Bacterial autolysins trim cell surface peptidoglycan to prevent detection by the Drosophila innate immune system
Figures
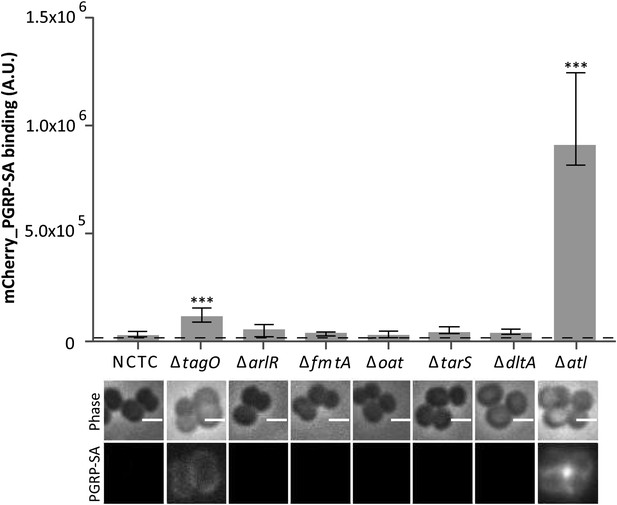
Staphylococcus aureus cells lacking the major autolysin Atl are better recognized by mCherry_PGRP-SA.
Exponentially growing bacteria from the parental NCTC8325-4 (NCTC), and its mutant strains lacking genes involved in cell wall metabolism (see main text for details) were incubated with mCherry_PGRP-SA in 96-well plates. Cells were pelleted by centrifugation and unbound protein was washed with PBS. mCherry_PGRP-SA bound to each bacterial strain was quantified using a fluorescent image analyzer (n≥ 10 wells for each strain). Results are shown as the median with 25% and 75% inter-quartile range. The dashed line represents the median value obtained when bacteria were absent. Statistically significant differences (p<0.001, indicated by asterisks) were observed only between mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to the parental strain and mutants NCTCΔtagO and NCTCΔatl. mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to bacterial cells was also imaged by fluorescence microscopy. The top panels show phase-contrast images of bacteria (white scale bar represents 1 µm) and the bottom panels show the mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to their surface. Binding of the protein was observed for NCTCΔtagO and NCTCΔatl, with the later exhibiting the highest binding.
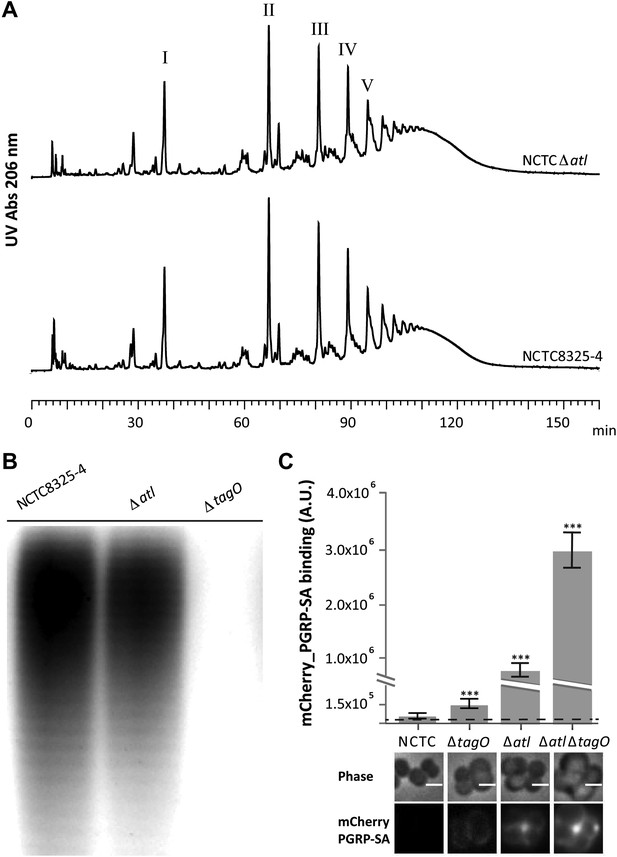
Better recognition of Staphylococcus aureus NCTCΔatl by PGRP-SA is not mediated by alterations in peptidoglycan muropeptide composition or lack of wall teichoic acids production.
(A) Staphylococcus aureus NCTCΔatl mutant has a similar peptidoglycan (PGN) muropeptide composition to the parental strain NCTC8325-4, as seen by HPLC analysis of mutanolysin-digested PGN. Roman numerals I to V indicate muropeptide species form monomers to pentamers, respectively. (B) NCTCΔatl mutant produces wall teichoic acids (WTAs), as shown by PAGE analysis of surface WTAs from NCTC8325-4, NCTCΔatl, and NCTCΔtagO (which lacks WTAs). (C) Deletion of both the tagO and atl genes had a synergistic effect on PGN exposure to the host receptor PGRP-SA, indicating independent mechanisms of WTA and Atl in PGN concealment. S. aureus parental strain NCTC8325-4 and mutant strains NCTCΔtagO, NCTCΔatl, and NCTCΔatlΔtagO were incubated with mCherry_PGRP-SA in 96-well plates. The average amount of mCherry_PGRP-SA bound to bacteria in each well was quantified using a fluorescent image analyzer (n = 10 wells, for each strain), and is represented as the median with 25% and 75% inter-quartile range. The dashed line represents the median value obtained with control samples (no bacteria added). Statistically significant differences (p<0.001) are indicated by asterisks and were observed between mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to the parental strain and each mutant as well as between mutants. mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to the cells was also confirmed by fluorescence microscopy (bottom). Gray panels show phase-contrast images of bacterial cells (white scale bar represents 1 μm) and black panels show mCherry_PGRP-SA binding.
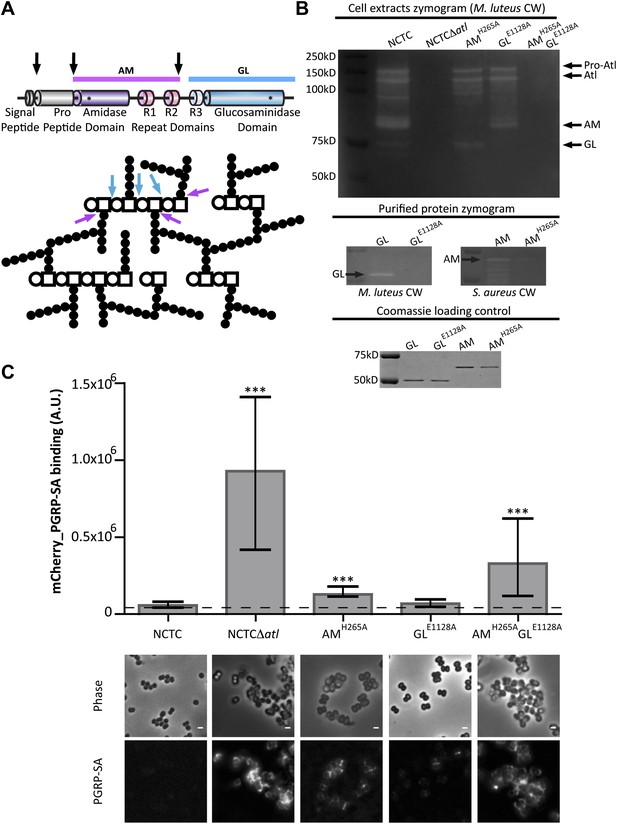
Amidase and glucosaminidase activities limit mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to the bacterial cell surface.
(A) Representation of the post-translational cleavage (black arrows) of the atl encoded protein. The processed amidase (AM, purple arrow) releases peptidoglycan (PGN) stem peptides by cutting the bond between the stem peptides (black circles) and the N-acetylmuramic acid residue (open square). The glucosaminidase (GL, blue arrow) releases muropeptides by cutting the glycosidic linkage between N-acetylmuramic acid (open square) and N-acetylglucosamine (open circle). For simplicity, only some examples of AM and GL cleavage sites are indicated by arrows. (B) Zymogram analysis of the activity of autolysins extracted from different Staphylococcus aureus atl mutant strains expressing inactive amidase (AMH265A), inactive glucosaminidase (GLE1128A), or both (AMH265A GLE1128A). Top: Cells were harvested at mid-exponential phase, and protein extracts were prepared and run in an SDS–PAGE gel containing Micrococcus luteus cell walls. PGN hydrolytic activity is seen as clear bands in the stained gel and showed that S. aureus encoding mutant proteins AM or GM were lacking only the expected activity. Middle: A similar analysis was carried out with purified proteins AM, GL, and their inactive forms, AMH265A and GLE1128A, respectively, showing that mutant proteins were not active. Bottom: SDS–PAGE of the protein samples loaded into the zymograms confirmed that similar amount of proteins were used. (C) S. aureus parental and atl mutant strains were incubated for mCherry_PGRP-SA in 96-well plates. mCherry_PGRP-SA bound to each bacterial strain is represented as the median with 25% and 75% inter-quartile range (n = 50 wells). A significant increase of mCherry_PGRP-SA binding, relative to the parental strain, was observed with S. aureus mutants expressing AMH265A and AMH265A GLE1128A (p<0.0001), but not the GLE1128A mutant. mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to S. aureus parental and atl mutant strains was also confirmed by fluorescence microscopy. Gray panels are phase-contrast images of bacterial cells (white scale bar represents 1 μm) and black panels show mCherry_PGRP-SA binding.
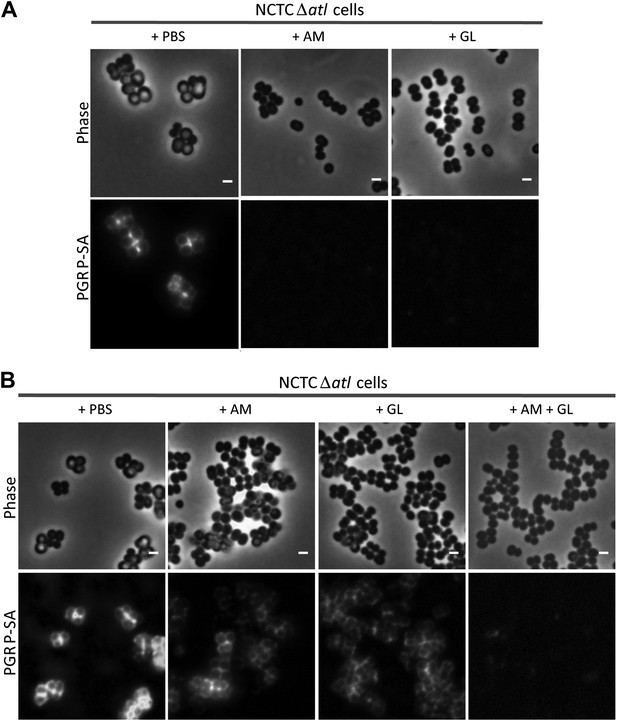
Combination of purified staphylococcal AM and GL completely abolishes binding of mCherry_PGRP-SA to the surface Staphylococcus aureus atl null mutant cells.
(A) mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to NCTCΔatl bacteria pre-incubated with purified AM and GL (0.37 µM and 0.44 µM, respectively) showed that both enzymes can impair binding of mCherry_PGRP-SA to the cell surface. PBS was used as negative control. (B) The use of lower concentrations of purified AM and GL in combination, to treat NCTCΔatl Staphylococcus aureus cells (final concentrations of 7.9 nM and 18.7 nM, respectively) was more effective than the single use of AM (final concentration of 7.9 nM) or GL (final concentration of 18.7 nM) in preventing binding of mCherry-PGRP-SA to the surface of NCTCΔatl. Gray panels are phase-contrast images of bacterial cells (white scale bar represents 1 μm) and black panels show mCherry_PGRP-SA binding.
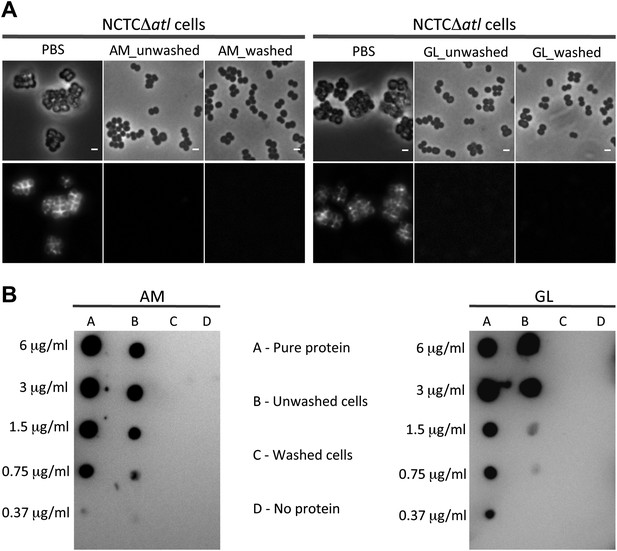
Activity, and not the presence of the Atl products, is required to avoid bacterial surface recognition by mCherry_PGRP-SA.
(A) NCTCΔatl cells were incubated with purified staphylococcal AM, GL, or PBS (negative control) and were either washed to clear these proteins from the cell surface, or unwashed to keep the proteins attached. Bacterial cells were then labeled with mCherry_PGRP-SA and imaged by fluorescence microscopy. In both cases (washed and unwashed), mCherry_PGRP-SA was unable to bind S. aureus NCTCΔatl cells, showing that the physical presence of the enzyme is not required for this effect. Gray panels are phase-contrast images of bacterial cells (white scale bar corresponds to 1 µm) and black panels are fluorescence microscopy images showing binding of mCherry_PGRP-SA to the surface of bacteria. (B) To confirm that AM (left) and GL (right) were absent from the washed samples, a dot-blot assay using anti-His antibody, which recognizes the His-tagged AM and GL enzymes, was performed before the addition of mCherry_PGRP-SA. Washed cells (lanes C) showed no presence of protein, whereas in unwashed cells (lanes B) the presence of each individual lytic enzyme was detected (detection limit for AM and GL is lower than 0.37 µg/ml, as seen in lanes A, which corresponds to the pure protein loaded onto the membrane at different concentrations). A sample of cells to which no protein was added was used as a negative control (lanes D).
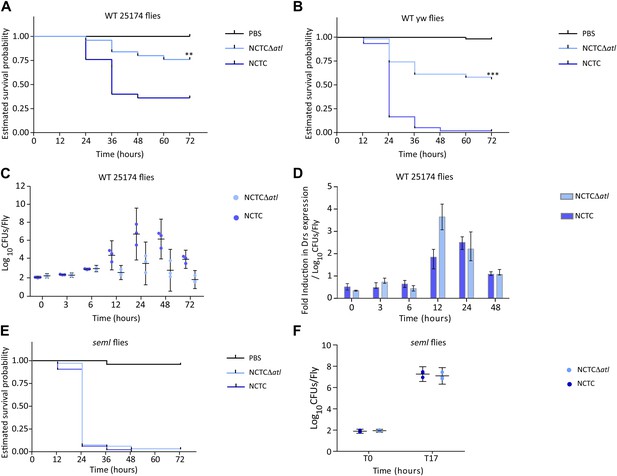
PGRP-SA is required to control infection by a Staphylococcus aureus mutant lacking the major autolysin Atl.
(A) Estimated survival curves of wild type (WT) 25174 flies infected with Atl producer NCTC8325-4 and NCTCΔatl strains were statistically different (p<0.005) and are indicated by asterisks. Absence of Atl activity in the S. aureus Δatl mutant resulted in bacteria that have a decreased ability to kill WT flies. Survival of infected flies (n = 75) was monitored at 12 h intervals for 3 days. (B) Estimated survival curves of WT yw flies, the parental lineage used to construct the peptidoglycan recognition protein (PGRP) seml mutant used in this study, were also produced as described above and gave similar results (p<0.0001, indicated by asterisks). (C) The number of bacteria harvested from infected flies at different time points after infection, during survival assays, was determined by plating in S. aureus growth medium and counting CFUs. (D) Drosomycin (Drs) expression was determined by qPCR at different time points after infection and is shown after normalization for the number of infecting bacteria present in flies (panel C). A stronger induction of drosomycin expression was observed in flies injected with NCTCΔatl bacteria, 12 h after infection. (E) PGRP-SA mutant flies succumbed equally well to infection by NCTC832-4 and NCTCΔatl bacteria (p>0.05), showing that in the absence of a functional PGRP-SA, NCTCΔatl bacteria can proliferate and kill the infected host. (F) Similar numbers of NCTC832-4 and NCTCΔatl bacteria were present in PGRP-SA mutant flies 17 h after infection (T17), confirming that the atl mutant proliferated as well as the parental bacterial strain in seml flies.
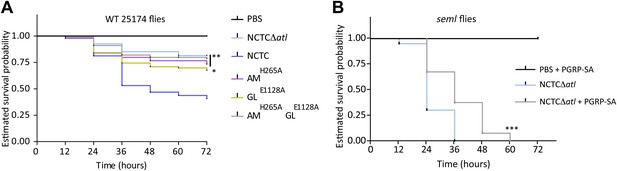
Lack of either Atl amidase or glucosaminidase activity, which leads to different types of released peptidoglycan fragments, results in decreased virulence of Staphylococcus aureus.
(A) Estimated survival curves of wild type (WT) 25174 flies infected with atl mutant strains impaired in amidase activity (AMH265A), glucosaminidase activity (GLE1128A), or both (AMH265AGLE1128A), were statistically different (p<0.05) from survival curves of flies infected with the Atl producer NCTC8325-4 strain, but not with the NCTCΔatl strain. Statistically significant differences (*p=0.01 and **p<0.001) are indicated by asterisks and were observed between the estimated survival curve of flies infected with the parental bacteria strain NCTC8325-4 and each survival curve of flies infected with the different atl mutant strains. WT 25174 flies infected with the different atl mutant strains succumbed in a similar manner (p>0.05). (B) Estimated survival curve of PGRP-SA seml mutant flies infected with NCTCΔatl bacteria pre-coated with mCherry-PGRP-SA showed that direct binding of the peptidoglycan (PGN) host receptor to the surface resulted in an increase of resistance of seml mutant flies to bacterial infection. Statistically significant differences (p<0.0001) are indicated by asterisks and were observed between the two estimated survival curves.
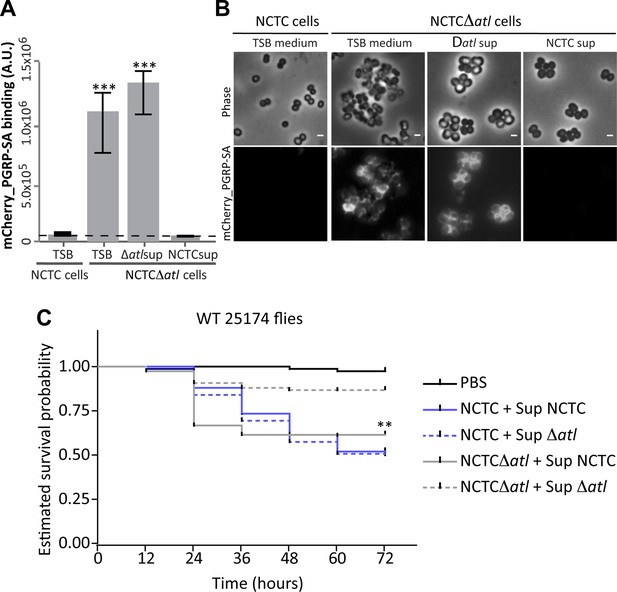
Atl products secreted by Staphylococcus aureus cells protect atl null mutant cells from PGRP-SA recognition and allow S. aureus to establish a successful infection in Drosophila.
(A) NCTCΔatl Staphylococcus aureus cells were incubated with TSB medium (control) or with supernatants (sterilized by filtration) from cultures of NCTC8325-4 (NCTCsup, containing atl encoded products) or NCTCΔatl (Δatlsup) strains. After washing with PBS, cells were mixed with mCherry_PGRP-SA in 96-well plates. Binding of the protein to the cells was determined as described in Figure 1. mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to NCTCΔatl cells pre-incubated with supernatant from Atl producer strain NCTC8325-4 was 100-fold lower than to the same cells pre-incubated with supernatant from a culture of NCTCΔatl mutant. The dashed line represents the median value obtained with no bacteria. Statistically significant differences (p<0.001) are indicated by asterisks. (B) Similar results were observed by fluorescence microscopy of NCTCΔatl S. aureus cells incubated with filtered supernatants from NCTC8325-4 or NCTCΔatl cells (TSB medium was used as negative control) and subsequently labeled with mCherry_PGRP-SA. Only the supernatant from Atl producer NCTC8325-4 modified the surface of NCTCΔatl cells and limited mCherry_PGRP-SA binding. The top panels are phase-contrast images of bacterial cells (white scale bar represents 1 µm) and the bottom panels show the mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to the bacterial surface. (C) Estimated survival curves for wild type Drosophila infected with S. aureus NCTC8325-4 and NCTCΔatl strains that were pre-incubated with bacteria-free supernatant from overnight cultures of each of the S. aureus strains. Flies were infected with approximately 100 S. aureus CFUs and fly survival was assessed every 12 h over 3 days. As expected, survival curves for flies infected with NCTC8325-4 bacteria pre-incubated with both supernatants were statistically indistinguishable (p>0.05). Treatment of NCTCΔatl cells with both supernatants resulted in distinct survival curves (p<0.001, indicated by asterisks), showing that NCTCΔatl cells recover the ability to kill flies if pre-incubated with supernatant from a culture of the Atl producer NCTC8325-4 strain.
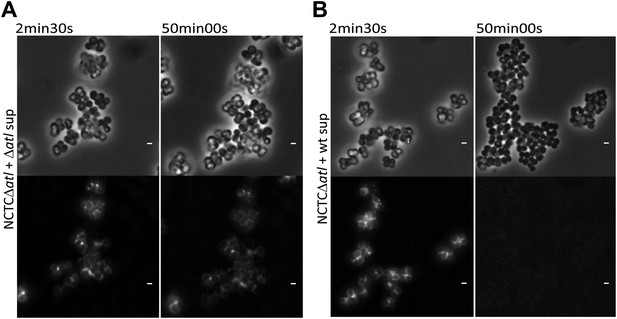
Time-lapse microscopy showing that atl encoded proteins can mediate release of mCherry_PGRP-SA previously bound to the surface of atl null mutant Staphylococcus aureus cells.
NCTCΔatl cells, labeled with mCherry-PGRP-SA, were placed on top of a thin layer of agarose containing filter-sterilized supernatant of cultures of NCTCΔatl mutant (A, Video 1) or NCTC8325-4 parental strain (B, Video 2), and observed by fluorescence microscopy in a time-lapse experiment. The supernatant from the Atl producer parental strain (B), in contrast to the supernatant from the atl null mutant (A), triggered the release of mCherry-PGRP-SA previously attached to the bacterial cell surface. Gray panels are phase-contrast images of bacterial cells (white scale bar corresponds to 1 µm) and black panels are fluorescence microscopy images showing binding of mCherry_PGRP-SA to the surface of bacteria.
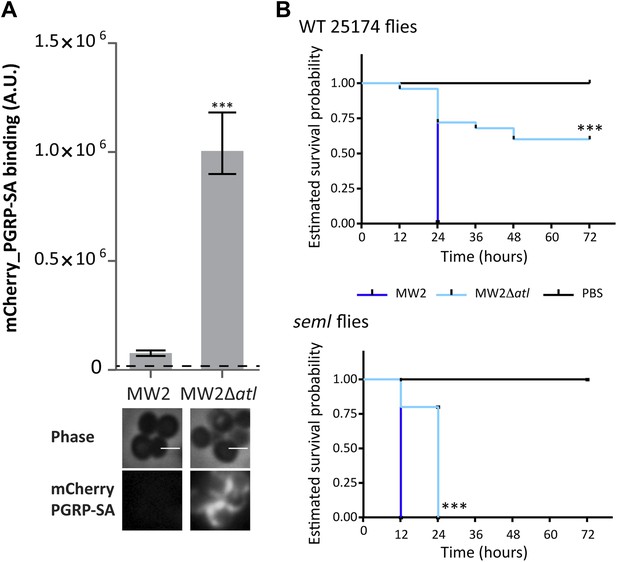
Atl encoded proteins are required to conceal CA-MRSA virulent strains from the Drosophila immune system.
(A) Staphylococcus aureus CA-MRSA MW2 strain and its atl null mutant, MW2Δatl, were incubated with mCherry_PGRP-SA in 96-well plates. The average amount of mCherry_PGRP-SA bound to bacteria in each well was quantified using a fluorescent image analyzer (n = 10 wells, for each strain), and is represented as the median with 25% and 75% inter-quartile range. The dashed line represents the median value obtained with control sample (no bacteria added). mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to MW2 cells was significantly different (p<0.05, indicated by asterisks) from the binding to MW2Δatl. mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to the bacterial cell surface of MW2 and MW2Δatl bacteria was also confirmed by fluorescence microscopy (bottom). Gray panels are phase-contrast images of bacterial cells (white scale bar corresponds to 1 μm) and black panels show mCherry_PGRP-SA binding. (B) Estimated survival curves for wild type (WT) and PGRP-SA deficient (seml) flies infected with S. aureus MW2 and MW2Δatl. MW2Δatl is impaired in its ability to kill WT flies, showing that lack of Atl strongly reduces MW2 pathogenicity. PGRP-SA deficient flies are killed in less than 24 h by both S. aureus strains, showing that flies control MW2Δatl infection in a PGRP-SA dependent manner. Statistically significant differences (p<0.0001) are indicated by asterisks and were observed between the two estimated survival curves.
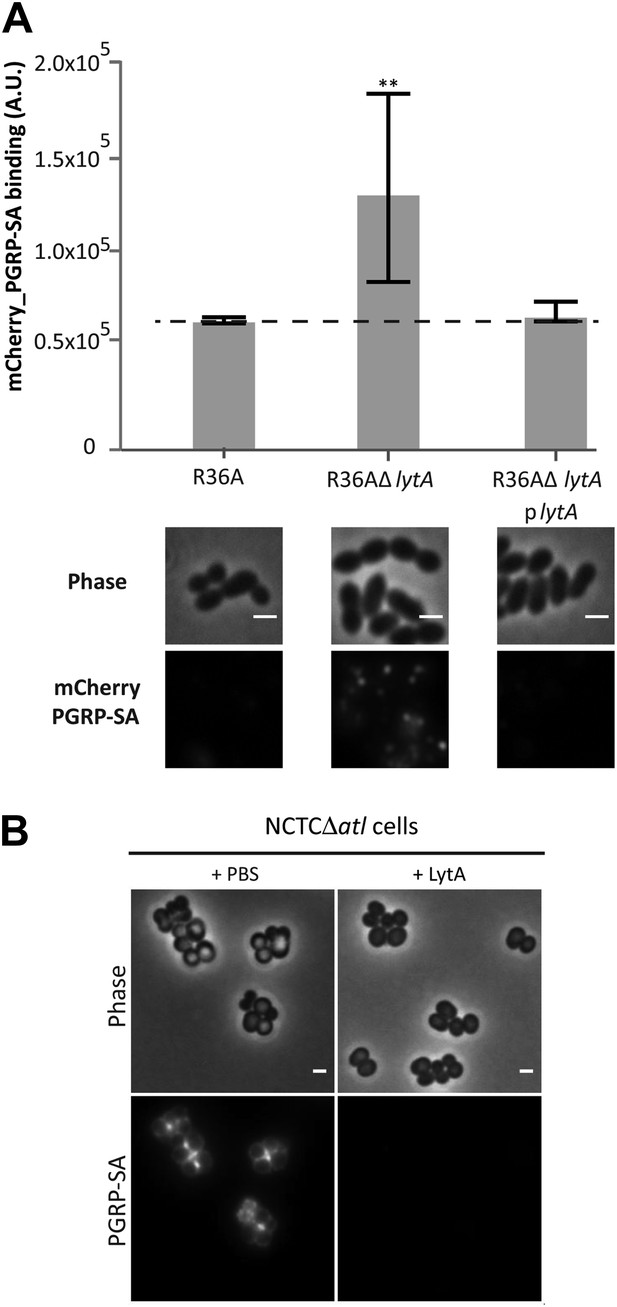
LytA activity can prevent Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus recognition by mCherry_PGRP-SA.
(A) Streptococcus pneumoniae parental strain R36A, a lytA null mutant (R36AΔlytA), and a complemented strain, expressing LytA from a replicative plasmid (R36AΔlytAplytA), were incubated with mCherry_PGRP-SA in 96-well plates. The average amount of mCherry_PGRP-SA bound to bacteria in each well was quantified using a fluorescent image analyzer (n = 10 wells, for each strain), and is represented as the median with 25% and 75% inter-quartile range. The dashed line represents the median value obtained with control sample (no bacteria added). mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to R36AΔlytA was significantly higher (p<0.05, indicated by asterisks) than that observed for the parental strain or R36AΔlytAplytA strain, showing that deletion of the lytA gene in S. pneumoniae increases surface recognition by mCherry_PGRP-SA. Binding of mCherry_PGRP-SA to S. pneumoniae cells was also imaged using fluorescence microscopy (bottom). Gray panels are phase-contrast images of bacterial cells (white scale bar represents 1 µm) and black panels show the mCherry_PGRP-SA binding to bacteria. (B) S. aureus NCTCΔatl cells were incubated with purified pneumococcal amidase (LytA) or with the commercially available mutanolysin, a muramidase from Streptomyces globisporus capable of degrading peptidoglycan into its muropeptide components. Bacterial cells were washed to clear these proteins from the cell surface, labeled with mCherry_PGRP-SA, and imaged by fluorescence microscopy, which showed that both pneumococcal LytA amidase and mutanolysin can prevent detection of NCTCΔatl S. aureus cells by mCherry_PGRP-SA.
Videos
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Strains and plasmids used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02277.016
-
Supplementary file 2
Primers used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02277.017





