Potential harmful effects of discontinuing ACE-inhibitors and ARBs in COVID-19 patients
Figures
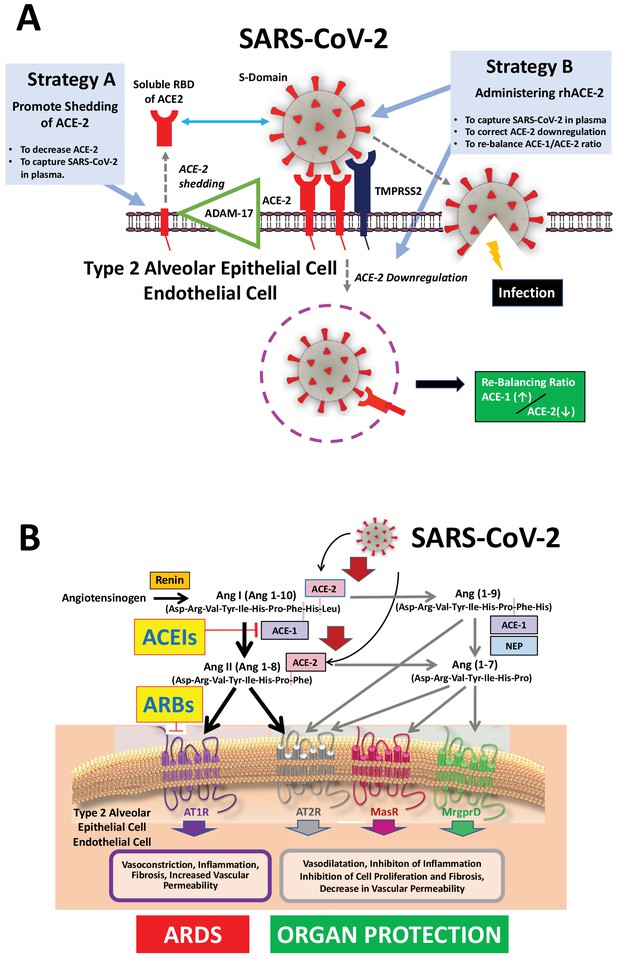
Mechanisms of COVID-19 by which the SARS-COV-2 virus infects the lower airway cells and modalities to increase circulating soluble ACE-2 for therapeutic use.
(A) By binding to endothelial and type 2 alveolar epithelial cells that express ACE-2 at high levels, the virus activates proteases, such as TMPRSS2. This allows fusion with the virus’ envelope to the cell membrane facilitating the virus to enter and infect the cell. Of note, type 2 alveolar epithelial cells are well equipped with a molecular machinery that allows rapid replication of the viruses thus enhancing pulmonary spreading of the infection. Once infected by SARS-COV-2 the lung cells downregulates expression of ACE-2. Therefore, the lungs remain exposed to, and are unprotected from, the detrimental actions of angiotensin II acting via the AT1R. Increasing circulating soluble ACE-2 levels represents a potential new therapeutic principle to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection. This can be achieved using different strategies: either by increasing ADAM-17-dependent shedding of ACE-2 facilitating its removal from tissue (Strategy A) or by intravenous administration of recombinant soluble ACE-2 to capture and thereby inactivate SARS-CoV-2 in plasma and preventing it from entering the cell (Strategy B). (B). The renin-angiotensin system in the pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2-associated ARDS. Ang II - via the AT1R - promotes inflammation, vasoconstriction, cell proliferation, and vascular leakage and eventually, pulmonary fibrosis. These effects are counteracted by ACE-2 dependent formation of Ang(1-7) activating the AT2R, MasR, and MrgD and formation of Ang(1-9) activating the AT2R. The potential beneficial effects of ACEIs and ARBs entail rescuing the downregulated ACE-1–Ang II–AT2R and the ACE-2–Ang(1-7)–AT2R and ACE-2–Ang(1-7)–MasR pathways in the lungs and capturing the virus in the circulation, thus impeding its binding to the lung cells and preventing damage to the lungs. Abbreviations used: ACE-1, angiotensin converting enzyme-1; ACE-2, angiotensin converting enzyme-2; ACEIs, angiotensin converting enyzme inhibitors; ARBs, angiotensin AT1 receptor blockers; AT1R, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; AT2R, angiotensin II type 2 receptor; NEP, neutral endopeptidase/Neprilysin; MrgprD, G-protein-coupled receptor MrgD; rhACE-2, recombinant soluble human ACE-2; soluble RBD of ACE-2, soluble receptor-binding domain of ACE-2; TMPRSS2, Transmembrane serine protease-2.





