Lung Disease: The soot of all evil
It is common knowledge that a black pigmented material in cigarette smoke (commonly called ‘tar’) stains the human lung. While the ugly images of black lungs on public health advertisements illustrate the damage that can be done by smoking and other sources of inhaled pollution, it was not previously known whether this dark pigment itself was harmful.
Many chemical components of smoke have been connected with tissue damage that can lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other diseases that affect lung function. However, the particles of carbon that dye the lung black have received relatively little attention from researchers because they appear to be rapidly taken up by immune cells, are relatively insoluble, and seem rather inert. Now, in eLife, Farrah Kheradmand, David Corry, James Tour and colleagues—including Ran You as first author—reveal important mechanisms by which these particles are able to trigger and sustain a permanent inflammatory process in the lungs (You et al., 2015).
The symptoms of COPD—which is a major cause of suffering and death worldwide (Raherison and Girodet, 2009)—result from the loss of air-sacs (alveoli) and from inflammation in the windpipe and smaller airways of the lung. These processes are driven by local inflammation that leads to the release of enzymes that digest the thin connective tissue between alveoli in a process called emphysema (Djekic et al., 2009). This decreases the surface area over which oxygen and carbon dioxide can be exchanged, and it also compromises the ‘springiness’ of the lungs. As the lungs become floppier and less springy, the airways inside them (themselves already inflamed by the smoke) become more prone to collapse, which makes it difficult for the patient to blow air back out of the lung. As this process progresses, patients develop increasing shortness of breath and respiratory failure.
You et al.—who are based at Baylor College of Medicine, Rice University and City of Hope National Medical Center—first assessed the composition of these black particles. They found that the staining in the lungs of smokers was localized within populations of immune cells called myeloid-derived dendritic cells. These cells consume pathogens and foreign materials in a process called phagocytosis, and then present the digested fragments to other immune cells so that the body can learn to recognize and attack them. You et al. found that the pigment within these cells is composed of clumps of spherical carbon particles: the particles had diameters in the range of 20–50 nanometers, hence the name nanocarbon black. The researchers also found the same material in the equivalent cells of mice that had been exposed to cigarette smoke.
You et al. then studied the effects of nanocarbon black on the mouse lung by administering it through the nose in quantities equivalent to those received by a lifetime smoker (but without the other components of cigarette smoke). This demonstrated that particles of nanocarbon black are sufficient to cause emphysema-like changes in the mouse lungs.
These changes appear to be caused by damage to DNA, which sets off a cascade of effects that culminate in the release of small proteins called interleukin 1β and 6 (Figure 1). Together, these cytokines enable immune cells called T cells to become T helper 17 cells, which promote inflammation and inhibit another type of T cell that normally act to constrain immune responses (Bettelli et al., 2006; Benwell and Lee, 2010). The tendency to cause DNA damage appears to depend on the size of the particles and their solubility in oil: this has important implications both for potential regulations governing the emission of carbon black and for further research on the biological effects of these pollutants.
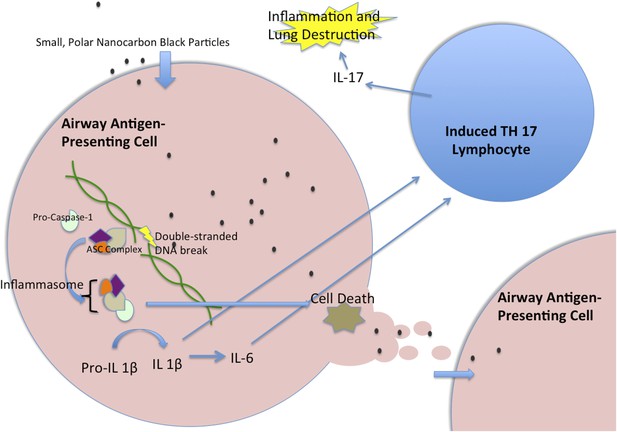
Nanocarbon black triggers perpetual inflammation in the lung.
Nanoparticles of carbon black are consumed by antigen-presenting cells, such as human myeloid dendritic cells, where they lead to DNA breaks. This, in turn, initiates the activation of a complex of proteins called the inflammasome, which includes the Caspase-1 protein (Taniguchi and Sagara, 2007). The activated inflammasome leads to the cleavage of Pro-IL1β to make a mature signal protein called IL-1β, while also initiating processes that will lead to the death of the cell. The mature IL-1β causes upregulation of several inflammatory pathways, including the increased transcription of IL-6. These cytokines then act together to trigger T lymphocytes to become T helper 17 (TH17) cells. These cells produce the inflammatory cytokine IL-17, which has been implicated in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. When the antigen-presenting cell dies, the nanoparticles are released to be taken up by another generation of antigen-presenting cells, which lead to another cycle of inflammation. IL = interleukin; ASC = Adaptor Protein Apoptosis-Associated Speck-Like Protein Containing CARD.
You et al. hypothesize that nanocarbon black is consumed by phagocytic immune cells and then damages the genetic material in these cells so that they die after sending signals to the immune system that promote inflammation. As they die, these cells release their toxic contents, which can then be eaten by another generation of immune cells: this sets up a cycle of inflammation that gradually dissolves connective tissue in the lung.
These findings shed light on an enigmatic question that has troubled medicine for decades: how does cigarette smoke continue to cause lung inflammation and damage years after a patient has stopped smoking? They will also help us to understand the effects of other sources of air pollution and particulates. Since every human on earth is exposed to at least one form of carbon-based pollution, such as wood-burning stoves, petroleum fumes or even electronic cigarette vapor, this research has major implications both for future scientific inquiry and for public health policy.
Further work is needed to characterize the carbon nanoparticles produced by various forms of combustion so that the many public health implications of these findings can be better explored. In the longer term, it may be possible to design new therapies that block the inflammation caused by these particles and slow down the destruction of lung tissue that causes so much suffering in people with emphysema.
References
-
Attacking the multi-tiered proteolytic pathology of COPD: new insights from basic and translational studiesPharmacology & Therapeutics 121:132–146.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.09.008
-
Epidemiology of COPDEuropean Respiratory Review 18:213–221.https://doi.org/10.1183/09059180.00003609
-
Regulatory molecules involved in inflammasome formation with special reference to a key mediator protein, ASCSeminars in Immunopathology 29:231–238.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-007-0082-3
Article and author information
Author details
Acknowledgements
The authors thank J Michael Wells for his assistance with this paper.
Publication history
Copyright
© 2015, Russell and Blalock
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 2,135
- views
-
- 104
- downloads
-
- 3
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
The elemental carbon in cigarette smoke causes inflammation and emphysema in the lung.
-
- Immunology and Inflammation
The gut biome, a complex ecosystem of micro- and macro-organisms, plays a crucial role in human health. A disruption in this evolutive balance, particularly during early life, can lead to immune dysregulation and inflammatory disorders. ‘Biome repletion’ has emerged as a potential therapeutic approach, introducing live microbes or helminth-derived products to restore immune balance. While helminth therapy has shown some promise, significant challenges remain in optimizing clinical trials. Factors such as patient genetics, disease status, helminth species, and the optimal timing and dosage of their products or metabolites must be carefully considered to train the immune system effectively. We aim to discuss how helminths and their products induce trained immunity as prospective to treat inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. The molecular repertoire of helminth excretory/secretory products (ESPs), which includes proteins, peptides, lipids, and RNA-carrying extracellular vesicles (EVs), underscores their potential to modulate innate immune cells and hematopoietic stem cell precursors. Mimicking natural delivery mechanisms like synthetic exosomes could revolutionize EV-based therapies and optimizing production and delivery of ESP will be crucial for their translation into clinical applications. By deciphering and harnessing helminth-derived products’ diverse modes of action, we can unleash their full therapeutic potential and pave the way for innovative treatments.





