, C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Microsoft excel data corresponding to Figure 5—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig5-figsupp1-data2-v2.xlsx
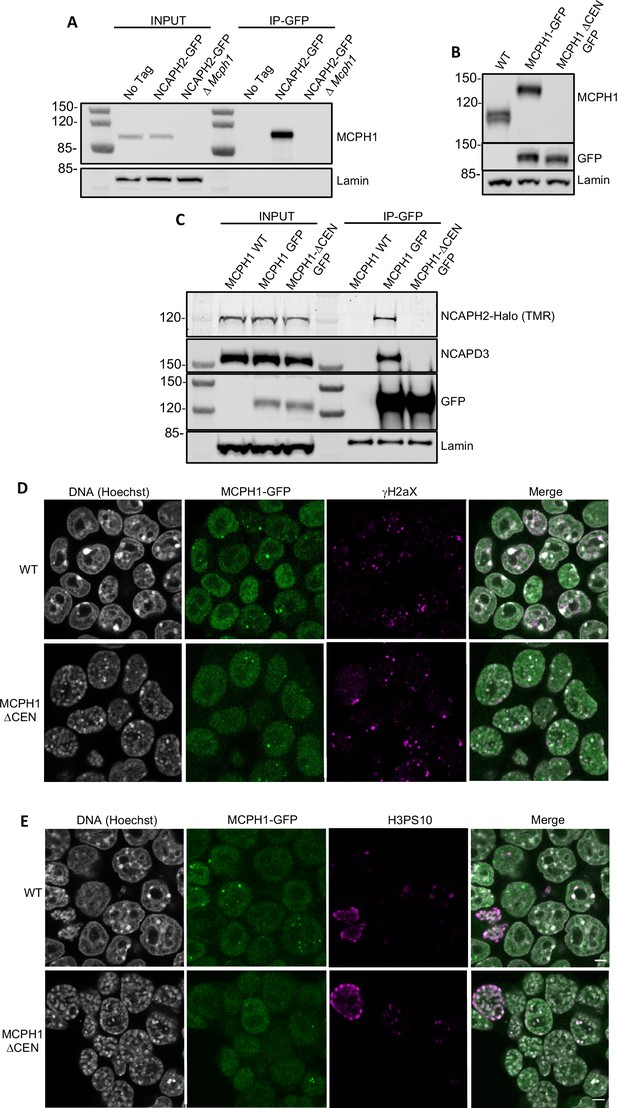
MCPH1 interaction with condensin II is essential to prevent interphasic chromosome condensation.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation of MCPH1 with NCAPH2-GFP. Nuclear extracts were prepared from wild type, Ncaph2GFP/GFP and Ncaph2GFP/GFP Mcph1Δ/Δcells. Immunoprecipitation was performed using GFP-trap agarose beads and analysed by western blot using an anti-MCPH1 antibody (IP-GFP). 5 % of the lysate used for IP was loaded as INPUT control. Anti-Lamin B1 antibody was used as a loading control. (B) Deletion of the central domain of MCPH1. To address if the central domain of MCPH1 is necessary to mediate the interaction with condensin II, we first introduced a GFP-tag at the C-terminal end of MCPH1 in Ncaph2Halo/Halo cells as the antibody against the protein was raised against the central domain. Then a second targeting was done to delete the central domain. As a result, the western blot represented in panel B using anti-MCPH1 antibody detects the wild-type protein or the GFP-tagged protein, homozygous Mcph1GFP/GFP but does not detect anything after deletion of the central domain. Using anti-GFP antibody reveals that the protein deleted for the central domain is present in the cell at similar levels as the wild-type GFP-tagged protein. A slight decrease in size is observed due to the deletion of the central domain. Anti-Lamin B1 antibody was used as a loading control. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation of NCAPH2-Halo with MCPH1-GFP. Nuclear extracts were prepared from Ncaph2Halo/Halo, Ncaph2Halo/HaloMcph1GFP/GFP and Ncaph2Halo/HaloMcph1ΔcenGFP/ΔcenGFP cells. Immunoprecipitation was performed using GFP-trap agarose beads and analysed by in-gel detection of NCAPH2-Halo using the Halo-ligand TMR or by western blot using an anti-NCAPD3 antibody (IP-GFP). 5 % of the lysate used for IP was loaded as input control. Anti-Lamin B1 antibody was used as a loading control. (D,E) Immunofluorescence analysis of the chromatin organisation in Ncaph2Halo/HaloMcph1GFP/GFP and Ncaph2Halo/HaloMcph1ΔcenGFP/ΔcenGFP cells. MCPH1-GFP is only detected in the cell nucleus enriched in dots colocalising with some γH2AX foci (D). The deletion of its central domain induces a similar condensation of interphasic chromosomes as the one observed after the complete loss of function of Mcph1 (E).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Raw data uncropped gels corresponding to Figure 6A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig6-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Raw data uncropped gels corresponding to Figure 6B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig6-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 3
Raw data uncropped gels corresponding to Figure 6C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig6-data3-v2.zip
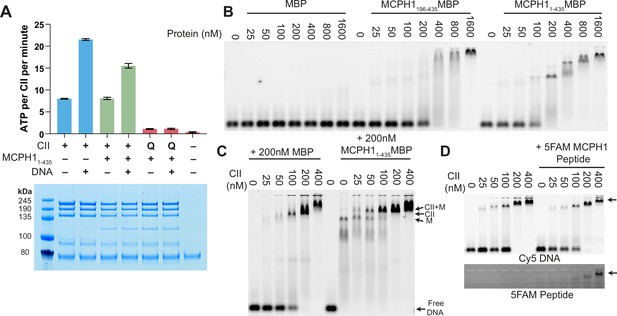
MCPH1 has little effect on condensin II ATP hydrolysis and DNA binding.
(A) ATPase rate of condensin II complex in the presence of MCPH1. Q refers to condensin II with an ATPase deficient mutation in the Q-loop. Below is an SDS page gel of the completed reaction. Error bars indicate standard deviation from three repeats. (B) EMSA assay of MBP, MCPH11-435-MBP and -MCPH1195-435-MBP using 50 bp of Cy5-labelled dsDNA. (C) EMSA assay of condensin II in the presence of MBP or MCPH11-435-MBP. (D) EMSA assay of condensin II in the presence or absence of 5FAM-MCPH1 peptide. Top image detecting Cy5 and bottom imaged detecting 5FAM.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Microsoft excel data corresponding to the standard curve in Figure 7A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig7-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 7—source data 2
Microsoft excel data corresponding to the ATPase curve in Figure 7A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig7-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 7—source data 3
raw data uncropped gels corresponding to Figure 7.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig7-data3-v2.zip
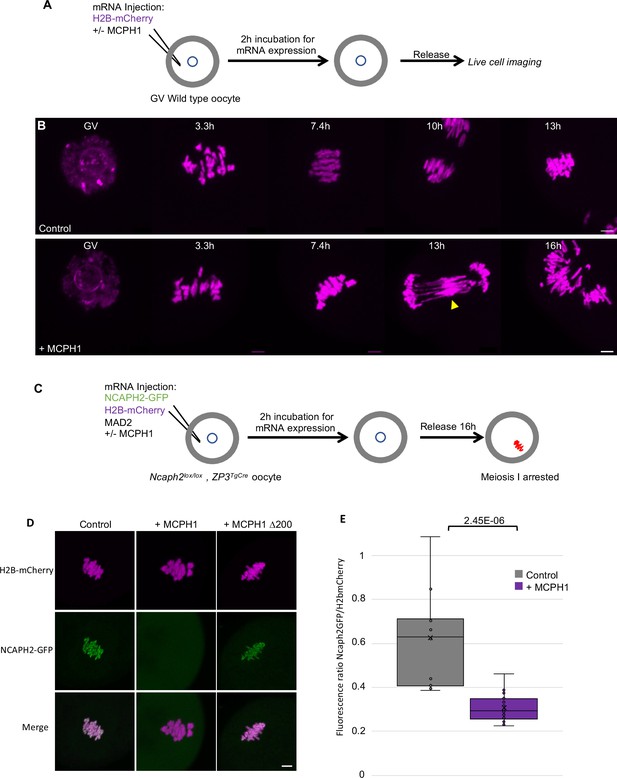
MCPH1 prevents the association of condensin II with chromosomes.
(A) Cartoon summarizing the experimental procedure corresponding to panel B. (B) Wild-type mouse oocytes were injected at the GV stage with in vitro transcribed mRNA coding for H2B-mCherry alone to mark the chromosomes in magenta (Control) or in combination with MCPH1 (+ MCPH1). Meiosis I progression was followed by live cell confocal imaging. The segregation defects observed in the presence of MCPH1 are indicated by a yellow arrowhead. Maximum intensity z projection images of the main time points are shown between 3.3 hr post GVBD onwards (number of oocytes analysed in three independent experiments and showing segregation defects: control:0/12;+ MCPH1: 18/19). (C) Cartoon summarizing the experimental procedure corresponding to panel D. (D) Oocytes from Ncaph2f/f Tg(Zp3Cre) females were injected at the GV stage with mRNA coding for H2B-mCherry, MAD2 and NCAPH2-GFP only (control) or in combination with MCPH1 (+ MCPH1) or MCPH1 deleted of the first N-terminal 200 amino acids (+ MCPH1 Δ200). Oocytes were arrested 16 hr after GVBD in metaphase I owing to MAD2 overexpression, and maximum-intensity z projection images of chromosomes were acquired by live cell confocal imaging (Total number of oocytes analysed in three experiments: control: 37,+ MCPH1: 58,+ MCPH1Δ200: 12). (E) Quantification of NCAPH2-GFP signal on the chromosomes. (Number of oocytes analysed in two independent experiments: control: 11;+ MCPH1: 14). In each graph the two tailed T-test p values are indicated is indicated. Scale bar, 5 μm.
-
Figure 8—source data 1
Microsoft excel file of fluorescence measurements in Figure 8E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig8-data1-v2.xlsx
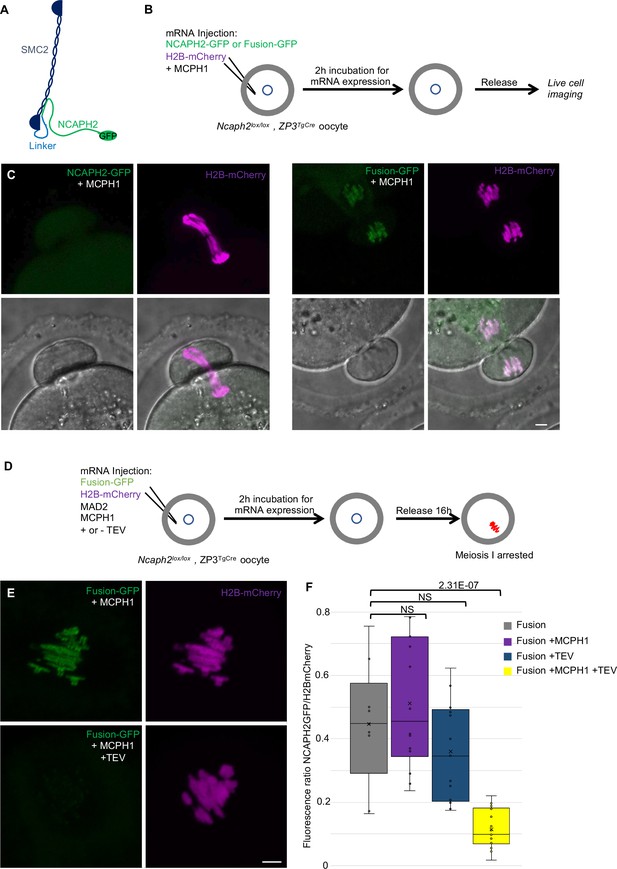
The closure of the SMC2-NCAPH2 interface prevents MCPH1 inhibitory effect.
(A) Schematic representation of the protein fusion between SMC2 C-terminus and the N-terminus of NCAPH2 using a linker comprising three TEV protease cleavage sites. (B) Cartoon summarizing the experimental procedure corresponding to panel C. (C) Oocytes from Ncaph2f/f Tg(Zp3Cre) females were injected at the GV stage with mRNA coding for H2B-mCherry and MCPH1 in combination with NCAPH2-GFP (NCAPH2-GFP+ MCPH1) or with the fusion (Fusion-GFP+ MCPH1). Meiosis I progression was followed by live cell confocal imaging. Maximum intensity z-projections images of the time points corresponding to anaphase I when segregation defects are observed (total number of oocytes showing chromosome segregation defects in three experiments: NCAPH2-GFP+ MCPH1: 17/19, Fusion-GFP+ MCPH1: 0/18). (D) Cartoon summarizing the experimental procedure corresponding to panel E. (E) Oocytes from Ncaph2f/f Tg(Zp3Cre) females were injected at the GV stage with mRNA coding for H2B-mCherry, MAD2 and Fusion-GFP only or in combination with TEV protease. Oocytes were arrested 16 hr after GVBD in metaphase I owing to MAD2 over-expression and maximum-intensity z-projection images of chromosomes were acquired by live cell confocal imaging. (F) Quantification of Fusion-GFP signal on the chromosomes (Total number of oocytes analysed in three experiments: Fusion: 9; Fusion+ MCPH1: 14, Fusion+ TEV: 13, Fusion+ TEV + MCPH1: 18). In each graph the two tailed T-test p values are indicated is indicated. Scale bar, 5 μm.
-
Figure 9—source data 1
Microsoft excel file of fluorescence measurements in Figure 9F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig9-data1-v2.xlsx
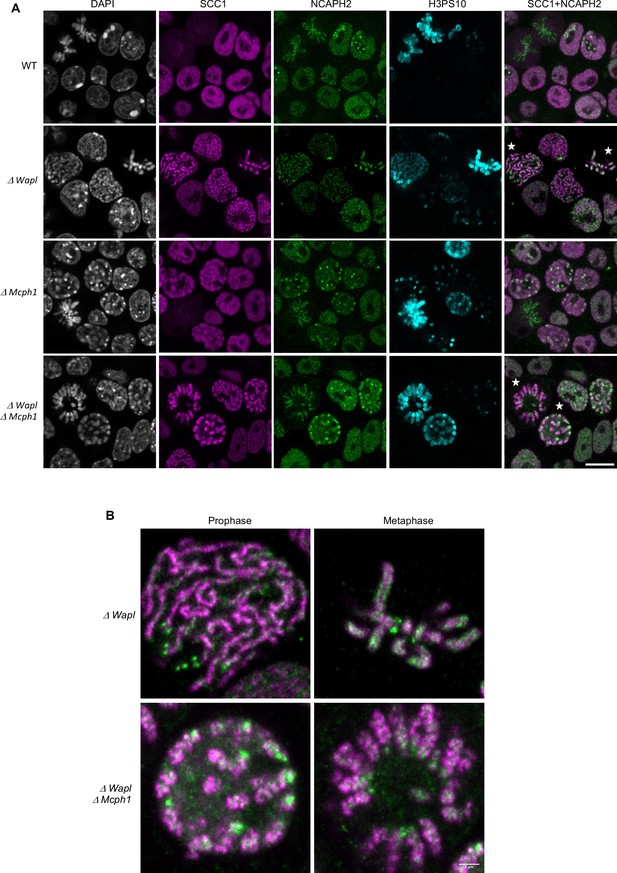
Mcph1 deletion induces the coiling of the vermicelli.
(A) Immunofluorescence analysis of the chromatin organisation in the four conditions: wild-type, ΔWapl, ΔMcph1, and ΔWapl ΔMcph1. In order to compare cells that are in G2, prophase or metaphase, Histone H3-serine 10 (cyan) was used as a cell cycle marker. The localisation of SCC1-Halo was analysed using Halo-JFX554, NCAPH2-GFP using nanobodies and DNA was detected using DAPI. (B) Magnified view of cells marked with a white star in panel A. Scale bar, 5 μm.
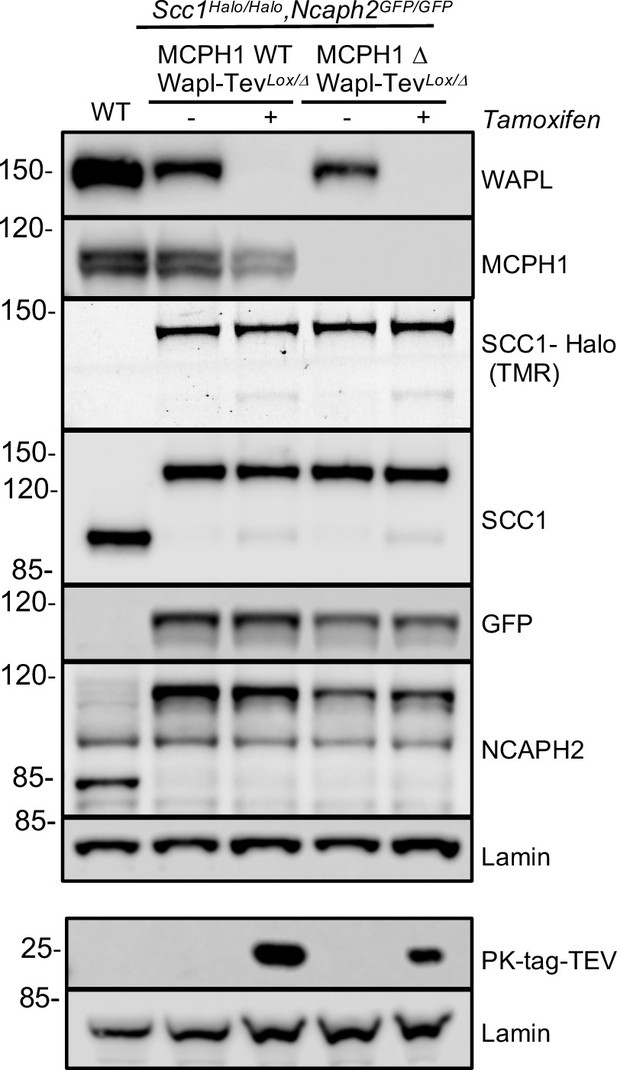
Western blot analysis of the four conditions analysed in Figure 10 and Figure 11.
The first cell line is: Ncaph2GFP/GFP Scc1Halo/Halo WaplTevLox/Δ Mcph1wt/wt. The second cell line is: Ncaph2GFP/GFP Scc1Halo/Halo WaplTevLox/Δ Mcph1Δ/Δ. Wapl can be deleted in both cell lines after Tamoxifen treatment giving four experimental conditions: Wild type, ΔWapl, ΔMcph1, and ΔWapl ΔMcph1.
-
Figure 10—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data uncropped blots corresponding to Figure 10—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig10-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
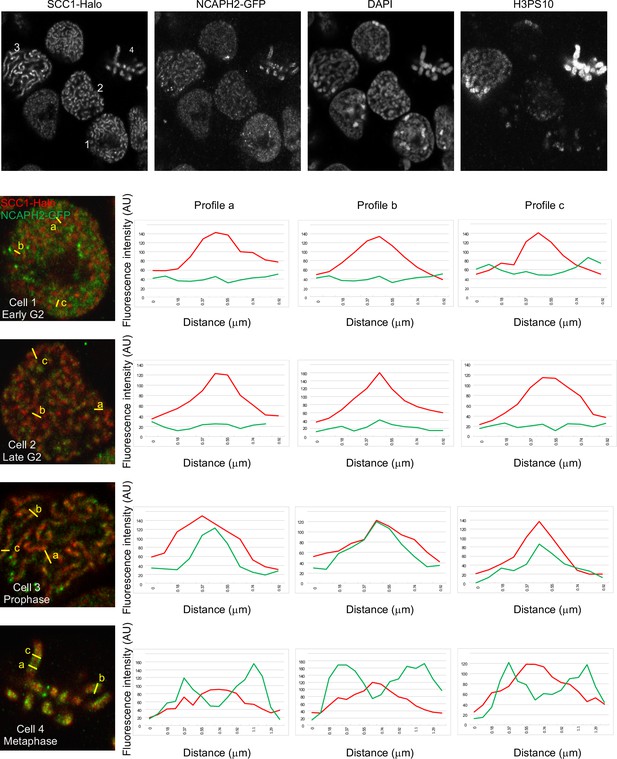
Quantification of NCAPH2-GFP and SCC1-Halo on the chromosome axes in ΔWapl cells.
In order to address if NCAPH2-GFP was enriched on the chromosome axis of ΔWapl cells, the fluorescence of SCC1-Halo (red) and NCAPH2 GFP (green) was quantified across the axis of three different structure (a, b and c) in four representative cells in early G2 (1), late G2 (2), prophase (3), and metaphase (4) (distinguished using the H3PS10 staining). The quantifications show that NCAPH2 is enriched on the chromosome axis only in prophase and metaphase.
-
Figure 10—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw data of the fluorescence quantification.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73348/elife-73348-fig10-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
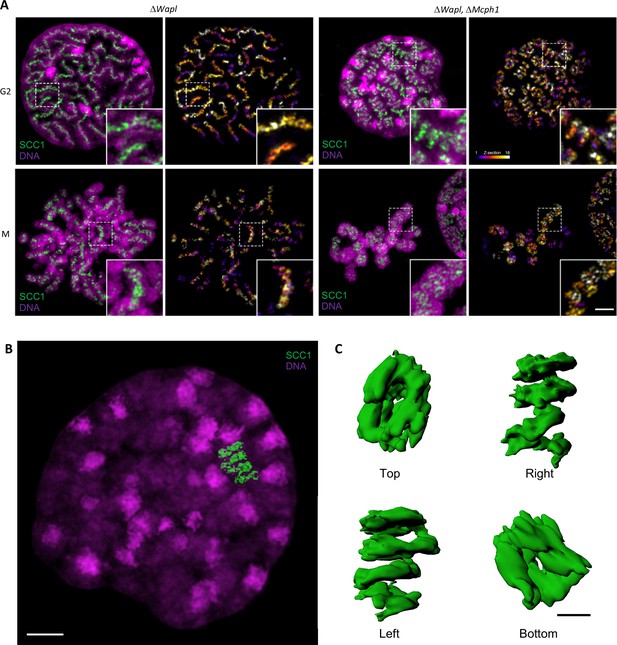
Super-resolution 3D-SIM analysis of G2 and metaphase cells deleted for Wapl or both Mcph1 and Wapl.
(A) Cells deleted for ΔWapl or ΔWapl+ΔMcph1 in G2 or metaphase (M) were analysed by 3D-SIM. Maximum intensity projections of 16 consecutive mid sections covering 2 µm in depth. The left panel shows DNA coloured in magenta and SCC1-Halo in green. The right panel shows the SCC1 signal with z-depth colour-coded. Scale bar, 5 μm (inset, 1 μm) (B) Representative SCC1-Halo solenoid structure corresponding to one chromosome from a ΔWapl+ΔMcph1 cell in G2 was segmented (green) and overlaid to the DNA (magenta). Scale bar, 2 μm. (C) 3D surface rendering of the segmented and isolated solenoid from panel B. View from the top, right, left, and bottom of one segmented solenoid. Scale bar, 1 μm.
3D video rendering of the segmented and isolated solenoid from Figure 11 panel B.
Tables
Peptides used in FP experiments.
| Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| 5FAM-MCPH1 | 5FAM- CGESSYDDYFSPDNLKER |
| MCPH1 | CGESSYDDYFSPDNLKER |
| MCPH1pS417 | CGESSYDDYF{pSER}PDNLKER |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | XL1-Blue Competent Cells | Thermo-competent | Prepared in the lab | Used to prepare plasmid DNA |
| Strain, strain background (S. frugiperda) | Sf9 insect cells | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 11496015 | |
| Strain, strain background (Trichoplusia ni) | High-Five insect cells | Thermo Fisher | Cat# B85502 | |
| strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | DH10EMBacY | Geneva biotech | ||
| genetic reagent (Mouse) | Ncaph2tm1a(EUCOMM)Wtsi, ZP3-Cre | Houlard et al., 2015 DOI:10.1038/ncb3167 | Isolation of Mouse oocytes deleted for Ncaph2 | |
| cell line (Mouse) | ES-E14 mouse embryonic stem cells | https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_C320 | RRID:CVCL_C320 | |
| cell line (Mouse) | E14-Ncaph2Halo/Halo | This paper | E14 cells homozygous Halo tag Cterminal NCAPH2 | |
| cell line (Mouse) | E14-Ncaph2Halo/Halo, Mcph1Δ/Δ | This paper | E14 cells homozygous Halo tag C-terminal NCAPH2, deleted for Mcph1 | |
| cell line (Mouse) | E14-Ncaph2GFP/GFP | This paper | E14 cells homozygous GFP tag C-terminal NCAPH2 | |
| cell line (Mouse) | E14-Ncaph2GFP/GFP Mcph1Δ | This paper | E14 cells homozygous GFP tag C-terminal NCAPH2, deleted for Mcph1 | |
| cell line (Mouse) | E14- Ncaph2Halo/Halo Mcph1GFP/GFP | This paper | E14 cells homozygous GFP tag C-terminal MCPH1 and Halo tag NCAPH2, | |
| cell line (Mouse) | E14- Ncaph2Halo/Halo Mcph1ΔCENGFP/ΔCENGFP | This paper | E14 cells homozygous GFP tag C-terminal MCPH1 deleted of central domain,and Halo tag NCAPH2, | |
| cell line (Mouse) | E14-SCC1Halo/Halo, Ncaph2GFP/GFP,WaplLox/Lox, Rosa26CreERT2-LoxSTOPTEV/ CreERT2-LoxSTOPTEV | This paper | See Figure 10 | |
| cell line (Mouse) | E14-SCC1Halo/Halo, Ncaph2GFP/GFP,WaplLox/Lox, Rosa26CreERT2-LoxSTOPTEV/ CreERT2-LoxSTOPTEVMcph1Δ/Δ | This paper | See Figure 10 | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pUC19-NCAPH2 Halo TV | This paper | Targeting Halo tag C-terminal Ncaph2 | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pUC19-NCAPH2 GFP TV | This paper | Targeting GFP tag C-terminal Ncaph2 | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pUC19-MCPH1 GFP TV | This paper | Targeting GFP tag C-terminal MCPH1 | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pUC19-MCPH1 ΔCEN TV | This paper | Targeting deletion of the central domain of MCPH1 | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pUC19-SCC1 Halo TV | This paper | Targeting Halo tag C-terminal SCC1 | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pUC19-Rosa26 STOPLoxTEV TV | This paper | Targeting the insertion of the STOP-Lox-TEV cassette at Rosa 26 | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pUC19-WAPL TEV LOX TV | This paper | Targeting the TEV sites and the LoxP sites in Wapl | |
| antibody | NCAPH2 (rabbit polyclonal) | Produced on demand by Eurogentec | WB: (1/1000) | |
| antibody | SCC1 (mouse monoclonal) | Millipore | 53 A303 | WB: (1/1000) |
| antibody | SMC2 (rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | D23C5 | WB: (1/500) |
| antibody | Lamin B1 (rabbit monoclonal) | Abcam | Ab133741 | WB: (1/1000) |
| antibody | MCPH1 (rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | D38G5 | WB: (1/1000) |
| antibody | CREST (human autoantibody) | Immunovision | HCTO-100 | IF: (1/500) |
| antibody | H3PS10 (mouse monoclonal) | Millipore | 3 H10 | WB: (1/1000) IF: (1/2000) |
| antibody | ΔH2AX (mouse monoclonal) | Millipore | JBW301 | WB: (1/1000) IF: (1/500) |
| antibody | CDK1 (rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | 77,055 | WB: (1/1000) |
| antibody | Phospho-CDK1 (rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | 9,111 | WB: (1/1000) |
| antibody | WAPL (rabbit polyclonal) | J.M. Peters Lab | WB: (1/1000) | |
| antibody | GFP (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Ab290 | WB: (1/1000) IF: (1/500) |
| antibody | PK-Tag (mouse monoclonal) | Biorad | MCA 1360 G | WB: (1/1000) |
| antibody | Cyclin B1 (rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | 4138T | IF: (1/200) |
| antibody | NCAPD3 (rabbit polyclonal) | Bethyl Laboratories | A300-604A-M | WB: (1/1000) |
| antibody | AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody anti mouse | Life Technology | A-11001 | Secondary antibody for IF |
| antibody | AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody anti rabbit | Life Technology | A-11008 | Secondary antibody for IF |
| antibody | AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody anti mouse | Life Technology | A-11005 | Secondary antibody for IF |
| antibody | AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody anti rabbit | Life Technology | A-11012 | Secondary antibody for IF |
| antibody | mouse anti-CAP-D3 antibody | Santa Cruz | Sc-81597 | WB (1:1000) |
| antibody | goat DyLight 800 florescent anti-mouse secondary antibodies | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat #5,257 | WB (1:5000) |
| recombinant DNA reagent | Mouse Ncaph2 cDNA | Origene | MC200537 | Initial cDNA used for cloning in pRNA |
| recombinant DNA reagent | Mouse Mcph1 cDNA | Dharmacon | 5697978 | Initial cDNA used for cloning in pRNA |
| recombinant DNA reagent | Mouse SMC2 cDNA | Source Bioscience | IRAV p968E12162D | Initial cDNA used for cloning in pRNA |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pRNA-NCAPH2-GFP | Houlard et al., 2015 DOI:10.1038/ncb3167 | In vitro transcription of NCAPH2 mRNA for mouse oocyte injection | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pRNA-Mad2 | Houlard et al., 2015 DOI:10.1038/ncb3167 | In vitro transcription of Mad 2 mRNA for mouse oocyte injection | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pRNA-H2b-mCherry | Houlard et al., 2015 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3167 | In vitro transcription of H2b-mCherry mRNA for mouse oocyte injection | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pRNA-MCPH1 | This paper | In vitro transcription of mouse MCPH1 mRNA for mouse oocyte injection | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pRNA-MCPH1-Δ200 | This paper | In vitro transcription of mouse MCPH1 deleted of the N-terminal 200aa mRNA for mouse oocyte injection | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pRNA-Fusion SMC2-NCAPH2 | This paper | In vitro transcription of the fusion SMC2-NCAPH2 mRNA for mouse oocyte injection | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pRNA-TEV | Houlard et al., 2015 DOI:10.1038/ncb3167 | In vitro transcription of TEV mRNA for mouse oocyte injection | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pSptCas9(BB)–2A-Puro | Addgene | 62,988 | Cloning of the SgRNA |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pUC19 | NEB | Cloning of the targeting construct for CRISPR/Cas9 targeting | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pLIB | Jan-Michael Peters lab, IMP | Addgene plasmid # 80,610 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pLIB MCPH1 | Genscript | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET His6 MBP TEV LIC cloning vector | Scott Gradia lab, UC Berkeley | Addgene plasmid # 29,656 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET His6 MBP MCPH1 1–435 | This study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET His6 MBP MCPH1 1–195 | This study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET His6 MBP MCPH1 196–435 | This study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET His6 MCPH1 1–435 MBP | This study | ||
| sequence-based reagent | GGTGGAAAGTAGTATATACC | This paper | Sg RNA used for: NCAPH2-GFP | |
| sequence-based reagent | GGTGGAAAGTAGTATATACC | This paper | Sg RNA used for: NCAPH2-Halo | |
| sequence-based reagent | GGTGTGCAATTCCTAGTGTG | This paper | Sg RNA used for: MCPH1 deletion Sg5' | |
| sequence-based reagent | AGCTGTTCCTTAGAACACGA | This paper | Sg RNA used for: MCPH1 deletion Sg3' | |
| sequence-based reagent | ACAGTGAGACATCTACAATG | This paper | Sg RNA used for: MCPH1-GFP | |
| sequence-based reagent | CATGGATTTCTCCGGTGAAT | This paper | Sg RNA used for: STOP-TEV | |
| sequence-based reagent | AATGGGTGCTTATAATTAGC | This paper | Sg RNA used for: WAPL-Lox-TEV Sg5' | |
| sequence-based reagent | ACAATGTCACAATGGCTCAT | This paper | Sg RNA used for: WAPL-Lox-TEV Sg3' | |
| sequence-based reagent | ATAATATGGAACCGTGGTCC | This paper | Sg RNA used for: SCC1-Halo | |
| sequence-based reagent | cgttgaggcttcttcctatg | This paper | Sg RNA used for: DELCEN-MCPH1 | |
| sequence-based reagent | AATGGGTGCTTATAATTAGC and ACAATGTCACAATGGCTCAT | This paper | Sg RNA used for: TEV sites in Wapl | |
| peptide, recombinant protein | 5FAM-MCPH1407-422 | Genscript | ||
| peptide, recombinant protein | MCPH1407-422 | Genscript | ||
| peptide, recombinant protein | MCPH1407-422pS417 | Genscript | ||
| commercial assay or kit | Click-iT EdU Alexa Fluor 488 Imaging kit | In vitrogen | C10337 | EdU fluorescent labeling |
| commercial assay or kit | Gibson assembly | NEB | E5510S | Cloning kit |
| commercial assay or kit | GFP-trap agarose beads | Chromotek | GTA-10 | GFP tagged protein purification |
| Commercial assay or kit | HiTrap Q HP | cytiva | Cat #17–0407 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | HiTrap Heparin HP | cytiva | Cat #17–0407 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | StrepTrap HP | cytiva | Cat #28–9075 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL | cytiva | Cat #29-0915-96 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 GL | cytiva | Cat # 28990944 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | HiLoad 16/60 Superdex 200 | GE Healthcare | Cat# GE28-9893-35 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | EnzChek phosphate assay kit | Invitrogen | Cat# E6 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | 4%–12% NuPAGE Bis-Tris gels | Invitrogen | Cat #NW04125 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Color Prestained Protein Standard, Broad Range 11–245 kDa | NEB | Cat # P7719 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Pierce Silver Stain Kit | Thermo Scientific | Cat # 24,612 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | InstantBlue Coomassie Protein Stain | Abcam | Cat #ab119211 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | cellfectin II | Gibco, Thermo Fisher | Cat #10362100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | FBS | Gibco, Thermo fisher | Cat #10082139 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Pierce Protease Inhibitor Tablets | Thermo Scientific | Cat #A32965 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Benzonase | millipore | Cat #E1014 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HisPur Ni-NTA Resin | Thermo Scientific | Cat #88,221 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Strep-tactin Sepharose resin | Iba-lifesciences | Cat # 2-1201-002 | |
| chemical compound, drug | HALO-PROTAC | Promega | CS2072A01 | In vivo degradation of Halo-NCAPH2 |
| chemical compound, drug | Halo-TMR | Promega | G8251 | Halo tagged protein detection |
| chemical compound, drug | Halo-JFX554 | Grimm et al., 2021 DOI:10.1021/jacsau.1c00006 | Halo tag detection by fluorescence | |
| chemical compound, drug | RO-3306 | Sigma | SML0569 | CDK1 inhibitor |
| chemical compound, drug | Lipofectamine 2000 | Thermofisher | 11668030 | E14 transfection reagent |
| chemical compound, drug | Q5 DNA polymerase | NEB | M0491L | PCR amplification |
| software, algorithm | CRISPOR | http://crispor.tefor.net/crispor.py | Guide RNA design | |
| software, algorithm | EasyFRAP | http://easyfrap.vmnet.upatras.gr | FRAP data analysis | |
| software, algorithm | Fiji 2.0.0-rc-49/1.52i | NIH Image | http://fiji.sc/ | Image analysis and quantification |
| Software | Image studio | Li-Cor |





