lncRNA read-through regulates the BX-C insulator Fub-1
Figures
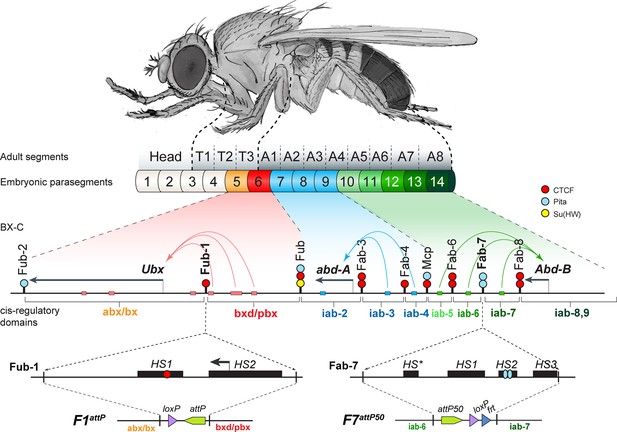
The organization of the genes and regulatory domains in BX-C.
The Drosophila melanogaster Bithorax complex (BX-C), which contains the Hox genes Ubx, abd-A, and Abd-B, is shown in relation to where these three genes are expressed in an embryo. There are nine cis-regulatory domains that are responsible for the regulation of Ubx (abx/bx and bxd/pbx domains), abd-A (iab-2–4 domains), and Abd-B (iab-5–7 and iab-8,9 domains), and for the development of parasegments 5–13 (PS)/segments (T3–A8). The anterior limit of expression of the three Hox gene is indicated by color coding: red: Ubx; blue: abd-A; green: Abd-B (reviewed in Maeda and Karch, 2015). The lines with colored circles mark chromatin boundaries. dCTCF, Pita, and Su(Hw) binding sites at the boundaries are shown as red, blue, and yellow circles/ ovals, respectively. Embryonic enhancers are indicated by pink, blue, and green bars on coordinate line. On the bottom of the figure, the molecular maps of the Fub-1 and Fab-7 boundaries are shown, including their deletions. Transposase/nuclease hypersensitive sites are shown as black boxes above the coordinate bar. The proximal and distal deficiency endpoints of the Fub-1 and Fab-7 deletions used in the replacement experiments are indicated by vertical lines. The attP, lox, and frt sites used in genome manipulations are shown as green, violet, and blue triangles, respectively.
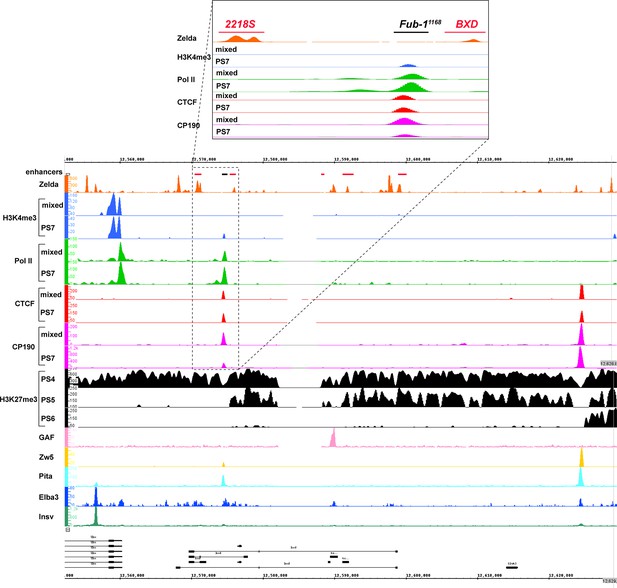
Chip-seq profiles of different chromatin proteins and histone modifications across bxd/pbx domain.
ChIP-seq profiles for H3K4me3, H3K27me3, Pol II, CTCF, CP190, Zw5, Pita, Elba3, Insv, Zld, and GAF (Bowman et al., 2014, p. 27; Fuda et al., 2015; Harrison et al., 2011; Ueberschär et al., 2019; Zolotarev et al., 2016). The putative enhancers are indicated by a pink bar below the coordinate line.

Fub-1 sequence conservation.
Sequence comparison of Fub-1 boundaries from D. virilis, D. pseudoobscura, D. erecta, D. sechellia, and D. melanogaster. The Fub-1 sequences of D. melanogaster and four other Drosophila species were assembled and stacked up with the ClustalO program to align the high homology region conserved among the five species. Sequences that are homologous in all four Drosophila species are highlighted in shades of blue representing degree of conservation. The dCTCF recognition sequence in HS1, GAGA-motifs, and predicted TSS is enclosed in red rectangles.
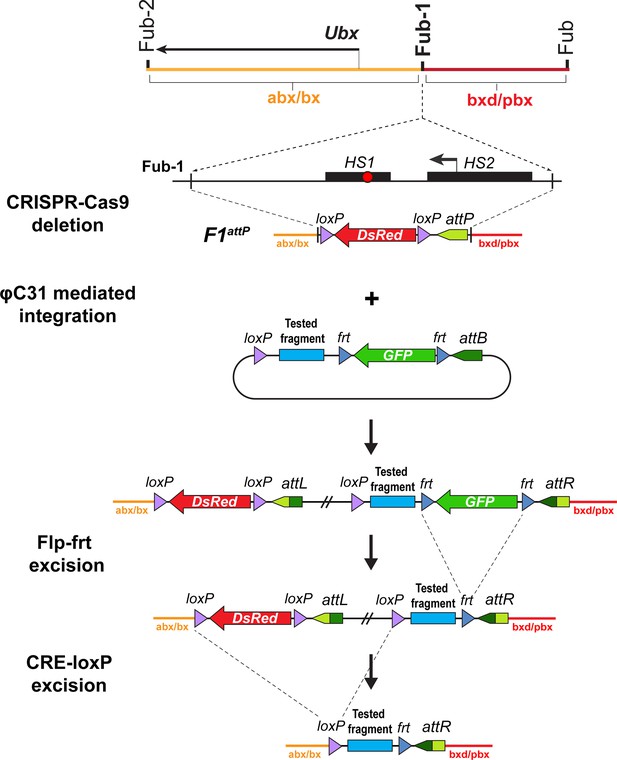
Strategy for creating Fub-1 deletion and replacement lines.
Top: schematic representation of the regulatory region containing the Ubx gene. The F1attP line was obtained through the substitution of a 1168 bp region with attP site and the dsRed gene, flanked by loxP sites. The coordinates of the deletion are dm6 3R:16,748,143.16,749,310. The plasmid that contains the test fragment and a GFP marker gene was injected into the F1attP line. In the next step, the GFP gene was excised by CRE-mediated recombination between the frt sites. During the final step, the dsRed gene was excised by recombination between the loxP sites. As a result, the tested elements were inserted in place of the 1168 bp deletion.
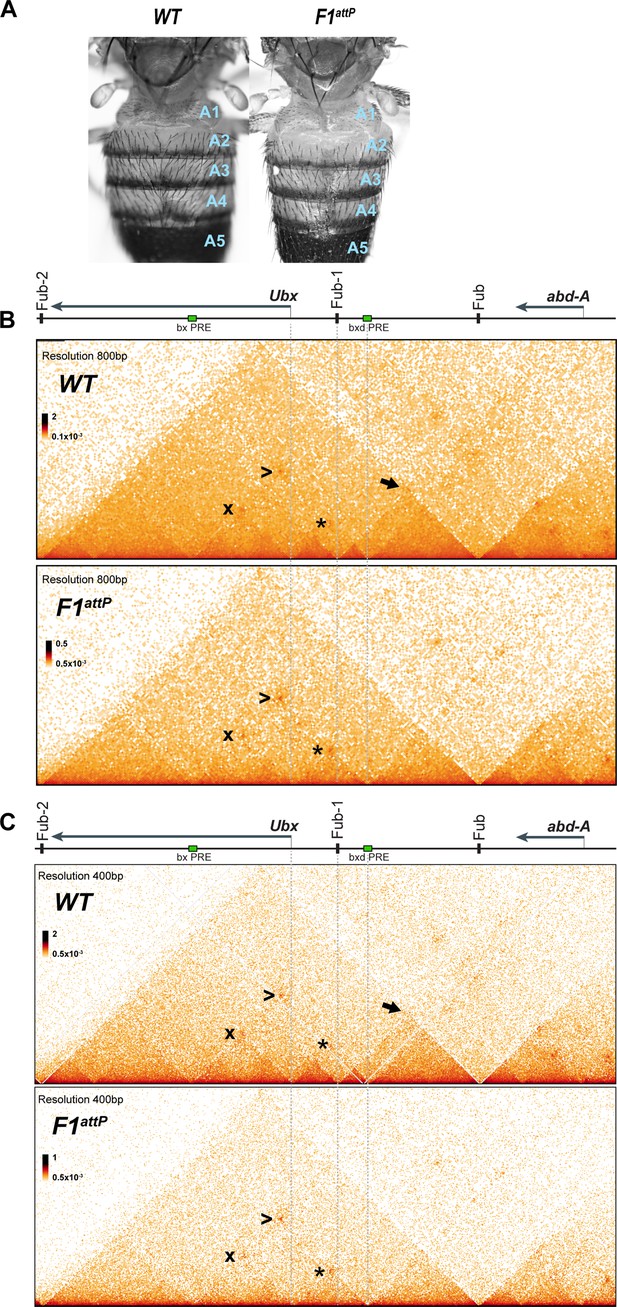
Chromatin topology in bxd/pbx domain in WT and in Fub-1 deletion.
(A) Morphology of the abdominal segments of WT and F1attP flies. (B) Micro-C contact map of the WT and F1attP 12–18 hr embryos at 800 bp resolution. The black arrow points to a sub-TAD formed by Fub-1 and Fub boundaries. The Ubx promoter is linked to the bxd PRE by a lower density of internal contacts domain (LDIC) that is marked at the apex by an interaction dot (*). The bxd PRE forms an interaction dot (>) with the bx PRE as does the Ubx promoter (x). (C) Micro-C contact map of the WT and F1attP 12–18 hr embryos at 400 bp resolution.
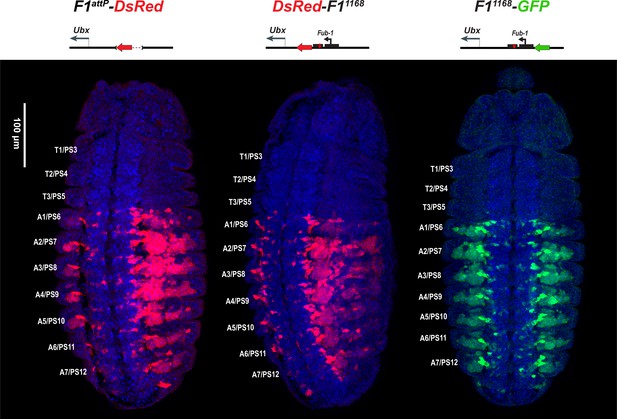
DsRed and GFP markers trap enhancer activity in Fub-1 replacements.
DsRed (in red) and GFP (in green) expression in stage 14 embryos in the Fub-1 deletion and in two replacements as indicated. DAPI was used to stain nuclei (in blue). DsRed expression in F1attP-DsRed begins in PS6/A1. In DsRed-F11168 and F11168-GFP, expression patterns of both markers are limited to PS6/A1-PS13/A8, consistent with the idea that the Ubx promoter region can function to demarcate the abx/bx and bxd/pbx domains.
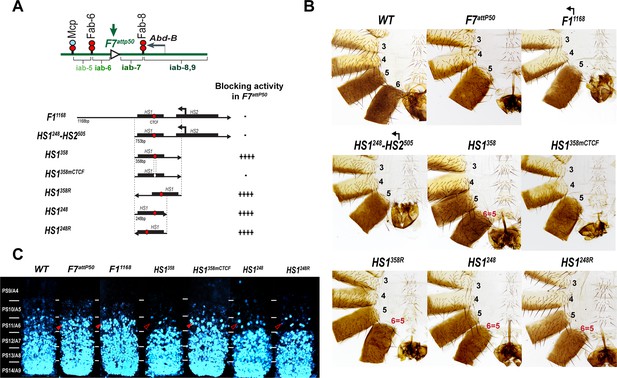
Testing boundary activity of Fub-1 sequences.
(A) Top: schematic presentation of Fab-7 substitution. Bottom: Fub-1 fragments used in the replacement experiments. On the right side, the insulator activity with the various fragments in the F7attP50 insertion site in adults as judged from cuticle preps. The number of ‘+’ signs reflects the strength of insulator activity, where ‘++++’ is full blocking, and ‘-’ is lack of detectable blocking activity, respectively. Designations are the same as described in Figure 1. (B) Morphology of the male abdominal segments (numbered) in F11168, HS1248-HS2505, HS1358, HS1358mCTCF, HS1358R, HS1248, and HS1248R replacements. (C) Abd-B expression in Fab-7 replacement embryos. Each panel shows a confocal image of the embryonic CNS of stage 15 embryos stained with antibodies against Abd-B (cyan). The filled red arrowheads show morphological features indicative of gain-of-function (GOF) transformations. The empty red arrowheads show the signs of the loss-of-function (LOF) transformation, which is directly correlated with the boundary function of tested DNA fragments. The WT expression pattern of Abd-B in the embryonic CNS is characterized by a stepwise gradient of increasing protein level from PS10/A5 to PS14/A8. In F7attP50 embryos, Abd-B expression level in PS11/A6 is roughly equal to that in PS12/A7, indicating that iab-7 drives Abd-B expression in PS11/A6 (GOF phenotype). Consistent with the adult phenotype, in F11168 and HS1248-HS2505 Abd-B expression in PS11/A6 is the same as in F7attP50. The Abd-B expression pattern in HS1358 and HS1248 replacement is also consistent with the adult cuticular phenotypes: Abd-B expression is reduced in both PS10/A5 and PS11/A6 (LOF phenotype) compared with WT. In contrast, mutation of dCTCF site in HS1358mCTCF results in the loss of blocking activity and Abd-B expression pattern similar to F7attP50.
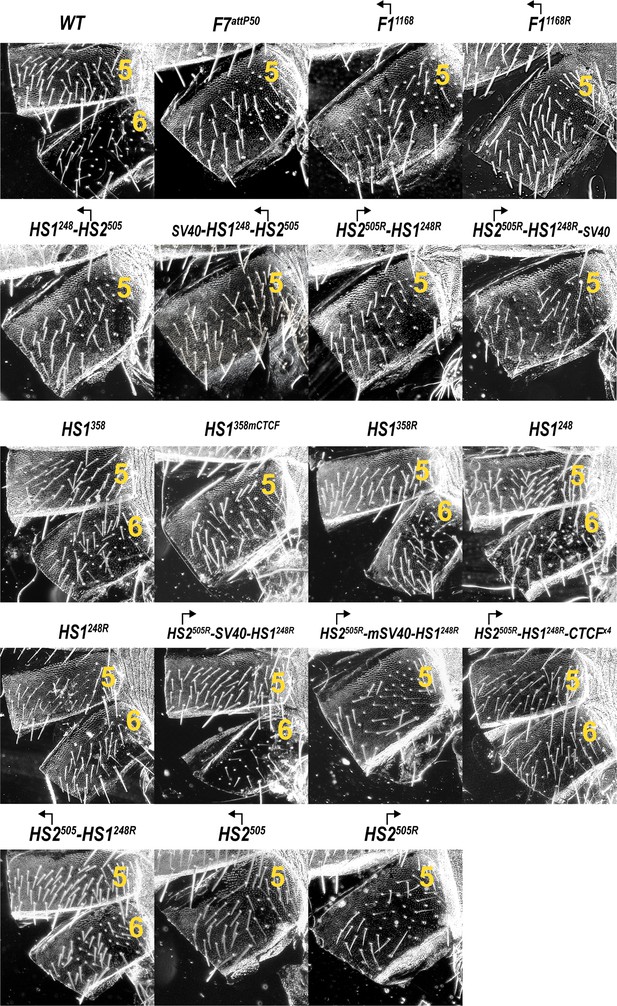
Morphology of the abdominal segments (numbered) in males carrying different variants of Fub-1 in Fab-7attP50 platform in the dark field.

Morphology of the abdominal segments (numbered) in males carrying HS2505 and HS2505R fragments in Fab-7attP50.
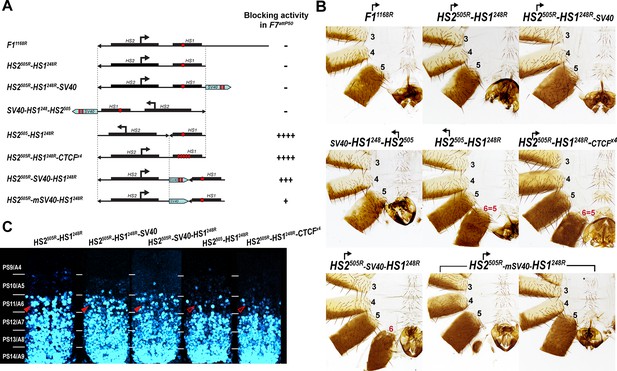
Read-through transcription inactivates HS1 insulator.
(A) Schematic representation of sequences tested in F7attP50. SV40 terminator is shown as a light blue arrow, and poly(A) sites are marked as vertical red lines. All other designations are the same as described in Figure 4. (B) Morphology of the male abdominal segments (numbered) of Fab-7 replacements. (C) Abd-B expression in CNS of Fab-7 replacement embryos. Embryos were stained and marked as in Figure 4.
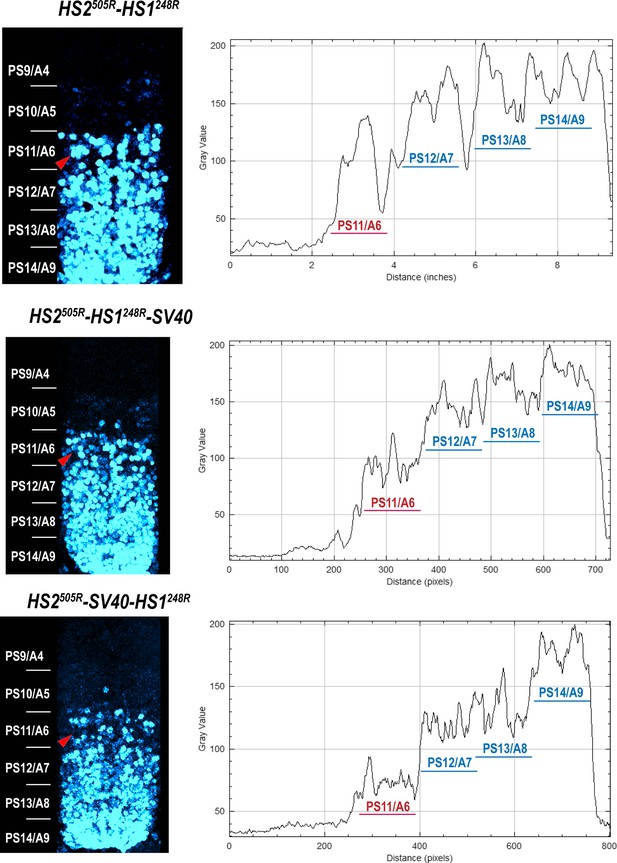
Abd-B expression in Fab-7 replacement embryos.
The panels on the left show confocal images of embryonic CNS of HS2505R-HS1248R, HS2505R-HS1248R-SV40, and HS2505R-SV40-HS1248R embryos. The panels on the right show plot profiles of relative fluorescence intensity in the respective images from the right panels. Note that the intensity of the Abd-B signal is lower in PS11/A6 in HS2505R-SV40-HS1248R compared to both HS2505R-HS1248R and HS2505R-HS1248R-SV40.
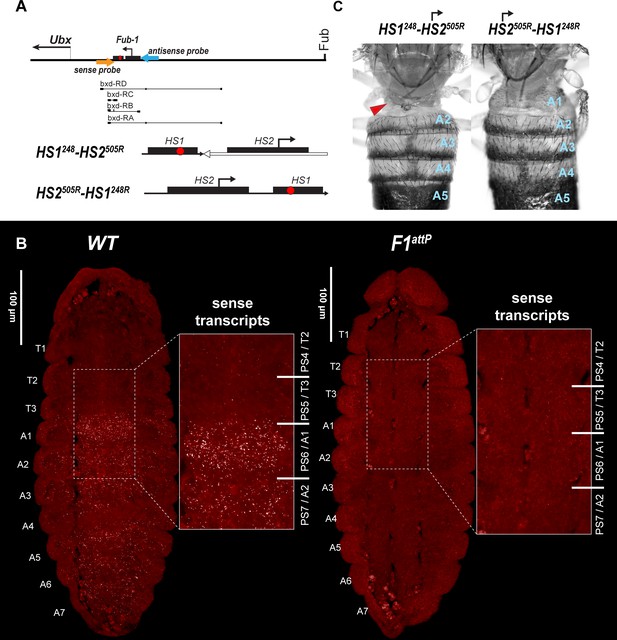
HS2 drives transcription in tissue-specific manner.
(A) Schematic presentation of bxd domain with HS1248-HS2505R and HS2505R-HS1248R replacements. The smFISH strand-specific probes are shown as orange and light blue arrows (Supplementary file 1b and c). All other designations are the same as described in Figure 1. Characterized bxd lncRNA transcripts are presented under coordinate line. (B) smFISH of stage 14 embryos of the indicated genotype with a probe that targets sense strand just proximal to Fub-1. In WT embryos Fub-1HS2 sense (distal to proximal) transcripts were detected from PS6/A1 through PS12/A7. By contrast, in Fub-1 deletion (F1attP) Fub-1HS2 transcripts were not detectable. (C) Morphology of the abdominal segments of HS1248-HS2505R and HS2505R-HS1248R flies. The red arrow shows the signs of the loss-of-function (LOF) phenotype: complete reduction of A1 segment and the appearance of postnatal tissue in its place.
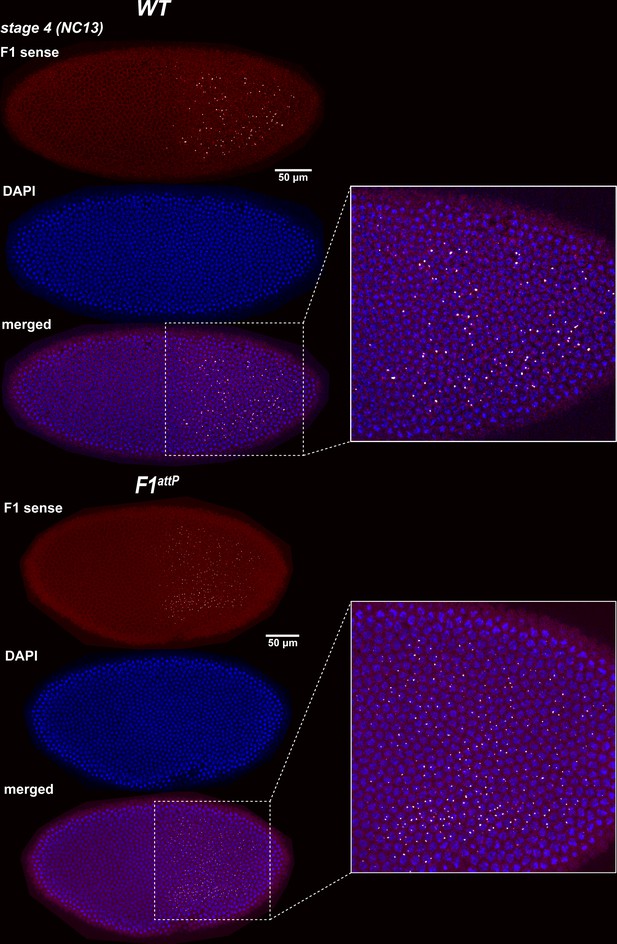
Expression of bxd and F1HS2 lncRNAs in NC13 WT and F1attP embryos.
Stage 4 (nuclear cycle 13) WT and F1attP embryos were hybridized with smFISH probes complementary to ‘sense’ strand sequences proximal to (downstream of) Fub-1. DAPI was used to stain nuclei (in blue). In WT, the smFISH probe is expected to detect both Fub-1HS2 and bxd lncRNAs. In F1attP embryos the Fub-1HS2 promoter is deleted. Hence, only bxd lncRNAs should be detected. Note that the intensity of the smFISH signal is higher in WT compared to F1attP. This finding indicates that both lncRNAs are expressed at this stage.

Expression of bxd and F1HS2 lncRNAs in stage 7/8 WT and F1attP embryos.
Stage 7/8 WT and F1attP embryos were hybridized to smFISH probes complementary to ‘sense’ strand sequences just proximal to (downstream of) Fub-1. DAPI was used to stain nuclei (in blue). During gastrulation, the broad band seen at stage 4 resolves into a series of stripes of equal width and intensity. Note that the intensity of the smFISH signal is noticeably higher in WT than in F1attP at this stage.
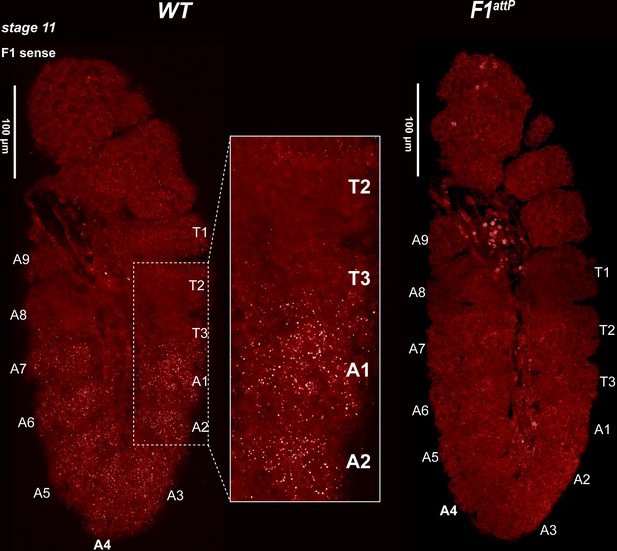
Expression of bxd and F1HS2 lncRNAs in stage 11 WT and F1attPembryos.
Stage 11 WT and F1attP embryos were hybridized with smFISH probes complementary to ‘sense’ strand sequences just proximal to (downstream of) Fub-1. At this stage, segmental grooves appear. In WT, the pattern resembles that of the Ubx RNA, except that there is no staining in PS5/T3. In F1attP, lncRNAs complementary to the smFISH probes are no longer detectable. This would suggest that the only lncRNAs expressed at this stage of development in WT correspond to F1HS2.

Halters morphology in WT and HS1248-HS2505R flies.
Images show a lateral view of female flies with their wings removed to visualize the halters. The segments in the dorsal cuticle are designated as follows: Al, A2, and A3. In HS1248-HS2505R flies, A1 segment is partially reduced in size and the residual cuticle is presumed to correspond to scar tissue that fills the space normally occupied by the A1 abdominal tergite.

Homeotic transformation of larval segments in HS1248-HS2505R.
(A) Ventral cuticle of WT and HS1248-HS2505R third-instar larva. WT larvae have 11 denticle belts marking the anterior half of each thoracic and abdominal segments. These are visible as black dots. In contrast, the smooth cuticle in the posterior part of each segment appears white. In WT, the T3 segment has 2–3 rows of small denticles, whereas in A1 there are 3 anterior rows of large denticles and 2 posterior rows of smaller denticles. The HS1248-HS2505R larvae exhibit a loss-of-function (LOF) transformation of the A1 segment toward T3. In HS1248-HS2505R, the number of denticle rows in A1 stays the same as in WT, but the band of denticles is narrower and denticles are much smaller than its wild-type equivalent. (B) Zoomed-in view of the T3, A1, and A2 denticle belts in WT and HS1248-HS2505R larvae.
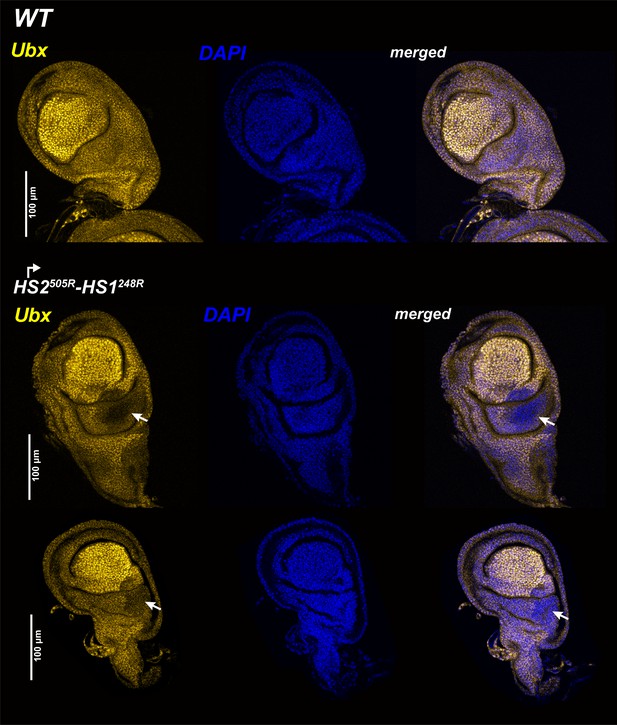
Ubx expression in halter discs.
WT and mutant halters discs were probed with Ubx antibodies. All tissues are from third-third instar larvae, anterior is to the left. Ubx staining is the greatest in the central pouch. In HS1248-HS2505R, staining is reduced but not eliminated in the posterior compartment of the haltere disc (arrow).
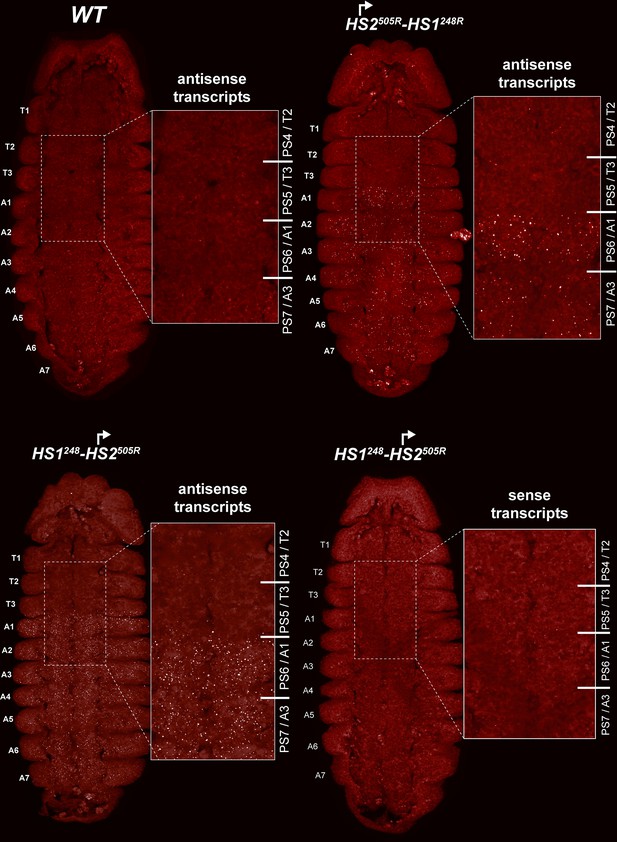
HS2 drives transcription in a tissue-specific manner.
smFISH of stage 14 embryos of indicated genotype with a probe that targets antisense strand just distal to Fub-1. In WT embryos, no antisense (proximal to distal) transcripts were detected. By contrast, in HS1248-HS2505R and HS2505R-HS1248R antisense transcripts are detected from PS6/A1 through PS12/A7. Note that the intensity of smFISH signal is higher in HS1248-HS2505R than in HS2505R-HS1248R. In HS1248-HS2505R embryos, Fub-1HS2 sense (distal to proximal) transcripts were not detected, indicating that HS2 drives transcription only in one direction.
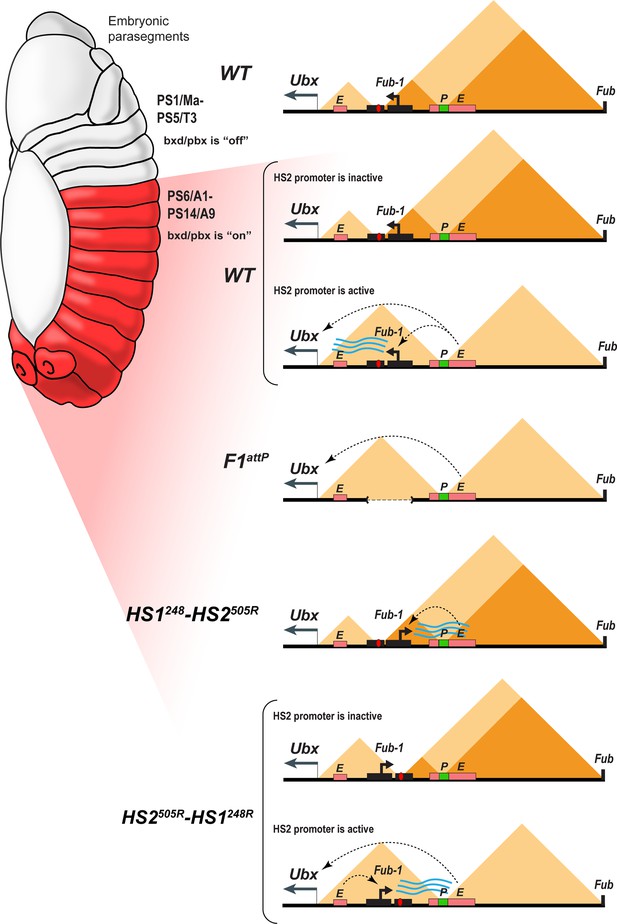
Model showing changes in TAD organization during Fub-1HS2 transcription.
Top: In WT, the 3D organization of the bxd/pbx regulatory domain transitions from one state to another when it activates Ubx expression (see also Mateo et al., 2019). In PS5 (T3) and more anterior parasegments, the bxd/pbx domain is encompassed in a large TAD that extends from Fub-1 to Fub (large triangle). Within this large TAD, there are two HDIC domains. One extends from Fub-1 to the bxd PRE, while the other extends from the bxd PRE to Fub. In PS6 and more posterior parasegments, the 3D organization of the domain is dynamic and depends upon whether the Fub-1 HS2 promoter is active or not. When the promoter is inactive (in between bursts), the Fub-1 boundary is expected to be functional and that TAD/HDIC organization would resemble that in more anterior parasegments. When the enhancers in bxd/pbx activate HS2, transcriptional read-through disrupts Fub-1 boundary activity generating a new TAD organization that links enhancers in bxd/pbx to the Ubx promoter. F1attP: deletion of the Fub-1 boundary eliminates the large Fub-1←→Fub TAD in all parasegments. In this case, an element upstream of the Ubx promoter functions to insulate abx/bx from bxd/pbx in PS5/T3. HS1248-HS2540R: In this replacement, HS2 is inverted so that the HS2 promoter is pointed away from HS1 toward the bxd/pbx regulatory domain. Though bxd/pbx activates the promoter in PS6/A1 and more posterior parasegments, Fub-1 boundary activity is not disrupted. HS2540R-HS1248R: In this replacement, Fub-1 is inverted. Though HS2 promoter activity in PS6 (A1) and more posterior parasegments is reduced in this configuration compared to WT, it is sufficient to disrupt Fub-1 boundary activity and enable bxd/pbx to regulate Ubx expression.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Cas9 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 55821 | y[1] M{GFP[E.3xP3]=vas-Cas9.RFP-}ZH-2A w[1118] |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | ΦC31 | This lab | N/A | w[1], ΦC31 (y+); TM6, Tb, Hm/Sb |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | This lab | N/A | w[1]; TM6, Tb, Hm/Sb | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Fub-1attP | This paper | N/A | Available from Paul Schedl laboratory in Princeton university. Contact pschedl@princeton.edu |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Fab-7attP50 | This lab | N/A | Available from Paul Schedl laboratory in Princeton university. Contact pschedl@princeton.edu |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | FLP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 8727 | P{w[+mC]=ovoFLP.R}M1A, w[*] |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Cre | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 851 | y[1] w[67c23] P{y[+mDint2]=Crey}1b; D[*]/TM3, Sb[1] |
| Antibody | Anti- Abd-B (mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | 1A2E9 | IF(1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-Ubx (mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma | FP3.38 | IF(1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-DsRed antibody (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-390909 | IF(1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP antibody (rabbit polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11122 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 546 (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11030 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11008 | IF(1:500) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Paraformaldehyde 20% solution, EM Grade | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 15713S | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Formaldehyde, 16%, methanol free, Ultra Pure | Polysciences Inc | 18814-10 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phosphate-buffered saline (10×) pH 7.4, RNase-free | Thermo Fisher | AM9624 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tween 20 | Sigma | P1379 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Triton X-100 | Bio-Rad | 161-0407 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris base | Sigma | 11814273001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Methanol | Fisher Chemical | 203403 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SSC, 20× | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15557044 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Formamide | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 17899 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dextran sulfate | Sigma | D8906 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Salmon Sperm DNA | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AM9680 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ribonucleoside Vanadyl Complex | NEB | S1402S | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nuclease-free BSA | Sigma | 126609 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Triethylammonium acetate | Sigma | 625718 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | dGTP (100 MM) | VWR | 76510-208 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | dTTP (100 MM) | VWR | 76510-224 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lonza NuSieve 3:1 Agarose | Thermo Fisher Scientific | BMA50090 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | T4 DNA ligase | NEB | M0202L | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Biotin-11-dCTP | Jen Bioscience | NU-809-BIOX | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Biotin-14-dATP | Jen Bioscience | NU-835-BIO14 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit | Life Technologies Corporation | Q32851 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phase Lock Gel, QuantaBio - 2302830, Phase Lock Gel Heavy | VMR | 10847-802 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NEBNext Ultra II DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina | NEB | E7645S | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ampure Xp 5 ml Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | NC9959336 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hifi Hotstart Ready Mix | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 501965217 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dynabeads MyOne Streptavidin C1 | Life Technologies Corporation | 65001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | cOmplete, EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail | Sigma | 11873580001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | N,N-Dimethylformamide | Sigma | 227056 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Potassium acetate solution | Sigma | 95843 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DSG (disuccinimidyl glutarate) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | PI20593 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | T4 Polynucleotide Kinase – 500 units | NEB | M0201S | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DNA Polymerase I, Large (Klenow) Fragment – 1000 units | NEB | M0210L | |
| Chemical compound, drug | End-it DNA End Repair Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | NC0105678 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Proteinase K recomb. 100 mg | Sigma | 3115879001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nuclease Micrococcal (s7) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | NC9391488 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | EGS (ethylene glycol bis(succinimidyl succinate)) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | PI21565 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fub-1 sense probe set | Biosearch Technologies | N/A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fub-1 antisense probe set | Biosearch Technologies | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji (ImageJ) | Schindelin et al., 2012 | fiji.sc | |
| Software, algorithm | NIS element | Nikon | https://www.microscope.healthcare.nikon.com/products/software/nis-elements/ | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 8 | GraphPad Software | https://www.graphpad.com | |
| Software, algorithm | HiGlass | Kerpedjiev et al., 2018 | http://higlass.io/ | |
| Software, algorithm | bwa | Li and Durbin, 2009 | https://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/ | |
| Software, algorithm | samtools | Github/open source | https://samtools.github.io | |
| Software, algorithm | pairsamtools | Github/open source; Goloborodko et al., 2023 | https://github.com/open2c/pairtools | |
| Software, algorithm | pairix | Github/open source; Lee et al., 2021 | https://github.com/4dn-dcic/pairix | |
| Software, algorithm | cooler | Abdennur et al., 2023 | https://github.com/open2c/cooler | |
| Software, algorithm | Miniconda | Anaconda | https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html | |
| Software, algorithm | Snakemake | Github/open source | https://snakemake.github.io |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Sequences of DNA fragments used.
(a) The sequence of chimeric DNA fragments used for Fab-7 replacement experiments. (b) Sequences of Fub-1 sense smFISH probes covering 1983 bp region in bxd domain. (c) Sequences of Fub-1 antisense smFISH probes covering 1463 bp region in bxd domain.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84711/elife-84711-supp1-v2.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84711/elife-84711-mdarchecklist1-v2.pdf





