Svep1 is a binding ligand of Tie1 and affects specific aspects of facial lymphatic development in a Vegfc-independent manner
Abstract
Multiple factors are required to form functional lymphatic vessels. Here, we uncover an essential role for the secreted protein Svep1 and the transmembrane receptor Tie1 during the development of subpopulations of the zebrafish facial lymphatic network. This specific aspect of the facial network forms independently of Vascular endothelial growth factor C (Vegfc) signalling, which otherwise is the most prominent signalling axis in all other lymphatic beds. Additionally, we find that multiple specific and newly uncovered phenotypic hallmarks of svep1 mutants are also present in tie1, but not in tie2 or vegfc mutants. These phenotypes are observed in the lymphatic vasculature of both head and trunk, as well as in the development of the dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel under reduced flow conditions. Therefore, our study demonstrates an important function for Tie1 signalling during lymphangiogenesis as well as blood vessel development in zebrafish. Furthermore, we show genetic interaction between svep1 and tie1 in vivo, during early steps of lymphangiogenesis, and demonstrate that zebrafish as well as human Svep1/SVEP1 protein bind to the respective Tie1/TIE1 receptors in vitro. Since compound heterozygous mutations for SVEP1 and TIE2 have recently been reported in human glaucoma patients, our data have clinical relevance in demonstrating a role for SVEP1 in TIE signalling in an in vivo setting.
Editor's evaluation
This study presents strong and compelling evidence that the extra-cellular matrix protein SVEP-1 interacts with the TIE1 receptor to promote aspects of lymphangiogenesis that are independent of canonical VEGF-C signaling. Using zebrafish models to show genetic interactions and cells to provide evidence of biochemical interaction, the study shows a functional requirement for these genes/proteins in specific aspects of lymphangiogenesis. These novel findings will be of interest to developmental and cell biologists and to those studying lymphatic disease as it potentially provides novel therapeutic targets.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.82969.sa0Introduction
The lymphatic system is part of the vasculature and provides essential functions for tissue fluid homeostasis, absorption of dietary fats, and immune surveillance. Malfunction of the lymphatic vasculature can lead to severe lymphedema, obesity, or chronic inflammatory diseases (Mäkinen et al., 2021; Oliver et al., 2020). Since treatment options are rare and often only transiently effective, understanding the molecular mechanisms driving lymphangiogenesis is a prerequisite for the development of new therapeutic approaches (Mäkinen et al., 2021). To that end, mice and zebrafish have served as popular model organisms to study the development of lymphatic vessels and are commonly used for analyzing the underlying genetic and molecular mechanisms (Mäkinen et al., 2007; Padberg et al., 2017; van Impel and Schulte-Merker, 2014). Furthermore, many genes that are essential for lymphangiogenesis in zebrafish are evolutionarily conserved. Their inactivation leads to lymphatic defects in zebrafish and mice, and mutations in their orthologues are causative for human diseases (Alders et al., 2009; Gordon et al., 2013; Hogan et al., 2009; Mauri et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2020). In the trunk vasculature of the zebrafish, so-called lympho-venous sprouts arise from the posterior cardinal vein at 32 hours post-fertilization (hpf). They migrate dorsally and either remodel an intersegmental artery into a vein, or they migrate along the so-called horizontal myoseptum (HM) as parachordal lymphangioblasts (PLs) at 2 days post fertilization (dpf). At 3 dpf, PLs migrate dorsally and ventrally to form the trunk lymphatic vasculature, consisting of the dorsal longitudinal lymphatic vessel, the intersegmental lymphatic vessels, and the thoracic duct (TD) (Hogan et al., 2009; Hogan and Schulte-Merker, 2017; Padberg et al., 2017). A separate lymphatic network, the facial lymphatics, arises in a distinctly different manner, originating from three progenitor populations: (1) the primary head sinus-lymphatic progenitors (PHS-LP), (2) a migratory angioblast cell near the ventral aorta, and (3) the major population sprouting from the common cardinal vein (CCV) (Eng et al., 2019). These progenitor populations proliferate, migrate and connect to each other in a relay-like mechanism (Eng et al., 2019). A third lymphatic bed is composed of the brain lymphatic endothelial cells (BLECs), which are single endothelial cells residing within the leptomeningeal layer of the zebrafish brain and that arise from the choroidal vascular plexus (Bower et al., 2017; van Lessen et al., 2017; Galanternik et al., 2017). During larval stages, BLECs are often positioned next to meningeal blood vessels and stay at the distal periphery of the optic tectum and other brain regions (van Lessen et al., 2017). However, molecular mechanisms supporting the development of BLECs and facial lymphatics still need to be examined in more detail.
The best-studied pathway driving lymphangiogenesis comprises the growth factor Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C (VEGFC), which is secreted as a pro-form that is processed through the concerted activity of Collagen and Calcium-Binding EGF domain-containing protein 1 (CCBE1) (Bos et al., 2011; Hogan et al., 2009; Jeltsch et al., 2014; Le Guen et al., 2014; Roukens et al., 2015) and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs (Adamts) 3/14 (Jeltsch et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2020) in the extracellular space. Fully processed VEGFC binds to its receptor VEGFR3 as well as VEGFR2 and induces lymphangiogenesis (Joukov et al., 1997; Karkkainen et al., 2004). Apart from the VEGFC/VEGFR3 pathway, TIE-ANG signalling was shown to be essential for lymphangiogenesis and vessel remodelling in mice and humans. This signalling cascade is composed of two receptor tyrosine kinases, tyrosine-protein kinase receptor 1 (TIE1) (Partanen et al., 1992) and tyrosine endothelial kinase (TEK), also known as tyrosine-protein kinase receptor 2 (TIE2) (Dumont et al., 1993), and multiple angiopoietin ligands including angiopoietin 1 (ANG 1) (Davis et al., 1996; Suri et al., 1996) and angiopoietin 2 (ANG 2) (Maisonpierre et al., 1997). In mammals, TIE signalling is activated through binding of Angiopoietins to TIE2 (Davis et al., 1996; Maisonpierre et al., 1997). TIE1 can either block or activate the signalling cascade in a context-dependent manner by forming heterodimers with TIE2 (Hansen et al., 2010; Marron et al., 2000; Saharinen et al., 2005; Savant et al., 2015; Seegar et al., 2010). Tie1 knockout mice display haemorrhages from E13.5 to P0, which lead to death and are preceded by lymphatic defects and edema formation from E12.5 onwards (D’Amico et al., 2010). In contrast to Tie1 mutant mice, Tie2 mutant mice die already at E9.5–10.5 due to defective cardiac development and vascular remodelling (Dumont et al., 1994; Sato et al., 1995). Conditional knockout of Tie2 in lymphatic cells revealed the importance of TIE2 for lymphatic vessel development in mice especially for Schlemm’s canal formation (Kim et al., 2017; Thomson et al., 2014). Recently, Korhonen et al. showed that conditional Tie1 deletion, Tie1;Tie2 double deletion and Ang2 blocking resulted in impaired postnatal lymphatic capillary network development in mice (Korhonen et al., 2022). In zebrafish, tie2 mutants do not have any overt vascular defects (Gjini et al., 2011; Jiang et al., 2020), while tie1 mutants show cardiac morphogenesis and vascular defects (Carlantoni et al., 2021).
In 2017, a new key player in lymphangiogenesis was discovered through genetic screens in zebrafish: sushi, von Willebrand factor type A, EGF, and pentraxin domain-containing protein 1 (svep1), also referred to as polydom (Karpanen et al., 2017; Morooka et al., 2017). Svep1 encodes a large extracellular matrix molecule, with a total of 3571 amino acids and a variety of protein domains. The C terminal half of Svep1 mainly consists of complement control protein (CCP), also called sushi domain, repeats and EGF domains, indicating a possible role in protein-binding stabilization. Svep1−/− mice show normal development of the primitive lymphatic plexus until E12.5, but then fail to undergo remodelling of lymphatic vessels and formation of lymphatic valves at later embryonic stages, accompanied by edema formation and death postnatally (Karpanen et al., 2017; Morooka et al., 2017). Recently, Michelini et al. reported possible implications of SVEP1 in lymphedema formation in human patients, underlining the importance of SVEP1 for the lymphatic vasculature (Michelini et al., 2021). Additionally, SVEP1 is also required for Schlemm’s canal formation in mice (Thomson et al., 2021). In zebrafish, svep1 mutants exhibit a near-complete loss of the TD, demonstrating an essential function during lymphangiogenesis in zebrafish (Karpanen et al., 2017; Morooka et al., 2017).
In the present study, we show defects in the lymphatic head vasculature in svep1 mutants, comprising a variable loss of BLECs and a specific facial lymphatic phenotype, which is complementary to the phenotypes observed in mutants of Vegfc/Vegfr3 pathway members. Therefore, we identified a lymphatic structure in the zebrafish that, in contrast to all other lymphatic structures, forms independently of the Vegfc/Vegfr3 pathway, but depends on Svep1.
Murine SVEP1 has been shown to bind to the α9 form of integrin (ITGA9) as well as the TIE2 ligands ANG1 and ANG2 in vitro (Morooka et al., 2017; Sato-Nishiuchi et al., 2012). However, until now, putative interaction partners of Svep1 have not been confirmed in vivo. In the present study, we first characterized novel lymphatic and blood vasculature defects of tie1 mutants, and subsequently realized that all phenotypic traits are shared between tie1 and svep1 mutants. These observations raised the question whether Svep1 and Tie1 interact, a notion that we tested both genetically and on a protein biochemistry level. Our results provide the first in vivo evidence for svep1 and tie1 genetic interaction, thus placing Svep1 as an important regulator of Tie1 function. Additionally, we show the interaction of SVEP1 and TIE1 in vitro for the respective versions of the zebrafish and human proteins. Since recent clinical data suggested SVEP1 as a genetic modifier of TIE2-related primary congenital glaucoma (PCG) (Young et al., 2020), our results have clinical relevance and will further help to understand the molecular basis of PCG.
Results
Svep1 is required for facial collecting lymphatic vessel formation in a Vegfc-independent manner
Since svep1 mutants had previously been analyzed for lymphatic defects only in the trunk vasculature, we examined the head vasculature of svep1 mutants to detect further possible malformations of the lymphatic system. At 5 dpf we observed that svep1 mutants showed specific facial lymphatic defects, which seemed to be complementary to the facial lymphatic defects found in mutants of the Vegfc/Vegfr3 pathway members (Figure 1A). While mutants for Vegfc/Vegfr3 pathway members like ccbe1, adamts3/14, and vegfc retained the facial collecting lymphatic vessel (FCLV) (red dotted line in Figure 1A, B) but lacked all other structures of the facial lymphatics, svep1 mutants showed a specific loss of the FCLV. All other parts of the mature facial lymphatic network (including lymphatic branchial arches, lateral facial lymphatic, medial facial lymphatic, and otolithic lymphatic vessel (blue dotted line in Figure 1A)) were only partially reduced in svep1 mutants. Although the formation of the FCLV was strongly affected in all svep1 mutants analyzed, the severity of the defects of facial lymphatic structures varied between individual svep1 mutant embryos (Figure 1—figure supplement 1). Only simultaneous interference of both the Vegfc and Svep1 signalling pathways completely blocked the development of all facial lymphatic structures (Figure 1—figure supplement 2). To further characterize the differential roles of Svep1 and Vegfc during the formation of the facial lymphatic network, we examined the expression patterns of svep1 and vegfc during sprouting of the PHS-LP, the progenitor cells of the FCLV, at 50 hpf using transgenic reporter lines. We detected svep1 expression in cells juxtaposed to the sprouting LECs around the PHS, which later will form the FCLV, while vegfc expression was more restricted to the lateral facial lymphatic sprout arising from the CCV in all embryos analyzed (Figure 1C, Figure 1—figure supplement 3). Taken together, these observations indicate a Vegfc-independent role of Svep1 during the development of distinct aspects of the facial lymphatics.
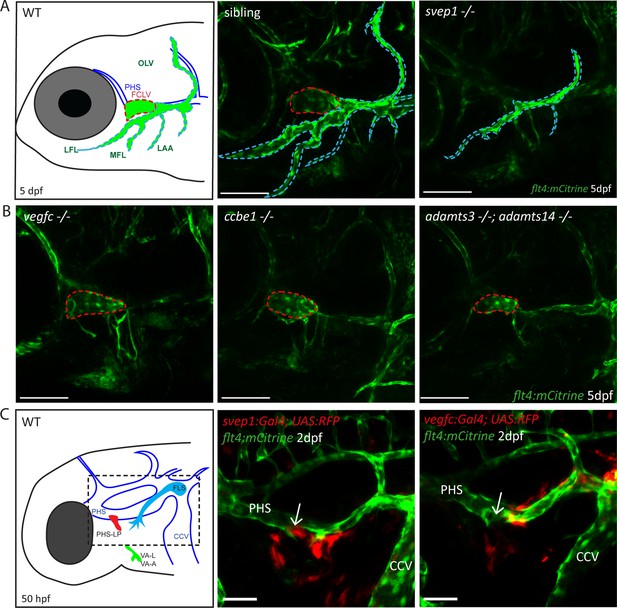
Svep1 is required for the development of the FCLV, in a Vegfc-independent manner.
(A) Schematic representation of facial lymphatic network at 5 dpf and maximum intensity projection of confocal images of flt4:mCitrine positive svep1 mutants (n = 10) and siblings (n = 6), highlighting facial lymphatic structures at 5 dpf. Scale bar = 100 µm. Note the absence of the FCLV (red dotted line) in svep1 mutants whereas other facial lymphatic structures are less strongly affected (OLV, LFL, MFL, and LAA marked by blue dotted lines). (B) Confocal images of flt4:mCitrine positive facial lymphatics in vegfc (n = 19), ccbe1 (n = 5), and adamts3;adamts14 (n = 2) mutants at 5 dpf. Scale bar = 100 µm. (C) Confocal images of svep1 and vegfc expression domains during sprouting from the PHS at 2 dpf, with schematic representation of different lymphatic progenitor populations. svep1 is expressed in close proximity to sprouting PHS-LPs, while vegfc expressing cells are more concentrated on the LECs arising from the CCV. Arrows point to sprouting PHS-LP. Scale bar = 50 µm. Expression patterns were confirmed in six embryos each (Figure 1—figure supplement 3). CCV, common cardinal vein; dpf, days post-fertilization; FCLV, facial collecting lymphatic vessel; FLS, facial lymphatic sprout; hpf, hours post-fertilization; LAA, lymphatic branchial arches; LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell; LFL, lateral facial lymphatic; MFL, medial facial lymphatic; OLV, otolithic lymphatic vessel; PHS, primary head sinus; PHS-LP, primary head sinus lymphatic progenitor; VA, ventral aorta; VA-A, ventral aorta angioblast; VA-L, ventral aorta lymphangioblast; WT, wildtype.
Svep1 is essential for sprouting of BLECs and is expressed in close proximity to BLECs
Since Svep1 is required for the formation of facial lymphatic structures (Figure 1), we wondered whether it is also involved in the development of an additional set of lymphatic endothelial cells, the BLECs. In mutants of the Vegfc/Vegfr3 pathway, BLECs are completely absent (Bower et al., 2017; van Lessen et al., 2017). In svep1 mutants, BLECs were found to be absent in most cases, but some embryos showed either reduced numbers or – in rare cases – even wildtype-like numbers of BLECs at 3 dpf (Figure 2A, B). In line with the idea that svep1 is required for the sprouting and migration of BLECs, we observed svep1 expressing cells in close proximity to the migrating BLECs at 3 dpf (Figure 2C, D). Thus, there is close juxtaposition of svep1 expressing cells with migrating LECs in all developing lymphatic structures examined, including the PLs in the trunk (Karpanen et al., 2017).
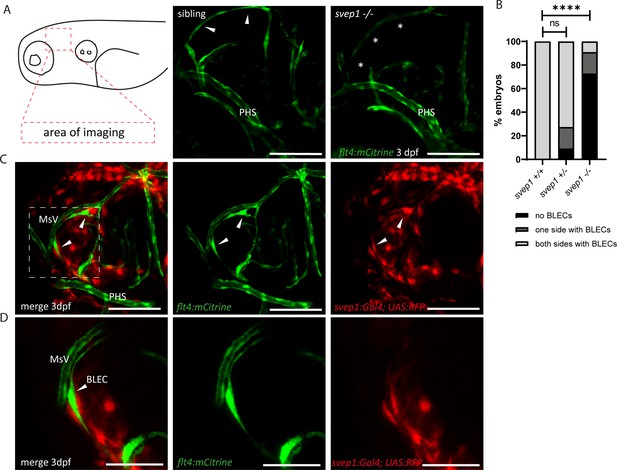
Svep1 is required for the sprouting of BLECs.
(A) Confocal images of sprouting BLECs, marked by flt4:mCitrine, at 3 dpf in svep1 mutants and siblings. Asterisks mark missing BLECs in svep1 mutants. Scale bar = 100 µm. (B) Quantification of BLECs at 3 dpf on each side of the embryo showed that svep1 mutants have significantly less BLECs on one or both sides of the brain hemispheres compared to siblings. For statistical analysis, no BLECs were counted as 0, BLECs being present on only one hemisphere as 1, whereas BLECs being detectable on both brain hemispheres were included as 2, for each embryo (svep1+/+: n = 10; svep1+/−: n = 12; svep1−/−: n = 12). Mann–Whitney test was applied for statistical analysis. Values are presented as means ± standard deviation (SD), ****p < 0.0001, ns = not significant. Scale bar = 100 µm. (C) Confocal images of svep1:Gal4; UAS:RFP, showing svep1 expression immediately adjacent to BLECs, marked by arrowheads, at 3 dpf. Scale bar = 100 µm. (D) Magnification and reduced stack numbers of boxed area in (C). Arrowhead marks BLEC. Scale bar = 50 µm. BLEC, brain lymphatic endothelial cell; dpf, days post-fertilization; MsV, mesencephalic vein; PHS, primary head sinus;.
svep1 and tie1 mutants show near-identical lymphatic defects
Murine SVEP1 has been shown to bind the TIE2 ligands ANG1 and ANG2 in vitro and to regulate expression of Tie1 as well as Tie2 (Morooka et al., 2017). It also has been suggested to play a role in TIE2-related PCG (Young et al., 2020). Hence, we wanted to investigate the role of Tie signalling in zebrafish lymphangiogenesis in order to assess potential interactions with svep1 in an in vivo situation. Lymphatic defects have not been previously reported in zebrafish mutants for either tie1 or tie2 (Carlantoni et al., 2021; Gjini et al., 2011; Jiang et al., 2020). Given the fact that there seems to be a very specific requirement for svep1 in FCLV development, we analysed facial lymphatic structures of tie1 and tie2 mutants in direct comparison to svep1 mutants. Since tie1 mutants developed strong edema at 4 dpf (data not shown), we focused our analysis on lymphatic phenotypes at 2 and 3 dpf to exclude secondary effects on the lymphatic vasculature. Significantly, tie1 mutant embryos showed the same facial lymphatic defects as svep1 mutant embryos at 3 dpf (Figure 3A), with the FCLV being strongly affected. We confirmed this observation also in a lyve1:DsRed transgenic background (Figure 3—figure supplement 1). This finding suggests that Tie1, either independently or in concert with Svep1 is responsible for FCLV formation in a Vegfc-independent manner. Examining other lymphatic cells, we found that tie1 mutants did not show any BLECs at 3 dpf and exhibited significantly reduced numbers of PLs at 2 dpf, similar to svep1 mutants (Figure 3B–E). Importantly, tie2 mutant embryos, when examined for the same anatomical features, were found to display normal facial lymphatics, BLECs and PL numbers (Figure 3A–C and E). Taken together, these findings demonstrate that loss of tie1, but not tie2, results in lymphatic defects highly similar to the ones seen in svep1 mutants, indicating that Svep1 constitutes an essential component acting in the Tie1 pathway.
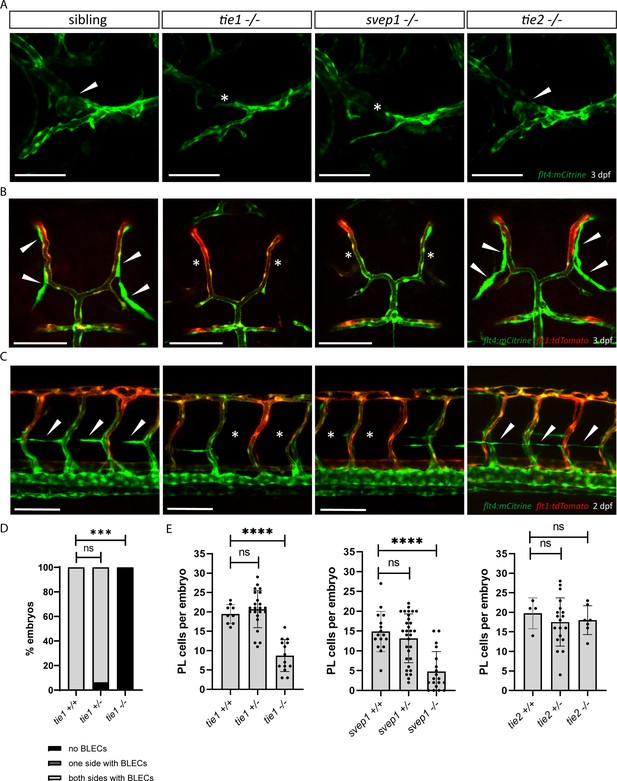
tie1 mutants phenocopy the loss of svep1, while tie2 is dispensable for lymphangiogenesis.
(A) Facial lymphatics at 3 dpf in flt4:mCitrine positive tie1, svep1 and tie2 mutants and sibling embryos (lateral view). Arrowheads point to FCLV and asterisks indicate the absence of FCLV. Scale bar = 100 µm. (B) flt4:mCitrine; flt1:tdTomato positive dorsal head vasculature in tie1, svep1, and tie2 mutants and in siblings at 3 dpf (dorsal view). In svep1 and tie1 mutants (but not in tie2 mutants) the presence of BLECs is strongly reduced. Arrowheads point to BLECs and asterisks indicate areas lacking BLECs. Scale bar = 100 µm. (C) Confocal images of PL cells, indicated by arrowheads, at 2 dpf in flt4:mCitrine; flt1:tdTomato positive tie1, svep1, and tie2 mutants and siblings, showing reduced PL numbers in svep1 and tie1 mutants. Asterisks indicate missing PLs. Scale bar = 100 µm. (D) Quantification of the presence of BLECs in tie1 mutants compared to siblings. (tie1+/+: n = 6; tie1+/−: n = 16; tie1−/−: n = 10) Mann–Whitney test was applied for statistical analysis. ***p = 0.001, ns = not significant. (E) Quantification of PL cell numbers in tie1 (tie1+/+: n = 9; tie1+/−: n = 23; tie1−/−: n = 14), svep1 (svep1+/+: n = 16; svep1+/−: n = 31; svep1−/−: n = 19), and tie2 (tie2+/+: n = 17; tie2+/−: n = 27; tie2−/−: n = 16) mutants compared to siblings. Mann–Whitney test was applied for statistical analysis. Values are presented as means ± standard deviation (SD), ****p < 0.0001, ns = not significant; BLEC, brain lymphatic endothelial cell; dpf, days post-fertilization; FCLV, facial collecting lymphatic vessel; PL, parachordal lymphangioblast.
tie1 and svep1 mutants display identical PL cell migration and survival defects
PLs first migrate along the HM and then start to migrate dorsally and ventrally along arteries to form the DLLV or the TD, respectively. Previously, it was shown that PLs in svep1 mutants fail to migrate dorsally or ventrally and rather remain at the HM (Karpanen et al., 2017). Here, we compared PL migration in svep1 and tie1 mutants using overnight imaging from 2.5 to 3.5 dpf to analyse if PLs in tie1 mutants phenocopy the PL migration defects of svep1 mutants (Figure 4A–L, Figure 4—videos 1–3). While around 40–50% of PLs in sibling embryos migrated along the artery, only 11% of PLs in tie1 and svep1 mutants showed migration in either dorsal or ventral direction along the artery (Figure 4M, N). Additionally, we observed around 33% apoptotic PLs in tie1 mutants and 55% in svep1 mutants. These apoptotic events could be a consequence of failed migration, or could be due to decreased survival as a direct consequence of absent Svep1 or Tie1 activity. To further characterize migration of PLs in svep1 and tie1 mutants, we tracked and plotted the migration route of individual PLs (Figure 4O, Q, Figure 4—figure supplements 1 and 2) and quantified the migration distance in the Y direction (i.e. migration in dorsal or ventral direction), mean velocity and total migration distance in tie1 and svep1 mutants (Figure 4P, R). PLs in svep1 as well as in tie1 mutants showed significantly less migration in ventral and dorsal directions compared to siblings, while the mean velocity and total migration distance were unchanged. Therefore, we can conclude that Svep1 and Tie1 are required for PL migration along the arteries in dorsal or ventral direction. Since we could observe the same specific migratory defects in both svep1 and tie1 mutants, these results further support a possible cross-talk between both proteins.
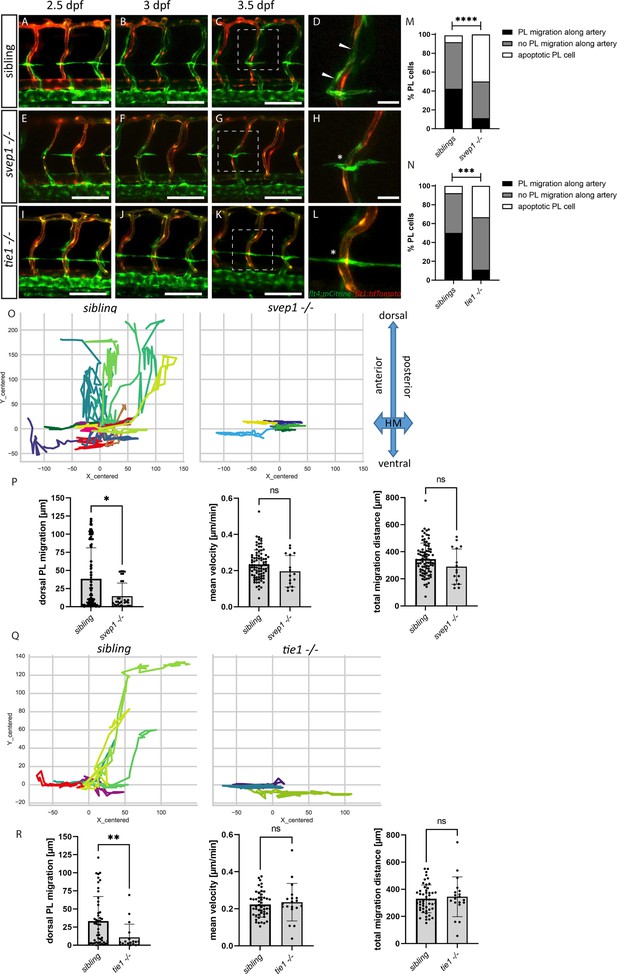
PL cell migration along arteries is severely affected in svep1 and tie1 mutants.
(A–L) Still frames from confocal time-lapse imaging of embryos in a flt4:mCitrine; flt1:tdTomato transgenic background. (A–D) PL migration (indicated by arrowheads) of sibling embryo along aISV from 2.5 to 3.5 dpf. (E–H) Failed PL migration (indicated by asterisk) of svep1 mutants and (I–L) tie1 mutants along artery from 2.5 to 3.5 dpf. (M, N) Classification of PL migration along arteries. Statistical analysis was performed using Mann–Whitney test comparing the % of PL migration along arteries in each sibling and mutant embryo (sibling: n = 96 PLs in 18 embryos; svep1−/−: n = 36 PLs in 15 embryos; siblings: n = 52 PLs in 14 embryos; tie1−/−: n = 28 PLs in 10 embryos); ****p < 0.0001, ***p = 0.0003. (O, Q) Representative cell tracking routes (tracks centred to origin) of single PL cells marked by different colours in siblings (n = 17 PLs in 4 embryos; n = 7 in 2 embryos), tie1−/− (n = 5 PLs in 2 embryos) and svep1−/− (n = 6 PLs in 3 embryos). (P, R) Quantification of dorsal and ventral PL migration (delta Y migration distance), mean velocity and total migration distance in svep1 and tie1 mutants compared to sibling embryos excluding apoptotic PLs quantified in (M, N) revealed decreased migration in dorsal and ventral direction in svep1 (*p = 0.0148) as well as tie1 mutants (**p = 0.0023). ns = not significant; aISV, arterial intersegmental vessel; dpf, days post fertilization; HM, horizontal myoseptum; PL, parachordal lymphangioblast. Scale bar = 100 µm (D, H, L = 25 µm).
tie1 mutants show blood vascular defects under reduced flow conditions
While svep1 mutants were initially identified on the basis of their lymphatic phenotype (Karpanen et al., 2017), Coxam et al. recently showed that svep1 mutant embryos display unique vascular defects under reduced flow conditions (Coxam et al., 2022). Treatment of embryos with 0.014% tricaine between 30 and 48 hpf leads to incomplete formation of the dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel (DLAV) with gaps and non-lumenized DLAV segments at 2 dpf in svep1 mutant embryos. This phenotype is accompanied by increased Vegfa/Vegfr signalling and increased number of Apelin positive tip cells (Coxam et al., 2022). To investigate if tie1 mutants mimic this very specific and unusual vascular defect, we treated embryos from tie1 heterozygous parents with 0.014% tricaine between 30 and 48 hpf, and subsequently imaged the intersegmental vessels in the trunk. Our analysis showed that tie1 mutants treated with tricaine exhibited significantly more gaps and fewer lumenized DLAV segments (Figure 5D) compared to both untreated tie1 mutants (Figure 5B) and treated siblings (Figure 5C, E, F), suggesting that Svep1 and Tie1 might interact not only in lymphangiogensis but also during blood vessel development. For tie2 and vegfc mutants we did not observe any defects in DLAV formation upon tricaine treatment, indicating that this phenotype is specific for loss of Svep1 and Tie1 (Figure 5—figure supplement 1). Additionally, upon tricaine treatment, and even in untreated conditions, apelin expressing ECs were increased in ISVs of tie1 mutants as already shown for svep1 morphants treated with tricaine in Coxam et al., 2022 (Figure 5G–J). Since we observed increased apelin expressing ECs in tie1 mutants already in untreated conditions, we investigated if svep1 morphants also show increased apelin expression even without tricaine treatment (Figure 5I, J). svep1 morphants already showed increased apelin expression in the ISVs in untreated conditions ( Figure 5—figure supplement 2). We confirmed our results using in situ hybridization ( Figure 5—figure supplement 3). These observations indicate that apelin expression is affected in tie1 mutants as well as svep1 morphants, and support the hypothesis of Tie1 and Svep1 acting in the same molecular pathway.
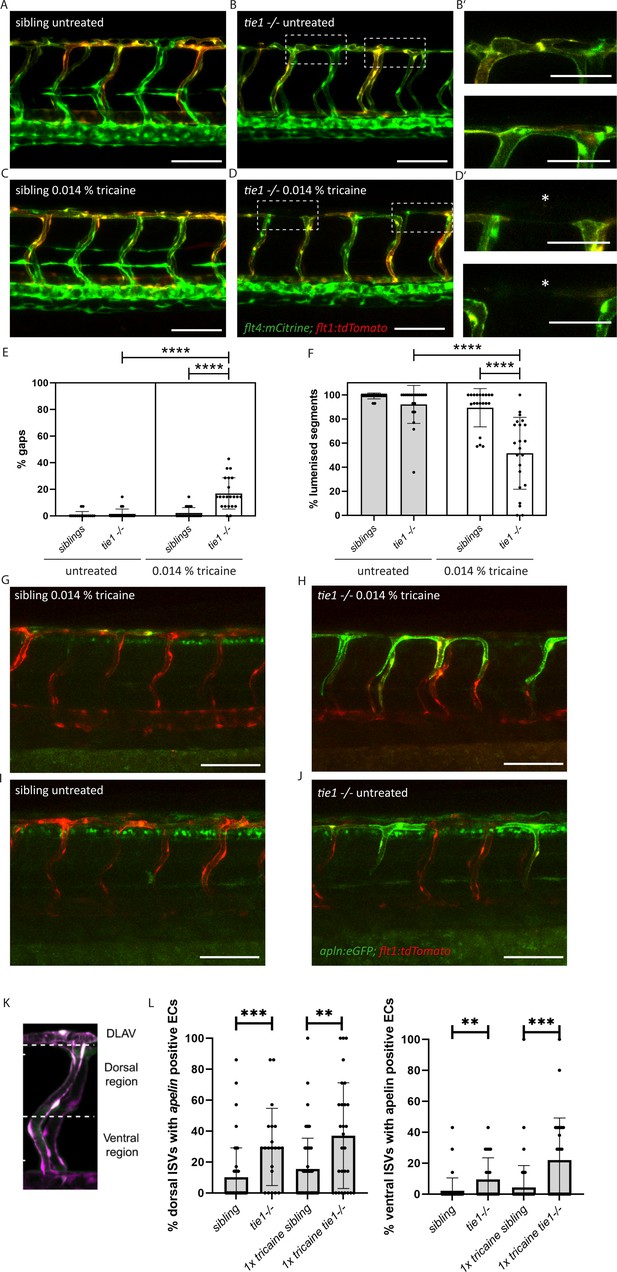
Reduced blood flow leads to vascular anastomosis defects in tie1 mutants, similar to the defects in svep1 mutants.
(A, B) Confocal images of sibling and tie1 mutant embryos at 2 dpf in a flt4:mCitrine and flt1:tdTomato transgenic background. (B’) Magnification and reduced stack of boxed area in (B). (C, D) Confocal images of sibling and tie1 mutant embryos treated with 0.014% tricaine from 30 until 48 hpf. Asterisks indicate incompletely formed DLAV segments. (D’) Magnification and reduced stack numbers of boxed area in (D). (E) Quantification of gaps in the DLAV in sibling and tie1 mutants that were either untreated or treated with 0.014% tricaine revealed significant increase of gaps in the DLAV in tie1 mutants. (F) Quantification of lumenized trunk segments of the DLAV in siblings and tie1 mutants, either untreated or treated with 0.014% tricaine (siblings untreated: n = 16; tie1−/− untreated: n = 20; siblings treated with 0.014% tricaine: n = 20; tie1−/− treated with 0.014% tricaine: n = 22), revealed significant decrease of lumenized segment numbers in the DLAV in tie1 mutants. Mann–Whitney test was applied for statistical analysis. (G, H) apelin:eGFP and flt1:tdTomato expression in 48-hpf-old embryos after tricaine treatment from 30 to 48 hpf and (I, J) in untreated conditions. (K) Maximum intensity projection of an aISV at 48 hpf, highlighting the ventral and dorsal region used for further quantifications in (J) adapted from Figure 5J of Coxam et al., 2022. (L) Quantification of ISVs with apelin expression in dorsal and ventral parts of the ISVs. Dorsal part was counted from DLAV until midline region. Lateral region was counted from midline region onwards in ventral direction. tie1 mutants showed significant increase of apelin positive ECs compared to siblings in untreated (dorsal: ***p = 0.0001; ventral: **p = 0.0028) and treated with 0.014% tricaine conditions (dorsal: **p = 0.0033; ventral: ***p = 0.0002) (siblings untreated: n = 53; tie1−/− untreated: n = 21; siblings treated with 0.014% tricaine: n = 66; tie1−/− treated with 0.014% tricaine: n = 28). Mann–Whitney test was applied for statistical analysis. Values are presented as means ± standard deviation (SD). ****p < 0.0001. Scale bar = 100 µm. hpf, hours post-fertilization; ISV, intersegmental vessel; DLAV, dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel; dpf, days post-fertilization.
tie2 loss of function does not exacerbate the tie1 mutant phenotype
To investigate a possible contribution of Tie2 to lymphatic Tie signalling as well as possible compensatory mechanisms, we examined tie1; tie2 double mutants at 2 dpf (Figure 6A–G). While tie1 mutants showed a highly significant reduction in PL numbers (Figure 6D, G), we found that an additional loss of one or two functional copies of tie2 did not further affect PL numbers in tie1 mutant embryos (Figure 6E–G). Additionally, loss of one tie1 allele in tie2 mutants did not result in any defects (Figure 6C, G). To further exclude contributions of Tie2 at later stages of lymphatic development on TD formation, we quantified the segments of TD across 10 consecutive trunk segments at 5 dpf. In line with our analysis at 2 dpf, heterozygous loss of tie1 did not reveal any defects in tie2 mutants (Figure 6H). These results therefore do not support a role of tie2 in zebrafish lymphatic development.
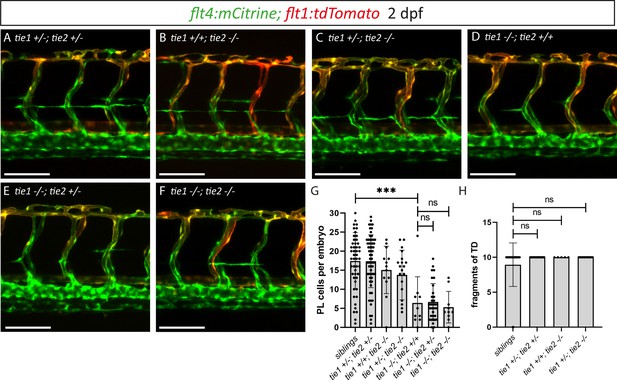
tie1; tie2 double mutants show no exacerbation of the tie1 mutant defects.
(A–F) Confocal images of blood and lymphatic vasculature in the trunk of 2 dpf old embryos derived from tie1; tie2 double heterozygous parents, showing no genetic interaction between tie1 and tie2. (G) Quantification of PLs at 2 dpf and of thoracic duct fragments at 5 dpf (siblings: n = 50; tie1+/−; tie2+/−: n = 62; tie1+/+; tie2−/−: n = 13; tie1+/−; tie2−/−: n = 20; tie1−/−; tie2+/+: n = 10; tie1−/−; tie2+/−: n = 32; tie1−/−; tie2−/−: n = 10). (H) TD fragments were counted over the anterior-most 10 somites (siblings: n = 47; tie1+/−; tie2+/−: n = 34; tie1+/+; tie2−/−: n = 5; tie1+/−; tie2−/−: n = 16). Mann–Whitney test was applied for statistical analysis. ***p = 0.0002, ns = not significant. Scale bar = 100 µm. dpf, days post-fertilization; PL, parachordal lymphangioblast; TD, thoracic duct.
Genetic interaction between svep1 and tie1 during PL migration in the trunk
After having excluded a potential role for Tie2 during lymphangiogenesis, and given the high phenotypic similarity between tie1 and svep1 mutants, we wondered whether both genes might act in the same pathway during lymphangiogenesis and would therefore show a genetic interaction. To this end, we quantified PL cell numbers in embryos from svep1; tie1 double heterozygous parents at 2 dpf. In svep1; tie1 double heterozygous embryos we could not observe any PL number reduction, reduction of BLECs or reduced facial lymphatics compared to siblings (Figure 7A, B, H; Figure 7—figure supplement 1), while tie1 and svep1 single mutants again showed severe reduction of PL cell numbers (Figure 7C, D, H). Importantly, these defects were significantly exacerbated in svep1+/−; tie1−/− compared to svep1+/+; tie1−/− mutant embryos (Figure 7D, F, H). In svep1−/−, tie+/− mutant embryos, we observed a tendency of fewer PLs compared to svep1 single mutants (Figure 7C, E, H). However, this effect was not significant. Taken together, this interaction study strengthens the idea that Svep1 converges in the Tie1 pathway.
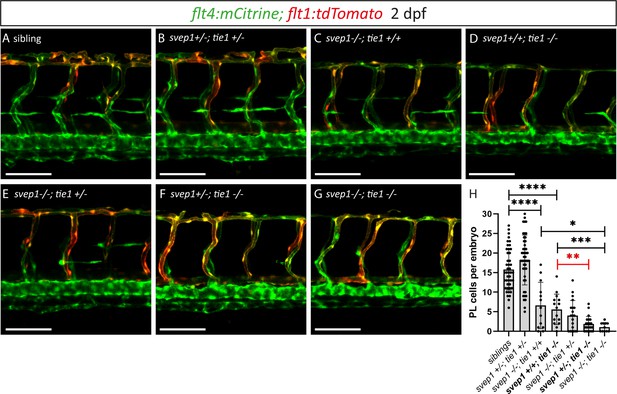
Heterozygous loss of svep1 exacerbates the PL phenotype in tie1 mutants, indicating genetic interaction between svep1 and tie1.
(A–G) Confocal images of blood and lymphatic vasculature in the trunk of 2-dpf-old embryos derived from svep1; tie1 double heterozygous fish, showing severely reduced PL numbers in svep1; tie1 double mutants and significant decrease of PL cell numbers in svep1+/−; tie1−/− compared to svep1+/+; tie1−/− (**p = 0.0012). (H) Quantification of PL cell numbers at 2 dpf using Mann–Whitney test (siblings: n = 45; svep1+/−; tie1+/−: n = 45; svep1−/−; tie1+/+: n = 13; svep1+/+; tie1−/−: n = 15; svep1−/−; tie1+/−: n = 20; svep1+/−; tie1−/−: n = 21; svep1−/−; tie1−/−: n = 11). Scale bar = 100 µm. Values are presented as means ± standard deviation (SD), ****p < 0.0001, ***p = 0.007, *p = 0.0163, ns = not significant. dpf, days post-fertilization; PL, parachordal lymphangioblast.
Svep1 is a binding ligand of Tie1
To interrogate whether Svep1 and Tie1 bind directly, we performed biochemical analyses using co-immunoprecipitation of Svep1 and Tie1 proteins. We co-transfected zebrafish Svep1 with zebrafish Tie1 or Tie2 constructs and detected Tie1 and Tie2 after immunoprecipitation of Svep1. Tie1 showed robust binding with Svep1 in every experiment (seven out of seven independent experiments; Figure 8A), while Tie2 co-precipitated with Svep1 in only two out of four experiments (Figure 8—figure supplement 1A). These results demonstrate that zebrafish Tie1 constitutes a binding partner for zebrafish Svep1. We performed the same experiment with human proteins, this time using only the C-terminus of human SVEP1 (aa: 2261–3571). We could observe that TIE1 showed binding to SVEP1, demonstrating that the SVEP1/TIE1 interaction is evolutionary conserved (Figure 8B). Additionally, we observed SVEP1 association with TIE2 (Figure 8—figure supplement 1B). In a second approach, we used purified SVEP1 protein (C-terminus) and the lysates of TIE1 or TIE2 transfected cells, to confirm our results and to obtain a better impression of the respective binding affinities. After pull-down of SVEP1, we detected binding of SVEP1 with TIE1 (Figure 8C) but no significant binding of TIE2 (Figure 8—figure supplement 1C). Therefore, we conclude that TIE1 is a ligand for SVEP1.
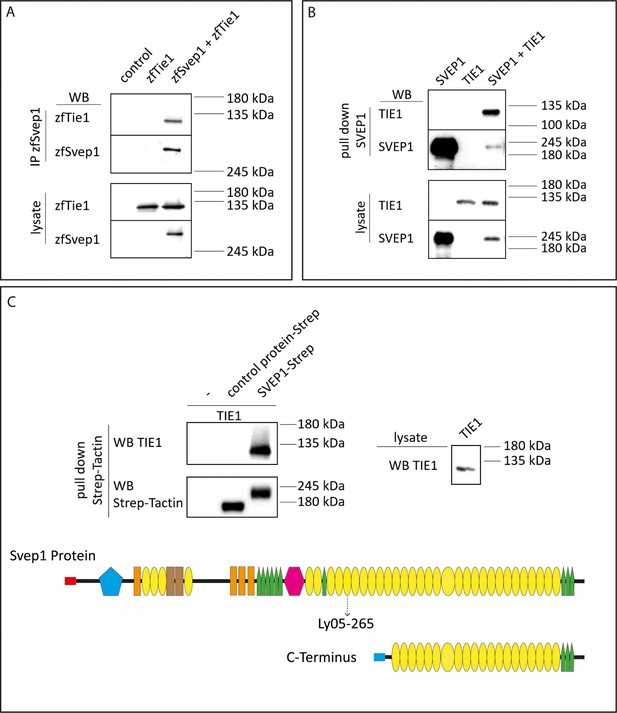
SVEP1 binds to TIE1.
(A) 293T HEK cells were transfected with zebrafish Svep1-HIS (zfSvep1) and zebrafish Tie1-HA (zfTie1). zfSvep1 was immunoprecipitated and associated Tie1 was detected by western blot. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of C-terminal human SVEP1 co-transfected in 293T HEK cells with human TIE1. (C) Pull-down of recombinant C-terminal human SVEP1-Strep-tag II protein, which was incubated with TIE1 transfected 293T HEK cell lysates, shows binding of TIE1. Protein structure with all domains indicated and C-terminal part used for pull-down assays (adapted from Figure 2F of Karpanen et al., 2017, published under the CC BY-NC 4.0 license, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/). It is not covered by the CC-BY 4.0 license and further reproduction of this panel would need to follow the terms of the CC BY-NC 4.0 license. Ly05-265 indicates position of stop codon in the zebrafish hu6985 allele (Karpanen et al., 2017), suggesting that the protein domains C-terminal to the nonsense allele are critical for function. Red and blue rectangle: signal peptide; blue pentagon: von Willebrand factor type A domain (vWF); orange rectangle: ephrin-receptor like domain; brown rectangle: Hyalin repeat; yellow ovals: SUSHI repeat; green pentagons: epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like and calcium-binding EGF-like domains; and pink hexagon: pentraxin domain (PTX).
© 2017, Karpanen et al. (C) Pull -down of recombinant C-terminal human SVEP1-Strep-tag II protein, which was incubated with TIE1 transfected 293 T HEK cell lysates, shows binding of TIE1. Protein structure with all domains indicated and C-terminal part used for pull down assays (adapted from Figure 2F of Karpanen et al., 2017, published under the CC BY-NC 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/). It is not covered by the CC-BY 4.0 license and further reproduction of this panel would need to follow the terms of the CC BY-NC 4.0 license)
-
Figure 8—source data 1
Raw data of western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/82969/elife-82969-fig8-data1-v1.pdf
Discussion
We had previously demonstrated a role for Svep1 in formation of functional lymphatic vessels in mice and zebrafish. We here extend this phenotypic analysis and show an essential role for zebrafish Svep1 during formation of specific aspects of the facial lymphatic network and of BLECs. Additionally, we uncover a crucial role for Tie1 signalling during lymphangiogenesis and DLAV formation under reduced flow conditions in zebrafish and provide strong in vivo evidence for svep1 and tie1 interaction. We also show direct binding of SVEP1 to TIE1 in vitro for the respective human and zebrafish proteins. The results thus establish Svep1 as a factor in Tie1 signalling in zebrafish, both in lymphatic and blood vascular beds. svep1 mutants display a very specific phenotype in the facial lymphatic bed, which is distinct from, and complementary to the phenotypes we observed in mutants of Vegfc/Vegfr3 pathway members (Figure 1). Previous studies demonstrated that mutations in vegfc, ccbe1, and adamts3; adamts14 lead to a complete loss of the facial lymphatic vasculature. These studies did not assess the effects on the recently described FCLV (Astin et al., 2014; Okuda et al., 2012; Padberg et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2020). In the present study, we show that the FCLV is still formed in mutants affecting the Vegfc/Vegfr3 signalling cascade, whereas mutations in either svep1 or tie1 result in a near-complete loss of this structure. In line with a differential requirement for svep1/tie1 for the development of the facial lymphatic vessels and the FCLV, we found that svep1 is expressed in close proximity to the lymphatic sprout arising from the PHS giving rise to the FCLV, while vegfc is expressed in cells that appear to be predominantly positioned around the migration route of the FLS arising from the CCV (Figure 1C). Based on this highly specific mutant phenotype, we conclude that Svep1 is essential for FCLV formation in a Vegfc-independent manner. Therefore, we here show for the first time that besides the previously postulated functional and morphological differences between FCLV and the facial lymphatics (Shin et al., 2019), there is also a difference in the pathways controlling the formation of both structures. Until recently, it was traditionally considered, that lymphatic vessels always (1) have a venous origin and (2) need Vegfc signalling to develop. In the last decade, it was shown that lymphatic vessels can also have non-venous origins in mice (Martinez-Corral et al., 2015) and also in the facial lymphatics of zebrafish (Eng et al., 2019). However, Vegfc signalling seemed to be always required for lymphatic vessel development. Interestingly, inactivation of Angpt1 and Angpt2 or Tie2 completely abolishes Schlemm’s canal development and leads to glaucoma formation in mice, while the Schlemm’s canal is still present and only reduced in mice lacking Vegfc and Vegfd or Vegfr3, indicating that in some lymphatic structures VEGFC is not strictly required (Bernier-Latmani and Petrova, 2017; Thomson and Quaggin, 2018). Here, we make the significant finding that a specific progenitor population of zebrafish facial lymphatic network, forming the FCLV, develops in a Vegfc-independent, but Svep1/Tie1-dependent mechanism. Since the Schlemm’s canal is a hybrid vessel (Kizhatil et al., 2014) and the FCLV seems to be also morphological and functional different from other lymphatic vessels (Shin et al., 2019), these two vessels not only share mechanistical but also functional differences to other lymphatic structures.
While the majority of mutants identified in forward genetic lymphatic screens affect known or novel members of the Vegfc signalling pathway with highly similar phenotypes, the svep1 mutants stand out due to phenotypic differences compared to mutants affecting the Vegfc/Vegfr3 pathway. This, however, raises the question how Svep1 exerts its effects during lymphangiogenesis. In the current study, we focused on a potential connection to the Tie signalling pathway, as murine ANG1 and ANG2 had been shown to bind Svep1 in vitro (Morooka et al., 2017). In mice, conditional knockout of Svep1 or Tie2 leads to high intraocular pressure and altered Schlemm’s canal morphology (Li et al., 2020; Thomson et al., 2014). Additionally, Tie2 and Tie1 expression levels are downregulated in Svep1 mutant mice (Morooka et al., 2017).
While Tie2 knockout mice display severe cardiovascular defects and die at E9.5 (Dumont et al., 1994; Sato et al., 1995), tie2 mutant zebrafish show unaltered vascular structures including unaffected trunk lymphatics (Gjini et al., 2011; Jiang et al., 2020). We here extend this notion to lymphatic structures in the head of the embryo: as is the case for PL cell numbers, neither the formation of facial lymphatics nor of BLECs depend on Tie2 activity. Teleost tie2 has actually been lost in the Acanthomorphata lineage, comprising 60% of contemporary teleost species (Jiang et al., 2020), suggesting either the loss of critical Tie2 function in most teleosts, or the adoption of essential functions for mammalian TEK function within the last 450 million years (dos Reis et al., 2015). This complicates functional comparison between mammalian and teleost Ang/Tie signalling. Tie1 mutant mice do not show any vascular defects until E13.5 and die from haemorrhages between E13.5 and P0, but display swellings at E12.5 caused by lymphatic malformations that precede the haemorrhaging (D’Amico et al., 2010; Puri et al., 1995; Sato et al., 1995). Additionally, postnatal Tie1 deletion causes impaired lymphatic capillary network development (Korhonen et al., 2022). We here show that tie1 mutant zebrafish embryos display severe lymphatic defects in the head and trunk vasculature, in addition to the previously reported cardiac and blood vascular phenotypes including impaired brain angiogenesis, reduced CCV width, and impaired caudal vein plexus formation (Carlantoni et al., 2021). Interestingly, the FCLV, which seems to have a comparable function to collecting lymphatic vessels, is affected in tie1 mutant zebrafish embryos, while Tie1;Tie2 double deletion in mice leads to defective postnatal collecting lymphatic vessel development (Korhonen et al., 2022). Further studies will be required in both mice and fish to determine to what extent Tie signalling affects LEC specification, proliferation, and survival. However, we here show definitively that Tie signalling is not only required in mice and humans for lymphatic vessel formation, but also in zebrafish.
Remarkably, lymphatic and non-lymphatic defects observed in tie1 mutant zebrafish embryos are very similar to the defects observed in svep1 mutants: while reduced PL numbers and TD length is a hallmark feature of many lymphatic mutants, the specific absence of the FCLV is unique, and common to both mutants. Furthermore, formation of BLECs is affected in both mutants, and the specific PL migration phenotype, with PL cells at the HM not migrating dorsally or ventrally, is also observed in both svep1 and tie1 mutants (Figure 4). In addition, we could show that tie1 mutants show similar vascular defects in DLAV formation under reduced flow conditions compared to svep1 mutants, while we did not observe any defects in vegfc and tie2 mutants. Another hallmark of the svep1 phenotype is the increase in apelin expression in the ISVs, which is again recapitulated in tie1 mutants. Therefore, we conclude that svep1/tie1 signalling is not only important for lymphangiogenesis but also for blood vessel development and acts, at least to some extent, in a Vegfc-independent manner. Finally, genetic interaction studies indicate that Svep1 provides essential input into the Tie1 pathway, as losing one copy of svep1 in tie1 mutants exacerbates the phenotype significantly when assessing PL cell numbers (Figure 7). Of note, elimination of both tie2 alleles did not alter the tie1 mutant phenotype (Figure 6). Since Young et al. reported Svep1 as a possible genetic modifier of TIE2 (Young et al., 2020), and Morooka et al. showed that Tie1 as well as Tie2 expression levels are downregulated in Svep1 deficient mice (Morooka et al., 2017), we assessed tie1 expression levels in zebrafish svep1 mutants. However, using in situ hybridization, we did not find any signs of miss-regulation of tie1 expression in svep1 mutants (Figure 7—figure supplement 2), indicating that at least in zebrafish downregulation of tie1 is not causative for the observed defects.
There are at least two possibilities how Svep1 could exert its effect on Tie1 function. First, and based on the observation that murine Svep1 can bind Tie receptor ligands (Morooka et al., 2017), zebrafish Svep1 could be an essential component of enabling or stabilizing binding of angiopoietins to Tie1. Second, and due to the close proximity of svep1 expressing cells to LECs, Svep1 could also act as a direct ligand for Tie1. Further studies will clarify whether angiopoietins are a required component of Svep1/Tie1 signalling, and to what extent there are species-specific differences between teleosts and mammals.
In summary, we here show that zebrafish Svep1 as well as human SVEP1 can bind to Tie1/TIE1, indicating SVEP1 as a novel binding partner of TIE1. For human SVEP1 we only used the C-terminus for binding assays, since we reasoned, based on a previously generated svep1 mutant line (Ly05-265) with a premature stop in CCP domain 9 (Karpanen et al., 2017), that the C-terminus is critical for Svep1 function. Further studies, such as ELISA or Biacore assays that allow quantitative assessment of binding affinities for TIE1 and TIE2, will be required to allow more qualified statements on whether and to which extend SVEP1 can also bind TIE2. Taken together, we provide the first in vivo and in vitro evidence that Svep1 interacts with Tie1, and that both genes, at least in certain vascular beds, act in a Vegfc-independent manner. Thus, we here clarify the importance of the respective roles of Tie1 as well as Tie2 in zebrafish, but also underline the significance of Svep1 and Tie1 signalling in different vascular beds. Together with the recent discovery that SVEP1 could act as a modifier of TEK-related PCG disease penetrance, further studies in zebrafish can serve as an in vivo model for clinically relevant aspects of Svep1/Tie signalling.
Materials and methods
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | Tg(flt4:mCitrine)hu7135 | van Impel et al., 2014 | ZFIN: hu7135 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | Tg(flt1enh:tdTomato)hu5333 | Bussmann and Schulte-Merker, 2011 | ZFIN: hu5333 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | Tg(lyve1:DsRed2)nz101 | Okuda et al., 2012 | ZFIN: nz101 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | Tg(UAS:RFP)nkuasrfp1a | Asakawa et al., 2008 | ZFIN: nkuasrfp1a | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | Tg(vegfc:Gal4FF)mu402 | Wang et al., 2020 | ZFIN: mu402 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | Tg(svep1:GAL4FF)hu8885 | Karpanen et al., 2017 | ZFIN: hu8885 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | adamts3hu10891 | Wang et al., 2020 | ZFIN: hu10891 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | adamts14hu11304 | Wang et al., 2020 | ZFIN: hu11304 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | vegfchu6410 | Helker et al., 2013; Le Guen et al., 2014 | ZFIN: hu6410 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | ccbe1hu10965 | Kok et al., 2015 | ZFIN: hu10965 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | svep1hu6123 | Karpanen et al., 2017 | ZFIN: hu6123 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | svep1hu4767 | Karpanen et al., 2017 | ZFIN: hu4767 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | tie1bns208 | Carlantoni et al., 2021 | ZFIN: bns208 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | tie2hu1667 | Gjini et al., 2011 | ZFIN: hu1667 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. rerio) | TgBAC(apln:EGFP)bns157 | Helker et al., 2020 | ZFIN: bns157 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | 293T HEK cells | Roukens et al., 2015 | ||
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293 EBNA | Manuel Koch | ||
| Transfected construct (D. rerio) | zfTie1-HA in PCS2+ | This paper | Provided by Naoki Mochizuki | |
| Transfected construct (D. rerio) | zfTie2-HA in PCS2+ | This paper | zfTie2 cDNA provided by Naoki Mochizuki | |
| Transfected construct (D. rerio) | zfSvep1-HIS in PCS2+ | This paper | ||
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | TIE1-HA in PCEP4 | This paper | TIE1 cDNA provided by Hellmut Augustin | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | TIE2-HA in PCEP4 | This paper | Provided by Manuel Koch | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | SVEP1-Strep II in PCEP4 | This paper | Provided by Manuel Koch | |
| Transfected construct (Mus musculus) | mouse nope ectodomain with Fc tag strep | This paper | Provided by Manuel Koch | |
| Antibody | anti-HA (rat monoclonal) | Roche | 11867423001 | 1:10,000 |
| Antibody | anti-rat (donkey polyclonal) | Invitrogen | # A18745 | 1:15,000 |
| Antibody | anti-HIS (rabbit polyclonal) | Invitrogen | # PA1-983B | 1:250 |
| Antibody | anti-HIS (mouse monoclonal) | Invitrogen | # MA1-135 | 1:250 |
| Antibody | anti-mouse (goat polyclonal) | dako | P0447 | 1:4000 |
| Antibody | anti-DIG primary antibody (sheep polyclonal) | Roche | 11093274910 | 1:2000 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | apelin in pGEM-t-easy | Provided by Christian Helker | For in situ probe generation | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | SVEP1-Strep II Purified recombinant protein | This paper | Provided by Manuel Koch | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DIG RNA Labeling Mix | Roche | 11277073910 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lipofectamin 2000 transfection reagent | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 11668030 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | FuGENE HD Transfection Reagen | Promega | E2311 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | T4 Ligase | Thermo Fisher Scientific | EL0012 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | FCS | Merck Chemicals GmbH | F7524 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Q5 Hot Start High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase | New England Biolabs GmbH | M0493 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM/F-12, GlutaMAX Supplement | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 10565018 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Strep-Tactin Superflow high capacity resin | IBA Lifesciences GmbH | 2-1208-002 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 6 | GraphPad Software, USA | ||
| Software, algorithm | Fiji-ImageJ (version 1.52); Manual tracking plugin; StrackReg plugin | DOI:10.1038/nmeth.2019; Fabrice Cordelières, Institut Curie, Orsay (France); DOI:10.1109/83.650848 | RRID:SCR_002285 | |
| Software, algorithm | Python (version 3.8) | Python.org | RRID:SCR_008394 | Code available at https://github.com/MuensterImagingNetwork/Hussmann_et_al_2022 |
| Other | Strep-Tactin HRP conjugate | Iba-lifesciences | 2-1502-001 | 1:10,000 |
Zebrafish strains and husbandry
Request a detailed protocolAnimal work followed guidelines of the animal ethics committees at the University of Münster, Germany, and fish were maintained following FELASA guidelines (Aleström et al., 2020). The following transgenic and mutant lines have been used in this study: Tg(flt4:mCitrine)hu7135 (van Impel et al., 2014), Tg(flt1enh:tdTomato)hu5333 (Bussmann and Schulte-Merker, 2011), Tg(lyve1:DsRed2)nz101 (Okuda et al., 2012), Tg(UAS:RFP)nkuasrfp1a (Asakawa et al., 2008), Tg(vegfc:Gal4FF)mu402 (Wang et al., 2020), Tg(svep1:GAL4FF)hu8885 (Karpanen et al., 2017), adamts3hu10891 (Wang et al., 2020), adamts14hu11304 (Wang et al., 2020), vegfchu6410 (Helker et al., 2013; Le Guen et al., 2014), ccbe1hu10965 (Kok et al., 2015), svep1hu6123 (Karpanen et al., 2017), svep1hu4767 (Karpanen et al., 2017) (only used for svep1;ccbe1 double knockout, Figure 1—figure supplement 2), tie1bns208 (Carlantoni et al., 2021), tie2hu1667 (Gjini et al., 2011), and TgBAC(apln:EGFP)bns157 (Helker et al., 2020).
Genotyping
Request a detailed protocolFor genotyping of svep1, adamts3, adamts14, vegfc, and tie2, KASPar (Biosearch Technologies) was used, and for ccbe1 and tie1 High-Resolution Melt Analysis (Samarut et al., 2016; Supplementary file 1).
Live imaging and microscopy
Request a detailed protocolLive imaging was carried out on 2, 3, and 5 dpf embryos. Before 24 hpf, 1-phenyl-2-thiourea (75 mM, Sigma, #P7629) was added to inhibit melanogenesis (Karlsson et al., 2001). For imaging, embryos were anesthetized with 42 mg/l tricaine (Sigma, #A5040) and embedded in 0.8% low melting agarose (Thermo Fischer, #16520100) dissolved in embryo medium. Embryo medium containing tricaine was layered on top of the agarose once solidified for overnight imaging. Additionally, embryos were kept at 28°C during overnight imaging. Embryos were imaged with an inverted Leica SP8 microscope using a ×20/×0.75 dry objective or a ×40/1.1 water immersion objective detection and employing Leica LAS X 3.5.7.23225 software. Scoring of PLs or TD fragments was performed using a Leica M165 FC and an X-Cite 200DC (Lumen Dynamics) fluorescent light source. Confocal stacks were processed using Fiji-ImageJ version 1.52 g. Brightfield images were taken using an Olympus SZX16 microscope and a LEICA DFC450 C camera. Images and figures were assembled using Adobe Illustrator. All data were processed using raw images with brightness, colour, and contrast adjusted for printing.
Cell tracking
Request a detailed protocolTo quantify the migration distance and mean velocity of the PLs from 2.5 to 3.5 dpf, the leading edge of each PL was manually tracked using ‘Manual Tracking’-Plugin (Fabrice Cordelières, Institut Curie, Orsay (France)) in Fiji-ImageJ (version 1.52 g source, Schindelin et al., 2012). For image stabilization ‘StackReg’ using rigid body (Thevenaz et al., 1998) was applied to the maximum intensity projections of the time-lapse movies prior to manual tracking. Mean track velocity and total migration distance (sum of all leading edge displacements) were calculated using a custom Python script (version 3.8). To plot the migration route, track start coordinates were centred to the origin and individual cell tracks were represented using a line plot (Python). Y PL migration was defined as the absolute value of the distance in Y direction (dorsal and ventral) from track origin to the last tracking point (ΔY). Scripts used for data analysis are available at GitHub. Data were analyzed using GraphPad for plotting and statistical analysis.
Tricaine treatment
Request a detailed protocolWhere applicable, embryos were treated with 0.014% tricaine (Sigma, #A5040) from 30 to 48 hpf to slow down heart rate and blood flow during DLAV formation as previously described (Coxam et al., 2022).
In situ hybridization
Request a detailed protocolAntisense RNA probes of tie1 were generated from amplified cDNA. Primers for cDNA generation are listed in Supplementary file 1. Antisense RNA probes of apelin were generated from cDNA kindly provided by Christian Helker (Helker et al., 2015). Since the reverse primer contained a T3 overhang, we proceeded with in vitro transcription using T3 RNA polymerase and digoxigenin (DIG)-labelled UTP (2 hr at 37°C). Fixation of 24 hpf embryos from a svep1 heterozygous incross was performed with 4% paraformaldehyd (PFA) overnight at 4°C. In situ hybridization was performed according to previous published protocols using 100 ng of each of the respective probes (Schulte-Merker, 2002). Staining procedure was monitored regularly over time to ensure proper detection of differences in staining intensities between embryos.
Cloning and expression of human SVEP1, TIE1, and TIE2
Request a detailed protocolThe C-terminal part of SVEP1 was amplified from human cDNA using Q5 polymerase and cloned into the sleeping beauty transposon system (Kowarz et al., 2015; NM_153366.4 aa: 2261–3571; N-terminal BM-40 signal peptide followed by a Twin-Strep-tag). After verification of the plasmid by sequencing, the expression construct was co-transfected with the transposase plasmid (10:1) into HEK293 EBNA cells (tested negative for mycoplasma) using FuGENE HD transfection reagent (Promega GmbH, Madison, USA) in DMEM/F12 supplemented with 6% fetal bovine serum. After high puromycin selection (3 µg/ml; Sigma), cells were expanded in triple flasks and protein production induced with doxycycline (0.5 µg/ml, Sigma). Supernatants of confluent cells were harvested every 3 days, filtered and recombinant proteins purified via Strep-TactinXT (IBA Lifescience, Göttingen, Germany) resin. SVEP1 was eluted with biotin-containing buffer (IBA Lifescience, Göttingen, Germany), dialyzed against TBS and stored at 4°C or −80°C. The human sequences of TIE1 (NP_005415.1 aa: 21–1138) and TIE2 (NP_000450.3 aa: 23–1124) were cloned into the PCEP episomal expression system (transient) including an HA-tag sequence at the C-terminal part in the reverse primers. For the PCR amplification, TIE2 was amplified from human cDNAs, and TIE1 from a plasmid kindly provided by Hellmut Augustin.
In vitro binding assay
Request a detailed protocolFor co-immunoprecipitation we first transfected 293T HEK cells with zebrafish Svep1-HIS, zebrafish Tie1-HA, zebrafish Tie2-HA, human SVEP1 (C-Terminus)-StrepII, human TIE1-HA or human TIE2-HA as well as the indicated combinations using Lipofectamin 2000 reagent. After 48 hr the cell lysates were collected using Ripa buffer (50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 1% NP-40, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, 0.5% Na-deoxycholate, 150 mM NaCl). For co-immunoprecipitation of zebrafish Svep1-HIS, the cell lysates were incubated for 1 hr with 30 µl G-Sepharose beads (17061801, GE Healthcare) and 3 µg of anti-HIS antibody (# PA1-983B, Invitrogen). For pull-down of human SVEP1-StrepII, we used Strep-TactinXT 4Flow high capacity resin (2-5030-025, iba-lifesciences). Afterwards, the beads were washed five times with Ripa buffer and boiled for 5 min at 95°C in sample buffer.
In an independent approach, the C-terminus of human StrepII tagged SVEP1 protein (amino acids 2261–3571) was generated and purified. This protein and a StrepII tagged control protein (3 µg) were incubated with 50 µl Strep-TactinXT 4Flow high capacity resin in 500 µl binding buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl at pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 0.02% Triton X-100) for 30 min and added to the cell lysate of TIE1-HA and TIE2-HA transfected cells. After 2 hr incubation, the beads were washed with Ripa buffer and processed like the co-transfection samples. All samples were subjected to western blot analysis using anti-HA high affinity antibody (11867423001, Roche) to detect co-precipitated TIE1 and TIE2. The respective secondary antibody was HRP conjugated and detected using Lumi-Light Western Blotting Substrate (12015200001, Roche) and ChemiDoc MP Imaging System (Biorad). For western blot analysis of zfSvep1-HIS we used anti-His mouse antibody (# MA1-135, Invitrogen) and for SVEP1 we used Strep-Tactin HRP conjugate (2-1502-001, iba-lifesciences).
| antibody | dilution | provider |
|---|---|---|
| anti-HA rat | 1:10000 | 11867423001, Roche |
| anti-rat donkey | 1:15000 | # A18745, Invitrogen |
| anti-HIS rabbit | 1:250 | # PA1-983B, Invitrogen |
| anti-HIS mouse | 1:250 | # MA1-135, Invitrogen |
| anti-mouse goat | 1:4000 | P0447, dako |
| Strep-Tactin HRP conjugate | 1:10000 | 2-1502-001, iba-lifesciences |
Statistics and reproducibility
Request a detailed protocolData sets were tested for normality (Shapiro–Wilk) and equal variance p-values of data sets with normal distribution were determined by Welch’s t-test or Student’s t-test. In case data values did not show normal distribution, a Mann–Whitney test was performed instead. All statistical tests were performed using GraphPad Prism 8 or Microsoft Excel. All experiments were carried out at least two times. Only tricaine treatment of vegfc mutants (Figure 5—figure supplement 1) was carried out once.
Data availability
Scripts used for data analysis available at GitHub at https://github.com/MuensterImagingNetwork/Hussmann_et_al_2022 (copy archived at Münster Imaging Network, 2023). Source Data files have been provided for Figures 8 and Figure 8 figure supplement 1.
References
-
Mutations in CCBE1 cause generalized lymph vessel dysplasia in humansNature Genetics 41:1272–1274.https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.484
-
Zebrafish: housing and husbandry recommendationsLaboratory Animals 54:213–224.https://doi.org/10.1177/0023677219869037
-
All tied up: mechanisms of schlemm’s canal maintenanceThe Journal of Clinical Investigation 127:3594–3597.https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI96840
-
Mural lymphatic endothelial cells regulate meningeal angiogenesis in the zebrafishNature Neuroscience 20:774–783.https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4558
-
Rapid BAC selection for Tol2 -mediated transgenesis in zebrafishDevelopment 138:4327–4332.https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.068080
-
Tie1 regulates zebrafish cardiac morphogenesis through Tolloid-like 1 expressionDevelopmental Biology 469:54–67.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.09.008
-
Loss of endothelial TIE1 receptor impairs lymphatic vessel development-brief reportArteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 30:207–209.https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.196618
-
The endothelial-specific receptor tyrosine kinase, TEK, is a member of a new subfamily of receptorsOncogene 8:1293–1301.
-
Zebrafish Tie-2 shares a redundant role with TIE-1 in heart development and regulates vessel integrityDisease Models & Mechanisms 4:57–66.https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.005033
-
Ccbe1 is required for embryonic lymphangiogenesis and venous sproutingNature Genetics 41:396–398.https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.321
-
Proteolytic processing regulates receptor specificity and activity of VEGF-CThe EMBO Journal 16:3898–3911.https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/16.13.3898
-
An evolutionarily conserved role for polydom/svep1 during lymphatic vessel formationCirculation Research 120:1263–1275.https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308813
-
Impaired angiopoietin/tie2 signaling compromises schlemm’s canal integrity and induces glaucomaThe Journal of Clinical Investigation 127:3877–3896.https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI94668
-
Lymphangiogenesis requires ang2/tie/PI3K signaling for VEGFR3 cell-surface expressionThe Journal of Clinical Investigation 132:e155478.https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI155478
-
Optimized sleeping beauty transposons rapidly generate stable transgenic cell linesBiotechnology Journal 10:647–653.https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201400821
-
A small molecule inhibitor of VE-PTP activates Tie2 in schlemm’s canal increasing outflow facility and reducing intraocular pressureInvestigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 61:12.https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.61.14.12
-
Molecular mechanisms of lymphatic vascular developmentCellular and Molecular Life Sciences 64:1915–1929.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7040-z
-
Lymphatic malformations: genetics, mechanisms and therapeutic strategiesCirculation Research 129:136–154.https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318142
-
Evidence for heterotypic interaction between the receptor tyrosine kinases TIE-1 and Tie-2The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275:39741–39746.https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M007189200
-
Nonvenous origin of dermal lymphatic vasculatureCirculation Research 116:1649–1654.https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.306170
-
From fish embryos to human patients: lymphangiogenesis in development and diseaseCurrent Opinion in Immunology 53:167–172.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2018.05.003
-
SVEP1 is important for morphogenesis of lymphatic system: possible implications in lymphedemaLymphology 54:12–22.
-
Polydom is an extracellular matrix protein involved in lymphatic vessel remodelingCirculation Research 120:1276–1288.https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308825
-
The lymphatic vasculature revisited-new developments in the zebrafishMethods in Cell Biology 138:221–238.https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mcb.2016.11.001
-
A novel endothelial cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase with extracellular epidermal growth factor homology domainsMolecular and Cellular Biology 12:1698–1707.https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.12.4.1698-1707.1992
-
Polydom/SVEP1 is a ligand for integrin α9β1The Journal of Biological Chemistry 287:25615–25630.https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.355016
-
Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysisNature Methods 9:676–682.https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2019
-
BookLooking at embryosIn: Nusslein-Volhard C, editors. In Zebrafish: A Practical Approach. New York, N.Y: Oxford University Press. pp. 39–58.
-
Valves are a conserved feature of the zebrafish lymphatic systemDevelopmental Cell 51:374–386.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.08.019
-
A pyramid approach to subpixel registration based on intensityIEEE Transactions on Image Processing 7:27–41.https://doi.org/10.1109/83.650848
-
A lymphatic defect causes ocular hypertension and glaucoma in miceThe Journal of Clinical Investigation 124:4320–4324.https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI77162
-
Morphological analysis of schlemm’s canal in miceMethods in Molecular Biology 1846:153–160.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8712-2_10
-
A fisheye view on lymphangiogenesisAdvances in Anatomy, Embryology, and Cell Biology 214:153–165.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-1646-3_12
-
SVEP1 as a genetic modifier of TEK-related primary congenital glaucomaInvestigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 61:6.https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.61.12.6
Article and author information
Author details
Funding
Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (CRC 1348 project B08)
- Melina Hußmann
- Stefan Schulte-Merker
The funders had no role in study design, data collection, and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by CRC 1348 (DFG, project B08 to M.H. and S.S.-M.) and by the CiM-IMPRS graduate school. The original human TIE1 plasmid was kindly provided by Hellmut Augustin.
Copyright
© 2023, Hußmann et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 1,591
- views
-
- 203
- downloads
-
- 23
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Citations by DOI
-
- 23
- citations for umbrella DOI https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.82969






